Check out daily check-in
- 2022-01-20 [1. The sum of two numbers](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/two-sum/)
- 2022-01-21 Number of palindrome
- 2022 1.22 Play RW badly
- 2022-01-23 [13. Roman numerals to integers](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/roman-to-integer/)
- 2022-01-24 Longest Common Prefix
- 2022-01-25 [Valid Parentheses](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/valid-parentheses/)
- 2022-01-27 [Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-array/)
- 2022-01-28[Remove element](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-element/)
- 2022-01-29 [实现 strStr()](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/implement-strstr/)
- 2022-1.39-2022-2.4 Touched
- 2022-02-05 [Search Insert Position](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/search-insert-position/)
- 2022-02-06[Maximum Subarray Sum](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-subarray/)
- 2022-02-07 [58. The length of the last word](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/length-of-last-word/)
- 2022-02-08 [66. Plus one](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/plus-one/)
- 2022-02-09 [Climbing Stairs](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/climbing-stairs/)
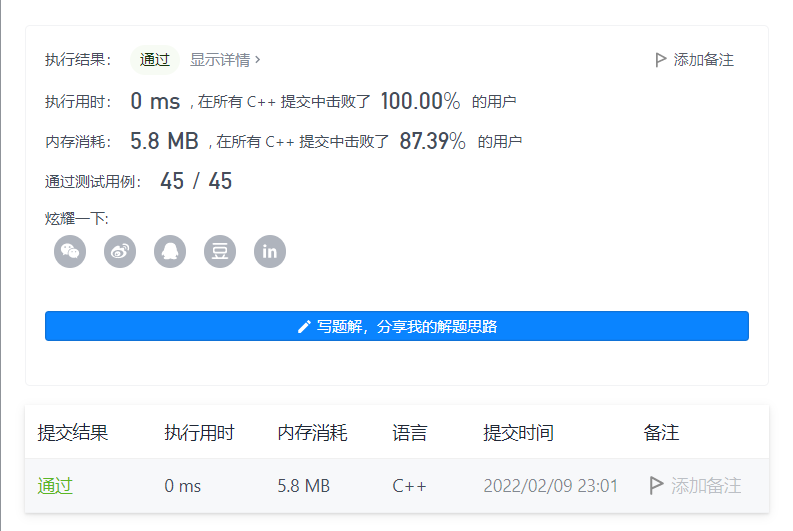
2022-01-20 1. The sum of two numbers
I just started brushing force buttons today, and it feels weird
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<nums.size()-1;i++)
{
for(j=i+1;j<nums.size();j++)
{
if(nums[j]==target-nums[i])
{
return {i,j};
