Data reference: CISP official
Table of contents
- safe installation
- Protect account security
- local security policy
- Security center
- System Service Security
- other security settings
- Software Security Acquisition
1. Safe installation (take the installation of windows system as an example)
Choose the right version
- Business Edition: Home Edition, Professional Edition, Professional Workstation Edition, Enterprise Edition
- Special editions: Education Edition, Enterprise Edition LTSC, etc.
installation source
- Official Channels & Reliable Mirrors (Hash)

install mirror
- Microsoft officially provides image creation tools
- Do not use Windows 10 images developed by other third parties

partition settings
- Windows 10 comes with the function of retaining data reset, no need to pay attention to partition settings
Login account settings
- microsoft account
- local account
security patch
- After the installation is complete, perform the patch upgrade first

2. Protect account security
System built-in account
- Administrator
- Guest
User Account
- Account created by user during installation

Disable default built-in accounts
- Net user administrator /active:no
- Net user guest /active:no

Change default account username
- The default built-in account is the target of the attack
- Options available in Local Security Policy

Set secure passwords for all accounts
What is a secure password: easy to remember for yourself, hard for others to guess
- Easy to remember by yourself: you need to be regular
- It is difficult for others to guess: the law is unknown to others
Example: Insecure "safe" password
Fighting against password cracking relies on strong passwords, security recommendations:
- sufficient length
- Combination of uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, special characters
Passwords that meet the "safe" requirements
-
Complexity: Passwords should consist of multiple characters, including uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters, to increase the difficulty of cracking.
-
Length: The password length should be long enough, at least 8 characters is generally recommended, but longer passwords are more secure.
-
Not easy to guess: Avoid using passwords that are associated with personal information (such as birthday, name, phone number) that can be easily guessed by others.
-
Randomness: Choose a random combination of characters for your password and don't use common words or phrases.
-
Periodic change: Change the password regularly, such as every three months, to prevent the password from being used for a long time.
-
No duplication: avoid using the same password in different accounts or systems, so as to avoid the risk of one leak affecting the security of other accounts and systems.
-
Use a password management tool: Consider using a password management tool to store and generate secure passwords, while ensuring that the password management tool itself is also protected.
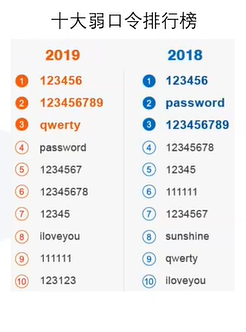
Examples of passwords with high security factors and password setting rules:

Other login verification methods
- face recognition
- fingerprint
- PIN (Personal Identification Number)
- picture (gesture)

3. Local Security Policy
1. Local Security Policy - Security Settings
Account Policy - Password Policy Settings (to avoid weak passwords)
- Password must meet complexity requirements
- Minimum password length
- Password minimum age
- Maximum Password Age
- Enforce Password History
- Store passwords with reversible encryption

Generally, there will be a domain host in the company, and the administrator will directly set security policies for the domain member computers in the company through the domain host.
Account Policy - Account Lockout Policy
- account lockout time
- Account Lockout Threshold
- Reset Account Lockout Counter

2. Local Security Policy - Audit Policy
effect
- Audit user operations and form a security log

Audit policy settings
- Audit login events
- Audit object access
- Audit Process Tracking
- Audit directory service access
- Audit privilege use
- Audit system events
- Audit account login events
- Audit account management

