Android system startup
1, "Introduction to the Android System Startup Process"
2, "Android init process startup process"
3. "Android zygote process startup process"
4. "Android SystemServer Process Startup Process"
5. "Android launcher startup process"
6. "Detailed Explanation of Android Activity Startup Process"
Android System Development Preparation
1, "Android Source Code Download and Compilation"
2. "Android 11 source code compilation and pixel3 flashing"
3. "Android Framework Code IDE Loading and Debugging"
Android System Development Practice
1. "Android Setting Default Input Method"
2, "android framework prefabricated APK application"
3. "Detailed Explanation of Restricting Apps from Starting at the Android System Level"
4. "Android compiles the framework module separately and pushes it"
5. "Android Framework Development System Problem Analysis"
Android system development core knowledge reserve articles
1, "Android Compilation System - envsetup and lunch code articles"
2. "Android Compilation System - Concept"
3. "Detailed Explanation of Android Log System"
4. "Android System Handler Detailed Explanation"
5. "Android System Binder Detailed Explanation"
6. "Detailed Explanation of the Relationship between Activity, View and Window in Android"
7. "Detailed Explanation of the Android View Drawing Process"
8. "Detailed Explanation of Android Reading System Attributes"
9. "Detailed Explanation of Android Window Management Mechanism"
10. "Getting to know the Android system for the first time"
11. "The communication method of AMS process in android notifying Zygote process fork new process"
Detailed explanation of Android core functions
1. "Android application market click to download APK installation details"
2, "Android gesture navigation (swipe from bottom to top to enter the multitasking page)"
4. "Detailed Explanation of Android Application Installation Process"
5, "android11 installation application triggers desktop icon refresh process"
6. "Detailed Explanation of Android System Multitasking Recents"
7. "Android System Navigation Bar View Analysis"
———————————————————————————————————————————
Table of contents
Second, the installation process
2.2 Package Installer install APK
2.3 PMS Execution Installation
1. Background introduction
Android APK installation process, there are four installation methods:
1. The installation of system applications and prefabricated applications is completed when the machine is powered on. There is no installation interface, and the installation is completed in the constructor of PKMS
2. Download and install the application from the network, complete it through the application store, call PackageManager.installPackages(), there is an installation interface
3. The ADB tool is installed without an installation interface. It starts the pm script, then calls the com.android.commands.pm.Pm class, and then calls PMS.installStage() to complete the installation
4. Third-party application installation, installed through the APK file in the SD card, has an installation interface, and the interface of the installation and uninstallation process is handled by the packageinstaller.apk application.
Both use PackageInstallObserver to monitor whether the installation is successful.
Second, the installation process
2.1 Process overview
The main process of application installation:
1. Write APK information into PackageInstaller.Session in the form of IO stream.
2. Call the commit method of PackageInstaller.Session, and hand over the APK information to PKMS for processing.
3. Copy APK
4, and finally install it
After clicking an uninstalled apk in the application market, send a broadcast to open PackageInstallerActivity, pull up the com.android.packageinstaller (breakpoint process) application, and pop up the installation interface. This is mainly composed of bindUi. After clicking, it will call startInstall() to install.
/PackageInstallerActivity.java
private void bindUi() {
mAlert.setIcon(mAppSnippet.icon);
mAlert.setTitle(mAppSnippet.label);
mAlert.setView(R.layout.install_content_view);
mAlert.setButton(DialogInterface.BUTTON_POSITIVE, getString(R.string.install),
(ignored, ignored2) -> {
if (mOk.isEnabled()) {
if (mSessionId != -1) {
mInstaller.setPermissionsResult(mSessionId, true);
finish();
} else {
//进行APK安装
startInstall();
}
}
}, null);
mAlert.setButton(DialogInterface.BUTTON_NEGATIVE, getString(R.string.cancel),
(ignored, ignored2) -> {
// Cancel and finish
setResult(RESULT_CANCELED);
if (mSessionId != -1) {
//如果mSessionId存在,执行setPermissionsResult()完成取消安装
mInstaller.setPermissionsResult(mSessionId, false);
}
finish();
}, null);
setupAlert();
......
