1.RAS

Ideas:
First judge whether a and b are equal, if they are equal, directly output no credit, find all factors of a and b, and record the occurrence times of all factors, if there is a factor that appears more than twice, or there is already a factor that is a certain factor When the number is the square number, output no credit, if the two numbers have no numbers other than 1 and itself, output full credit, and output partial credit in the rest
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include <unordered_map>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
map<int, int>yinzi;
bool zhi(int a) {
int panduan = 1;
for (int e = 2; e <= sqrt(a); e++) {
if (a % e == 0) {
panduan = 0;
break;
}
}
return panduan;
}
void yin(int a) {
for (int e = 2; e <= a/e; e++) {
if (a % e == 0) {
yinzi[e]++;
yinzi[a / e]++;
}
//printf("%lld\n", e);
}
//cout << "HH" << endl;
}
signed main() {
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
if (a == b) {
cout << "no credit";
return 0;
}
if (a != b && zhi(a) && zhi(b)) {
cout << "full credit";
return 0;
}
yin(a);
yin(b);
map<int, int>::iterator it;
for (it = yinzi.begin(); it != yinzi.end(); it++) {
int zan = sqrt(it->first);
if (zan * zan == it->first || it->second > 1) {
cout<< "no credit";
return 0;
}
}
cout << "partial credit";
}2. Array operation

Ideas:
The title seems very complicated, but the actual meaning is to change the entire array into the last number, how to change it, start from the end to find the number that is not equal to the first and last number, and then cover the interval after this number to this Before counting, for example, it was originally 01234777, and it became 01777777, and then start to search from the back, each time ans++ is covered, and finally output ans