}
}
}
return {};
}
};
Why can return {} directly here?
Because it is a new type of intpair
I have never seen this usage, so I found a better answer on the Internet:
As long as the constructor is not explicit, it can newIntegerbe called in return iinstead of return Integer(i)this complicated expression.
But what if there is a new type IntPairwhose constructor has 2 ints? return IntPair(i, j)Then you can only return obediently , and you can return {i, j}go directly after the list is initialized.
As for why not get a syntax like return i, jor return (i, j)? Because there is a comma expression in the C language, that is to say, i,jit is actually a comma expression of the sum, iand jwhat is returned is j. C++ is compatible with C (at least the old standard), so it has to find another way to simplify the code.
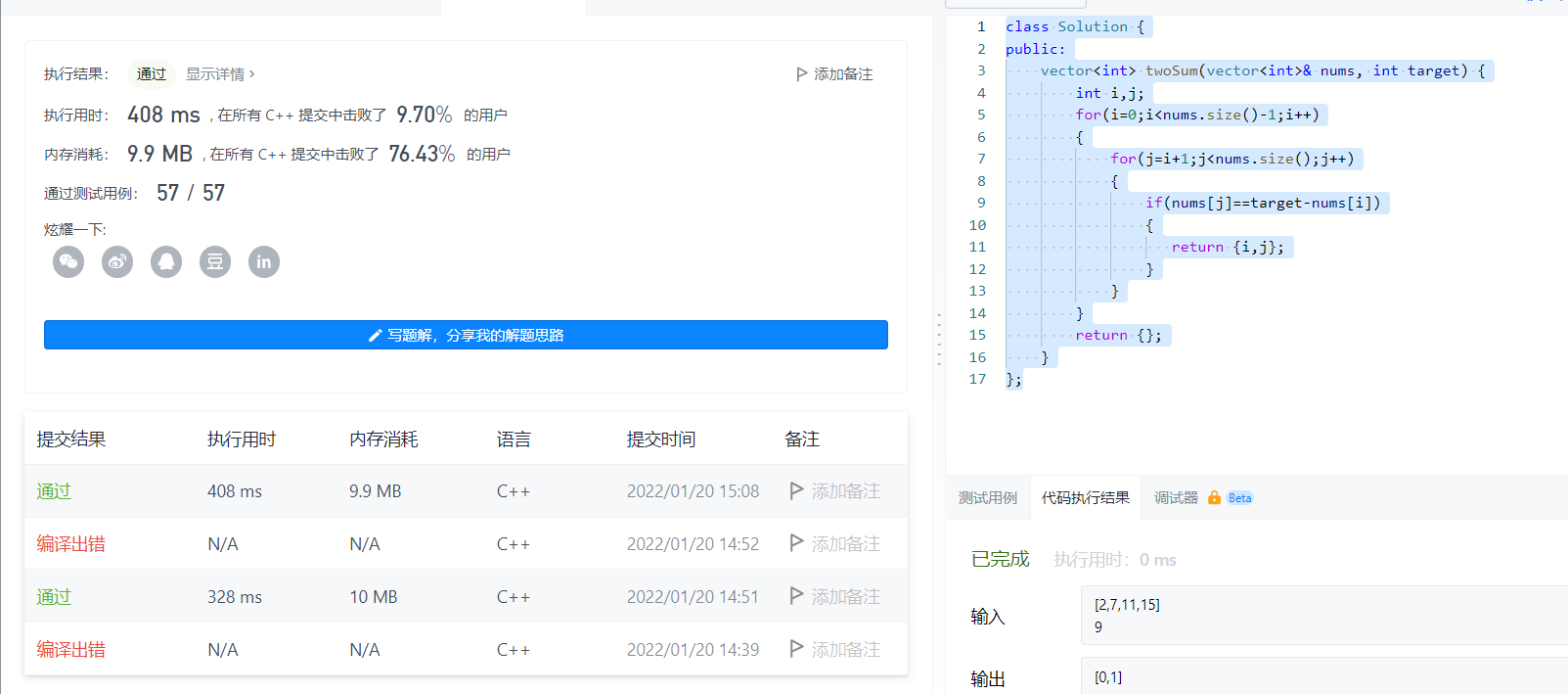
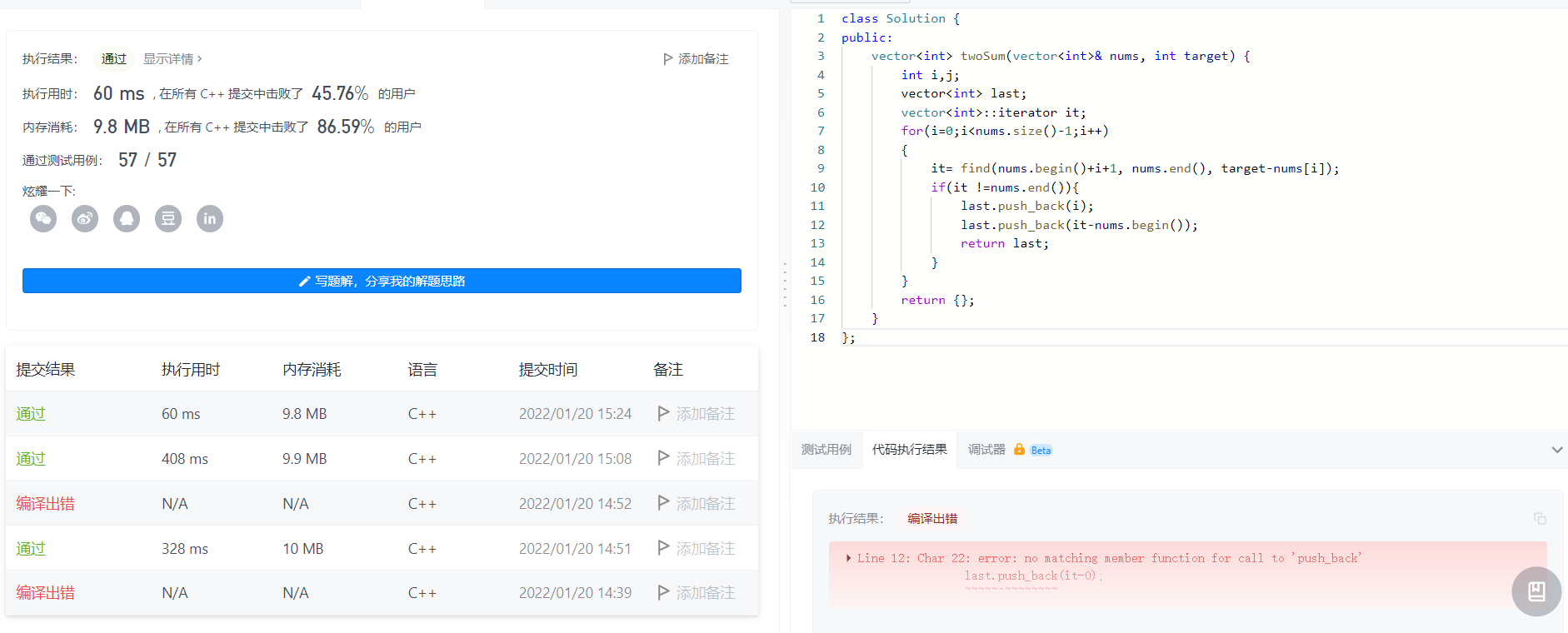
use iterator find
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int i,j;
vector<int> last;
vector<int>::iterator it;
for(i=0;i<nums.size()-1;i++)
{
it= find(nums.begin()+i+1, nums.end(), target-nums[i]);
if(it !=nums.end()){
last.push_back(i);
last.push_back(it-nums.begin());
return last;
}
}
return {};
}
};
Use find here, the result of find is still an iterator, but it points to a different location,
It-nums.begin Iterator subtraction obtains the phase difference between the two, that is, always it-0 to obtain the distance of it
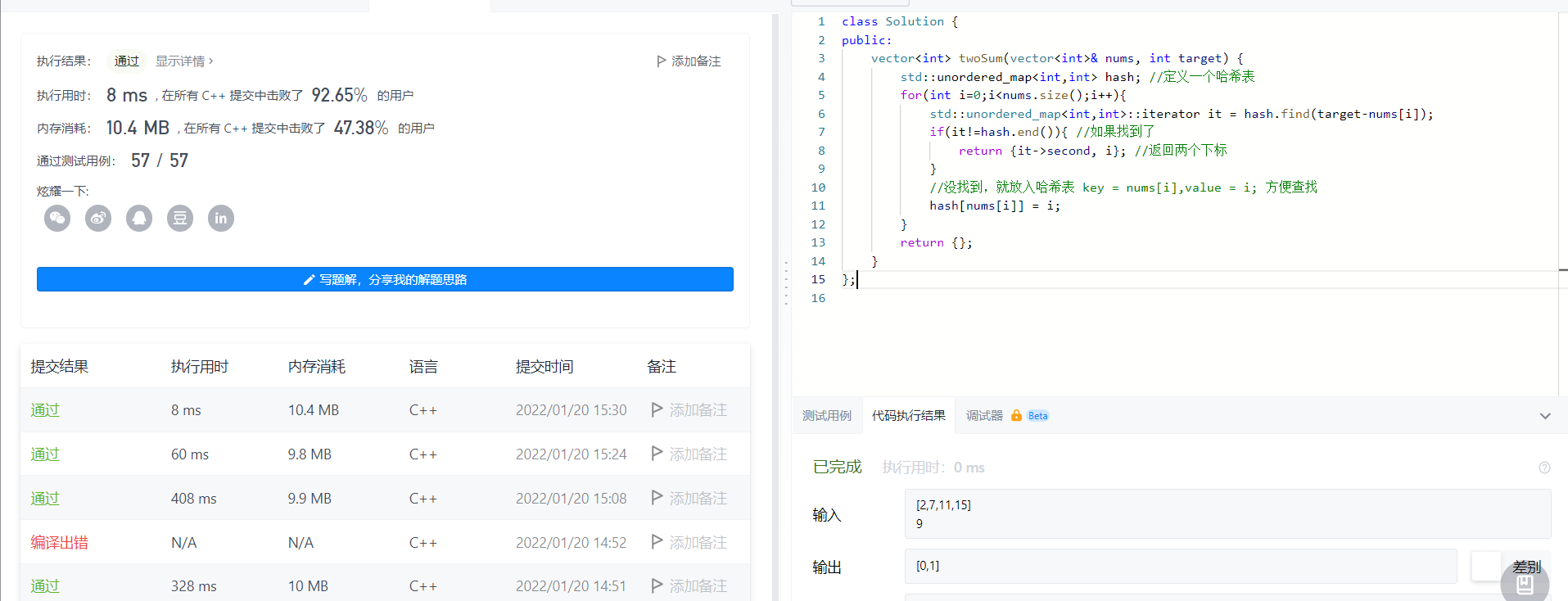
Using Map Optimization
unordered_map can be more convenient for searching
