I. Introduction
In the previous section, we had a basic understanding of data sharding through the following chapters:
Spring Boot integrates ShardingSphere to implement data fragmentation (1) | Spring Cloud 40
Spring Boot integrates ShardingSphere to realize data fragmentation (2) | Spring Cloud 41
Spring Boot integrates ShardingSphere to realize data fragmentation (3) | Spring Cloud 42
Continuing from the previous chapter, this chapter will explain and demonstrate the following parts:
- Sharding algorithm based on time range (
INTERVAL) realizes monthly data sharding - Create a custom
ShardingSpheresharding algorithm and implement monthly data sharding
Let's start with the text.
2. Time Range Sharding Algorithm
2.1 Introduction
-
type:
INTERVAL -
Configurable properties:
| attribute name | type of data | illustrate | Defaults |
|---|---|---|---|
datetime-pattern |
String |
The timestamp format of the shard key must follow the format Java DateTimeFormatterof . For example: yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss, yyyy-MM-ddor HH:mm:ssetc. but does not java.time.chrono.JapaneseDatesupport Gy-MMetc. related to |
|
datetime-lower |
String |
The lower bound value of the time slice, the format is consistent with the timestamp format datetime-patterndefined by |
|
datetime-upper(optional) |
String |
The upper bound value of the time slice, the format is consistent with the timestamp format datetime-patterndefined by |
current time |
sharding-suffix-pattern |
String |
The suffix format of the fragmented data source or real table must be followed Java DateTimeFormatter 的格式and must datetime-interval-unitbe consistent with . For example: yyyyMMcorrespond toMONTHS |
|
datetime-interval-amount(optional) |
int |
Fragment key time interval, after which time interval will enter the next shard | 1 |
datetime-interval-unit(optional) |
String |
The shard key time interval unit must follow the enumeration value Java ChronoUnitof . For example:MONTHS |
DAYS |
-
Category:
org.apache.shardingsphere.sharding.algorithm.sharding.datetime.IntervalShardingAlgorithm -
Precautions:
This algorithm actively ignores time zone information
datetime-patternfor . This means that whendatetime-lower, datetime-upperand the incoming shard key contains time zone information, time zone conversion will not occur due to time zone inconsistencies. There is a special case when the incoming sharding keyjava.time.Instantis , which will carry the time zone information of the system and convert it intodatetime-patterna string format, and then proceed to the next step of sharding.
ShardingSphereBuilt-in provides a variety of sharding algorithms , please refer to the official website:
https://shardingsphere.apache.org/document/5.2.1/cn/user-manual/common-config/builtin-algorithm/sharding/
2.2 Example of use
2.2.1 Overall project structure
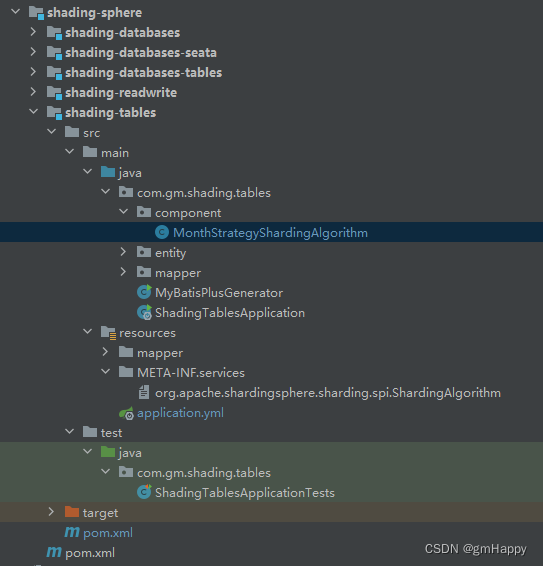
2.2.2 Maven dependencies
shading-sphere/shading-tables/pom.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>shading-sphere</artifactId>
<groupId>com.gm</groupId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>shading-tables</artifactId>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shardingsphere</groupId>
<artifactId>shardingsphere-jdbc-core-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>5.2.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.5.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-generator</artifactId>
<version>3.5.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.velocity</groupId>
<artifactId>velocity-engine-core</artifactId>