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
vector<int>shuzu;
int main() {
int asdf;
cin >> asdf;
while (asdf--) {
int a;
cin >> a;
shuzu.clear();
while (a--) {
int b;
cin >> b;
shuzu.push_back(b);
}
int ans = 0;
int daxiao = 1;
int jiluzh = shuzu.size() - 1;
while (jiluzh>0) {
for (int e = jiluzh-1; e >= 0; e--) {
if (shuzu[e] != shuzu[shuzu.size() - 1]) {
jiluzh = e + 1;
break;
}
if (e == 0) {
jiluzh = 0;
break;
}
daxiao++;
}
if (jiluzh <= 0) {
break;
}
ans++;
jiluzh -= daxiao;
daxiao *= 2;
//cout << daxiao << endl;
//cout << jiluzh << endl;
system("pause");
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
}3. AB number pairs
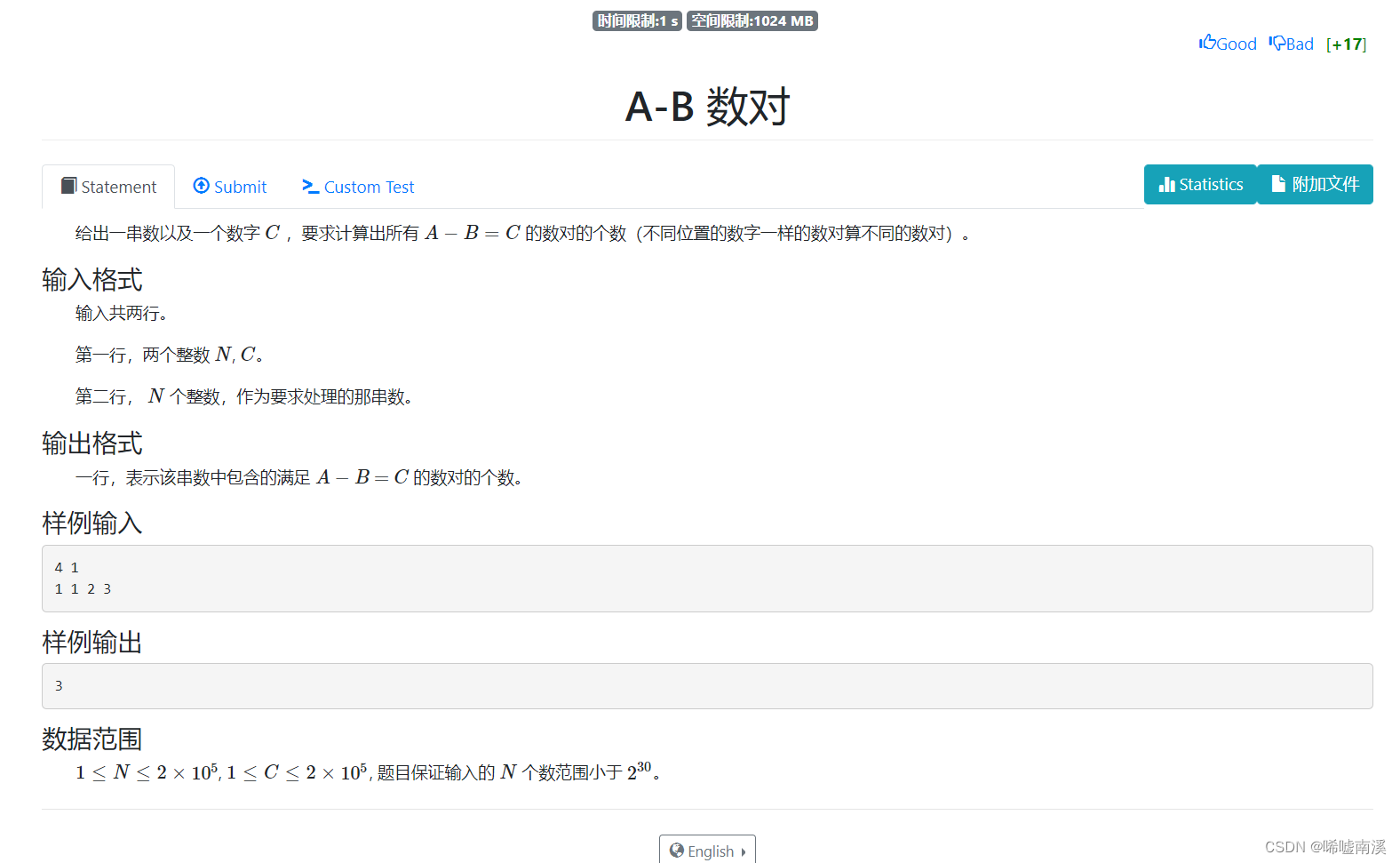
Ideas:
Create an array to count the number of occurrences of each number, another dynamic array to count how many kinds of numbers there are, and then traverse the dynamic array, if there is a number that matches the current digit, and += the number of current digits * the number of matching numbers, final output and
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
int shu[10000000];
vector<int>shu2;
signed main() {
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
while (a--) {
int c;
cin >> c;
shu[c]++;
if (shu[c] == 1) {
shu2.push_back(c);
}
}
int he = 0;
for (int e = shu2.size()-1; e >= 0; e--) {
if (shu2[e]-b>=0&&shu[shu2[e] - b] >= 1) {
he = he+shu[shu2[e]] * shu[shu2[e] - b];
}
}
cout << he;
}4. Digital computing
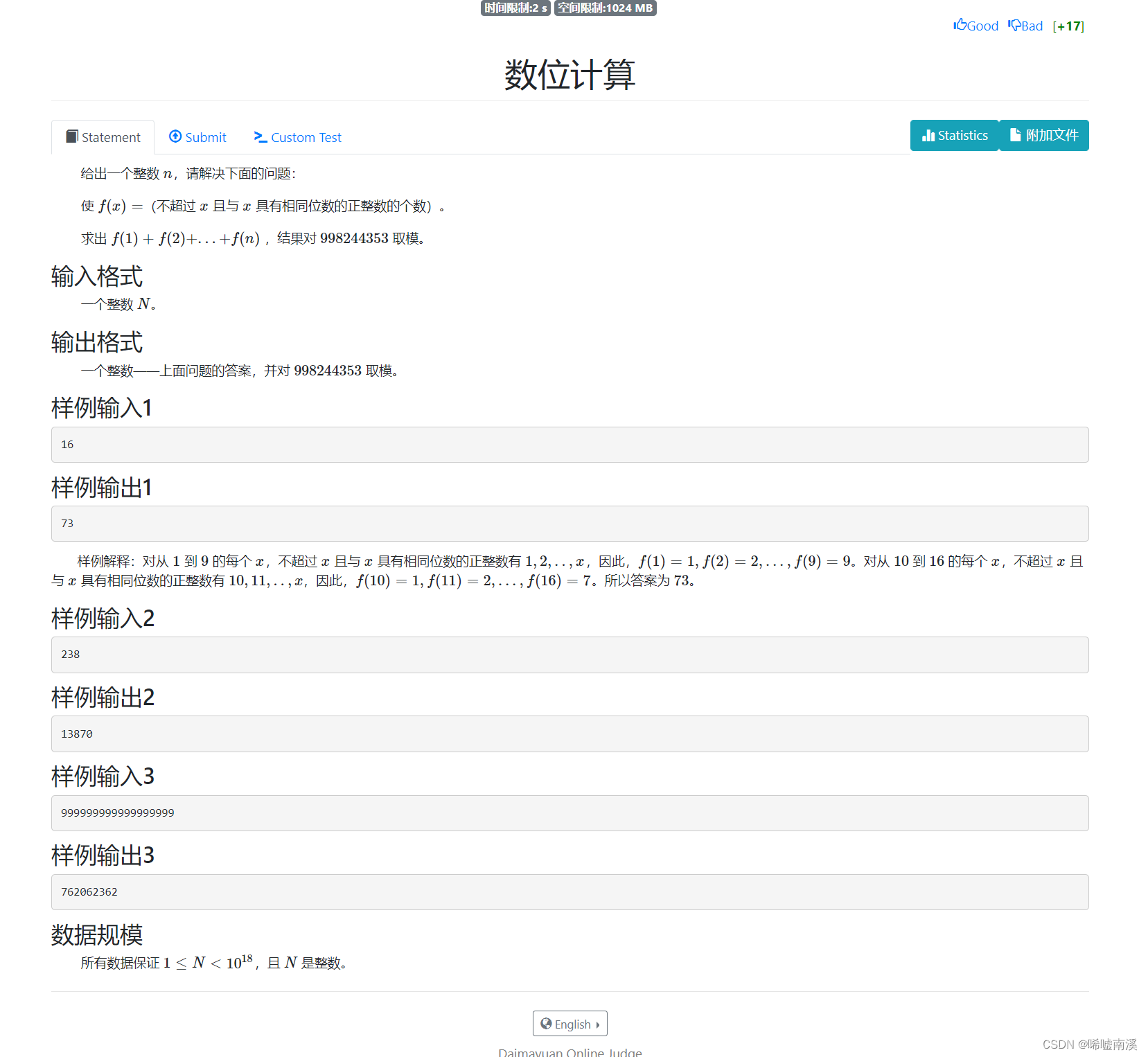
Ideas:
Segmented solution, use the arithmetic sequence formula to calculate the sum of each interval and then add them up
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
const int mod = 998244353;
signed main() {
string a;
cin >> a;
reverse(a.begin(), a.end());
unsigned long long he = 0;
int shu = 0;
for (int e = a.size() - 1; e >= 0; e--) {
shu *= 10;
shu += a[e] - '0';
}
for (int e = 0; e < a.size(); e++) {
if (e != a.size() - 1) {
if (e == 0) {
he += 45;
he %= mod;
}
else {
int a3 = pow(10, e + 1);
int a4 = pow(10, e);
unsigned long long a1 = ((a3 - 1 - a4 + 1) + 1);
a1 %= mod;
unsigned long long a2 = (a3 - 1 - a4 + 1);
a2 %= mod;
he +=(a1* a2/2)%mod;
}
}
else {
int aaa = pow(10, e);
unsigned long long linshi = shu - aaa + 1;
linshi %= mod;
unsigned long long linshi2 = shu - aaa + 2;
linshi2 %= mod;
unsigned long long l2 = linshi2 * linshi / 2;
l2 %= mod;
he += l2;
}
}
cout << he%mod;
}5. The New King Game

Ideas:
Custom sorting, when the total income of two people is the largest, whoever is the first is the optimal sorting, the abstraction is enlarged to the entire queue, and then the result is calculated;
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int mod = 1000000007;
bool cmp(pair<int ,int>a,pair<int,int>b) {
return b.second + a.second * b.first < a.second + b.second * a.first;
}
vector<pair<int, int>>ren;
signed main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
while (n--) {
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
ren.push_back(make_pair(a,b));
}
sort(ren.begin(), ren.end(), cmp);
int res =ren[0].second;
int sum = 1;
for (int e =0; e<ren.size(); e++) {
