Table of contents
2. Explanation of the content of the arp protocol:
NAT protocol: address translation protocol
DNS protocol: domain name resolution protocol
data link layer:
prerequisite knowledge
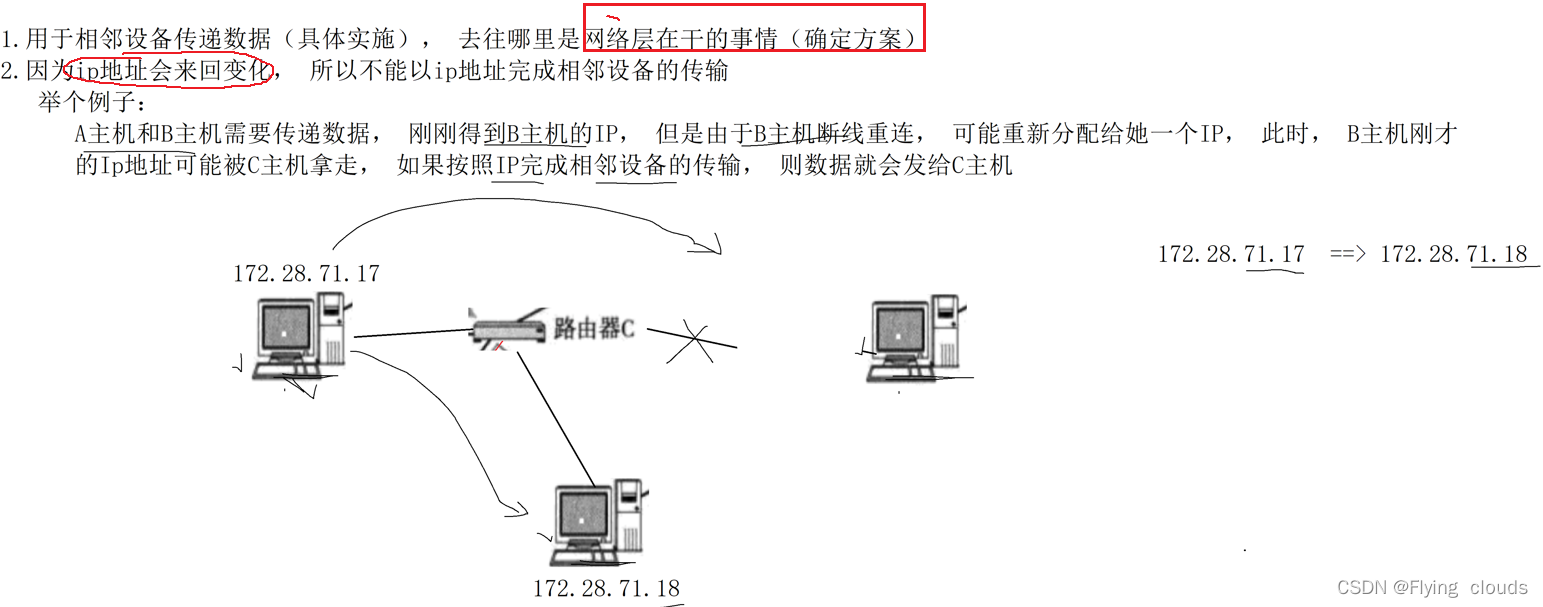
Because the ip address may change and cannot completely identify a host, the transmission between adjacent devices uses the MAC address
Ethernet protocol:
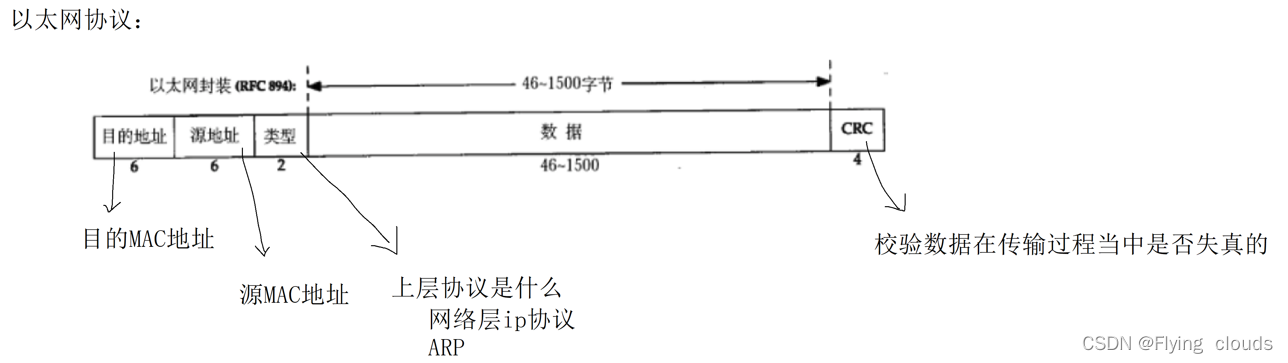
The Ethernet protocol needs to know the destination MAC address and the source MAC address. It is easy to get the source MAC address, but the destination MAC is not so easy to get. If we want to give a relative that has never sent data before How can we get his MAC address if we only know its IP address when the neighboring device sends information ?
This requires the ARP protocol
arp protocol
1. Function: Obtain the MAC address through the IP address, and obtain the MAC address of the adjacent device through the IP address
2. After obtaining the MAC address of the adjacent device, the destination MAC address in the Ethernet protocol can be filled.
1. ARP protocol format