}
//点击”安装“,跳转 InstallInstalling - 开始安装
private void startInstall() {
// Start subactivity to actually install the application
Intent newIntent = new Intent();
newIntent.putExtra(PackageUtil.INTENT_ATTR_APPLICATION_INFO, mPkgInfo.applicationInfo);
newIntent.setData(mPackageURI);
newIntent.setClass(this, InstallInstalling.class);
String installerPackageName = getIntent().getStringExtra( Intent.EXTRA_INSTALLER_PACKAGE_NAME);
...
if (installerPackageName != null) {
newIntent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_INSTALLER_PACKAGE_NAME, installerPackageName);
}
newIntent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_FORWARD_RESULT);
startActivity(newIntent);
finish();
}Among them, the R.layout.install_content_view layout view is as follows:
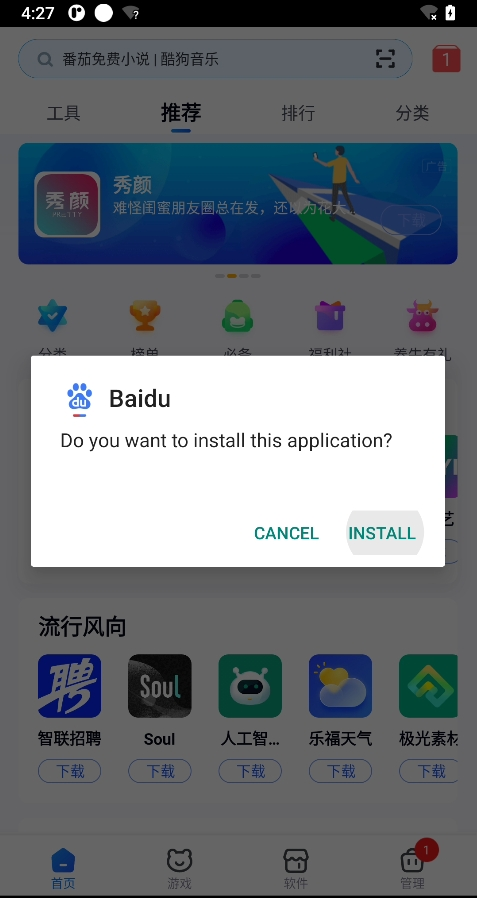
An Intent is assembled in the startInstall method, and jumps to the Activity InstallInstalling, and closes the current PackageInstallerActivity. In InstallInstalling, it is mainly used to send package information to the package manager and handle package management callbacks.
2.2 Package Installer install APK
After starting InstallInstalling, enter the onCreate method:
//InstallInstalling
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
ApplicationInfo appInfo = getIntent()
.getParcelableExtra(PackageUtil.INTENT_ATTR_APPLICATION_INFO);
mPackageURI = getIntent().getData();
......
setupAlert();
requireViewById(R.id.installing).setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
if (savedInstanceState != null) {
mSessionId = savedInstanceState.getInt(SESSION_ID);
mInstallId = savedInstanceState.getInt(INSTALL_ID);
try {
//.根据mInstallId向InstallEventReceiver注册一个观察者,launchFinishBasedOnResult会接收到安装事件的回调,无论安装成功或者失败都会关闭当前的Activity(InstallInstalling)。如果savedInstanceState为null,代码的逻辑也是类似的
InstallEventReceiver.addObserver(this, mInstallId,
this::launchFinishBasedOnResult);
} catch (EventResultPersister.OutOfIdsException e) {
// Does not happen
}
} else {
......
