Article directory
- 1. DoS attack
- 2. DDoS attack
- 3. Defense against denial of service attacks
1. DoS attack
1. Introduction to DoS attack
DoS(Denial of Service, denial of service) refers to preventing or denying legitimate users access to network servers. The attack behavior that causes DoS is called DoS attack. A large number of illegal application packets are sent to the designated target host. The purpose is to completely consume the resources of the target host, so that the computer or network cannot provide normal services.
DoS攻击的原理Network attacks are carried out with the help of network system or protocol defects, as well as configuration loopholes, causing network congestion, system resource exhaustion, or system application deadlock, preventing the target host and network system from responding to normal user service requests in a timely manner, causing service performance to be affected. loss, or even service interruption.
最常见的DoS攻击Including computer network bandwidth attacks and connectivity attacks. Bandwidth attack refers to impacting the network with a huge amount of traffic, so that all available network resources are exhausted, and finally legitimate user requests cannot be passed. A connectivity attack refers to hitting the computer with a large number of connection requests, so that all available operating system resources are exhausted, and finally the computer can no longer process legitimate user requests.
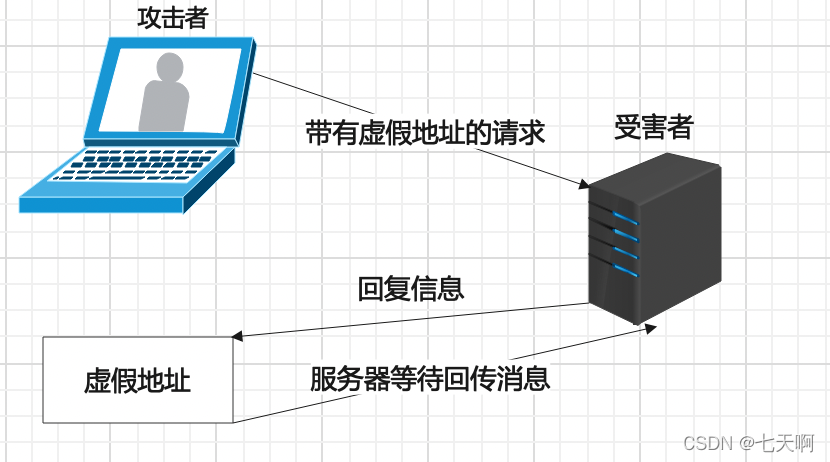
DoS攻击的基本过程Firstly, the attacker sends many requests with false addresses to the server, and the server waits for the return information after sending the reply information. Since the address is forged, the server has not been able to wait for the returned message, and the resources allocated to this request have never been released. When the server waits for a certain period of time, the connection will be cut off due to timeout, and the attacker will send a batch of new requests again. In the case of repeatedly sending false address requests, the server resources will eventually be exhausted, resulting in service failures. Interrupt, as shown in the figure below:
2. Classification of DoS attacks
2.1. Classification according to the object of attack
Denial of service attacks can be "physical" (aka "hardware") or "logical" (aka "software").
1. Attacks in physical form, such as stealing, destroying physical equipment, and destroying power supplies.
2. Logical attack, such as destroying network, system resources and services through software, such as mail service, DNS service, CPU resources, etc.
2.2. Classification by attack target
According to the target of the attack, denial of service attacks can be divided into node type and network connection type.
1. Node type:
designed to consume node (Host) resources. Node type can be further subdivided into main type and application type.
●Host-type attack: its target is mainly the public resources in the host, such as CPU, disk, etc., so that the host cannot respond to all services.
●Application-based attack: its target is a specific application in the network, such as mail service, DNS service, Web service, etc. Other services used by the victim may not be affected or be affected to a lesser extent (compared to the attacked service) at the time of the attack.
2. Network connection type: designed to consume network connection and bandwidth.
2.3. Classification by attack method
According to the attack mode, denial of service attacks can be divided into resource consumption, service suspension and physical destruction.