2. Explanation of the content of the arp protocol:

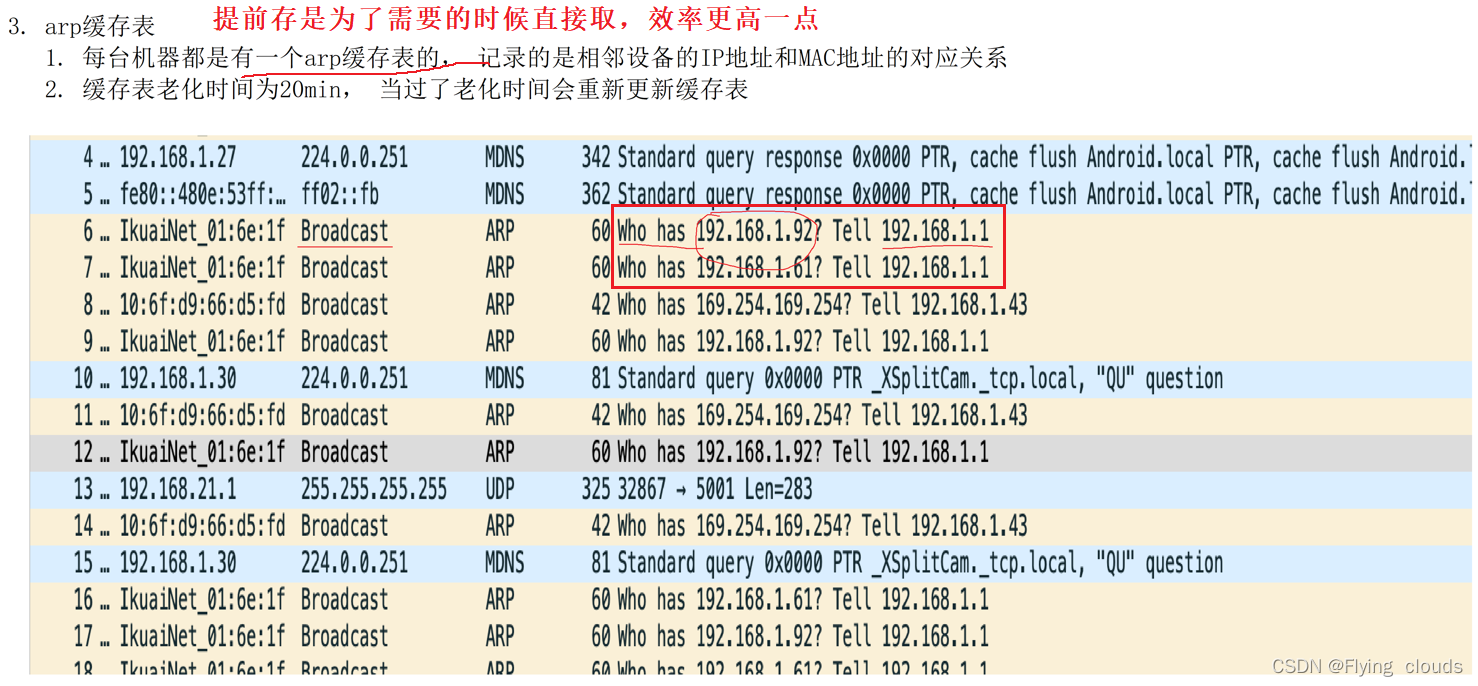
arp cache table
NAT protocol: address translation protocol
1. Function: replace the private network IP in the network data with the public network IP, or replace the public network IP in the network data with the private network IP
example:

2. NAT mode
1. Static NAT, NAT maintains a private network IP corresponding to a public network IP
2. Dynamic NAT: The NAT gateway maintains many public IPs. When data arrives at the NAT gateway, find an idle public IP to replace
The above two methods are one-to-one on the private network and the public network. In this case, the problem of IP address exhaustion is not alleviated.
The following is the important way:
3. NATP: Dynamic NAT overloading
When replacing the IP address, not only the private network IP is replaced with the public network IP, but also the port of the transport layer needs to be replaced
Benefits: One public network IP + port can serve the conversion of multiple private network IPs at the same time, which can greatly alleviate the problem of IP address exhaustion

3. Summary of NAT
1. NAT conversion is transparent to both communication parties, without perception
2. The NAT gateway will save the mapping relationship after conversion, and after the response comes back, it will convert again
3. Data can only be transferred from the private network to the public network first, not from the public network to the private network
4. NAPT adds port conversion, which can greatly alleviate the problem of IP address exhaustion
DNS protocol: domain name resolution protocol
1. Function: Convert domain name to IP address
A domain name is a string of character strings separated by dots, which essentially corresponds to an IP address
2. Domain name level:
First-level domain name:
.com . con .dov .us .org .net
secondary domain:
baidu.com jd.com taobao.com
Third-level domain name:
baike.baidu.com
3. Domain name server:

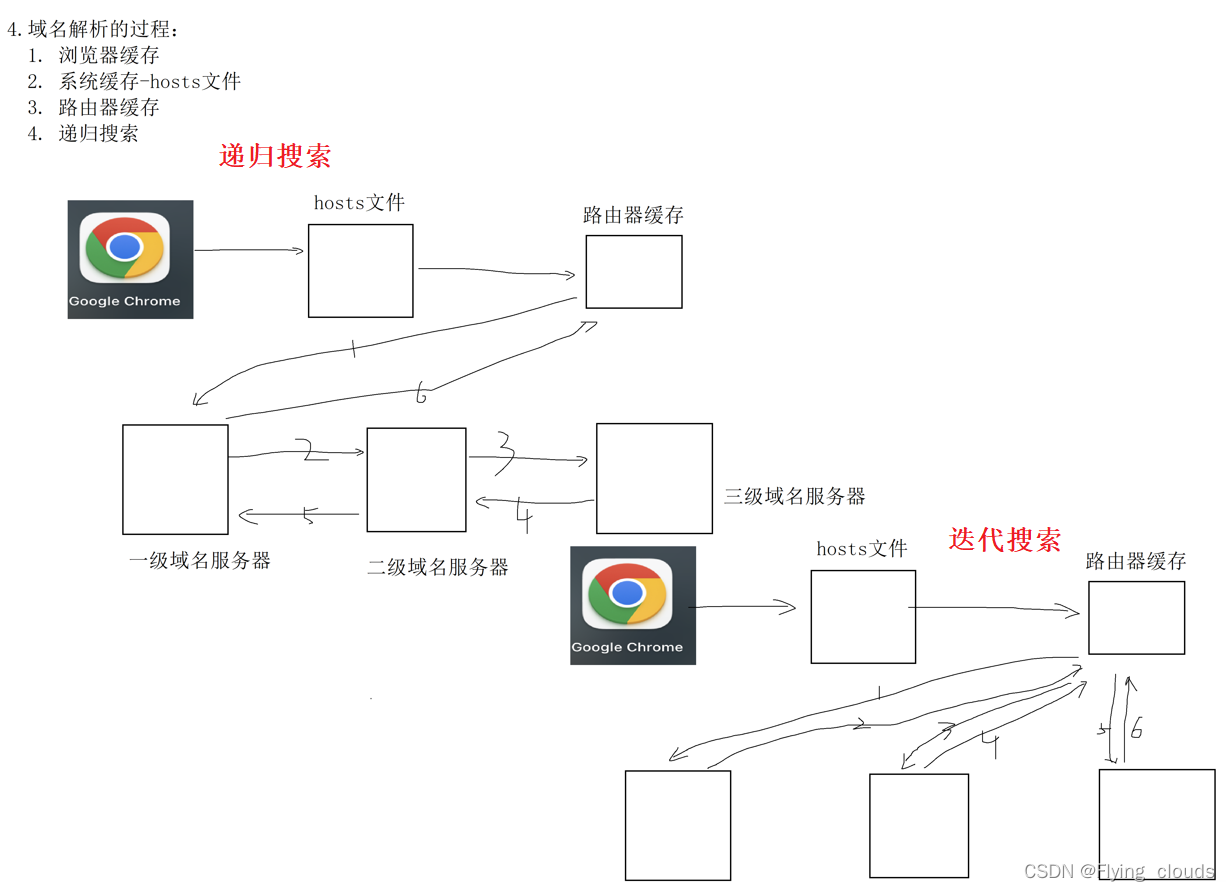
4. The process of domain name resolution