if (e > 0)res = (res + (sum * ren[e].second) % mod) % mod;
sum = (sum * ren[e].first) % mod;
}
cout << res;
}6. Perfect number
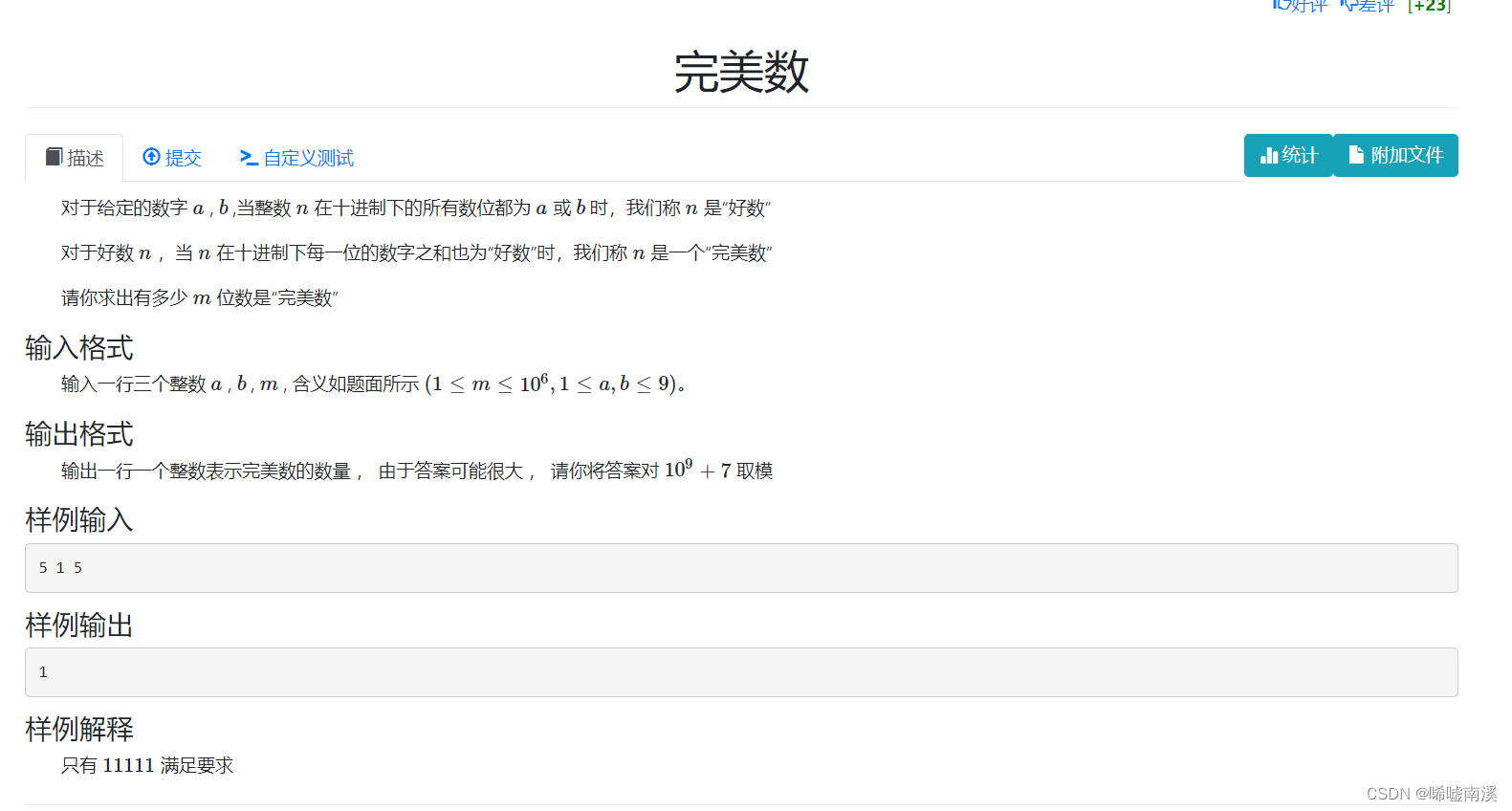
Ideas:
That is to say, you are given m positions, and you can put a or b in each position. If each position of the sum of all positions is still a or b, then it is a perfect number, and we can use permutations and combinations To solve this problem, from 0 a, m b to m a, 0 b, if it matches, add the number of permutations and combinations. If you encounter some small problems when taking the modulus, you can use the inverse element when calculating permutations and combinations and fast exponentiation to fix this
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 1e6;
int biao[N+5];
int a, b, m;
int panduan(int c) {
while (c) {
if (c % 10 != a && c % 10 != b) {
return 0;
}
c /= 10;
}
return 1;
}
inline int ksm(int a, int b, int p) {
int ans = 1;
while (b) {
if (b & 1) { ans= ans* a % p; }
a = a * a % p;
b >>=1;
}
return ans;
}
int jieguo(int c) {
return biao[m] % mod * ksm(biao[m - c], mod - 2, mod) % mod * ksm(biao[c], mod - 2, mod) % mod;
}
signed main() {
cin >> a >> b >> m;
biao[0] = 1;
for (int e = 1; e <=N; e++) {
biao[e] = (biao[e - 1] * e )% mod;
}
int he = 0;
for (int e = 0; e <=m; e++) {
int xy = a * e + b * (m - e);
if (panduan(xy)) {
he += jieguo(e)%mod;
he %= mod;
// cout << he << endl;
}
}
cout << he%mod;
}7. Lusir's game

Ideas:
The data is not big, it is directly divided into two
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
vector<int>tu;
signed main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
int maxx= 0;