File file = new File(mPackageURI.getPath());
try {
PackageParser.PackageLite pkg = PackageParser.parsePackageLite(file, 0);
params.setAppPackageName(pkg.packageName);
params.setInstallLocation(pkg.installLocation);
params.setSize(
PackageHelper.calculateInstalledSize(pkg, false, params.abiOverride));
} catch (PackageParser.PackageParserException e) {
Log.e(LOG_TAG, "Cannot parse package " + file + ". Assuming defaults.");
Log.e(LOG_TAG,
"Cannot calculate installed size " + file + ". Try only apk size.");
params.setSize(file.length());
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(LOG_TAG,
"Cannot calculate installed size " + file + ". Try only apk size.");
params.setSize(file.length());
}
try {
//向InstallEventReceiver注册一个观察者返回一个新的mInstallId,
//其中InstallEventReceiver继承自BroadcastReceiver,用于接收安装事件并回调给EventResultPersister。
mInstallId = InstallEventReceiver
.addObserver(this, EventResultPersister.GENERATE_NEW_ID,
this::launchFinishBasedOnResult);
} catch (EventResultPersister.OutOfIdsException e) {
launchFailure(PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_INTERNAL_ERROR, null);
}
try {
//PackageInstaller的createSession方法内部会通过IPackageInstaller与PackageInstallerService进行进程间通信,最终调用的是PackageInstallerService的createSession方法来创建并返回mSessionId
mSessionId = getPackageManager().getPackageInstaller().createSession(params);
} catch (IOException e) {
launchFailure(PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_INTERNAL_ERROR, null);
}
}
mCancelButton = mAlert.getButton(DialogInterface.BUTTON_NEGATIVE);
mSessionCallback = new InstallSessionCallback();
}
}In onCreate, use PackageInstaller to create Session and return mSesionId, then in onResume, it will start InstallingAsynTask, write the package information into the session corresponding to mSessionId, and then submit.
//InstallInstalling
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
// This is the first onResume in a single life of the activity
if (mInstallingTask == null) {
PackageInstaller installer = getPackageManager().getPackageInstaller();
//获取sessionInfo
PackageInstaller.SessionInfo sessionInfo = installer.getSessionInfo(mSessionId);
if (sessionInfo != null && !sessionInfo.isActive()) {
//创建内部类InstallingAsyncTask的对象,调用execute(),最终进入onPostExecute()
mInstallingTask = new InstallingAsyncTask();
mInstallingTask.execute();
} else {
// we will receive a broadcast when the install is finished
mCancelButton.setEnabled(false);
setFinishOnTouchOutside(false);
}
}
}
private final class InstallingAsyncTask extends AsyncTask<Void, Void,
PackageInstaller.Session> {
@Override
protected PackageInstaller.Session doInBackground(Void... params) {
PackageInstaller.Session session;
try {
session = getPackageManager().getPackageInstaller().openSession(mSessionId);
} catch (IOException e) {
return null;
}
session.setStagingProgress(0);
try {
File file = new File(mPackageURI.getPath());
try (InputStream in = new FileInputStream(file)) {
long sizeBytes = file.length();
//从session中获取输出流
try (OutputStream out = session
.openWrite("PackageInstaller", 0, sizeBytes)) {
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024 * 1024];
......
}
}
return session;
} catch (IOException | SecurityException e) {
......
}
@Override
protected void onPostExecute(PackageInstaller.Session session) {
if (session != null) {
Intent broadcastIntent = new Intent(BROADCAST_ACTION);
broadcastIntent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_FOREGROUND);
broadcastIntent.setPackage(getPackageName());
broadcastIntent.putExtra(EventResultPersister.EXTRA_ID, mInstallId);
PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getBroadcast(
InstallInstalling.this,
mInstallId,
broadcastIntent,
PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT);
//包写入session进行提交
session.commit(pendingIntent.getIntentSender());
mCancelButton.setEnabled(false);
setFinishOnTouchOutside(false);
} else {
getPackageManager().getPackageInstaller().abandonSession(mSessionId);
if (!isCancelled()) {
launchFailure(PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_INVALID_APK, null);
}
}
}
}In the doInBackground() of InstallingAsyncTask, the APK information will be written into PackageInstaller.Session in the form of IO stream according to the Uri of the package, and finally the commit method of PackageInstaller.Session will be called in onPostExecute() to install.
