The original title is as follows: leetcode.114 Expand a binary tree into a linked list
Given the root node root of the binary tree, please expand it into a single linked list:
The expanded singly linked list should also use TreeNode, where the right sub-pointer points to the next node in the linked list, while the left sub-pointer is always null.
The expanded singly linked list should be in the same order as the binary tree preorder traversal.
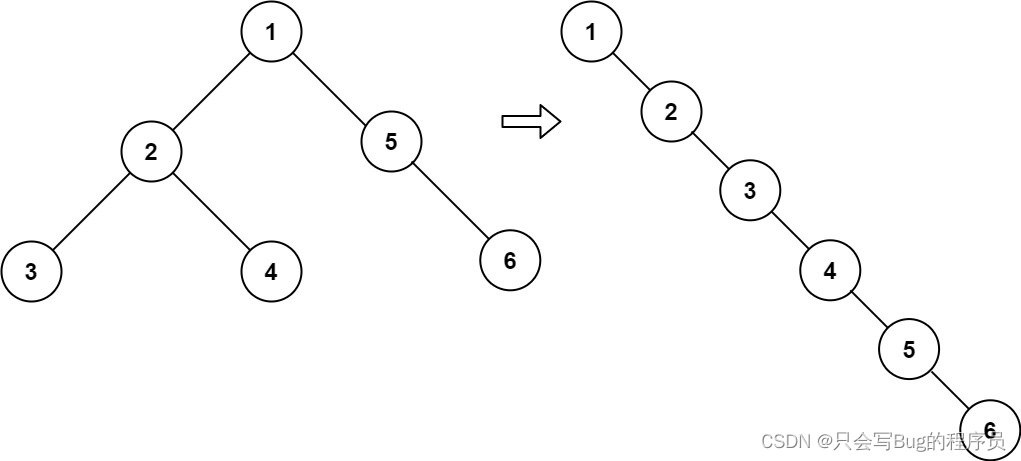
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,2,5,3,4,null,6]
Output: [1,null,2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
Method 1:
Continuously flatten the binary tree through depth-first traversal,
- For example, in the above figure, by creating an array, and continuously stuffing nodes to the head, so as to realize the post-order arrangement, first stuffing the right node, and then stuffing the left node
- Traversal is to continuously take nodes from the head, and then continuously splice the current node at the end of the target node
- For example, 2 is spliced behind 1, forming 1 > 2, and the pointer points to 2
- Then 3 is spliced behind the current pointer, and the pointer currently points to 2, so 1 > 2 > 3 is formed, and the pointer points to the end node 3
- The right node is spliced behind the current pointer, and the pointer points to 3, so 1 > 2 > 3 > 4
- And so on, complete the splicing operation
- If the node has child nodes, repeat operations 1 and 2
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {void} Do not return anything, modify root in-place instead.
*/
var flatten = function(root) {
let newNode = new TreeNode(0);
const result = newNode;
const list = [];
if (root) {
list.push(root);
}
while(list.length) {
const item = list.shift();
if (item.right) {
list.unshift(item.right);
}
if (item.left) {
list.unshift(item.left);
}
newNode.right = new TreeNode(item.val);
newNode = newNode.right;
}
if (result.right) {
root.right = result.right.right;
root.left = null;
}
};
Method 2 (recursive):
- Traversing upwards from the leftmost bottom
- 1 < 2 > 3 -> 2 > 1, (the left node of the current node, directly replace the right node)
- Search down from 2, find 1, 1 has no right node, connect the old right node of 2 to 1, form 2 > 1 > 3
- Such a node is completed, and so on
- There is also a parent node on the 2 node, such as 2 < 5 > 4
- It is necessary to splice all the left node 2 on the parent node 5, that is, 5 > 2 > 1 > 3
- Traverse the nodes to the right in turn, and find that there is no node on the right side of 3, at this time, splicing the original right node of 5 behind 3,
- You can get a new tree, 5 > 2 > 1 > 3 > 4
- Pass up sequentially to get a complete single linked list number
- This method, through the recursive form, starts from the smallest node to level up, slowly level up to the whole world, and radiates from the point to the surface
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {void} Do not return anything, modify root in-place instead.
*/
var flatten = function(root) {
if (!root) return;
flatten(root.left);
flatten(root.right);
// 拉平一个节点
const right = root.right;
root.right = root.left;
root.left = null;
let p = root;
while (p.right) {
p = p.right;
}
p.right = right;
};