while (n--) {
int b;
cin >> b;
tu.push_back(b);
if (b > maxx) {
maxx = b;
}
}
int l = 0, r = maxx;
while (l+1< r) {
double mid = (l + r) / 2;
double nl = mid;
int panduan = 1;
//cout << "nl" << nl << endl;
for (int e = 0; e <tu.size(); e++) {
nl = nl+(nl - tu[e]);
if (nl < 0) {
panduan = 0;
break;
}
}
//cout << "panduan" << panduan << endl;
if (panduan) {
r = mid;
}
else {
l = mid;
}
//cout << l << " " << r<<endl;
}
int panduan = 1;
int nl = l;
for (int e = 0; e < tu.size(); e++) {
nl = nl + (nl - tu[e]);
if (nl < 0) {
panduan = 0;
break;
}
}
if (panduan) {
cout << l;
}
else {
cout << r;
}
}
8. BFS Exercise 1

Ideas:
bfs run again
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 300050;
int a[N], f[N];
int main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
int n, num;
cin >> num >> n;
vector<int>v(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> v[i];
a[v[i]] = -1;
}
queue<int>que;
que.push(num);
int res = 0;
while (!que.empty() && n)
{
int len = que.size();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
int ans = que.front();
que.pop();
if (a[ans] == -1)
{
a[ans] = res;
n--;
}
if (ans * 3 < 100050 && f[ans * 3] == 0)
{
que.push(ans * 3);
f[ans * 3] = 1;
}
if (ans * 2 < 100050 && f[ans * 2] == 0)
{
que.push(ans * 2);
f[ans * 2] = 1;
}
if (ans - 1 > 0 && f[ans - 1] == 0)
{
que.push(ans - 1);
f[ans - 1] = 1;
}
if (ans + 1 < 100050 && f[ans + 1] == 0)
{
que.push(ans + 1);
f[ans + 1] = 1;
}
}
res++;
}
for (auto i : v)
{
cout << a[i]<<" ";
}
return 0;
}
Nine.01 Sequence 2

Ideas:
We only need to ensure that there are k 0s between two 1s, and the remaining positions can be arranged randomly