In it, you will see a PackageInstaller, which is the APK installer, which is actually created in the getPackageInstaller of the ApplicationPackageManager:
//ApplicationPackageManager
@Override
public PackageInstaller getPackageInstaller() {
synchronized (mLock) {
if (mInstaller == null) {
try {
mInstaller = new PackageInstaller(mPM.getPackageInstaller(),
mContext.getPackageName(), getUserId());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
return mInstaller;
}
}Here, mPM.getPackageInstaller() will be passed in, that is, an instance of IpacageInstaller, and its specific implementation is PackageInstallerService, which uses IPC. When it is initialized, it will read the install_sessions file in the /data/system directory. This file saves the unfinished Install Session of the system. PMS will create a PackageInstallerSession object based on the content of the file and insert it into mSessions.
//PackageInstallerService.java
public PackageInstallerService(Context context, PackageManagerService pm,
Supplier<PackageParser2> apexParserSupplier) {
mContext = context;
mPm = pm;
mPermissionManager = LocalServices.getService(PermissionManagerServiceInternal.class);
mInstallThread = new HandlerThread(TAG);
mInstallThread.start();
mInstallHandler = new Handler(mInstallThread.getLooper());
mCallbacks = new Callbacks(mInstallThread.getLooper());
mSessionsFile = new AtomicFile(
new File(Environment.getDataSystemDirectory(), "install_sessions.xml"),
"package-session");
//这个文件保存了系统未完成的`Install Session`
mSessionsDir = new File(Environment.getDataSystemDirectory(), "install_sessions");
mSessionsDir.mkdirs();
mApexManager = ApexManager.getInstance();
mStagingManager = new StagingManager(this, context, apexParserSupplier);
}Let's look at Session again, which is the installation session bound to mSeesionId, which represents an ongoing installation. The Session class is the encapsulation of the PackageInstallerSession (system server) obtained by IPackageInstaller.openSession(sessionId).
The specific implementation of session creation and opening is in PackageInstallerService, which mainly initializes the installation information and environment of apk, creates a sessionId, and binds the installation session with the sessionId.
Then we go back to InstallingAsyncTask, where we call the session.commit method:
//PackageInstaller
public void commit(@NonNull IntentSender statusReceiver) {
try {
//调用PackageInstallerSession的commit方法,进入到java框架层
mSession.commit(statusReceiver, false);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
//PackageInstallerSession.java
public void commit(@NonNull IntentSender statusReceiver, boolean forTransfer) {
......
//如果尚未调用,则会话将被密封。此方法可能会被多次调用以更新状态接收者验证调用者权限
if (!markAsSealed(statusReceiver, forTransfer)) {
return;
}
//不同的包
if (isMultiPackage()) {
final SparseIntArray remainingSessions = mChildSessionIds.clone();
final IntentSender childIntentSender =
new ChildStatusIntentReceiver(remainingSessions, statusReceiver)
.getIntentSender();
boolean sealFailed = false;
for (int i = mChildSessionIds.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
final int childSessionId = mChildSessionIds.keyAt(i);
// seal all children, regardless if any of them fail; we'll throw/return
// as appropriate once all children have been processed
if (!mSessionProvider.getSession(childSessionId)
.markAsSealed(childIntentSender, forTransfer)) {
sealFailed = true;
}
}
if (sealFailed) {
return;
}
}
dispatchStreamValidateAndCommit();
}
private void dispatchStreamValidateAndCommit() {
mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_STREAM_VALIDATE_AND_COMMIT).sendToTarget();
}The type of mSession is IPackageInstallerSession, which means that IPackageInstallerSession is used to communicate between processes, and finally the commit method of PackageInstallerSession will be called. A MSG_STREAM_VALIDATE_AND_COMMIT signal is sent here and processed in the handler:
public boolean handleMessage(Message msg) {
case MSG_STREAM_VALIDATE_AND_COMMIT:
handleStreamValidateAndCommit();
break;
case MSG_INSTALL:
handleInstall(); //
break;
......