<version>2.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.yaml</groupId>
<artifactId>snakeyaml</artifactId>
<version>1.33</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
-
shardingsphere-jdbc-core-spring-boot-starteruse version5.2.1 -
JDBCTheORMframe selectionmybatis-plus
2.2.3 Logic table t_share_month
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_share_month_202304`;
CREATE TABLE `t_share_month_202304` (
`id` bigint NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`create_time` datetime NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4 COLLATE = utf8mb4_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_share_month_202305`;
CREATE TABLE `t_share_month_202305` (
`id` bigint NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`create_time` datetime NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4 COLLATE = utf8mb4_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_share_month_202306`;
CREATE TABLE `t_share_month_202306` (
`id` bigint NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`create_time` datetime NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4 COLLATE = utf8mb4_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
2.2.4 Configuration file
shading-sphere/shading-tables/src/main/resources/application.yml:
spring:
application:
name: @artifactId@
shardingsphere:
# 数据源配置
datasource:
names: ds1
ds1:
type: com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.0.35:3306/db1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&rewriteBatchedStatements=true&allowMultiQueries=true&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
username: root
password: '1qaz@WSX'
# 定义规则
rules:
sharding:
# 数据分片规则配置
tables:
# 指定某个表的分片配置,逻辑表名
t_share_month:
actual-data-nodes: ds1.t_share_month_202$->{
304..306}
#actual-data-nodes: ds1.t_share_month_${2022..2030}${(1..12).collect{t ->t.toString().padLeft(2,'0')}}
table-strategy:
standard:
sharding-column: create_time
sharding-algorithm-name: t_share_month_table_inline
key-generate-strategy:
column: id
key-generator-name: snowflake
# 分片算法配置
sharding-algorithms:
# 分片算法名称
t_share_month_table_inline:
type: INTERVAL
props:
datetime-pattern: yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss
datetime-lower: 2023-04-01 00:00:00
datetime-interval-unit: MONTHS
sharding-suffix-pattern: yyyyMM
# 分布式序列算法配置(如果是自动生成的,在插入数据的sql中就不要传id,null也不行,直接插入字段中就不要有主键的字段)
keyGenerators:
# 分布式序列算法名称
snowflake:
# 分布式序列算法类型
type: SNOWFLAKE
props:
sql-show: true #显示sql
Configuration brief description:
- The logical table performs monthly data sharding
t_share_monthaccording to the sharding keycreate_time
Precautions:
- When the physical table of some months is not actually created, the distributed sequence will not take effect. At this time, if the primary key of the physical table adopts the distributed sequence, it will prompt:
Cause: java.sql.SQLException: Field 'id' doesn't have a default value.
3. Custom Fragmentation Algorithm
ShardingSphereTwo ways to extend custom algorithms are supported: SPIand ClassBased. CLASS_BASEIn fact, it has already been realized SPI.
For the directory structure and dependencies, please refer to chapters 2.2.1 and 2.2.2 .
ShardingSphereBuilt-in provides a variety of sharding algorithms , please refer to the official website:
https://shardingsphere.apache.org/document/5.2.1/cn/user-manual/common-config/builtin-algorithm/sharding/
3.1 Create a custom sharding algorithm
Create a new class MonthStrategyShardingAlgorithmand implement StandardShardingAlgorithmthe interface.