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
std::unordered_map<int,int> hash; //定义一个哈希表
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){
std::unordered_map<int,int>::iterator it = hash.find(target-nums[i]);
if(it!=hash.end()){ //如果找到了
return {it->second, i}; //返回两个下标
}
//没找到,就放入哈希表 key = nums[i],value = i; 方便查找
hash[nums[i]] = i;
}
return {};
}
};
It turns out that unorderd_map is more suitable for queries because it is an optimized red-black tree
2022-01-21 Number of palindrome
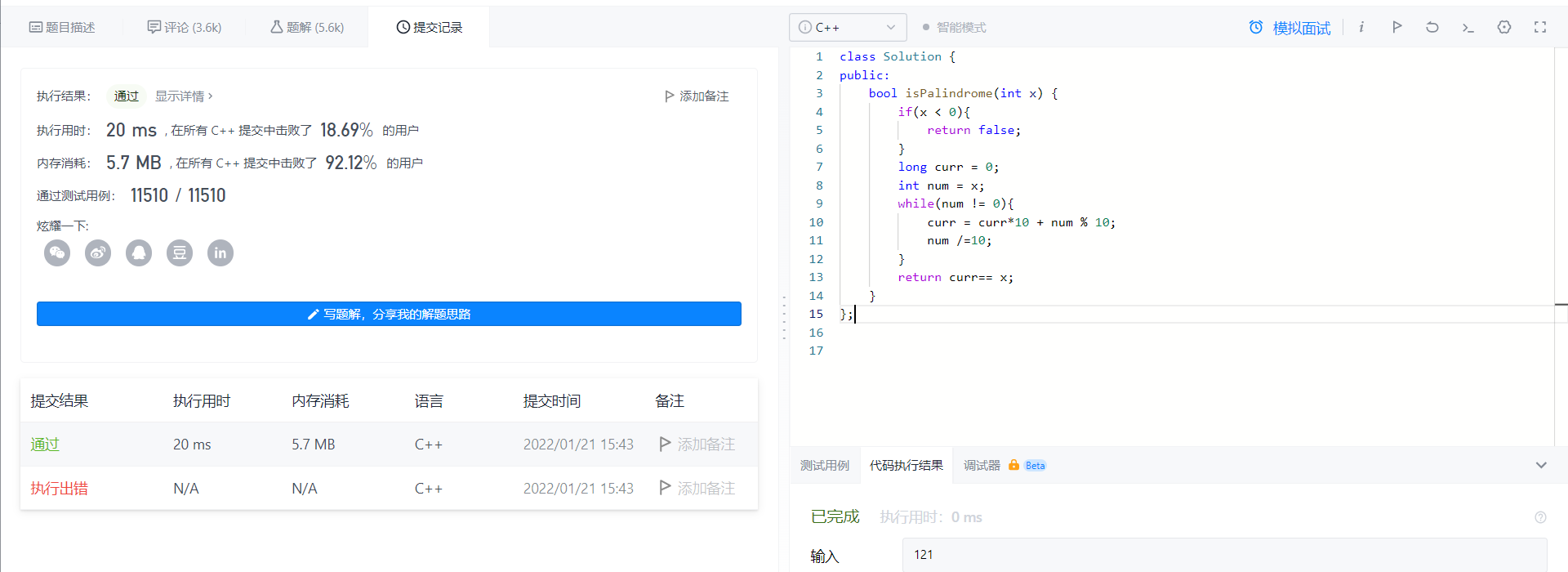
class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(int x) {
if(x < 0){
return false;
}
long curr = 0;
int num = x;
while(num != 0){
curr = curr*10 + num % 10;
num /=10;
}
return curr== x;
}
};
It's relatively simple, take out the single digit each time, then adjust a variable, and invert it
Of course we can do optimization, that is to say, multiples of 10 obviously cannot be used as palindrome numbers,
Or, for an odd number of numbers, half of the middle is enough, not all of them need to be transposed
class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(int x) {
if (x < 0 || (x % 10 == 0 && x != 0)) {
return false;
}
long curr = 0;
int num = x;
while(num != 0){
curr = curr*10 + num % 10;
num /=10;
}
return curr== x;
}
};

Although it is only optimized a little, the time is reduced a lot
2022 1.22 Play RW badly
2022-01-23 13. Convert Roman numerals to integers
class Solution {
public:
int romanToInt(string s) {
int store;
int result=0;
//打表
unordered_map<string,int> table = {
{"I", 1}, {"IV", 4}, {"V", 5}, {"IX", 9},