}
private void handleStreamValidateAndCommit() {
......
if (unrecoverableFailure != null) {
onSessionVerificationFailure(unrecoverableFailure);
// fail other child sessions that did not already fail
for (int i = nonFailingSessions.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
PackageInstallerSession session = nonFailingSessions.get(i);
session.onSessionVerificationFailure(unrecoverableFailure);
}
}
}
if (!allSessionsReady) {
return;
}
mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_INSTALL).sendToTarget();
}In handleStreamValidateAndCommit, the message MSG_INSTALL is sent again. In fact, what is actually executed is in handleInstall:
private void handleInstall() {
......
// 对于 multiPackage 会话,请在锁之外读取子会话,因为在持有锁的情况下读取子会话可能会导致死锁 (b123391593)。
List<PackageInstallerSession> childSessions = getChildSessionsNotLocked();
try {
synchronized (mLock) {
installNonStagedLocked(childSessions);
}
} catch (PackageManagerException e) {
final String completeMsg = ExceptionUtils.getCompleteMessage(e);
Slog.e(TAG, "Commit of session " + sessionId + " failed: " + completeMsg);
destroyInternal();
dispatchSessionFinished(e.error, completeMsg, null);
}
}
private void installNonStagedLocked(List<PackageInstallerSession> childSessions)
throws PackageManagerException {
......
if (!success) {
sendOnPackageInstalled(mContext, mRemoteStatusReceiver, sessionId,
isInstallerDeviceOwnerOrAffiliatedProfileOwnerLocked(), userId, null,
failure.error, failure.getLocalizedMessage(), null);
return;
}
mPm.installStage(installingChildSessions);
} else {
mPm.installStage(installingSession);
}
}Finally, the installStage method of PMS is executed. In the above process, the Session is maintained through the PackageInstaller, and the installation package is written to the Session. The real installation process is about to look at the PMS.
2.3 PMS Execution Installation
//PackageManagerService.java
void installStage(List<ActiveInstallSession> children)
throws PackageManagerException {
//创建了类型未INIT_COPY的消息
final Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(INIT_COPY);
//创建InstallParams,它对应于包的安装数据
final MultiPackageInstallParams params =
new MultiPackageInstallParams(UserHandle.ALL, children);
params.setTraceMethod("installStageMultiPackage")
.setTraceCookie(System.identityHashCode(params));
msg.obj = params;
Trace.asyncTraceBegin(TRACE_TAG_PACKAGE_MANAGER, "installStageMultiPackage",
System.identityHashCode(msg.obj));
Trace.asyncTraceBegin(TRACE_TAG_PACKAGE_MANAGER, "queueInstall",
System.identityHashCode(msg.obj));
//将InstallParams通过消息发送出去
mHandler.sendMessage(msg);
}
The handler processes the message of INIT_COPY:
//PackageManagerService.java
void doHandleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case INIT_COPY: {
HandlerParams params = (HandlerParams) msg.obj;
if (params != null) {
if (DEBUG_INSTALL) Slog.i(TAG, "init_copy: " + params);
Trace.asyncTraceEnd(TRACE_TAG_PACKAGE_MANAGER, "queueInstall",
System.identityHashCode(params));
Trace.traceBegin(TRACE_TAG_PACKAGE_MANAGER, "startCopy");
//执行APK拷贝动作
params.startCopy();
Trace.traceEnd(TRACE_TAG_PACKAGE_MANAGER);
}
break;
}
......
}
final void startCopy() {
if (DEBUG_INSTALL) Slog.i(TAG, "startCopy " + mUser + ": " + this);
handleStartCopy();
handleReturnCode();
} Two methods handleStartCopy and handleReturnCode are called here, and their implementation is in InstallParams.
