Table of contents
1. For loop to traverse the list
yuansu = ['study', '1', 'yuansu', 'name', 'python']
for yuansu_1 in yuansu:
print(yuansu_1)

2. Create a list of values
"""使用list()将range()的结果直接转换为数字列表"""
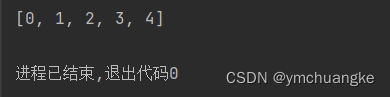
numbers = list(range(5))
print(numbers)
2.1 Use functions to perform some basic operations on lists of values
2.1.1max() Calculate the maximum value in the value list
2.1.2min() Calculate the minimum value in the value list
2.1.3sum() calculates the sum of the values in the value list
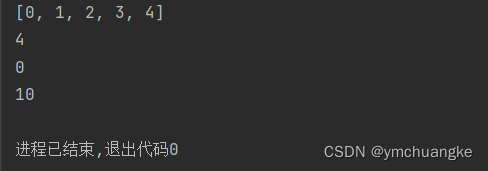
numbers = list(range(5))
print(numbers)
print(max(numbers))
print(min(numbers))
print(sum(numbers))
3. Use part of the list
3.1 slice
Definition : Processing part of the elements of a list is called a slice.
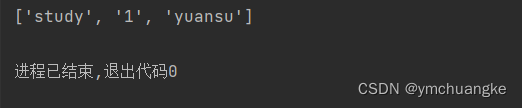
"""使用[x:y]指定索引,第二个索引-1(差一)"""
yuansu = ['study', '1', 'yuansu', 'name', 'python']
print(yuansu[1:3])

"""使用[x:y]指定索引,x可以不写,则默认从0开始遍历"""
yuansu = ['study', '1', 'yuansu', 'name', 'python']
print(yuansu[:3])
"""使用[x:y]指定索引,x可以为负,则默认从末尾开始计数"""
yuansu = ['study', '1', 'yuansu', 'name', 'python']
print(yuansu[-3:-1])

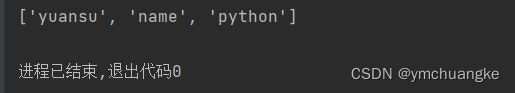
"""使用[x:y]指定索引,x可以为负,则默认从末尾开始计数"""
yuansu = ['study', '1', 'yuansu', 'name', 'python']
print(yuansu[-3:])
3.2 Traversing slices
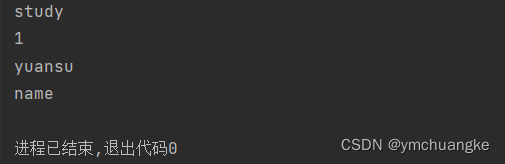
#以这个为例,其它类比即可
yuansu = ['study', '1', 'yuansu', 'name', 'python']
for yuansu_1 in yuansu[:4]:
print(yuansu_1)
3.3 Copy list
"""语法说明:"""
新变量 = 旧变量[:]
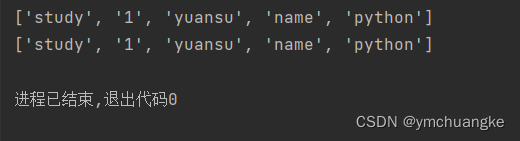
yuansu = ['study', '1', 'yuansu', 'name', 'python']
yuansu_new = yuansu[:]
print(yuansu_new)
print(yuansu)
Four. Tuple
Explanation : The list can be modified, such as append(), sort(), sorted(), etc. You can use tuples when you don't need to modify the elements of the list.
Flags : Lists are [] and tuples are ().
yuanzu = ('1','2','3')
print(yuanzu)

Modify tuple variables : Remember that tuples cannot perform list operations, but you can assign values to tuple variables! (Equivalent to redefining the tuple to override the previous definition).
yuanzu = ('1','2','3')
print(yuanzu)
yuanzu = ('1','2','4')
print(yuanzu)

Traversing tuples : The operation is the same as that of lists.