Above: jdk-BlockingQueue source code learning
Source code download: https://gitee.com/hong99/jdk8
Introduction of semaphore&cyclicbarrier&CountDownLatch
Basic functions of semaphore
Semaphore is referred to as semaphore for short, and is mainly used to control the number of threads that access specific resources. The bottom layer uses the state of AQS.
package com.aqs;
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
/**
* @author: csh
* @Date: 2022/12/13 21:11
* @Description:信号线学习
*/
public class SemaphoreStudy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建10个线程
Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(2);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread(new Task("线程"+i,semaphore)).start();
}
}
static class Task extends Thread{
Semaphore semaphore;
public Task( String name, Semaphore semaphore) {
this.setName(name);
this.semaphore = semaphore;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
semaphore.acquire();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"获取到线程");
Thread.sleep(1000);
semaphore.release();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"释放了线程");
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}result
Thread-3获取到线程
Thread-1获取到线程
Thread-3释放了线程
Thread-7获取到线程
Thread-5获取到线程
Thread-1释放了线程
Thread-7释放了线程
Thread-9获取到线程
Thread-11获取到线程
Thread-5释放了线程
Thread-9释放了线程
Thread-15获取到线程
Thread-11释放了线程
Thread-13获取到线程
Thread-15释放了线程
Thread-17获取到线程
Thread-13释放了线程
Thread-19获取到线程
Thread-17释放了线程
Thread-19释放了线程
Process finished with exit code 0From the above, we can see that by controlling this semaphore, the access of threads can be controlled. Many current limiting scenarios are actually similar implementations.
Basic function understanding of cyclicbarrier
The cyclicbarrier barrier is mainly to specify the number of threads to let the thread wait until the number of threads is executed before continuing to go down, like many current limits or condition numbers are reached before letting go, it is also a similar logic.
Simple example: For example, when crossing a river, you have to fight for 10 people to cross the river. Therefore, in this process, if you don’t have 10 people, you don’t go. When you reach 10 people, you go down.
package com.aqs;
import java.util.concurrent.BrokenBarrierException;
import java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier;
/**
* @author: csh
* @Date: 2022/12/16 21:02
* @Description:栅栏学习
*/
public class CyclicBarrierStudy {
static class CyclicBarrierFactory implements Runnable{
private CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier;
private int index;
public CyclicBarrierFactory(CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier, int index) {
this.cyclicBarrier = cyclicBarrier;
this.index = index;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"当前线坐标:"+index);
index--;
cyclicBarrier.await();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws BrokenBarrierException, InterruptedException {
CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(10, new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("准备完毕,准备执行任务!");
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread(new CyclicBarrierFactory(cyclicBarrier,i)).start();
}
//等待
cyclicBarrier.await();
System.out.println("全部执行完成!");
}
}result
Thread-7当前线坐标:7
Thread-3当前线坐标:3
Thread-2当前线坐标:2
Thread-0当前线坐标:0
Thread-5当前线坐标:5
Thread-9当前线坐标:9
Thread-8当前线坐标:8
Thread-1当前线坐标:1
Thread-6当前线坐标:6
Thread-4当前线坐标:4
准备完毕,准备执行任务!
全部执行完成!CountDownLatch basic function understanding
CountDownLatch is very similar to CyclicBarrier, but the difference is that CyclicBarrier is mainly for thread and concurrency control and can be reset (reused), while CountDownLatch cannot be reset (can only be used once), mainly based on counting.
package com.aqs;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
/**
* @author: csh
* @Date: 2022/12/16 23:33
* @Description:线程计数器学习
*/
public class CountDownLatchStudy {
static class ThreadFactory implements Runnable {
private CountDownLatch countDownLatch;
public ThreadFactory(CountDownLatch countDownLatch) {
this.countDownLatch = countDownLatch;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("当前线程统计数量剩余" + (countDownLatch.getCount() - 1) + "执行了!");
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(10);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread(new ThreadFactory(countDownLatch)).start();
}
while (countDownLatch.getCount() > 1) {
System.out.println("线程等待中,当前还有线程:" + countDownLatch.getCount());
}
countDownLatch.await();
System.out.println("全部执行完毕!");
}
}result
当前线程统计数量剩余9执行了!