In handleStartCopy, the following operations are done:
- Check the size of the space, if there is not enough space, release the useless space
- Overwrite the file in the original installation location, and determine the return value of the function according to the return result, and set installFlags
- Determine if there are any installed package verifiers, and delay detection if so. Mainly divided into three steps: first create a verification Intent, then set the relevant information, then get the validator list, and finally send the verification Intent to each validator
public void handleStartCopy() {
......
//解析包 返回最小的细节:pkgName、versionCode、安装所需空间大小、获取安装位置等
pkgLite = PackageManagerServiceUtils.getMinimalPackageInfo(mContext,
origin.resolvedPath, installFlags, packageAbiOverride);
......
//覆盖原有安装位置的文件,并根据返回结果来确定函数的返回值,并设置installFlags。
if (ret == PackageManager.INSTALL_SUCCEEDED) {
int loc = pkgLite.recommendedInstallLocation;
if (loc == PackageHelper.RECOMMEND_FAILED_INVALID_LOCATION) {
ret = PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_INVALID_INSTALL_LOCATION;
} else if (loc == PackageHelper.RECOMMEND_FAILED_ALREADY_EXISTS) {
ret = PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_ALREADY_EXISTS;
} else if (loc == PackageHelper.RECOMMEND_FAILED_INSUFFICIENT_STORAGE) {
ret = PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_INSUFFICIENT_STORAGE;
} else if (loc == PackageHelper.RECOMMEND_FAILED_INVALID_APK) {
ret = PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_INVALID_APK;
} else if (loc == PackageHelper.RECOMMEND_FAILED_INVALID_URI) {
ret = PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_INVALID_URI;
} else if (loc == PackageHelper.RECOMMEND_MEDIA_UNAVAILABLE) {
ret = PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_MEDIA_UNAVAILABLE;
} else {
.......
}
}
//安装参数
final InstallArgs args = createInstallArgs(this);
mVerificationCompleted = true;
mIntegrityVerificationCompleted = true;
mEnableRollbackCompleted = true;
mArgs = args;
if (ret == PackageManager.INSTALL_SUCCEEDED) {
final int verificationId = mPendingVerificationToken++;
// apk完整性校验
if (!origin.existing) {
PackageVerificationState verificationState =
new PackageVerificationState(this);
mPendingVerification.append(verificationId, verificationState);
sendIntegrityVerificationRequest(verificationId, pkgLite, verificationState);
ret = sendPackageVerificationRequest(
verificationId, pkgLite, verificationState);
......
}
}Then look at the handleReturnCode method:
@Override
void handleReturnCode() {
......
if (mRet == PackageManager.INSTALL_SUCCEEDED) {
//执行APKcopy拷贝
mRet = mArgs.copyApk();
}
//执行安装
processPendingInstall(mArgs, mRet);
}
}How is the copy process of APK copied:
//packageManagerService.java
int copyApk() {
Trace.traceBegin(TRACE_TAG_PACKAGE_MANAGER, "copyApk");
try {
return doCopyApk();
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(TRACE_TAG_PACKAGE_MANAGER);
}
}
private int doCopyApk() {
......
int ret = PackageManagerServiceUtils.copyPackage(
origin.file.getAbsolutePath(), codeFile);
......