com/gm/shading/tables/component/MonthStrategyShardingAlgorithm.java:
import com.google.common.collect.Range;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.sharding.api.sharding.standard.PreciseShardingValue;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.sharding.api.sharding.standard.RangeShardingValue;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.sharding.api.sharding.standard.StandardShardingAlgorithm;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.util.*;
@Slf4j
public class MonthStrategyShardingAlgorithm implements StandardShardingAlgorithm<LocalDateTime> {
/** 配置值需要储存 */
private Properties props;
private static final DateTimeFormatter yyyyMM = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyyMM");
@Override
public String doSharding(Collection<String> collection, PreciseShardingValue<LocalDateTime> preciseShardingValue) {
LocalDateTime dateTime = preciseShardingValue.getValue();
String tableSuffix = dateTime.format(yyyyMM);
String logicTableName = preciseShardingValue.getLogicTableName();
String table = logicTableName.concat("_").concat(tableSuffix);
System.out.println("MonthStrategyShardingAlgorithm.doSharding table name: {}" + table);
return collection.stream().filter(s -> s.equals(table)).findFirst().orElseThrow(() -> new RuntimeException("逻辑分表不存在"));
}
@Override
public Collection<String> doSharding(Collection<String> collection, RangeShardingValue<LocalDateTime> rangeShardingValue) {
// 逻辑表名
String logicTableName = rangeShardingValue.getLogicTableName();
// between and 的起始值
Range<LocalDateTime> valueRange = rangeShardingValue.getValueRange();
Set<String> queryRangeTables = extracted(logicTableName, valueRange.lowerEndpoint(), valueRange.upperEndpoint());
ArrayList<String> tables = new ArrayList<>(collection);
tables.retainAll(queryRangeTables);
System.out.println("MonthStrategyShardingAlgorithm.doSharding tables collection name: {}" + tables);
return tables;
}
/**
* 根据范围计算表明
*
* @param logicTableName 逻辑表明
* @param lowerEndpoint 范围起点
* @param upperEndpoint 范围终端
* @return 物理表名集合
*/
private Set<String> extracted(String logicTableName, LocalDateTime lowerEndpoint, LocalDateTime upperEndpoint) {
Set<String> rangeTable = new HashSet<>();
while (lowerEndpoint.isBefore(upperEndpoint)) {
String str = getTableNameByDate(lowerEndpoint, logicTableName);
rangeTable.add(str);
lowerEndpoint = lowerEndpoint.plusMonths(1);
}
// 获取物理表明
String tableName = getTableNameByDate(upperEndpoint, logicTableName);
rangeTable.add(tableName);
return rangeTable;
}
/**
* 根据日期获取表明
*
* @param dateTime 日期
* @param logicTableName 逻辑表名
* @return 物理表名
*/
private String getTableNameByDate(LocalDateTime dateTime, String logicTableName) {
String tableSuffix = dateTime.format(yyyyMM);
return logicTableName.concat("_").concat(tableSuffix);
}
@Override
public Properties getProps() {
return props;
}
@Override
public void init(Properties properties) {
this.props = properties;
}
@Override
public String getType() {
return "CREATE_TIME";
}
}
3.2 Using a custom fragmentation algorithm based on ClassBased
The complete configuration file is as follows:
server:
port: 8844
spring:
application:
name: @artifactId@
shardingsphere:
# 数据源配置
datasource:
names: ds1
ds1:
type: com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.0.35:3306/db1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&rewriteBatchedStatements=true&allowMultiQueries=true&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
username: root
password: '1qaz@WSX'
# 定义规则
rules:
sharding:
# 数据分片规则配置
tables:
# 指定某个表的分片配置,逻辑表名
t_share_month:
actual-data-nodes: ds1.t_share_month_202$->{
304..306}
#actual-data-nodes: ds1.t_share_month_${2022..2030}${(1..12).collect{t ->t.toString().padLeft(2,'0')}}
table-strategy:
standard:
sharding-column: create_time
sharding-algorithm-name: t_share_month_table_inline
key-generate-strategy:
column: id
key-generator-name: snowflake
# 分片算法配置
sharding-algorithms:
# 分片算法名称
t_share_month_table_inline:
type: CLASS_BASED
props:
strategy: standard
# 自定义标准分配算法
algorithmClassName: com.gm.shading.tables.component.MonthStrategyShardingAlgorithm
# 分布式序列算法配置(如果是自动生成的,在插入数据的sql中就不要传id,null也不行,直接插入字段中就不要有主键的字段)
keyGenerators:
# 分布式序列算法名称
snowflake:
# 分布式序列算法类型
type: SNOWFLAKE
props:
sql-show: true #显示sql
mybatis:
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
Custom algorithm core configuration:
# 分片算法名称
t_share_month_table_inline:
type: CLASS_BASED
props:
strategy: standard
# 自定义标准分配算法
algorithmClassName: com.gm.shading.tables.component.MonthStrategyShardingAlgorithm
3.3 Using a custom fragmentation algorithm based on SPI
3.3.1 SPI configuration
Add the full class name of the custom fragmentation algorithm in META-INF/services/org.apache.shardingsphere.sharding.spi.ShardingAlgorithmthe file :
com.gm.shading.tables.component.MonthStrategyShardingAlgorithm
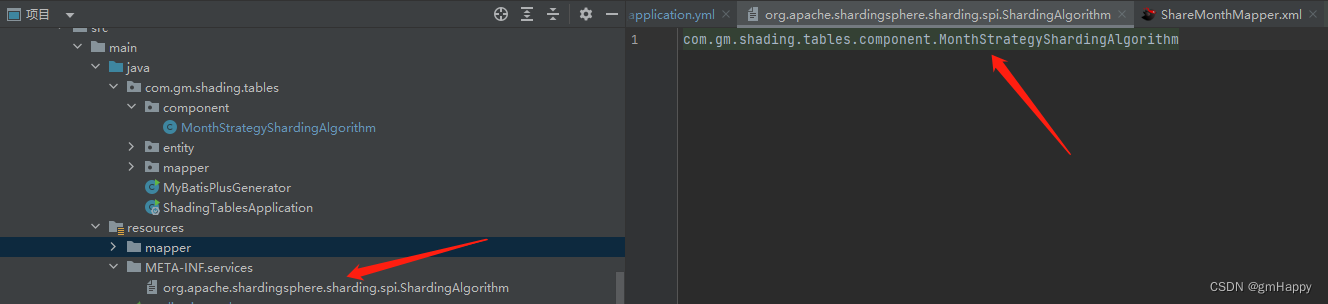
3.3.2 Configuration file
The complete configuration file is as follows:
server:
port: 8844
spring:
application:
name: @artifactId@
shardingsphere:
# 数据源配置
datasource:
names: ds1
ds1:
type: com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.0.35:3306/db1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&rewriteBatchedStatements=true&allowMultiQueries=true&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
username: root
password: '1qaz@WSX'
# 定义规则
rules:
sharding:
# 数据分片规则配置
tables:
# 指定某个表的分片配置,逻辑表名
t_share_month:
actual-data-nodes: ds1.t_share_month_202$->{
304..306}
#actual-data-nodes: ds1.t_share_month_${2022..2030}${(1..12).collect{t ->t.toString().padLeft(2,'0')}}
table-strategy:
standard:
sharding-column: create_time
sharding-algorithm-name: t_share_month_table_inline
key-generate-strategy:
column: id
key-generator-name: snowflake
# 分片算法配置
sharding-algorithms:
# 分片算法名称
t_share_month_table_inline:
type: CREATE_TIME
# 分布式序列算法配置(如果是自动生成的,在插入数据的sql中就不要传id,null也不行,直接插入字段中就不要有主键的字段)
keyGenerators:
# 分布式序列算法名称
snowflake:
# 分布式序列算法类型
type: SNOWFLAKE
props:
sql-show: true #显示sql
mybatis:
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
Custom algorithm core configuration:
# 分片算法配置
sharding-algorithms:
# 分片算法名称
t_share_month_table_inline:
type: CREATE_TIME
Precautions:
- The property of the fragmentation algorithm in the configuration file must correspond
typeto the value of the method in the custom fragmentation algorithm .getType()
3.4 source code
For the complete source code of the above example, please see: https://gitee.com/gm19900510/springboot-cloud-example.git