当前线程统计数量剩余9执行了!
线程等待中,当前还有线程:10
当前线程统计数量剩余9执行了!
当前线程统计数量剩余9执行了!
当前线程统计数量剩余9执行了!
当前线程统计数量剩余9执行了!
当前线程统计数量剩余9执行了!
当前线程统计数量剩余9执行了!
当前线程统计数量剩余9执行了!
当前线程统计数量剩余9执行了!
线程等待中,当前还有线程:3
全部执行完毕!Source code learning
java.util.concurrent.Semaphore source code learning
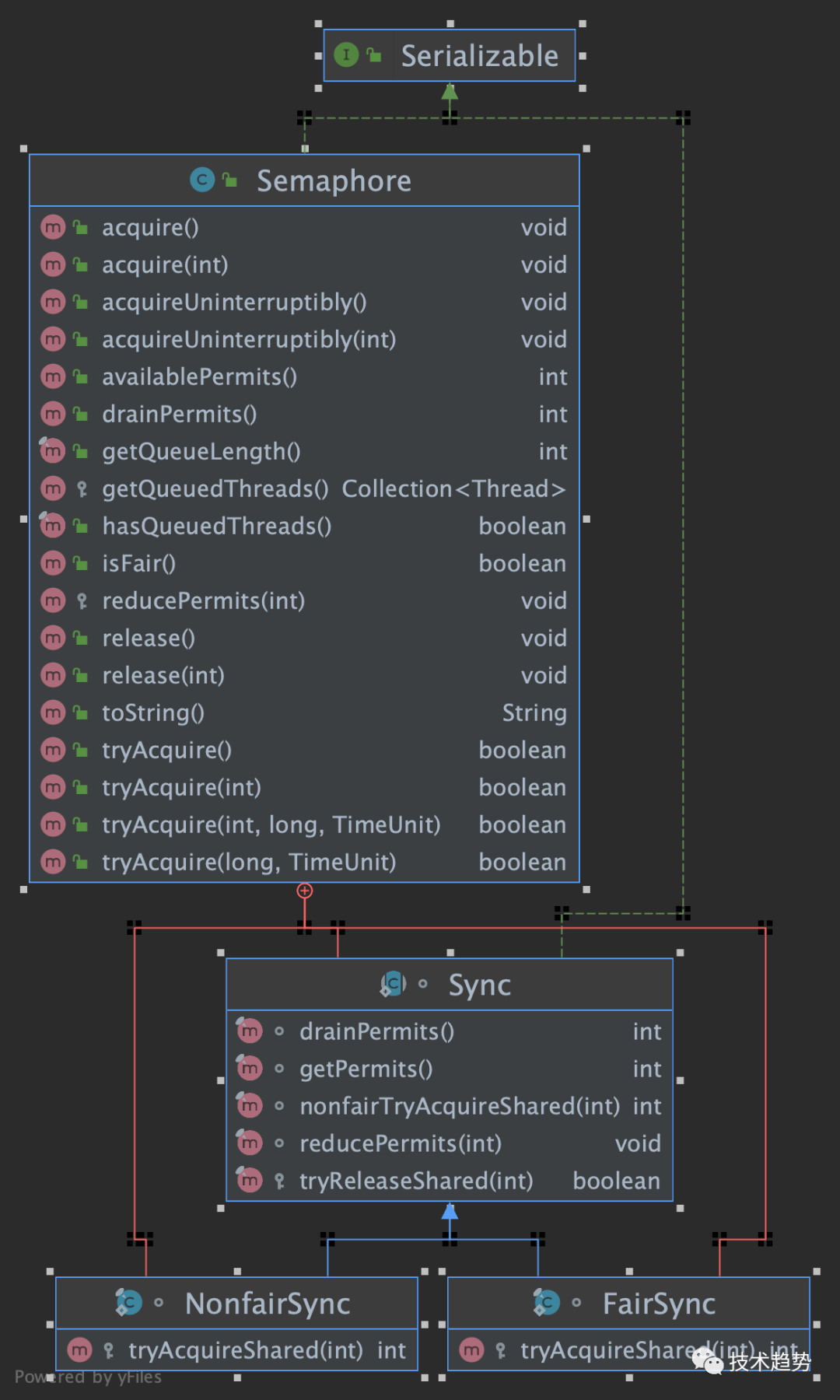
The semaphore is the function of implementing the lock through AQS, which can be specified as a fair lock or an unfair lock. Of course, it is a bit similar to the implementation of reentrant locks (you can refer to the previous article). Let's take a look at some public methods.
