Table of contents
Article Directory
LLDP
LLDP (Link Layer Discovery Protocol, Link Layer Discovery Protocol) is an L2 data link layer device discovery protocol defined in 802.1ab, which is used to exchange basic information between network devices in the LAN for mutual discovery and identification Neighboring devices and their capability parameters. It solves the problem of exchanging data link layer information between devices of different manufacturers in a standard protocol.
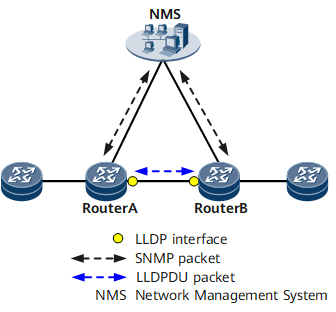
The LLDP protocol has a wide range of application scenarios, such as: automatically discovering devices in the network, generating network topology diagrams, monitoring device status, troubleshooting and network fault recovery, etc. LLDP is also often used in combination with other network management protocols (eg SNMP) to provide more comprehensive device management functions.
For example: in the application scenario of building a network topology based on the LLDP protocol, when a network device sends an LLDPDU, it will publish its own device information and port information to neighboring devices, and the neighboring devices can add this information to their own In the topology table, the topology structure of the entire network is gradually constructed.
LLDPDU
The LLDP protocol uses LLDPDUs (LLDP Data Units) as protocol messages. LLDPDU adopts TLV (Type-Length-Value, Type-Length-Value) data structure, the Length and Value of each TLV can vary according to the specific Type, and one LLDPDU can contain multiple TLVs.
More specifically, LLDPDU has 2 different message encapsulation formats: Ethernet II and SNAP (Subnetwork Access Protocol, Subnetwork Access Protocol).
Ethernet II LLDPDU
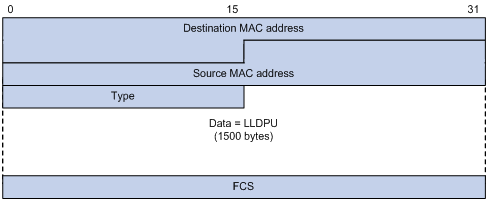
- Destination MAC address : It is a fixed multicast MAC address 0x0180-C200-000E.
- Source MAC address : If there is a port address, use the port MAC address, otherwise use the bridge device MAC address.
- Type (message type) : 0x88CC.
- Data : TLVs for LLDPDUs.
- FCS (Frame Check Sequence)
SNAP LLDPDU
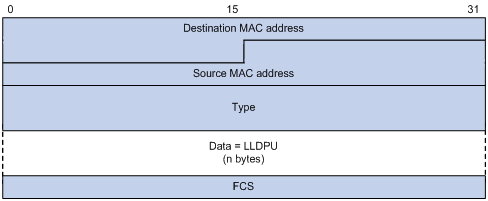
- Destination MAC address : It is a fixed multicast MAC address 0x0180-C200-000E.
- Source MAC address : If there is a port address, use the port MAC address, otherwise use the bridge device MAC address.
- Type (message type) : 0xAAAA-0300-0000-88CC.
- Data : TLVs for LLDPDUs.
- FCS (Frame Check Sequence)
LLDPDU TLVs
The TLVs that LLDP can encapsulate include the following four types:
- basic TLV;
- TLVs defined in 802.1;
- TLVs defined in 802.3;
- LLDP-MED (Media Endpoint Discovery, Media Endpoint Discovery) TLV defined by 802.3.
In general, each LLDPDU can carry 28 TLVs.
Basic TLV

The four dark blue Chasis ID TLVs, Port ID TLVs, TTL TLVs and End TLVs are mandatory, and the rest of the TLVs are optional.
- Chassis ID TLV : used to transmit the unique identifier of the device, such as: the device's MAC address , IP address, etc. Uniquely identifies a network device on the network.
- Port ID TLV : The unique identifier of the port used to transmit the device, such as: port number , port name.
- Time To Live TLV : Indicates the lifetime of the LLDPDU (the maximum number of hops for the message to propagate in the network).
- End TLV : Indicates the end of LLDPDU TLVs.
- System Name TLV : The system name used to transmit the device.
- System Description TLV : used to transmit the system description information of the device, such as: device model, manufacturer information, etc.
- System Capabilities TLV : It is used to transmit the system capability information of the device, such as whether to support routing, switching, power management, etc.
- Port Description TLV : Used to transmit port description information about the device, such as: port type, rate, etc.
- Management Address TLV : Used to transmit the management address of the device for network management and configuration.
- Organizationally Specific TLV : Used to extend the LLDP protocol to transmit custom information defined by a specific vendor or organization.