3. Local Policies - Security Options
Set security options according to business needs
- Message title, message text when user tries to log in
- Network access to sharing and security modes for local accounts (classic and guest only)
- Local accounts with blank passwords allow only console logins
- ......
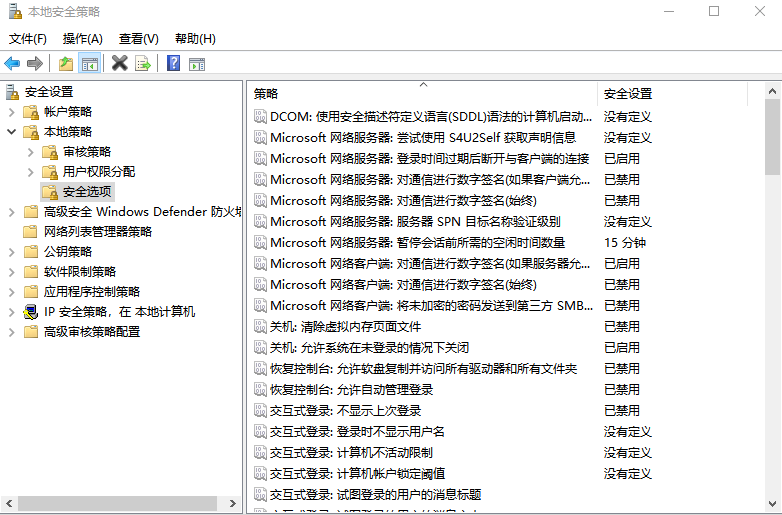
example
- Network Access: Do not allow anonymous enumeration of SAM accounts, set to Enabled
- Network access: Shares that can be accessed anonymously, delete the value in the policy setting
- Network access: Named pipes for anonymous access, remove the value in the policy setting
- Network access: Remotely accessible registry paths, remove values in policy settings

Concept explanation:
-
Do not allow anonymous enumeration of SAM accounts : This is a network security setting designed to prevent unauthorized users from obtaining information about SAM (Security Account Manager) accounts through enumeration operations. System security can be enhanced by disabling anonymous enumeration of SAM accounts. On Windows, you can find and edit the security policy setting to disable anonymous enumeration of SAM accounts.
-
Anonymously Accessible Shares : This refers to folders or resources shared on the network that can be accessed by anonymous users. In order to improve the security of the system, it is generally recommended to disallow anonymous access to shares to ensure that only authenticated and authorized users can access shared resources. You can find and modify sharing settings, disable anonymous access, or limit access to shared resources.
-
Anonymously Accessible Named Pipes : Named pipes are a mechanism for inter-process communication. Allowing anonymous access to named pipes can pose a security risk because it can be exploited by unauthenticated users to perform malicious operations. It is recommended that anonymous access to named pipes be prohibited on the network to limit access to pipes. You can find and change security policy settings or pipeline access accordingly.
-
Remotely accessible registry path : The registry is a key component used to store configuration information in the Windows operating system, and remote access to the registry path means that the specified registry path can be remotely accessed and modified on the network. To enhance system security, it is recommended to restrict or disallow remote access to sensitive registry paths. You can find and edit registry access settings to control which registry paths are accessible remotely.
4. Security Center
Virus and Threat Protection
- Make sure Virus and Threat Protection is enabled
- Make sure virus and threat protection are up to date
- Ransomware protection is recommended to be turned on (default is not turned on)

Firewall and Network Protection
Make sure the firewall is enabled (enabled by default)
- domain network
- private network
- public network
advanced settings
- Use a firewall to protect inbound and outbound connections

Firewall and network protection advanced settings
inbound rules
outbound rules
Connection Security Rules
monitor
- firewall
- Connection Security Rules
- security association

outbound rules, inbound rules
- Block or allow specific programs or ports to connect
- Pre-set rules exist by default
- Preset rules are not applicable and custom rules can also be created
Set up inbound rules
- new rule
- Make port definition settings
- Enter the port you want to connect to open
- select the appropriate rule
- Set application scenarios
- define name
Set outbound rules
- new rule
- Make port definition settings
- port of the input connection
- select the appropriate rule
- Set application scenarios
- define name

Application and Browser Control
- Check application and file alerts (default)
- Smartscreen Open for Microsoft Edge
- Browsing isolation default
- Exploit Protection Default

5. System service security
System Service Security Issues
- Autorun without user login (partially "startup" by default)
- Run with higher privileges
Turn off unnecessary services
unused service
Services with Security Risks
- Example: Interactive Services
- Planned task Task Scheduler
- Remote Operation Registry Remote Registry
- ......

6. Other security settings
Turn off administrative sharing
- By default, the system partition and windows installation directory are all shared, which poses a security risk

solution strategy
- Modify the registry to turn off administrative sharing
Turn off autoplay
- The autoplay function is enabled by default, designed for user convenience
- Mechanism of U Disk Virus Propagation and Exploitation
solution
- Local group policy to turn off autoplay (gpedit.msc)

7. Safe acquisition of software
protection software
- The system comes with Windows defender
- third party enhancements
other software
- Microsoft App Store
- Official website
- reliable platform