method name |
describe |
Remark |
Semaphore(int) |
Construction method |
|
Semaphore(int,boolean) |
build method |
true for fair lock, false for unfair |
acquire() |
acquire lock |
|
acquireUninterruptibly() |
acquire lock |
with interrupt |
tryAcquire() |
try to acquire the lock |
|
tryAcquire(long,TimeUnit) |
try to acquire the lock |
with timeout |
release() |
release lock |
|
acquire(int) |
Get the specified thread |
|
acquireUninterruptibly(int) |
Get the specified thread |
with interrupt |
tryAcquire(int) |
Attempt to get the specified number of threads |
|
tryAcquire(int,long,TimeUnit) |
Attempt to get the specified number of threads |
with timeout |
release(int) |
Release the locks of the specified number of threads |
|
availablePermits() |
get status |
|
drainPermits() |
Quinoa Fetch Current Status |
|
isFair() |
Is it unfair |
|
hasQueuedThreads |
Is there a queue |
|
getQueueLength |
queue length |
|
convert to string |
package java.util.concurrent;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer;
//信号量源码实现
public class Semaphore implements java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -3222578661600680210L;
/** All mechanics via AbstractQueuedSynchronizer subclass */
private final Sync sync;
//继承aqs
abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1192457210091910933L;
//构造方法带初始线程数
Sync(int permits) {
setState(permits);
}
//获取同步状态
final int getPermits() {
return getState();
}
//没有锁的话尝试获取锁
final int nonfairTryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
for (;;) {
//获取状态
int available = getState();
//如果不是取消和共享进尝试更改状态 一直循环
int remaining = available - acquires;
if (remaining < 0 ||
compareAndSetState(available, remaining))
return remaining;
}
}
//尝试释放指定个数锁
protected final boolean tryReleaseShared(int releases) {
//循环
for (;;) {
//获取同步状态
int current = getState();
//当前状态-解锁个数
int next = current + releases;
//小于当前数量 跑出异常
if (next < current) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum permit count exceeded");
//更新状态
if (compareAndSetState(current, next))
return true;
}
}
//减少指定数量的线程许可
final void reducePermits(int reductions) {
for (;;) {
int current = getState();
int next = current - reductions;
//大于当前数量 抛出异常
if (next > current) // underflow
throw new Error("Permit count underflow");
//尝试释放
if (compareAndSetState(current, next))
return;
}
}
//清空当前线程的所有许可
final int drainPermits() {
for (;;) {
int current = getState();
//全部置为初始化
if (current == 0 || compareAndSetState(current, 0))
return current;
}
}
}
//非公平实现
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2694183684443567898L;
//构造方法
NonfairSync(int permits) {
super(permits);
}
//非公平获取线程资源(随机)
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquireShared(acquires);
}
}
//公平锁实现
static final class FairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2014338818796000944L;
//构造方法 指定初始数量
FairSync(int permits) {
super(permits);
}
//公平获取acquires个线程资源
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
for (;;) {
//如果有排队返回-1
if (hasQueuedPredecessors())
return -1;
//获取当前状态
int available = getState();
//如果得到后的值小于0或更新成功 则返回
int remaining = available - acquires;
if (remaining < 0 ||
compareAndSetState(available, remaining))
return remaining;
}
}
}
//指定线程数量构建方法(默认为非公平锁)
public Semaphore(int permits) {
sync = new NonfairSync(permits);
}
//指定线程数量及锁类型构建方法 true公平锁 false非公平锁
public Semaphore(int permits, boolean fair) {
sync = fair ? new FairSync(permits) : new NonfairSync(permits);
}
//带中断异常释放锁
public void acquire() throws InterruptedException {
sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(1);
}
//获取一个信号信许可
public void acquireUninterruptibly() {
sync.acquireShared(1);
}
//获取许可
public boolean tryAcquire() {
return sync.nonfairTryAcquireShared(1) >= 0;
}
//带超时时间获取一个许可
public boolean tryAcquire(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