1. Resource consumption: refers to the attacker trying to consume the legitimate resources of the target, such as network bandwidth, memory and disk space, CPU usage, etc. According to different resource types, resource consumption can be divided into two types: bandwidth exhaustion and system resource exhaustion. The essence of a bandwidth exhaustion attack is that the attacker consumes all the available bandwidth of the target network through techniques such as amplification.
系统资源耗尽攻击: Refers to the consumption of system memory, CPU, or other resources in the program, making it unable to meet the needs of normal service provision. SYN Flood attack is to send a large number of data packets to the target service, causing the connection queue of the service to be exhausted, and can no longer provide services for other normal connection requests.
2. Suspension of service: refers to the attacker exploiting some defects in the service to cause the service to crash or stop.
3. Physical damage: refers to denial of service attacks caused by physical contact such as lightning, electric current, water, and fire.
2.4. Classification by Victim Type
According to the type of victim, denial of service attacks can be divided into server-side denial-of-service attacks and client-side denial-of-service attacks.
1. Server-side denial of service attack: refers to that the target of the attack is a specific server, so that it cannot provide services (or cannot provide certain services to some clients), such as attacking a Web server to make it inaccessible.
2. Client denial of service attack: for a specific client, making it unable to use a certain service, such as "kicking" in games and chat rooms, that is, making a specific user unable to log in to the game system or chat room , so that it cannot use the services of the system.
2.5. Classification according to whether the attack is aimed at the victim
Most of the denial-of-service attacks (regardless of the type or frequency of occurrence) are aimed at the server, and the attacks against the client generally occur less, and because the area involved is small, the harm will be much smaller. According to whether the attack directly targets the victim, the denial of service attack can be divided into direct denial of service attack and indirect denial of service attack. An indirect attack is an attack to make a mail account unavailable, and attacking the mail server to make the entire mail server unavailable.
2.6. Classification by attack location
Denial of service attacks can be divided into local attacks and remote (network) attacks according to the attack location. A local attack refers to an attack directly on the local host without going through the network, while a remote attack must be connected through the network. Since a local attack requires the attacker to be in the same location as the victim, this is too demanding on the attacker, and usually only an insider can do it. Local attacks can often be addressed with physical security measures and tight controls on insiders.
3. Common DoS attacks
Attackers of denial-of-service attacks try their best to make the target machine stop providing services or resource access, these resources include disk space, memory, processes, and even network bandwidth, thereby preventing normal users from accessing. As long as it can cause trouble to the target, suspend certain services or even crash the host, it is a denial of service attack.
The attacker conducts a denial of service attack, which actually allows the server to achieve two effects. One is to force the server's buffer to be full and not receive new requests; connect.
3.1, Land program attack
Land program attack is an attack method that sends a large number of data packets with the same source address and destination address to the target host, causing the target host to occupy a large amount of system resources when parsing the Land packets, thereby completely paralyzing the network function. The method is to set both the source address and the destination address in a specially designed SYN packet to the address of an attacked server, so that the server will send a SYN-ACK response packet to itself after receiving the data packet, and the SYN-ACK It also causes an ACK packet sent to itself and creates an empty connection. Each such empty connection will be temporarily stored in the server. When the queue is long enough, normal connection requests will be discarded, causing the server to refuse service.
3.2. SYN flood attack
SYN Flood is currently one of the most popular methods of DoS (Denial of Service) and DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service). An attack method in which the attacker's resources are exhausted (full CPU load or insufficient memory). Its implementation process is as follows.
1. The attacker sends a TCP message containing the SYN flag to the attacked server. The SYN will indicate the port used by the client and the initial sequence number of the TCP connection. At this time, the first handshake is established with the attacked server.
2. After the victim server receives the attacker's SYN, it will return a SYN+ACK message, indicating that the attacker's request is accepted, and at the same time the TCP sequence number is increased by 1, and the ACK is confirmed, so that it is established with the attacked server 2nd handshake.
3. The attacker also returns a confirmation message ACK to the victim server, and the TCP sequence number is also increased by 1. At this point, a TCP connection is completed, and the third handshake is completed.