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<ll, ll>PII;
const int N = 1000050, MOD = 1e9 + 7;
ll fact[N], infact[N];
ll qmi(int a, int b)
{
ll res = 1;
while (b)
{
if (b & 1) res = res * a % MOD;
a = a * (ll)a % MOD;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
void init()
{
fact[0] = infact[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++)
fact[i] = fact[i - 1] * i % MOD;
infact[N - 1] = qmi(fact[N - 1], MOD - 2);
for (int i = N - 2; i; i--)
infact[i] = infact[i + 1] * (i + 1) % MOD;
}
int C(int a, int b)
{
return (fact[a] * infact[b] % MOD * infact[a - b] % MOD) % MOD;
}
int main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
int n, k;
init();
cin >> n >> k;
int i = 1;
ll res = 1;
while (i <= n - (i - 1) * k)
{
res = (res + C(n - (i - 1) * k, i) % MOD) % MOD;
i++;
}
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}
10. Divisible Bachelor
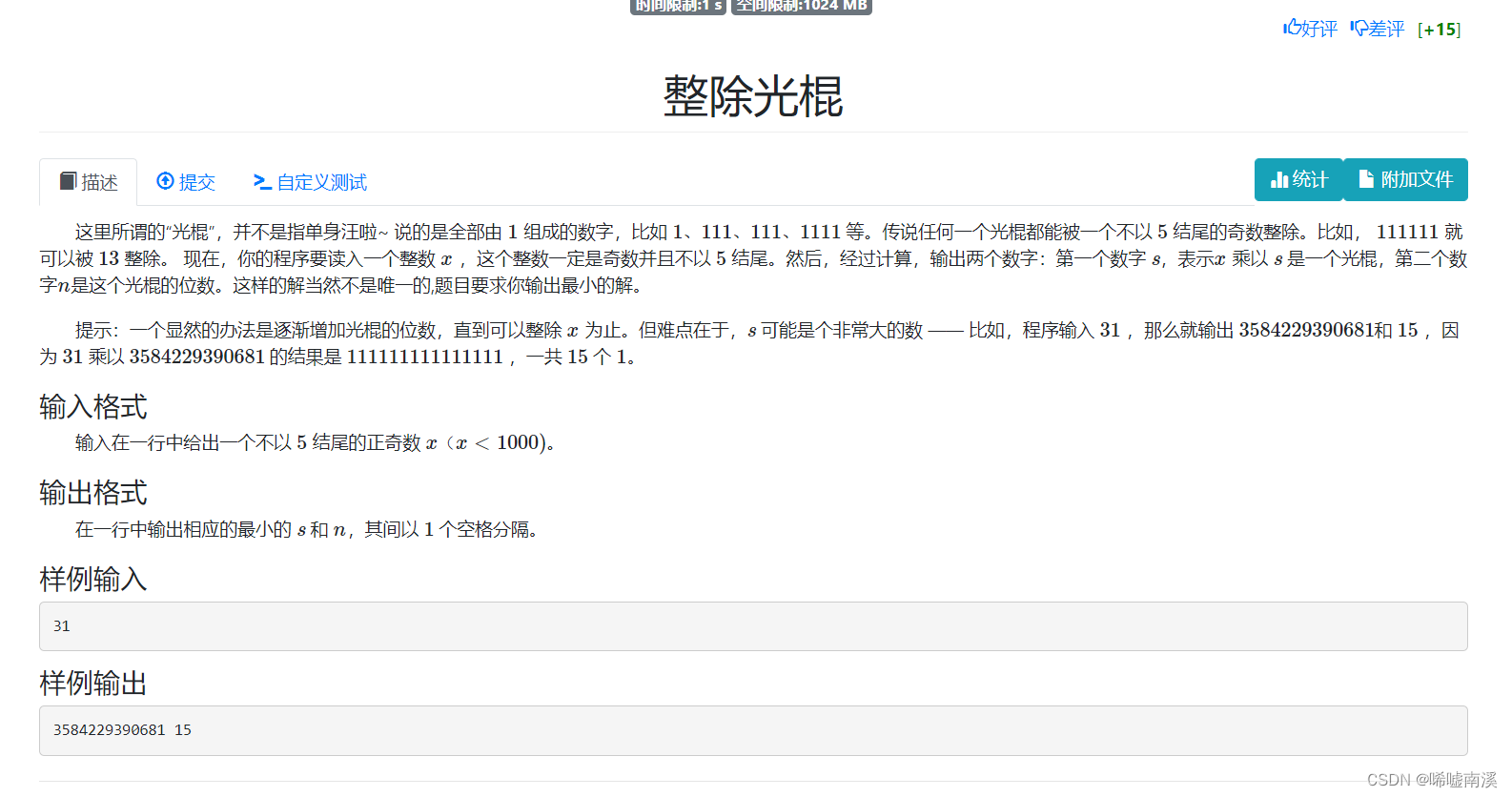
Ideas:
We can just enumerate all bachelor numbers directly, see which bachelor number can be divisible by x, and finally output the length and quotient of the enumerated bachelor numbers. At the same time, because the data is large, we need to use high precision.
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1000050, MOD = 1e9 + 7;
typedef long long ll;
int n;
void write(int x) {
if (x > 9) write(x / 10);
putchar(x % 10 | '0');
}
int main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n;
int r = 1, ans = 1;
while (r < n)
{
r *= 10;
r += 1;
ans++;
}
while (1)
{
write(r / n);
r %= n;
if (r == 0)break;
ans++;
r *= 10;
r += 1;
}
putchar(' ');
write(ans);
return 0;
}