return ret;
}
//继续追踪下去,他会到PackagemanagerSeriveUtils的copyFile方法
//PackagemanagerSeriveUtils
private static void copyFile(String sourcePath, File targetDir, String targetName)
throws ErrnoException, IOException {
if (!FileUtils.isValidExtFilename(targetName)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid filename: " + targetName);
}
Slog.d(TAG, "Copying " + sourcePath + " to " + targetName);
final File targetFile = new File(targetDir, targetName);
final FileDescriptor targetFd = Os.open(targetFile.getAbsolutePath(),
O_RDWR | O_CREAT, 0644);
Os.chmod(targetFile.getAbsolutePath(), 0644);
FileInputStream source = null;
try {
source = new FileInputStream(sourcePath);
FileUtils.copy(source.getFD(), targetFd);
} finally {
IoUtils.closeQuietly(source);
}
}Here, the Apk is copied to the /data/app directory through the operation of the file stream. After finishing the copy, it is time to enter the real installation, the process is as follows:
/PackageManagerService.java
private void processPendingInstall(final InstallArgs args, final int currentStatus) {
if (args.mMultiPackageInstallParams != null) {
args.mMultiPackageInstallParams.tryProcessInstallRequest(args, currentStatus);
} else {
//安装结果
PackageInstalledInfo res = createPackageInstalledInfo(currentStatus);
//创建一个新线程来处理安转参数来进行安装
processInstallRequestsAsync(
res.returnCode == PackageManager.INSTALL_SUCCEEDED,
Collections.singletonList(new InstallRequest(args, res)));
}
}
//排队执行异步操作
private void processInstallRequestsAsync(boolean success,
List<InstallRequest> installRequests) {
mHandler.post(() -> {
if (success) {
for (InstallRequest request : installRequests) {
//进行检验,如果之前安装失败,则清除无用信息
request.args.doPreInstall(request.installResult.returnCode);
}
synchronized (mInstallLock) {
//安装的核心方法,进行解析apk安装
installPackagesTracedLI(installRequests);
}
for (InstallRequest request : installRequests) {
//再次检验清除无用信息
request.args.doPostInstall(
request.installResult.returnCode, request.installResult.uid);
}
}
for (InstallRequest request : installRequests) {
//备份、可能的回滚、发送安装完成先关广播
restoreAndPostInstall(request.args.user.getIdentifier(), request.installResult,
new PostInstallData(request.args, request.installResult, null));
}
});
}I saw the core method installPackagesTracedLI, and then internally executed the installPackagesLI method:
//PackageMmanagerSerice.java
private void installPackagesLI(List<InstallRequest> requests) {
.......
//分析当前任何状态,分析包并对其进行初始化验证
prepareResult =
preparePackageLI(request.args, request.installResult);
......
//根据准备阶段解析包的信息上下文,进一步解析
final ScanResult result = scanPackageTracedLI(
prepareResult.packageToScan, prepareResult.parseFlags,
prepareResult.scanFlags, System.currentTimeMillis(),
request.args.user, request.args.abiOverride);
.......
//验证扫描后包的信息好状态,确保安装成功
reconciledPackages = reconcilePackagesLocked(
reconcileRequest, mSettings.mKeySetManagerService);
//提交所有的包并更新系统状态。这是安装流中唯一可以修改系统状态的地方,必须在此阶段之前确定所有可预测的错误
commitRequest = new CommitRequest(reconciledPackages,
mUserManager.getUserIds());
commitPackagesLocked(commitRequest);
.......
//完成APK安装
executePostCommitSteps(commitRequest);
}As can be seen from the above code, installPackagesLI mainly does the following things:
- Analyze any current state, analyze the package and perform initialization verification on it
- Parse the information context of the package according to the preparation stage, and further parse
- Verify the status of the package information after scanning to ensure successful installation
- Submit all Sao Oh Omiao packages and update the system status
- Complete APK installation
Use PackageParser2.parsePackage() in preparePackageLI() to parse AndroidManifest.xml to obtain information such as the four major components; use ParsingPackageUtils.getSigningDetails() to parse signature information; rename the final path of the package, etc.
After completing the parsing and verification preparations, the last step is to install the apk. Here executePostCommitSteps is called to prepare app data and perform dex optimization.
//PackageManagerService.java
private void executePostCommitSteps(CommitRequest commitRequest) {
//进行安装
prepareAppDataAfterInstallLIF(pkg);
.......
final boolean performDexopt =
(!instantApp || Global.getInt(mContext.getContentResolver(),
Global.INSTANT_APP_DEXOPT_ENABLED, 0) != 0)
&& !pkg.isDebuggable()
&& (!onIncremental);
//为新的代码路径准备应用程序配置文件
mArtManagerService.prepareAppProfiles(
pkg,
resolveUserIds(reconciledPkg.installArgs.user.getIdentifier()),
if (performDexopt) {
......