In the three-way handshake of the TCP connection, assuming that a user suddenly crashes or goes offline after sending a SYN message to the server, the server cannot receive the client's ACK message after sending the SYN+ACK response message (Part 3 The second handshake cannot be completed), in this case, the server will generally retry (send SYN+ACK to the client again), and discard the unfinished connection after waiting for a period of time. The length of this time is called SYN Timeout, and generally speaking, this time is on the order of minutes (about 30 seconds to 2 minutes). It is not a big problem for a user to have an exception and cause a thread of the server to wait for 1 minute, but if there is a malicious attacker who simulates this situation in large numbers (forging IP addresses), the server will maintain a very large semi-connection list consumes a lot of resources. Even simply saving and traversing will consume a lot of CPU time and memory, not to mention constantly retrying SYN+ACK on the IPs in this list. In fact, if the server's TCP/IP stack is not strong enough, the final result is often a stack overflow crash. The normal request rate of the client is very small), at this time, from the perspective of normal customers, the server loses its response, and this situation is called the server end has been attacked by SYN Flood (SYN flood attack). The anti-attack method is to notify the firewall to block connection requests or discard these data packets when receiving a large number of SYN data packets, and perform system audit.
3.2. IP spoofing DoS attack
This attack is implemented using the RST bit. Assuming that a legitimate user (61.61.61.61) has established a normal connection with the server, the attacker constructs the attacking TCP data, disguises his IP as 61.61.61.61, and sends a TCP data segment with RST bits to the server . After receiving such data, the server thinks that there is an error in the connection sent from 61.61.61.61, and it will clear the established connection in the buffer. At this time, if the legal user 61.61.61.61 sends legal data again, the server has no such connection, and the user must start to establish a connection again. During the attack, the attacker will forge a large number of IP addresses and send RST data to the target, so that the server does not serve legitimate users, thus realizing a denial of service attack on the victim server.
3.4. Smurf attack
Combining IP spoofing and ICMP reply, Smurf attack is an ICMP attack method with amplified effect. The method is that the attacker pretends to be the victim and sends a request to a broadcast device on a certain network, and the broadcast device will forward the request to the Other broadcasting devices on the network cause these devices to respond to the attacked, so as to achieve the purpose of causing a large number of attacks at a relatively small cost.
For example, if an attacker pretends to be the IP of the victim and uses ping to send ICMP packets to the broadcast address of a Class C network, 254 hosts on the network will send ICMP response packets to the IP of the victim, so that the attacker's The attack behavior is magnified by 254 times.
3.5、Ping of Death
This kind of attack achieves the purpose of the attack by sending ICMP packets larger than 65536 bytes to cause the operating system memory overflow, system crash, restart, kernel failure and other consequences. It is generally impossible to send ICMP packets larger than 65536 bytes, but the packets can be divided into fragments and then reassembled on the target host, which will eventually cause the buffer of the attacked target to overflow.
The method to prevent the system from Ping of Death attacks is the same as that of Smurf and Fraggle attacks. You can filter out ICMP packets on the firewall, or disable ping on the server, and enable the ping service only when necessary.
3.6. Teardrop attack
Teardrop (Teardrop) attack is an attack method based on UDP pathologically fragmented data packets. It uses the information contained in the header header of the packet that realizes trust in IP fragments in the TCP/IP stack to realize its own attack. The IP segment contains information indicating which segment of the original packet the segment contains. Some operating systems TCP/IP (including Windows NT before Service pack 4) will There will be system crashes, restarts, etc.
The detection method is to analyze the fragmented data packet received, and calculate whether the fragment offset (Offset) of the data packet is wrong. This attack can be prevented by adding system patches, discarding received pathologically fragmented data packets, and auditing this attack.
3.7. WinNuke attack
WinNuke attack is also called out-of-band transmission attack. Its characteristic is to attack the target port. The attacked target ports are usually 139, 138, 137, 113, and 53, and the URG bit is set to "1", that is, emergency mode. The attack can be detected by judging whether the destination port of the data packet is 139, 138, 137, etc., and judging whether the URG bit is "1".
Properly configured firewall devices or filtering routers can prevent this attack method (drop the packet) and audit this attack (record the time of the event, the MAC address and IP address of the source and destination hosts).