{"X", 10}, {"XL", 40}, {"L", 50}, {"XC", 90}, {"C", 100}, {"CD", 400},
{"D", 500}, {"CM", 900}, {"M", 1000}};
int size = int(s.size());
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
//这里的find 和end都是返回迭代器,如果找不到,迭代器指针就会返回到end,只要不等于end,说明就能找到
if(i+1 < size && table.find(s.substr(i, 2)) != table.end()){
result += table[s.substr(i,2)];
i++;
}else{
result +=table[s.substr(i,1)];
}
}
return result;
}
};

2022-01-24 Longest Common Prefix
Because there are many, it is the most convenient to compare two, so just write one to compare two
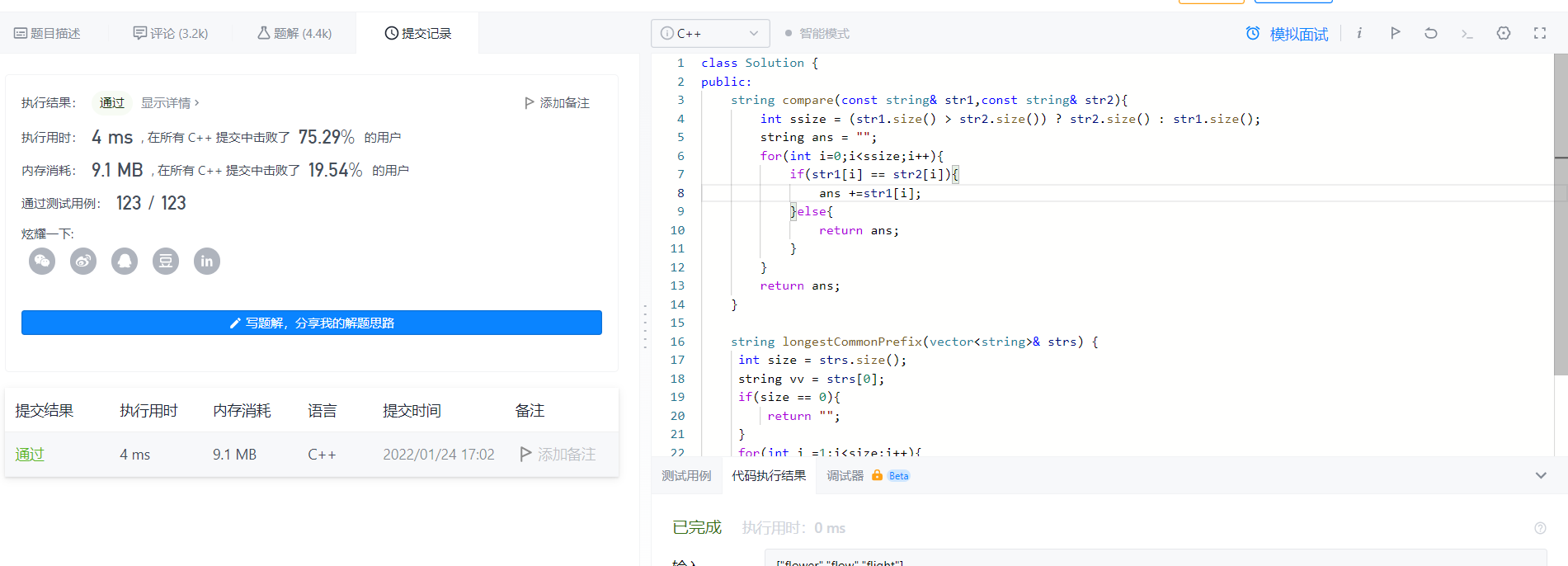
class Solution {
public:
string compare(const string& str1,const string& str2){
int ssize = (str1.size() > str2.size()) ? str2.size() : str1.size();
string ans = "";
for(int i=0;i<ssize;i++){//比较
if(str1[i] == str2[i]){
ans +=str1[i];
}else{
return ans;
}
}
return ans;
}
string longestCommonPrefix(vector<string>& strs) {
int size = strs.size();
string vv = strs[0];
if(size == 0){
return "";
}
for(int i =1;i<size;i++){
vv = compare(vv,strs[i]);
}
return vv;
}
};
2022-01-25 Valid brackets
This is a stack question
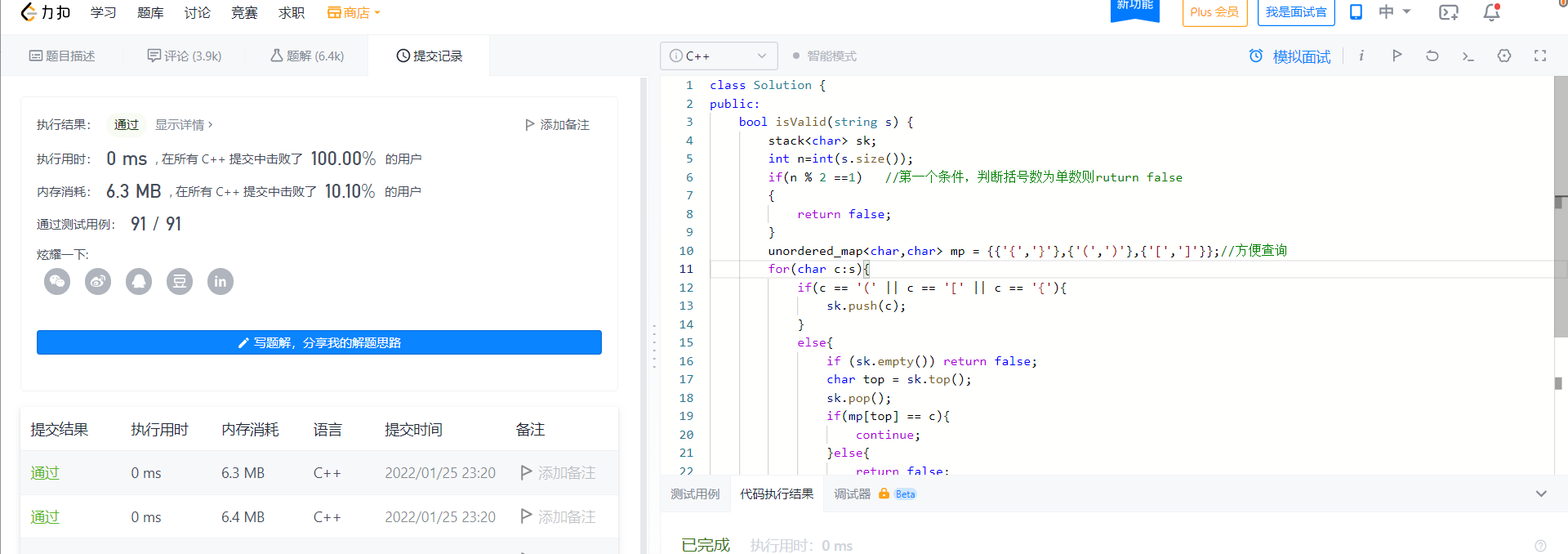
class Solution {
public:
bool isValid(string s) {
stack<char> sk;
int n=int(s.size());
if(n % 2 ==1) //第一个条件,判断括号数为单数则ruturn false
{
return false;
}
unordered_map<char,char> mp = {
{'{','}'},{'(',')'},{'[',']'}};//方便查询
for(char c:s){
if(c == '(' || c == '[' || c == '{'){
sk.push(c);
}
else{
if (sk.empty()) return false;
char top = sk.top();
sk.pop();
if(mp[top] == c){
continue;
}else{
return false;
}
}
}
if (sk.empty()){