//其中分配了 dexopt 所需的库文件
PackageSetting realPkgSetting = result.existingSettingCopied
? result.request.pkgSetting : result.pkgSetting;
if (realPkgSetting == null) {
realPkgSetting = reconciledPkg.pkgSetting;
}
//执行dex优化
mPackageDexOptimizer.performDexOpt(pkg, realPkgSetting,
null /* instructionSets */,
getOrCreateCompilerPackageStats(pkg),
mDexManager.getPackageUseInfoOrDefault(packageName),
dexoptOptions);
Trace.traceEnd(TRACE_TAG_PACKAGE_MANAGER);
}
}In the prepareAppDataAfterInstallLIF method, after a series of calls, mInstaller.createAppData will be called in the end, which is also the entry point for calling the Installd daemon process:
public class Installer extends SystemService {
@Override
public void onStart() {
if (mIsolated) {
mInstalld = null;
} else {
//通过Binder调用到进程installd
connect();
}
}
private void connect() {
IBinder binder = ServiceManager.getService("installd");
......
if (binder != null) {
mInstalld = IInstalld.Stub.asInterface(binder);
try {
invalidateMounts();
} catch (InstallerException ignored) {
}
} else {
Slog.w(TAG, "installd not found; trying again");
BackgroundThread.getHandler().postDelayed(() -> {
connect();
}, DateUtils.SECOND_IN_MILLIS);
}
}
public long createAppData(String uuid, String packageName, int userId, int flags, int appId,
String seInfo, int targetSdkVersion) throws InstallerException {
if (!checkBeforeRemote()) return -1;
try {
//进行安装操作
return mInstalld.createAppData(uuid, packageName, userId, flags, appId, seInfo,
targetSdkVersion);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw InstallerException.from(e);
}
}
}You can see that the createAppData method of Installd is finally called for installation. Installer is a Java API interface provided by the Java layer, and Installd is a Daemon process with root authority started in the init process.
In the last step of processInstallRequestsAsync, restoreAndPostInstall is called, and the POST_INSTALL message will be sent when the installation is complete:
//PackageManagerService.java
private void restoreAndPostInstall(
int userId, PackageInstalledInfo res, @Nullable PostInstallData data) {
.......
if (!doRestore) {
if (DEBUG_INSTALL) Log.v(TAG, "No restore - queue post-install for " + token);
Trace.asyncTraceBegin(TRACE_TAG_PACKAGE_MANAGER, "postInstall", token);
Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(POST_INSTALL, token, 0);
mHandler.sendMessage(msg);
}
}
void doHandleMessage(Message msg) {
.......
case POST_INSTALL: {
.......
//处理安装结果
handlePackagePostInstall(parentRes, grantPermissions,
killApp, virtualPreload, grantedPermissions,
whitelistedRestrictedPermissions, autoRevokePermissionsMode,
didRestore, args.installSource.installerPackageName, args.observer,
args.mDataLoaderType);
}
}
private void handlePackagePostInstall(PackageInstalledInfo res, boolean grantPermissions,
boolean killApp, boolean virtualPreload,
String[] grantedPermissions, List<String> whitelistedRestrictedPermissions,
int autoRevokePermissionsMode,
boolean launchedForRestore, String installerPackage,
IPackageInstallObserver2 installObserver, int dataLoaderType) {
......
sendPackageBroadcast(Intent.ACTION_PACKAGE_ADDED, packageName,
extras, 0 /*flags*/,
null /*targetPackage*/, null /*finishedReceiver*/,
updateUserIds, instantUserIds, newBroadcastWhitelist);
}Finally, the ACTION_PACKAGE_ADDED broadcast is sent, and the launcher will add the application icon to the desktop after receiving this broadcast.