Among them, the Management Address (management address) is the address provided by the network device to the NMS (network management system) to identify a device and manage it.
802.1 defined TLVs
- Port VLAN ID TLV : VLAN ID of the port.
- Port And Protocol VLAN ID TLV : Protocol VLAN ID of the port.
- VLAN Name TLV : The port's VLAN name.
- Protocol Identity TLV : The protocol type supported by the port.
802.3 defined TLVs
- MAC/PHY Configuration/Status TLV : port rate and duplex status, whether port rate auto-negotiation is supported, whether auto-negotiation function is enabled, and current rate and duplex status.
- Power Via MDI TLV : The power supply capability of the port.
- Link Aggregation TLV : Whether the port supports link aggregation and whether link aggregation is enabled.
- Maximum Frame Size TLV : The maximum frame length supported by the port, taking the MTU (Max Transmission Unit, maximum transmission unit) configured on the port.
802.3 defined LLDP-MED TLV
LLDP-MED (Media Endpoint Discovery) TLV provides many functions for VoIP (Voice over IP, transmitting voice over IP) application scenarios, including: basic configuration, network policy configuration, address information and directory management, etc. It meets the cost-effective, easy-to-deploy, and easy-to-manage requirements of different manufacturers of voice equipment, and solves the problem of deploying voice equipment in Ethernet, providing convenience for voice equipment producers, sellers, and users.
- LLDP-MED Capabilities TLV : The MED device type of the current device and the LLDP-MED TLV type that can be encapsulated in LLDPDU.
- Network Policy TLV : VLAN ID of the port, supported applications (such as voice and video), application priority, and usage policies, etc.
- Extended Power-via-MDI TLV : The power supply capability of the current device.
- Hardware Revision TLV : The hardware version of the MED device.
- Firmware Revision TLV : The firmware version of the MED device.
- Software Revision TLV : The software version of the MED device.
- Serial Number TLV : The serial number of the MED device.
- Manufacturer Name TLV : The manufacturer of the MED device.
- Model Name TLV : The module name of the MED device.
- Asset ID TLV : Asset identifier for MED equipment for inventory management and asset tracking.
- Location Identification TLV : Location identification information for use by other devices in location-based applications.
LLDP message flow
After the device starts the LLDP protocol, LLDP messages will be periodically sent from each port of the device, and the LLDP protocol of the adjacent device (directly connected device) will receive and analyze these messages to obtain relevant information.
The LLDP protocol supports each port to work in 4 modes, including:
- TxRx : The device both sends and receives LLDP messages.
- Tx : The device only sends but does not receive LLDP messages.
- Rx : The device only receives but does not send LLDP messages.
- Disable : Neither send nor receive LLDP messages.
When a port works in TxRx or Tx mode, the port will not only periodically send LLDP messages to neighbor devices, but also send LLDP messages immediately when the local configuration of the device changes, so as to notify neighbor devices as soon as possible. However, in order to prevent a large number of LLDP messages from being sent due to frequent changes in local information, the port needs to delay for a period of time after sending an LLDP message before continuing to send the next message.
When the working mode of the device is switched from Disable/Rx to TxRx/Tx, or a new neighbor device is discovered (that is, a new LLDP message is received and the information of the device sending the message has not been saved locally), the device will be automatically enabled The fast sending mechanism shortens the sending cycle of LLDP messages to 1s and returns to the normal sending cycle after sending a specified number of LLDP messages continuously.
When the port works in TxRx or Rx mode, the port will check the validity of the received LLDP message and the TLVs it carries, and then save the neighbor information to the local after passing the check, and set the neighbor information in the local device according to the TTL TLV If the value is zero, the neighbor information will be aged immediately.
LLDP protocol stack
The implementation of the LLDP protocol stack in the network device mainly completes the following tasks:
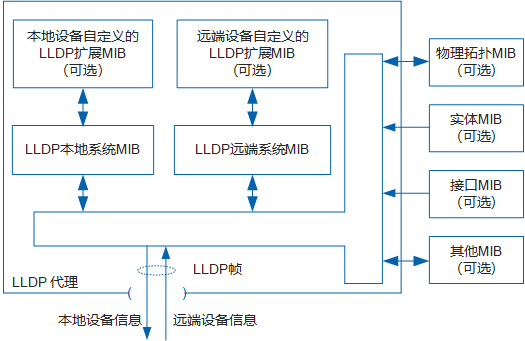
- Initializes and maintains information in the local MIB repository.
- Extracts information from the local MIB repository and encapsulates the information into LLDP messages.
- Recognizes and processes received LLDP messages.
- Maintain the LLDP MIB information base of the remote device.
- When there is a change in the information in the MIB information base of the local or remote device, a notification event is issued.