return sync.tryAcquireSharedNanos(1, unit.toNanos(timeout));
}
//释放一个许可
public void release() {
sync.releaseShared(1);
}
//带中断释放指定permits数量的许可
public void acquire(int permits) throws InterruptedException {
if (permits < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(permits);
}
//获取指定数量的许可
public void acquireUninterruptibly(int permits) {
if (permits < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
sync.acquireShared(permits);
}
//获取指定数量的许全部获取成功才返回true
public boolean tryAcquire(int permits) {
if (permits < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
return sync.nonfairTryAcquireShared(permits) >= 0;
}
//带过期时间及判断是否中断获取指定数量的许可
public boolean tryAcquire(int permits, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
if (permits < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
return sync.tryAcquireSharedNanos(permits, unit.toNanos(timeout));
}
//释放指定数量的许可
public void release(int permits) {
if (permits < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
sync.releaseShared(permits);
}
//查看剩余许可
public int availablePermits() {
return sync.getPermits();
}
//获取并返回立即可用的许可
public int drainPermits() {
return sync.drainPermits();
}
//减少指定数量的许可(不等待)
protected void reducePermits(int reduction) {
if (reduction < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
sync.reducePermits(reduction);
}
//判断是否公平锁,如果是 true 否 false
public boolean isFair() {
return sync instanceof FairSync;
}
//判断当前是否有排队线程
public final boolean hasQueuedThreads() {
return sync.hasQueuedThreads();
}
//获取队列长度
public final int getQueueLength() {
return sync.getQueueLength();
}
//获取队列的线程集合
protected Collection<Thread> getQueuedThreads() {
return sync.getQueuedThreads();
}
//转字符串方法
public String toString() {
return super.toString() + "[Permits = " + sync.getPermits() + "]";
}
}java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier source code learning
package java.util.concurrent;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
//栅栏源码实现
public class CyclicBarrier {
//供栅栏判断的条件
private static class Generation {
boolean broken = false;
}
/** 重入锁*/
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
/** 上锁条件 */
private final Condition trip = lock.newCondition();
/** 锁数量*/
private final int parties;
/* 运行的线程*/
private final Runnable barrierCommand;
/** 当前状态 */
private Generation generation = new Generation();
//已执行数量
private int count;
//重置屏bujj 唤醒所有锁 并更新执行状态为可执行
private void nextGeneration() {
// signal completion of last generation
trip.signalAll();
// set up next generation
count = parties;
generation = new Generation();
}
//打破屏障
private void breakBarrier() {
//更新状太卡
generation.broken = true;
//赋值总数
count = parties;
//幻醒
trip.signalAll();
}
//带超时间的
private int dowait(boolean timed, long nanos)
throws InterruptedException, BrokenBarrierException,
TimeoutException {
//获取锁并上锁
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
//获取当前实例
final Generation g = generation;
//如果为直 直接抛出异常
if (g.broken)
throw new BrokenBarrierException();
//如果线程中断直接打破壁垒并抛出异常
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
breakBarrier();
throw new InterruptedException();
}
//总数减1 获取当前下标
int index = --count;
if (index == 0) { // tripped
//执行标记
boolean ranAction = false;
try {
//获取线程
final Runnable command = barrierCommand;
//不为空则执行
if (command != null)
command.run();
//设为直
ranAction = true;
//重置屏bujj
nextGeneration();
//返回0
return 0;
} finally {
//如果为false则打破屏障
if (!ranAction)
breakBarrier();
}
}
//循环直理 其中不超时则等待 如果直过时间中断退出 抛出异常
for (;;) {
try {
if (!timed)
trip.await();
else if (nanos > 0L)
nanos = trip.awaitNanos(nanos);
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
if (g == generation && ! g.broken) {
breakBarrier();
throw ie;
} else {
// We're about to finish waiting even if we had not
// been interrupted, so this interrupt is deemed to
// "belong" to subsequent execution.