2. DDoS attack
1. Introduction to DDoS attack
Distributed denial of service is a special form of denial of service attack based on DoS. It is a distributed and coordinated large-scale attack method, mainly targeting relatively large sites, such as sites of commercial companies, search engines, or government departments. A DoS attack can be realized as long as a single machine and a Modem are needed; while a DDoS attack uses a group of controlled machines to launch an attack on a machine, such a rapid attack is difficult to guard against, so it is relatively destructive.
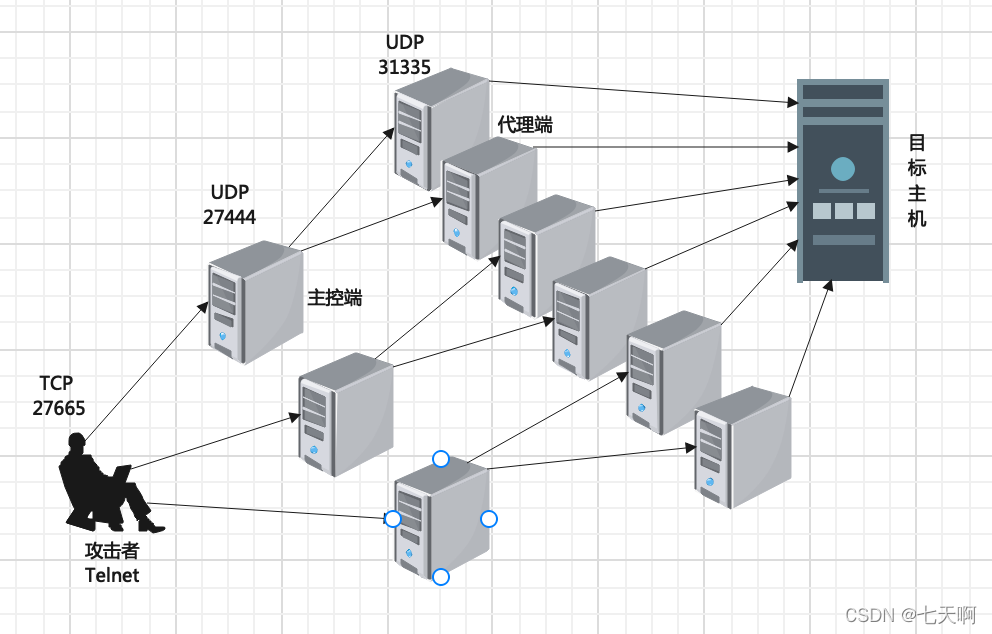
DDoS attacks are divided into three layers: the attacker, the main control end and the agent end, and the three play different roles in the attack.
1. Attacker:
The computer used by the attacker is the attack console, which can be any host on the network, or even an active laptop. The attacker manipulates the entire attack process, and it sends attack commands to the master.
2. Main control end:
The main control end is some hosts illegally invaded and controlled by attackers, and these hosts also control a large number of proxy hosts respectively. Specific programs are installed on the main control host, so they can receive special instructions from the attacker and send these commands to the proxy host.
3. Agent:
The agent is also a group of hosts invaded and controlled by the attacker, on which the attacker program runs, and receives and executes the commands sent by the master. The proxy host is the executor of the attack and actually sends the attack to the victim host.
The first step for an attacker to launch a DDoS attack is to find a host with a vulnerability on the Internet and install a backdoor program on it after entering the system. The more hosts the attacker invades, the stronger his attack team will be; The attack program is installed on the hosts, some of the hosts act as the main control end of the attack, and the other part of the hosts act as the agent end of the attack. Finally, each part of the hosts performs its own duties and launches an attack on the attack target under the dispatch of the attacker. Since the attacker is manipulating behind the scenes, he will not be tracked by the monitoring system during the attack, and his identity is not easy to be discovered.
2. Common tools for DDoS attacks
2.1、Trinoo
Trinoo's attack method is to send all zero 4-byte UDP packets to the random port of the attacked target host. In the process of processing these junk data packets beyond its processing capacity, the network performance of the attacked host will continue to decline until it cannot provide Normal service, even crashes.