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
};
2022-01-27 Remove duplicates in sorted array
Violence
That is to scan the array again,
If the previous one is different from the latter one, put it in a new array,

double pointer optimization

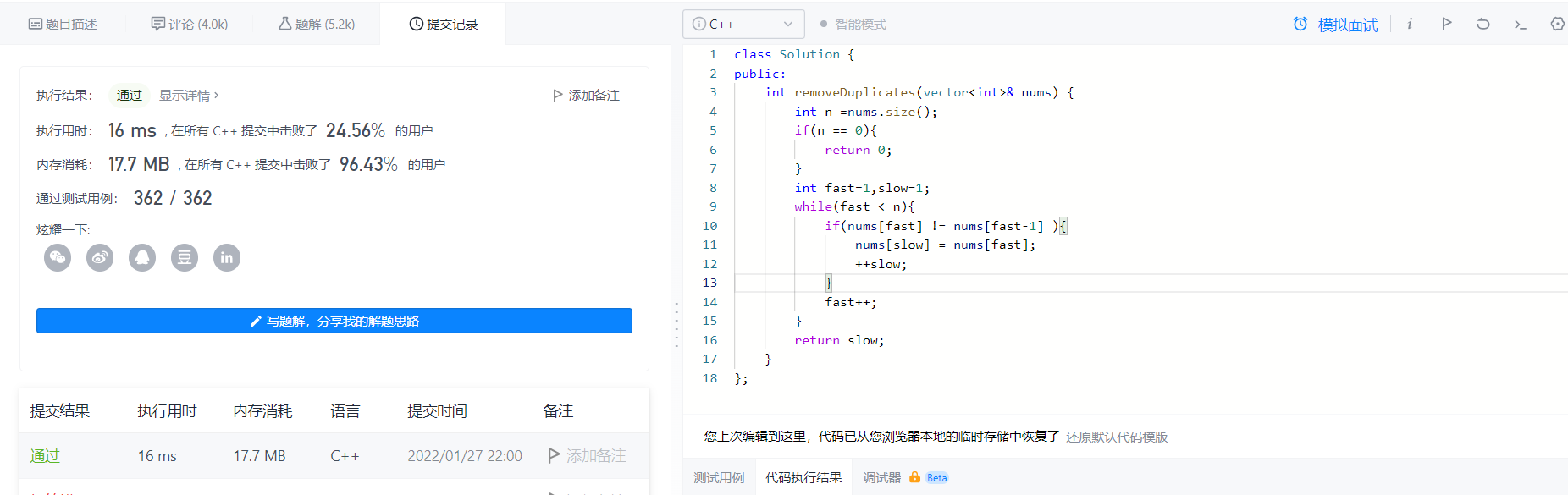
class Solution {
public:
int removeDuplicates(vector<int>& nums) {
int n =nums.size();
if(n == 0){
return 0;
}
int fast=1,slow=1;
while(fast < n){
if(nums[fast] != nums[fast-1] ){
nums[slow] = nums[fast];
++slow;
}
fast++;
}
return slow;
}
};
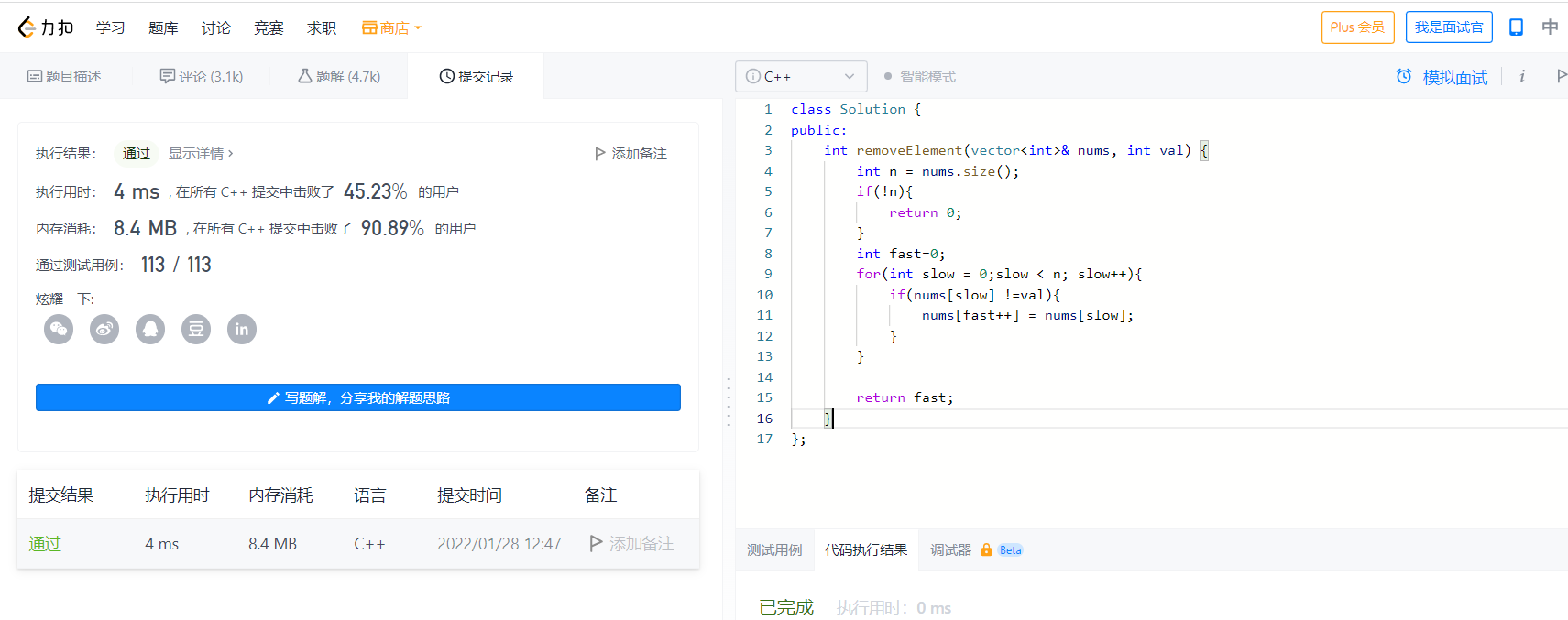
2022-01-28 Remove element
Same as yesterday's double pointer
class Solution {
public:
int removeElement(vector<int>& nums, int val) {
int n = nums.size();
if(!n){
return 0;
}
int fast=0;
for(int slow = 0;slow < n; slow++){
if(nums[slow] !=val){
nums[fast++] = nums[slow];
}
}
return fast;
}
};
2022-01-29 Implement strStr()
Violence

class Solution {
public:
int strStr(string haystack, string needle) {
int hay = haystack.size();
int nee = needle.size();
if(nee == 0){
return 0;
}
for(int i = 0;i <= hay-nee ;i++){
bool flag = true;
for(int j = 0;j< nee;j++){
if(haystack[i+j] != needle[j]){
flag = false;
break;
}
}
if (flag) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
};
KMP algorithm
The most important thing about the KMP algorithm is the next array
It is not easy to understand, the prefix table is used to roll back the array
The prefix table is used for fallback. It records where the pattern string should start to re-match when the pattern string does not match the main string (text string).
I can't understand here. . .
dove
2022-1.39-2022-2.4 Touched
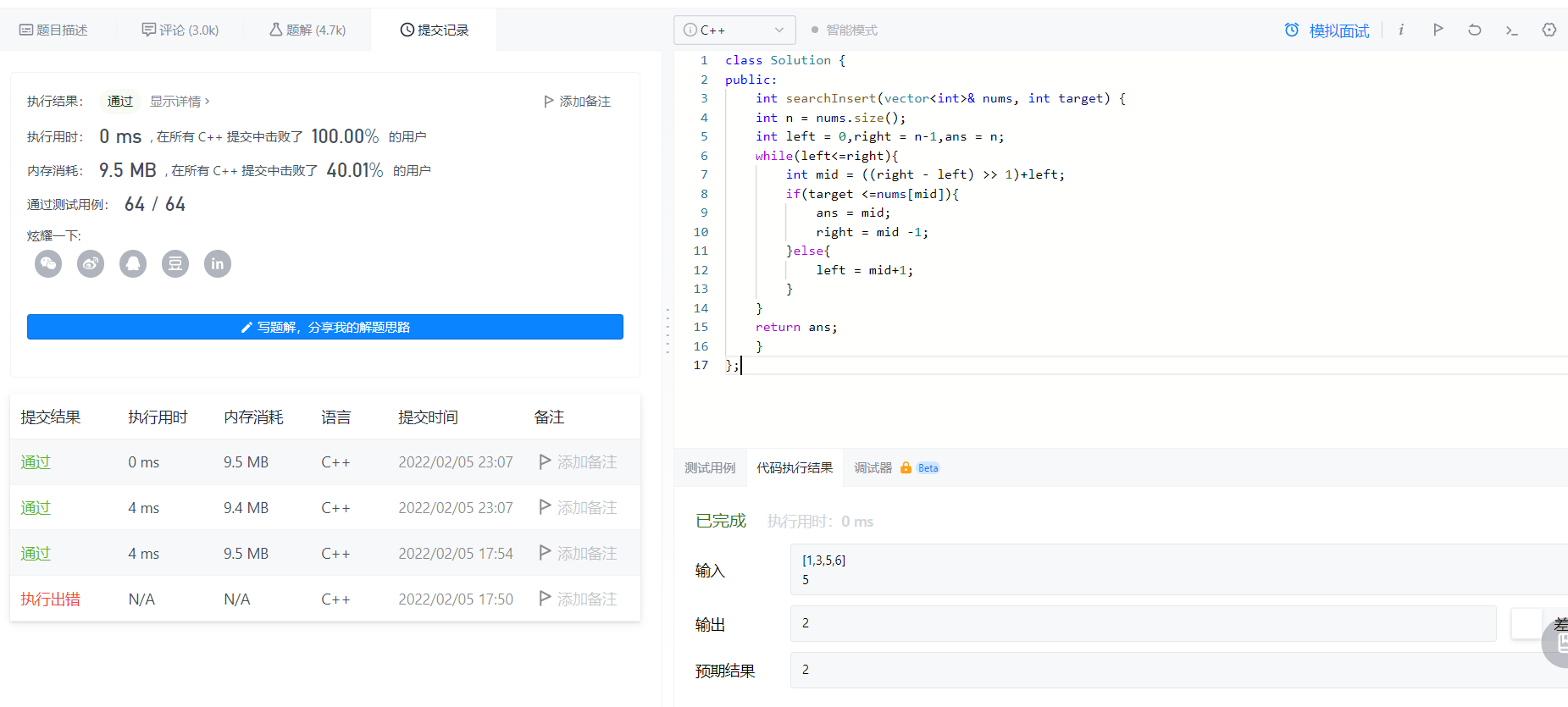
2022-02-05Search insertion position
class Solution {
public:
int searchInsert(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
for(int i=0;i<=nums.size()-1;i++){
if(nums[i] >= target){
return i;
}
}
return nums.size();
}
};

A simple violence, the first interval is written wrong, resulting in an empty array,
dichotomy
Find the value by dichotomy, and then make up the pos position
class Solution {
public:
int searchInsert(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int n = nums.size();
int left = 0,right = n-1,ans = n;
while(left<=right){
int mid = ((right - left) >> 1)+left;
if(target <=nums[mid]){
ans = mid;
right = mid -1;
}else{
left = mid+1;
}
}
return ans;
}
};
2022-02-06 Maximum subarray sum
At first I wanted to use the prefix sum to do it, but found that the result was wrong, and did not consider the largest case in the middle, not the prefix sum

class Solution {
public:
static bool comp(int x ,int y)
{
return x > y;
}
int maxSubArray(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int> res;
int x = 0;
for(int i=0;i<=nums.size();i++){
x+=nums[i];
res.push_back(x);
}
sort(res.begin(),res.end(),comp);
return res.front();
}
};
Change thinking
Violence
class Solution
{
public:
int maxSubArray(vector<int> &nums)
{
//类似寻找最大最小值的题目,初始值一定要定义成理论上的最小最大值
int max = INT_MIN;
int numsSize = int(nums.size());
for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++)
{
int sum = 0;
for (int j = i; j < numsSize; j++)
{
sum += nums[j];
if (sum > max)
{
max = sum;
}
}
}
return max;
}
};
But it will definitely time out
dynamic programming
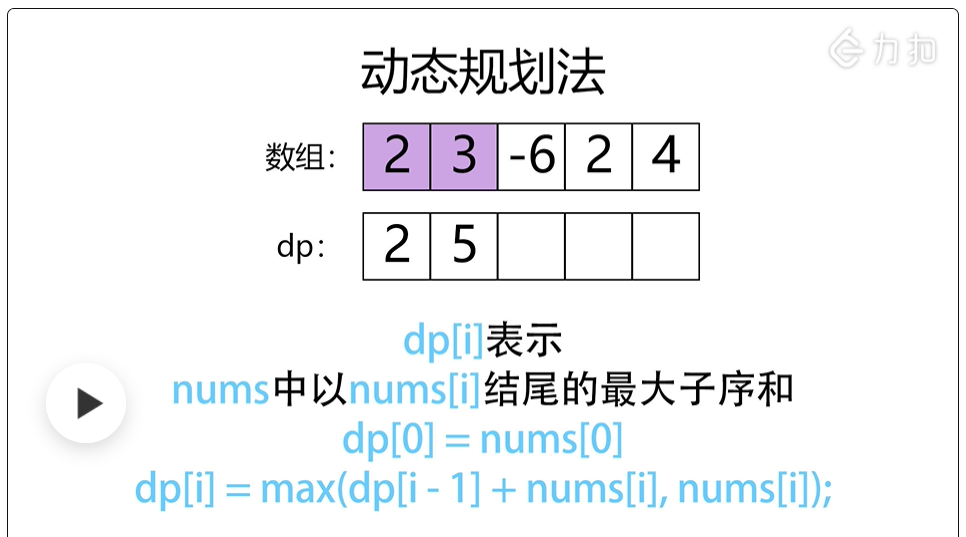
Here dynamic programming, it first guarantees that the first value is the initial value, and then ensures that each of the previous ones is the largest, and the sum is the largest, otherwise, he will clear the previous number and replace it with the current one The value of , (here is greedy)
dynamic programming


class Solution {
public:
int maxSubArray(vector<int>& nums) {
int pre = 0;
int ans = nums[0];
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){
pre = max(pre + nums[i],nums[i]);
ans = max(pre,ans);
}
return ans;
}
};
2022-02-07 58. The length of the last word
We can do the reverse directly here, he requires the length of the last string

class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLastWord(string s) {
int length = s.size()-1;
while(s[length] == ' '){
length--;
}
int t=0;
while(length >=0 && s[length] != ' '){
length--;
t++;
}
return t;
}
};
Here is a little tip
单引号是字符,一个字节,双引号是字符串有一个结束符,“b”是两个字节b + \0,而‘b’只有一个字节。
So here we use single quotes
2022-02-08 66. Plus one
The essence of finding a question is to directly +1 the last digit and then return without difficulty
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> plusOne(vector<int>& digits) {
int size = digits.size();
digits[size-1]+=1;
return digits;
}
};
This is an abbreviated version, only 91 samples passed
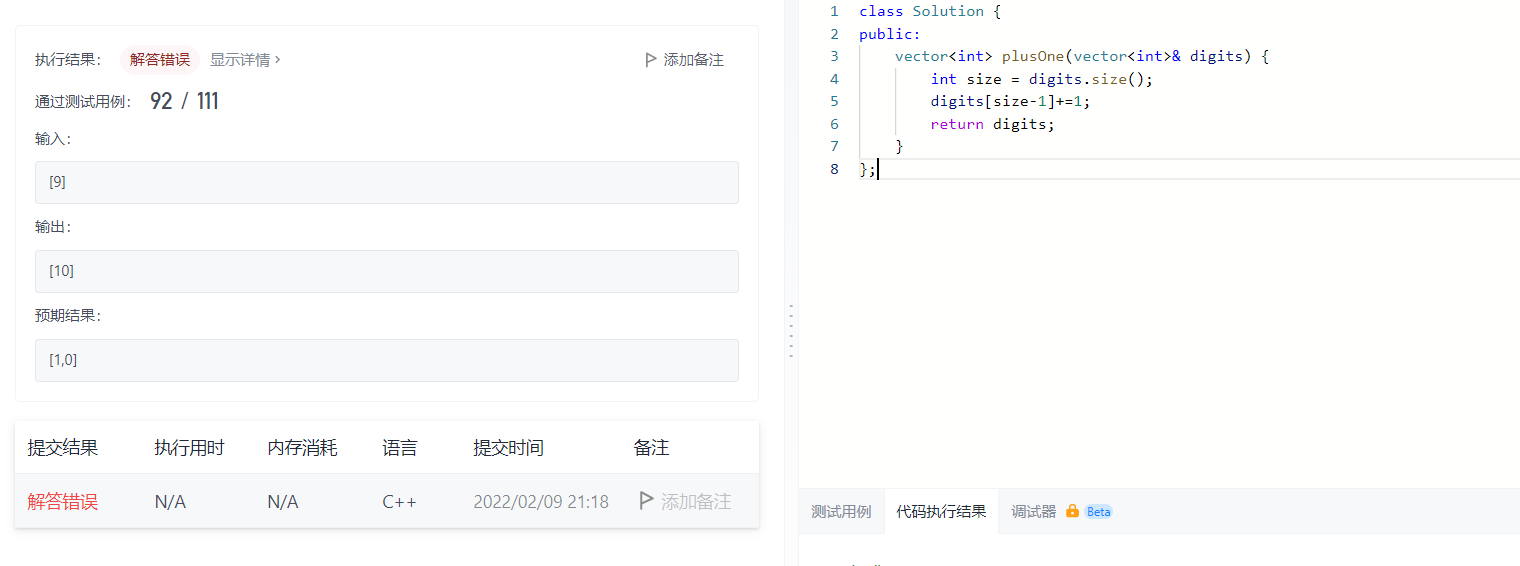
That is to say, you need to enter 1 when you reach ten
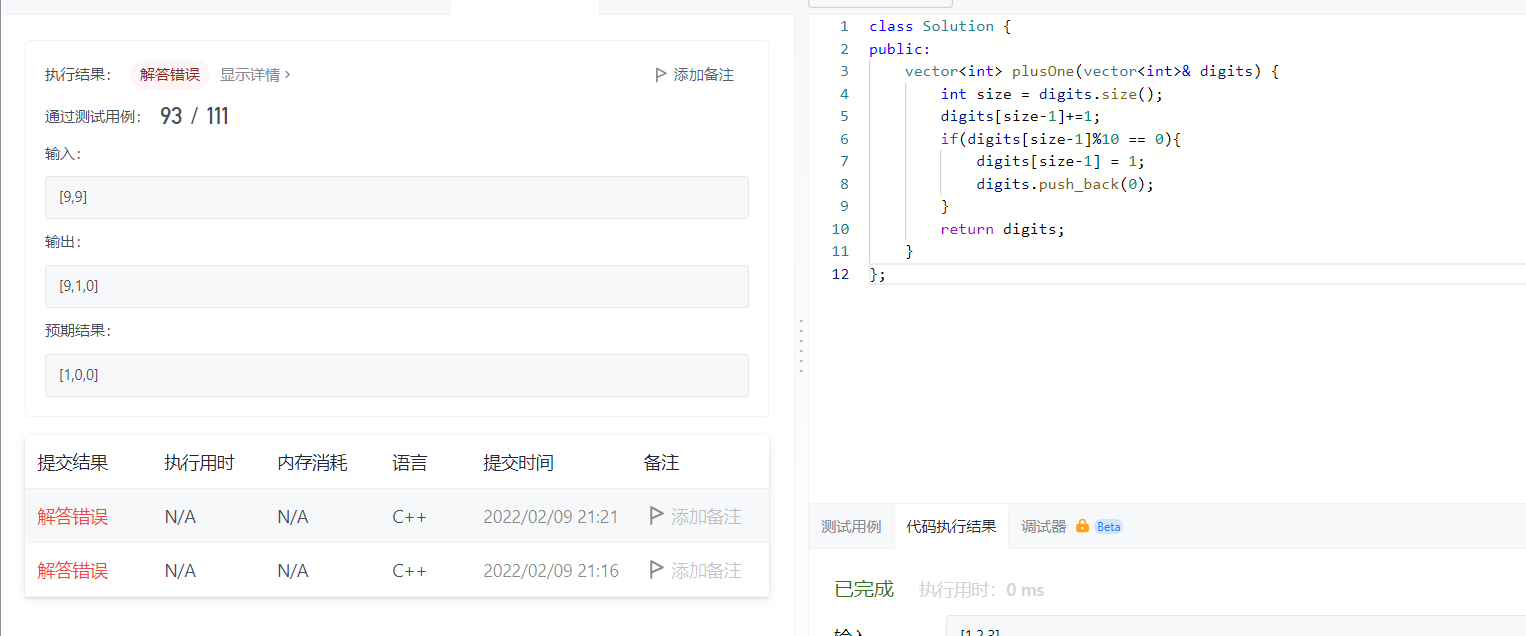
After making some supplementary modifications, I found that something strange happened, 99 needs 100
To do this, my idea may be a for, brute force, find the ones greater than 10, and then disassemble and insert
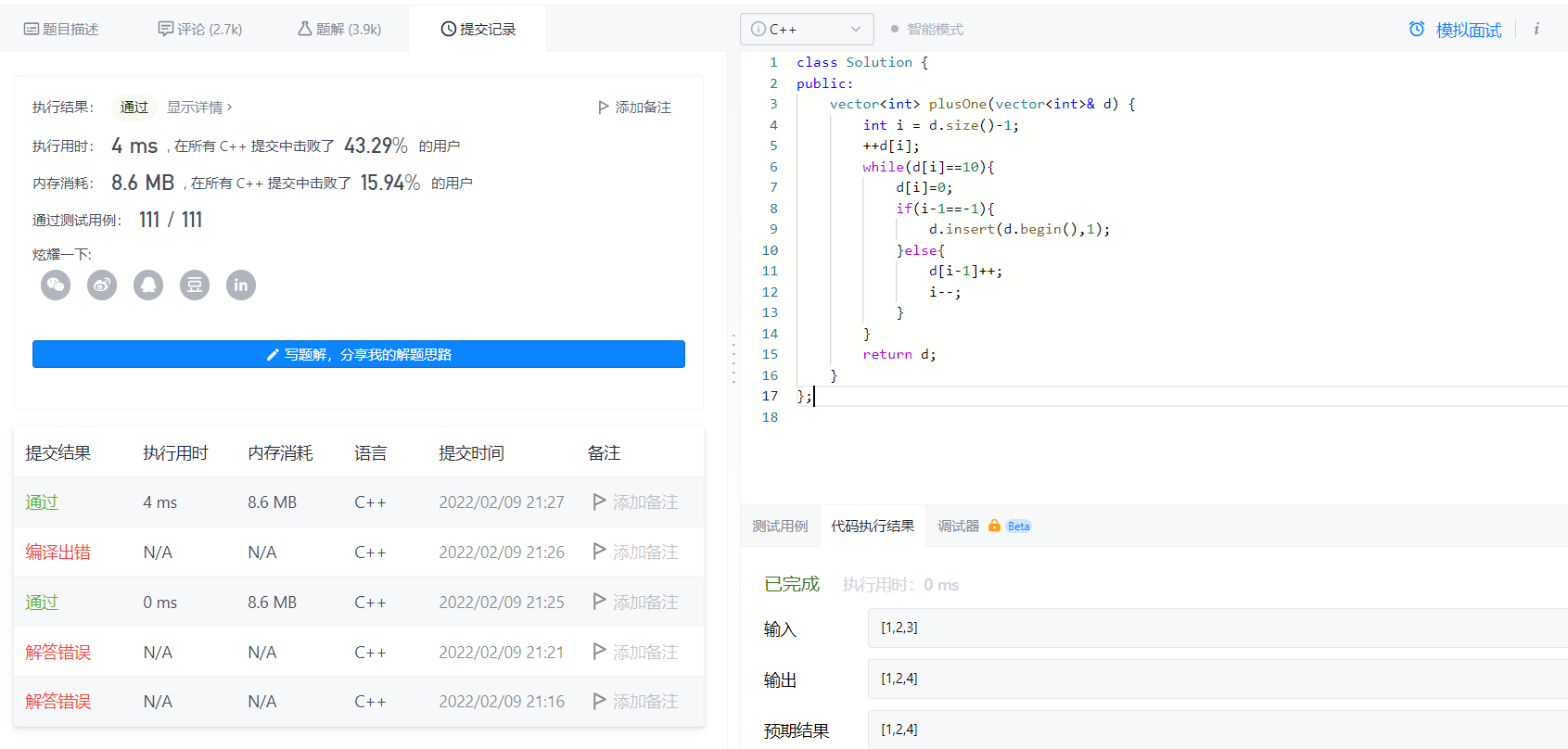
found a version
Check if the value is 10 in reverse order, then advance one, change to 0, this version is 0ms
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> plusOne(vector<int>& d) {
int i = d.size()-1;
++d[i];
while(d[i]==10){
d[i]=0;
if(i-1==-1){
d.insert(d.begin(),1);
}else{
d[i-1]++;
i--;
}
}
return d;
}
};
2022-02-09 Stair climbing
Dynamic programming, using sliding window ideas
class Solution {
public:
int climbStairs(int n) {
int p=0,q=0,r=1;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
p = q;
q = r;
r = p+q;
}
return r;
}
};