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
//为打破状态
if (g.broken)
throw new BrokenBarrierException();
//返回下标
if (g != generation)
return index;
//超过时间抛出异常
if (timed && nanos <= 0L) {
breakBarrier();
throw new TimeoutException();
}
}
} finally {
//最终解锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
//构造方法
public CyclicBarrier(int parties, Runnable barrierAction) {
if (parties <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.parties = parties;
this.count = parties;
this.barrierCommand = barrierAction;
}
//指定数量构造方法
public CyclicBarrier(int parties) {
this(parties, null);
}
//获取剩余未执行数量
public int getParties() {
return parties;
}
//等待 (一直等到全部线程执行完) 这里是循环致全部结束
public int await() throws InterruptedException, BrokenBarrierException {
try {
return dowait(false, 0L);
} catch (TimeoutException toe) {
throw new Error(toe); // cannot happen
}
}
//带超时时间的等待
public int await(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException,
BrokenBarrierException,
TimeoutException {
return dowait(true, unit.toNanos(timeout));
}
//是否打破状态
public boolean isBroken() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return generation.broken;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//重置(带锁)
public void reset() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
breakBarrier(); // break the current generation
nextGeneration(); // start a new generation
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//获取当前执行数量
public int getNumberWaiting() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return parties - count;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}The cyclicbarrier is implemented internally through reentrant locks. In fact, it is also an implementation method of aqs, but it is relatively independent and uses the function of reentrant locks, so it is not as complicated as others.
java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch source code learning
//计数器实现
public class CountDownLatch {
/**
*
*使用aqs计数
*/
private static final class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 4982264981922014374L;
//同步锁
Sync(int count) {
setState(count);
}
//获取总数(state)
int getCount() {
return getState();
}
//尝试指定数量的计数
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
return (getState() == 0) ? 1 : -1;
}
//获取指定数量的计数
protected boolean tryReleaseShared(int releases) {
// Decrement count; signal when transition to zero
//循环
for (;;) {
int c = getState();
if (c == 0)
return false;
int nextc = c-1;
if (compareAndSetState(c, nextc))
return nextc == 0;
}
}
}
//同步锁
private final Sync sync;
//构造方法 默认用了同步锁 数量必须大于0
public CountDownLatch(int count) {
if (count < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("count < 0");
this.sync = new Sync(count);
}
//等待方法的实现 如果已中断抛出异常 未中断则一直cas等待
public void await() throws InterruptedException {
sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(1);
}
//带超时等待
public boolean await(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
return sync.tryAcquireSharedNanos(1, unit.toNanos(timeout));
}
//减少一个数量
public void countDown() {
sync.releaseShared(1);
}
//获取当前待处理数量
public long getCount() {
return sync.getCount();
}
//转string方法
public String toString() {
return super.toString() + "[Count = " + sync.getCount() + "]";
}
}It can be seen that this counter is simpler, of course, the usage scenarios are also very limited and are generally one-off.
at last
Last time I saw a few blocking queues, I really didn’t want to read them all, because it was too long, thousands of lines long, it was really easy to read these counters later, and a few classmates also I kept asking these few questions and just took a look. In fact, these few seem to be rarely used in work, but many of them are used in the bottom layer of various counting or concurrency frameworks, such as semaphores, which are generally used for current limiting, and counters or fences generally appear in errors Timed notifications or alarms in scenarios where the number of times or a certain amount is reached.