Trinoo对IP地址不进行修改,采用的通信端口如下:
1、攻击者主机到主控端主机:27665/TCP ;
2、主控端主机到代理端主机: 27444/UDP ;
3、代理端主机到主服务器主机: 31335/UDP;
2.2、TFN
TFN consists of two parts, the master program and the agent program. Its main attack methods are SYN storm, ping storm, UDP bomb and SMURF, and it has the ability to forge data packets.
2.3、TFN2K
TFN2K is developed from TFN. Based on the characteristics of TFN, TFN2K has some new features. The network communication between its main control end and agent end is encrypted, and many false data packets may be mixed in the middle, while TFN does not encrypt ICMP communication. The attack method adds Mix and Targa3, and TFN2K can configure the agent-side process side.
2.4、Barbed wire
Stacheldraht is also derived from TFN, so it has the characteristics of TFN. In addition, it increases the encrypted communication capability of the master control terminal and the agent terminal, and it can fake the command source, which can prevent RFC 2267 filtering of some routers. There is a built-in agent upgrade module in Stacheldraht, which can automatically download and install the latest agent program.
3. Detection of DDoS vulnerabilities
3.1. According to abnormal situation analysis,
when the traffic of the network suddenly increases sharply and exceeds the usual limit value, we must be vigilant and detect the communication at this time; when a certain service of the website always fails, we should pay more attention; Be careful when you find oversized ICP and UDP data packets passing through or suspicious data packet content. In short, when the machine has abnormal conditions, it is best to analyze these conditions and prevent problems before they happen.
3.2. Using DDoS detection tools
When attackers want to succeed in their attack schemes, they must first scan for system vulnerabilities. Some network intrusion detection systems currently on the market can prevent attackers from scanning. Additionally, some scanner tools can spot an agent planted by an attacker and remove it from the system.
4. Defense against DDoS attacks
1. Early detection of system attack vulnerabilities and timely installation of system patches. Establish a complete backup mechanism for some important information, such as the backup of system configuration information. Be cautious about setting passwords for some privileged accounts (such as administrator accounts), and it is best to use strong passwords. Through such a series of measures, the opportunities for attackers can be reduced to a minimum.
2. In terms of network management, check the physical environment of the system frequently and prohibit unnecessary network services. Frequently check the system configuration information, and pay attention to check the daily security log.
3. Use network security devices (such as firewalls) to strengthen the security of the network, configure their security rules, and filter out all possible forged data packets.
4. A better defense measure is to coordinate with network service providers and let them help implement routing access control and limit the total bandwidth.
5. When it is discovered that a DDoS attack is being attacked, it is necessary to start the coping strategy in time, track the attack package as quickly as possible, and contact the ISP and relevant emergency organizations in time to analyze the affected system and determine other nodes involved, so as to block known Attack node traffic.
6. If you are a potential DDoS attack victim, when you find that the computer is used by the attacker as the master control terminal and the agent terminal, you should not take it lightly because the system has not been damaged for the time being. The attacker has discovered the loopholes in the system, which is very important for the system. big threat. Therefore, once the tool software of DDoS attack is found in the system, it should be removed in time to avoid future troubles.
3. Defense against denial of service attacks
The defense against denial of service attacks generally includes two aspects:
1. For the constantly evolving attack forms, especially those that use a variety of deception techniques, it can be effectively detected;
2. Reduce the impact on business systems or networks, so as to ensure Continuity and availability of business systems.
First of all, it can accurately distinguish and block attack traffic from network traffic; then detect and discover attacks to reduce the impact of attacks on services; at the same time, it can be deployed on multiple boundaries of the network to block different types of internal and external attacks; finally, the network system is guaranteed to have Strong scalability and good reliability.
通常以采取以下手段来保障网络能够抵御拒绝服务攻击:
1、增加网络核心设备的冗余性,提高对网络流量的处理能力和负载均衡能力。
2、通过路由器配置访问列表,过滤掉非法流量。
3、部署防火墙,提高网络抵御网络攻击的能力。
4、部署入侵检测设备,提高对不断更新的DoS攻击的识别和控制能力。
related articles: