CycleGAN code
Reference Code
参考代码链接:https://github.com/Lornatang/CycleGAN-PyTorch
数据集百度云:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1UryUwsCoyqG_xhH7VJXdLw?pwd=hqkb
Principle of CycleGAN
cycleGAN is a kind of unsupervised machine learning developed by Generative Adversarial Networks. It is developed on the basis of pix2pix. It is mainly used for image generation and conversion of unpaired pictures, and can realize style conversion, such as taking photos Convert to an oil painting style, or convert a photo from an orange to an apple, from a horse to a zebra, and more. Because it can be converted without paired data sets, it will be much simpler in data preparation and has great application prospects.
CycleGAN is essentially two mirror-symmetrical GANs forming a ring network. The two GANs share two generators and each has a discriminator, that is, there are two discriminators and two generators. A one-way GAN has two losses, two or four losses in total.
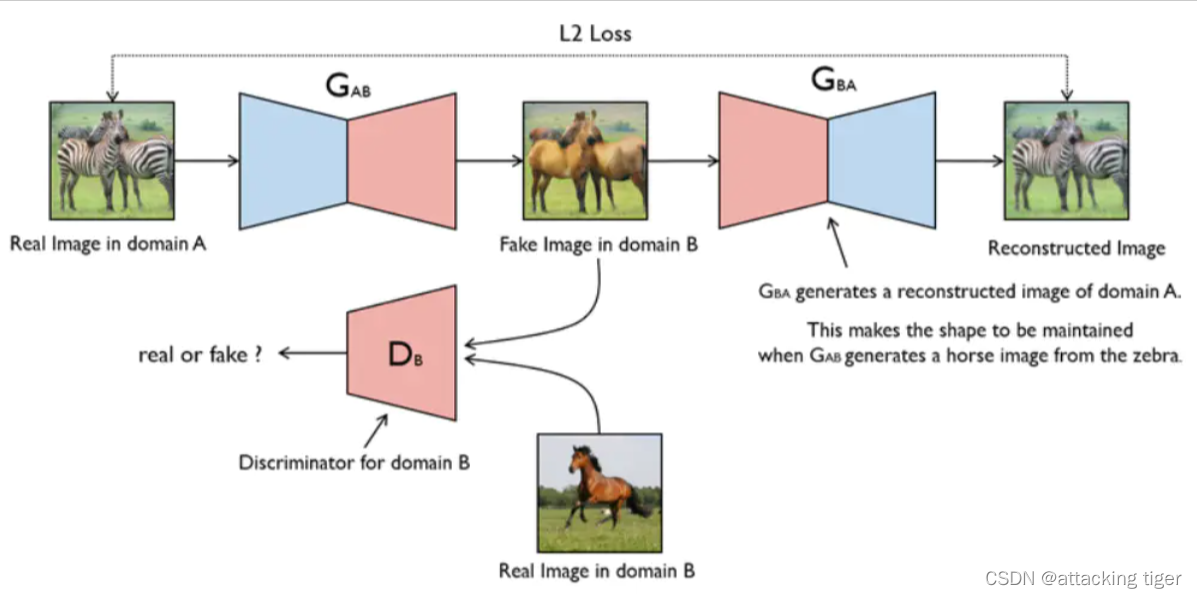
code introduction
models
The main function is to set an initialization parameter, which is called when training starts.
A generator and discriminator network are built.
In addition to weakening the disappearance of the gradient, the residual block in the generator can also be understood as a kind of adaptive depth, that is, the network can adjust the depth of the number of layers by itself, at least it can degenerate into the input without getting worse. It can make the network deeper and smoother, making the training of deep neural network possible.
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch
## 定义参数初始化函数
def weights_init_normal(m):
classname = m.__class__.__name__ ## m作为一个形参,原则上可以传递很多的内容, 为了实现多实参传递,每一个moudle要给出自己的name. 所以这句话就是返回m的名字.
if classname.find("Conv") != -1: ## find():实现查找classname中是否含有Conv字符,没有返回-1;有返回0.
torch.nn.init.normal_(m.weight.data, 0.0, 0.02) ## m.weight.data表示需要初始化的权重。nn.init.normal_():表示随机初始化采用正态分布,均值为0,标准差为0.02.
if hasattr(m, "bias") and m.bias is not None: ## hasattr():用于判断m是否包含对应的属性bias, 以及bias属性是否不为空.
torch.nn.init.constant_(m.bias.data, 0.0) ## nn.init.constant_():表示将偏差定义为常量0.
elif classname.find("BatchNorm2d") != -1: ## find():实现查找classname中是否含有BatchNorm2d字符,没有返回-1;有返回0.
torch.nn.init.normal_(m.weight.data, 1.0, 0.02) ## m.weight.data表示需要初始化的权重. nn.init.normal_():表示随机初始化采用正态分布,均值为0,标准差为0.02.
torch.nn.init.constant_(m.bias.data, 0.0) ## nn.init.constant_():表示将偏差定义为常量0.
##############################
## 残差块儿ResidualBlock
##############################
class ResidualBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_features):
super(ResidualBlock, self).__init__()
self.block = nn.Sequential( ## block = [pad + conv + norm + relu + pad + conv + norm]
nn.ReflectionPad2d(1), ## ReflectionPad2d():利用输入边界的反射来填充输入张量
nn.Conv2d(in_features, in_features, 3), ## 卷积
nn.InstanceNorm2d(in_features), ## InstanceNorm2d():在图像像素上对HW做归一化,用在风格化迁移
nn.ReLU(inplace=True), ## 非线性激活
nn.ReflectionPad2d(1), ## ReflectionPad2d():利用输入边界的反射来填充输入张量
nn.Conv2d(in_features, in_features, 3), ## 卷积
nn.InstanceNorm2d(in_features), ## InstanceNorm2d():在图像像素上对HW做归一化,用在风格化迁移
)
def forward(self, x): ## 输入为 一张图像
return x + self.block(x) ## 输出为 图像加上网络的残差输出
##############################
## 生成器网络GeneratorResNet
##############################
class GeneratorResNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_shape, num_residual_blocks): ## (input_shape = (3, 256, 256), num_residual_blocks = 9)
super(GeneratorResNet, self).__init__()
channels = input_shape[0] ## 输入通道数channels = 3
## 初始化网络结构
out_features = 64 ## 输出特征数out_features = 64
model = [ ## model = [Pad + Conv + Norm + ReLU]
nn.ReflectionPad2d(channels), ## ReflectionPad2d(3):利用输入边界的反射来填充输入张量
nn.Conv2d(channels, out_features, 7), ## Conv2d(3, 64, 7)
nn.InstanceNorm2d(out_features), ## InstanceNorm2d(64):在图像像素上对HW做归一化,用在风格化迁移
nn.ReLU(inplace=True), ## 非线性激活
]
in_features = out_features ## in_features = 64
## 下采样,循环2次
for _ in range(2):
out_features *= 2 ## out_features = 128 -> 256
model += [ ## (Conv + Norm + ReLU) * 2
nn.Conv2d(in_features, out_features, 3, stride=2, padding=1),
nn.InstanceNorm2d(out_features),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
]
in_features = out_features ## in_features = 256
# 残差块儿,循环9次
for _ in range(num_residual_blocks):
model += [ResidualBlock(out_features)] ## model += [pad + conv + norm + relu + pad + conv + norm]
# 上采样两次
for _ in range(2):
out_features //= 2 ## out_features = 128 -> 64
model += [ ## model += [Upsample + conv + norm + relu]
nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2),
nn.Conv2d(in_features, out_features, 3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.InstanceNorm2d(out_features),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
]
in_features = out_features ## out_features = 64
## 网络输出层 ## model += [pad + conv + tanh]
model += [nn.ReflectionPad2d(channels), nn.Conv2d(out_features, channels, 7), nn.Tanh()] ## 将(3)的数据每一个都映射到[-1, 1]之间
self.model = nn.Sequential(*model)
def forward(self, x): ## 输入(1, 3, 256, 256)
return self.model(x) ## 输出(1, 3, 256, 256)
##############################
# Discriminator
##############################
class Discriminator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_shape):
super(Discriminator, self).__init__()
channels, height, width = input_shape ## input_shape:(3, 256, 256)
# Calculate output shape of image discriminator (PatchGAN)
self.output_shape = (1, height // 2 ** 4, width // 2 ** 4) ## output_shape = (1, 16, 16)
def discriminator_block(in_filters, out_filters, normalize=True): ## 鉴别器块儿
"""Returns downsampling layers of each discriminator block"""
layers = [nn.Conv2d(in_filters, out_filters, 4, stride=2, padding=1)] ## layer += [conv + norm + relu]
if normalize: ## 每次卷积尺寸会缩小一半,共卷积了4次
layers.append(nn.InstanceNorm2d(out_filters))
layers.append(nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True))
return layers
self.model = nn.Sequential(
*discriminator_block(channels, 64, normalize=False), ## layer += [conv(3, 64) + relu]
*discriminator_block(64, 128), ## layer += [conv(64, 128) + norm + relu]
*discriminator_block(128, 256), ## layer += [conv(128, 256) + norm + relu]
*discriminator_block(256, 512), ## layer += [conv(256, 512) + norm + relu]
nn.ZeroPad2d((1, 0, 1, 0)), ## layer += [pad]
nn.Conv2d(512, 1, 4, padding=1) ## layer += [conv(512, 1)]
)
def forward(self, img): ## 输入(1, 3, 256, 256)
return self.model(img) ## 输出(1, 1, 16, 16)
# ## test
# img_shape = (3, 256, 256)
# n_residual_blocks = 9
# G_AB = GeneratorResNet(img_shape, n_residual_blocks)
# D_A = Discriminator(img_shape)
# img = torch.rand((1, 3, 256, 256))
# fake = G_AB(img)
# print(fake.shape)
# fake_D = D_A(img)
# print(fake_D.shape)
datasets
The root in it represents the stored folder. The naming format is as follows: ./datasets/facades
can call the train_data_loader() function, and the data in dictionary format can be obtained through data['A'] and data['B' ] operation to take out different types of pictures.
import glob
import random
import os
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
from PIL import Image
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
## 如果输入的数据集是灰度图像,将图片转化为rgb图像(本次采用的facades不需要这个)
def to_rgb(image):
rgb_image = Image.new("RGB", image.size)
rgb_image.paste(image)
return rgb_image
## 构建数据集
class ImageDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, root, transforms_=None, unaligned=False, mode="train"): ## (root = "./datasets/facades", unaligned=True:非对其数据)
self.transform = transforms.Compose(transforms_) ## transform变为tensor数据
self.unaligned = unaligned
self.files_A = sorted(glob.glob(os.path.join(root, "%sA" % mode) + "/*.*")) ## "./datasets/facades/trainA/*.*"
self.files_B = sorted(glob.glob(os.path.join(root, "%sB" % mode) + "/*.*")) ## "./datasets/facades/trainB/*.*"
def __getitem__(self, index):
image_A = Image.open(self.files_A[index % len(self.files_A)]) ## 在A中取一张照片
if self.unaligned: ## 如果采用非配对数据,在B中随机取一张
image_B = Image.open(self.files_B[random.randint(0, len(self.files_B) - 1)])
else:
image_B = Image.open(self.files_B[index % len(self.files_B)])
# 如果是灰度图,把灰度图转换为RGB图
if image_A.mode != "RGB":
image_A = to_rgb(image_A)
if image_B.mode != "RGB":
image_B = to_rgb(image_B)
# 把RGB图像转换为tensor图, 方便计算,返回字典数据
item_A = self.transform(image_A)
item_B = self.transform(image_B)
return {
"A": item_A, "B": item_B}
## 获取A,B数据的长度
def __len__(self):
return max(len(self.files_A), len(self.files_B))
utils
This module designs a buffer and a function for updating the learning rate.
When updating the discriminators, the previously generated pictures are used instead of the latest pictures. Therefore, a picture buffer is set up to store 50 previously generated pictures.
The initial learning rate is 0.0003, and the total epoch is 50. When it is 0-30, the learning rate is 0.0003. When it is 30-50, the learning rate gradually decreases linearly to 0, so it is necessary to update the learning rate.
The required variables are: the total training epoch, the current epoch, and the epoch that starts to decay, so that the linear change of lr can be achieved.
import random
import time
import datetime
import sys
from torch.autograd import Variable
import torch
import numpy as np
from torchvision.utils import save_image
## 先前生成的样本的缓冲区
class ReplayBuffer:
def __init__(self, max_size=50):
assert max_size > 0, "Empty buffer or trying to create a black hole. Be careful."
self.max_size = max_size
self.data = []
def push_and_pop(self, data): ## 放入一张图像,再从buffer里取一张出来
to_return = [] ## 确保数据的随机性,判断真假图片的鉴别器识别率
for element in data.data:
element = torch.unsqueeze(element, 0)
if len(self.data) < self.max_size: ## 最多放入50张,没满就一直添加
self.data.append(element)
to_return.append(element)
else:
if random.uniform(0, 1) > 0.5: ## 满了就1/2的概率从buffer里取,或者就用当前的输入图片
i = random.randint(0, self.max_size - 1)
to_return.append(self.data[i].clone())
self.data[i] = element
else:
to_return.append(element)
return Variable(torch.cat(to_return))
## 设置学习率为初始学习率乘以给定lr_lambda函数的值
class LambdaLR:
def __init__(self, n_epochs, offset, decay_start_epoch): ## (n_epochs = 50, offset = epoch, decay_start_epoch = 30)
assert (n_epochs - decay_start_epoch) > 0, "Decay must start before the training session ends!" ## 断言,要让n_epochs > decay_start_epoch 才可以
self.n_epochs = n_epochs
self.offset = offset
self.decay_start_epoch = decay_start_epoch
def step(self, epoch): ## return 1-max(0, epoch - 30) / (50 - 30)
return 1.0 - max(0, epoch + self.offset - self.decay_start_epoch) / (self.n_epochs - self.decay_start_epoch)
cycle_gan
This is the training function, start training.
First configure the hyperparameters, optimizer, data set, and loss function, and then start training.
Print the log during the training process, and save the test result picture of the test set every 100 times.
Save the model after training
import argparse
import os
from tkinter import Image
import numpy as np
import math
import itertools
import datetime
import time
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
from torchvision.utils import save_image, make_grid
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torchvision import datasets
from torch.autograd import Variable
from models import *
from dataset import *
from utils import *
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch
from PIL import Image
## 超参数配置
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--epoch", type=int, default=0, help="epoch to start training from")
parser.add_argument("--n_epochs", type=int, default=5, help="number of epochs of training")
parser.add_argument("--dataset_name", type=str, default="facades", help="name of the dataset")## ../input/facades-dataset
parser.add_argument("--batch_size", type=int, default=1, help="size of the batches")
parser.add_argument("--lr", type=float, default=0.0003, help="adam: learning rate")
parser.add_argument("--b1", type=float, default=0.5, help="adam: decay of first order momentum of gradient")
parser.add_argument("--b2", type=float, default=0.999, help="adam: decay of first order momentum of gradient")
parser.add_argument("--decay_epoch", type=int, default=3, help="epoch from which to start lr decay")
parser.add_argument("--n_cpu", type=int, default=2, help="number of cpu threads to use during batch generation")
parser.add_argument("--img_height", type=int, default=256, help="size of image height")
parser.add_argument("--img_width", type=int, default=256, help="size of image width")
parser.add_argument("--channels", type=int, default=3, help="number of image channels")
parser.add_argument("--sample_interval", type=int, default=100, help="interval between saving generator outputs")
parser.add_argument("--checkpoint_interval", type=int, default=-1, help="interval between saving model checkpoints")
parser.add_argument("--n_residual_blocks", type=int, default=9, help="number of residual blocks in generator")
parser.add_argument("--lambda_cyc", type=float, default=10.0, help="cycle loss weight")
parser.add_argument("--lambda_id", type=float, default=5.0, help="identity loss weight")
opt = parser.parse_args()
# opt = parser.parse_args(args=[]) ## 在colab中运行时,换为此行
print(opt)
## 创建文件夹
os.makedirs("images/%s" % opt.dataset_name, exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs("save/%s" % opt.dataset_name, exist_ok=True)
## input_shape:(3, 256, 256)
input_shape = (opt.channels, opt.img_height, opt.img_width)
## 创建生成器,判别器对象
G_AB = GeneratorResNet(input_shape, opt.n_residual_blocks)
G_BA = GeneratorResNet(input_shape, opt.n_residual_blocks)
D_A = Discriminator(input_shape)
D_B = Discriminator(input_shape)
## 损失函数
## MES 二分类的交叉熵
## L1loss 相比于L2 Loss保边缘
criterion_GAN = torch.nn.MSELoss()
criterion_cycle = torch.nn.L1Loss()
criterion_identity = torch.nn.L1Loss()
## 如果有显卡,都在cuda模式中运行
if torch.cuda.is_available():
G_AB = G_AB.cuda()
G_BA = G_BA.cuda()
D_A = D_A.cuda()
D_B = D_B.cuda()
criterion_GAN.cuda()
criterion_cycle.cuda()
criterion_identity.cuda()
## 如果epoch == 0,初始化模型参数; 如果epoch == n, 载入训练到第n轮的预训练模型
if opt.epoch != 0:
# 载入训练到第n轮的预训练模型
G_AB.load_state_dict(torch.load("saved/%s/G_AB_%d.pth" % (opt.dataset_name, opt.epoch)))
G_BA.load_state_dict(torch.load("saved/%s/G_BA_%d.pth" % (opt.dataset_name, opt.epoch)))
D_A.load_state_dict(torch.load("saved/%s/D_A_%d.pth" % (opt.dataset_name, opt.epoch)))
D_B.load_state_dict(torch.load("saved/%s/D_B_%d.pth" % (opt.dataset_name, opt.epoch)))
else:
# 初始化模型参数
G_AB.apply(weights_init_normal)
G_BA.apply(weights_init_normal)
D_A.apply(weights_init_normal)
D_B.apply(weights_init_normal)
## 定义优化函数,优化函数的学习率为0.0003
optimizer_G = torch.optim.Adam(
itertools.chain(G_AB.parameters(), G_BA.parameters()), lr=opt.lr, betas=(opt.b1, opt.b2)
)
optimizer_D_A = torch.optim.Adam(D_A.parameters(), lr=opt.lr, betas=(opt.b1, opt.b2))
optimizer_D_B = torch.optim.Adam(D_B.parameters(), lr=opt.lr, betas=(opt.b1, opt.b2))
## 学习率更行进程
lr_scheduler_G = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.LambdaLR(
optimizer_G, lr_lambda=LambdaLR(opt.n_epochs, opt.epoch, opt.decay_epoch).step
)
lr_scheduler_D_A = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.LambdaLR(
optimizer_D_A, lr_lambda=LambdaLR(opt.n_epochs, opt.epoch, opt.decay_epoch).step
)
lr_scheduler_D_B = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.LambdaLR(
optimizer_D_B, lr_lambda=LambdaLR(opt.n_epochs, opt.epoch, opt.decay_epoch).step
)
## 先前生成的样本的缓冲区
fake_A_buffer = ReplayBuffer()
fake_B_buffer = ReplayBuffer()
## 图像 transformations
transforms_ = [
transforms.Resize(int(opt.img_height * 1.12)), ## 图片放大1.12倍
transforms.RandomCrop((opt.img_height, opt.img_width)), ## 随机裁剪成原来的大小
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(), ## 随机水平翻转
transforms.ToTensor(), ## 变为Tensor数据
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5)), ## 正则化
]
## Training data loader
dataloader = DataLoader( ## 改成自己存放文件的目录
ImageDataset("datasets/facades", transforms_=transforms_, unaligned=True), ## "./datasets/facades" , unaligned:设置非对其数据
batch_size=opt.batch_size, ## batch_size = 1
shuffle=True,
num_workers=opt.n_cpu,
)
## Test data loader
val_dataloader = DataLoader(
ImageDataset("datasets/facades", transforms_=transforms_, unaligned=True, mode="test"), ## "./datasets/facades"
batch_size=5,
shuffle=True,
num_workers=1,
)
## 每间隔100次打印图片
def sample_images(batches_done): ## (100/200/300/400...)
"""保存测试集中生成的样本"""
imgs = next(iter(val_dataloader)) ## 取一张图像
G_AB.eval()
G_BA.eval()
real_A = Variable(imgs["A"]).cuda() ## 取一张真A
fake_B = G_AB(real_A) ## 用真A生成假B
real_B = Variable(imgs["B"]).cuda() ## 去一张真B
fake_A = G_BA(real_B) ## 用真B生成假A
# Arange images along x-axis
## make_grid():用于把几个图像按照网格排列的方式绘制出来
real_A = make_grid(real_A, nrow=5, normalize=True)
real_B = make_grid(real_B, nrow=5, normalize=True)
fake_A = make_grid(fake_A, nrow=5, normalize=True)
fake_B = make_grid(fake_B, nrow=5, normalize=True)
# Arange images along y-axis
## 把以上图像都拼接起来,保存为一张大图片
image_grid = torch.cat((real_A, fake_B, real_B, fake_A), 1)
save_image(image_grid, "images/%s/%s.png" % (opt.dataset_name, batches_done), normalize=False)
def train():
# ----------
# Training
# ----------
prev_time = time.time() ## 开始时间
for epoch in range(opt.epoch, opt.n_epochs): ## for epoch in (0, 50)
for i, batch in enumerate(dataloader): ## batch is a dict, batch['A']:(1, 3, 256, 256), batch['B']:(1, 3, 256, 256)
# print('here is %d' % i)
## 读取数据集中的真图片
## 将tensor变成Variable放入计算图中,tensor变成variable之后才能进行反向传播求梯度
real_A = Variable(batch["A"]).cuda() ## 真图像A
real_B = Variable(batch["B"]).cuda() ## 真图像B
## 全真,全假的标签
valid = Variable(torch.ones((real_A.size(0), *D_A.output_shape)), requires_grad=False).cuda() ## 定义真实的图片label为1 ones((1, 1, 16, 16))
fake = Variable(torch.zeros((real_A.size(0), *D_A.output_shape)), requires_grad=False).cuda() ## 定义假的图片的label为0 zeros((1, 1, 16, 16))
## -----------------
## Train Generator
## 原理:目的是希望生成的假的图片被判别器判断为真的图片,
## 在此过程中,将判别器固定,将假的图片传入判别器的结果与真实的label对应,
## 反向传播更新的参数是生成网络里面的参数,
## 这样可以通过更新生成网络里面的参数,来训练网络,使得生成的图片让判别器以为是真的, 这样就达到了对抗的目的
## -----------------
G_AB.train()
G_BA.train()
## Identity loss ## A风格的图像 放在 B -> A 生成器中,生成的图像也要是 A风格
loss_id_A = criterion_identity(G_BA(real_A), real_A) ## loss_id_A就是把图像A1放入 B2A 的生成器中,那当然生成图像A2的风格也得是A风格, 要让A1,A2的差距很小
loss_id_B = criterion_identity(G_AB(real_B), real_B)
loss_identity = (loss_id_A + loss_id_B) / 2 ## Identity loss
## GAN loss
fake_B = G_AB(real_A) ## 用真图像A生成的假图像B
loss_GAN_AB = criterion_GAN(D_B(fake_B), valid) ## 用B鉴别器鉴别假图像B,训练生成器的目的就是要让鉴别器以为假的是真的,假的太接近真的让鉴别器分辨不出来
fake_A = G_BA(real_B) ## 用真图像B生成的假图像A
loss_GAN_BA = criterion_GAN(D_A(fake_A), valid) ## 用A鉴别器鉴别假图像A,训练生成器的目的就是要让鉴别器以为假的是真的,假的太接近真的让鉴别器分辨不出来
loss_GAN = (loss_GAN_AB + loss_GAN_BA) / 2 ## GAN loss
# Cycle loss 循环一致性损失
recov_A = G_BA(fake_B) ## 之前中realA 通过 A -> B 生成的假图像B,再经过 B -> A ,使得fakeB 得到的循环图像recovA,
loss_cycle_A = criterion_cycle(recov_A, real_A) ## realA和recovA的差距应该很小,以保证A,B间不仅风格有所变化,而且图片对应的的细节也可以保留
recov_B = G_AB(fake_A)
loss_cycle_B = criterion_cycle(recov_B, real_B)
loss_cycle = (loss_cycle_A + loss_cycle_B) / 2
# Total loss ## 就是上面所有的损失都加起来
loss_G = loss_GAN + opt.lambda_cyc * loss_cycle + opt.lambda_id * loss_identity
optimizer_G.zero_grad() ## 在反向传播之前,先将梯度归0
loss_G.backward() ## 将误差反向传播
optimizer_G.step() ## 更新参数
## -----------------------
## Train Discriminator A
## 分为两部分:1、真的图像判别为真;2、假的图像判别为假
## -----------------------
## 真的图像判别为真
loss_real = criterion_GAN(D_A(real_A), valid)
## 假的图像判别为假(从之前的buffer缓存中随机取一张)
fake_A_ = fake_A_buffer.push_and_pop(fake_A)
loss_fake = criterion_GAN(D_A(fake_A_.detach()), fake)
# Total loss
loss_D_A = (loss_real + loss_fake) / 2
optimizer_D_A.zero_grad() ## 在反向传播之前,先将梯度归0
loss_D_A.backward() ## 将误差反向传播
optimizer_D_A.step() ## 更新参数
## -----------------------
## Train Discriminator B
## 分为两部分:1、真的图像判别为真;2、假的图像判别为假
## -----------------------
# 真的图像判别为真
loss_real = criterion_GAN(D_B(real_B), valid)
## 假的图像判别为假(从之前的buffer缓存中随机取一张)
fake_B_ = fake_B_buffer.push_and_pop(fake_B)
loss_fake = criterion_GAN(D_B(fake_B_.detach()), fake)
# Total loss
loss_D_B = (loss_real + loss_fake) / 2
optimizer_D_B.zero_grad() ## 在反向传播之前,先将梯度归0
loss_D_B.backward() ## 将误差反向传播
optimizer_D_B.step() ## 更新参数
loss_D = (loss_D_A + loss_D_B) / 2
## ----------------------
## 打印日志Log Progress
## ----------------------
## 确定剩下的大约时间 假设当前 epoch = 5, i = 100
batches_done = epoch * len(dataloader) + i ## 已经训练了多长时间 5 * 400 + 100 次
batches_left = opt.n_epochs * len(dataloader) - batches_done ## 还剩下 50 * 400 - 2100 次
time_left = datetime.timedelta(seconds=batches_left * (time.time() - prev_time)) ## 还需要的时间 time_left = 剩下的次数 * 每次的时间
prev_time = time.time()
# Print log
sys.stdout.write(
"\r[Epoch %d/%d] [Batch %d/%d] [D loss: %f] [G loss: %f, adv: %f, cycle: %f, identity: %f] ETA: %s"
% (
epoch,
opt.n_epochs,
i,
len(dataloader),
loss_D.item(),
loss_G.item(),
loss_GAN.item(),
loss_cycle.item(),
loss_identity.item(),
time_left,
)
)
# 每训练100张就保存一组测试集中的图片
if batches_done % opt.sample_interval == 0:
sample_images(batches_done)
# 更新学习率
lr_scheduler_G.step()
lr_scheduler_D_A.step()
lr_scheduler_D_B.step()
## 训练结束后,保存模型
torch.save(G_AB.state_dict(), "save/%s/G_AB_%d.pth" % (opt.dataset_name, epoch))
torch.save(G_BA.state_dict(), "save/%s/G_BA_%d.pth" % (opt.dataset_name, epoch))
torch.save(D_A.state_dict(), "save/%s/D_A_%d.pth" % (opt.dataset_name, epoch))
torch.save(D_B.state_dict(), "save/%s/D_B_%d.pth" % (opt.dataset_name, epoch))
print("save my model finished !!")
# ## 每间隔几个epoch保存一次模型
# if opt.checkpoint_interval != -1 and epoch % opt.checkpoint_interval == 0:
# # Save model checkpoints
# torch.save(G_AB.state_dict(), "saved_models/%s/G_AB_%d.pth" % (opt.dataset_name, epoch))
# torch.save(G_BA.state_dict(), "saved_models/%s/G_BA_%d.pth" % (opt.dataset_name, epoch))
# torch.save(D_A.state_dict(), "saved_models/%s/D_A_%d.pth" % (opt.dataset_name, epoch))
# torch.save(D_B.state_dict(), "saved_models/%s/D_B_%d.pth" % (opt.dataset_name, epoch))
## 函数的起始
if __name__ == '__main__':
train()
test
The test process is actually to use the previously trained generator model parameters, put them into a new generator, put the picture in to see the effect of the corresponding generated picture, and the test does not need a discriminator. Put the generated pictures into the output/A, output/B folders.
import argparse
import torch
import os
from torchvision import transforms
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torchvision.utils import save_image
from torch.autograd import Variable
from models import GeneratorResNet
from dataset import ImageDataset
def test():
## 超参数设置
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--batchSize', type=int, default=1, help='size of the batches')
parser.add_argument('--dataroot', type=str, default='D:/XCH/GAN_ZOO/datasets/facades', help='root directory of the dataset')
parser.add_argument('--channels', type=int, default=3, help='number of channels of input data')
parser.add_argument('--n_residual_blocks', type=int, default=9, help='number of channels of output data')
parser.add_argument('--size', type=int, default=256, help='size of the data (squared assumed)')
parser.add_argument('--cuda', type=bool, default=True, help='use GPU computation')
parser.add_argument('--n_cpu', type=int, default=8, help='number of cpu threads to use during batch generation')
parser.add_argument('--generator_A2B', type=str, default='D:/XCH/GAN_ZOO/save/facades/G_AB_4.pth', help='A2B generator checkpoint file')
parser.add_argument('--generator_B2A', type=str, default='D:/XCH/GAN_ZOO/save/facades/G_BA_4.pth', help='B2A generator checkpoint file')
opt = parser.parse_args()
print(opt)
#################################
## test准备工作 ##
#################################
## input_shape:(3, 256, 256)
input_shape = (opt.channels, opt.size, opt.size)
## 创建生成器,判别器对象
netG_A2B = GeneratorResNet(input_shape, opt.n_residual_blocks)
netG_B2A = GeneratorResNet(input_shape, opt.n_residual_blocks)
## 使用cuda
if opt.cuda:
netG_A2B.cuda()
netG_B2A.cuda()
## 载入训练模型参数
netG_A2B.load_state_dict(torch.load(opt.generator_A2B))
netG_B2A.load_state_dict(torch.load(opt.generator_B2A))
## 设置为测试模式
netG_A2B.eval()
netG_B2A.eval()
## 创建一个tensor数组
Tensor = torch.cuda.FloatTensor if opt.cuda else torch.Tensor
input_A = Tensor(opt.batchSize, opt.channels, opt.size, opt.size)
input_B = Tensor(opt.batchSize, opt.channels, opt.size, opt.size)
'''构建测试数据集'''
transforms_ = [ transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5,0.5,0.5), (0.5,0.5,0.5)) ]
dataloader = DataLoader(ImageDataset(opt.dataroot, transforms_=transforms_, mode='test'),
batch_size=opt.batchSize, shuffle=False, num_workers=opt.n_cpu)
#################################
## test开始 ##
#################################
'''如果文件路径不存在, 则创建一个 (存放测试输出的图片)'''
if not os.path.exists('output/A'):
os.makedirs('output/A')
if not os.path.exists('output/B'):
os.makedirs('output/B')
for i, batch in enumerate(dataloader):
## 输入数据 real
real_A = Variable(input_A.copy_(batch['A']))
real_B = Variable(input_B.copy_(batch['B']))
## 通过生成器生成的 fake
fake_B = 0.5*(netG_A2B(real_A).data + 1.0)
fake_A = 0.5*(netG_B2A(real_B).data + 1.0)
## 保存图片
save_image(fake_A, 'output/A/%04d.png' % (i+1))
save_image(fake_B, 'output/B/%04d.png' % (i+1))
print('processing (%04d)-th image...' % (i))
print("测试完成")
if __name__ == '__main__':
test()
training result
(Only trained for 5 cycles, saving time)
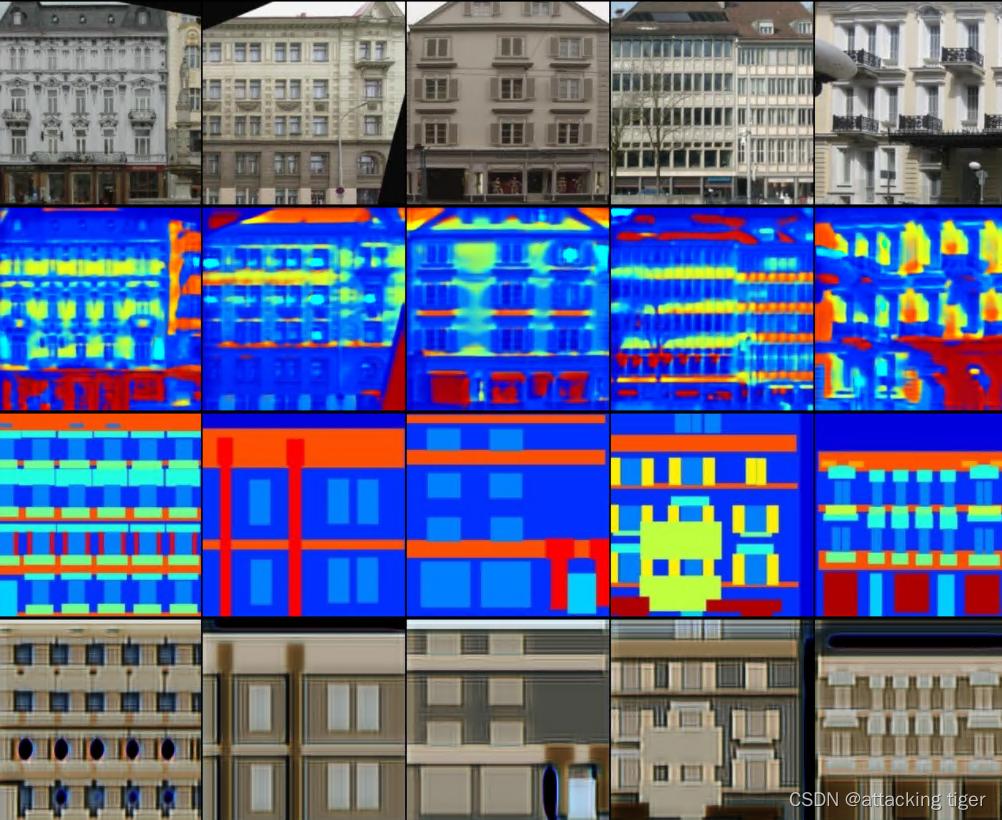

put in a file
import os
import glob
import random
import torch
import itertools
import datetime
import time
import sys
import argparse
import numpy as np
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.nn as nn
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torch.autograd import Variable
from PIL import Image
from torchvision.utils import save_image, make_grid
#########################################################################
############################ datasets.py ###################################
## 如果输入的数据集是灰度图像,将图片转化为rgb图像(本次采用的facades不需要这个)
def to_rgb(image):
rgb_image = Image.new("RGB", image.size)
rgb_image.paste(image)
return rgb_image
## 构建数据集
class ImageDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, root, transforms_=None, unaligned=False, mode="train"): ## (root = "./datasets/facades", unaligned=True:非对其数据)
self.transform = transforms.Compose(transforms_) ## transform变为tensor数据
self.unaligned = unaligned
self.files_A = sorted(glob.glob(os.path.join(root, "%sA" % mode) + "/*.*")) ## "./datasets/facades/trainA/*.*"
self.files_B = sorted(glob.glob(os.path.join(root, "%sB" % mode) + "/*.*")) ## "./datasets/facades/trainB/*.*"
def __getitem__(self, index):
image_A = Image.open(self.files_A[index % len(self.files_A)]) ## 在A中取一张照片
if self.unaligned: ## 如果采用非配对数据,在B中随机取一张
image_B = Image.open(self.files_B[random.randint(0, len(self.files_B) - 1)])
else:
image_B = Image.open(self.files_B[index % len(self.files_B)])
# 如果是灰度图,把灰度图转换为RGB图
if image_A.mode != "RGB":
image_A = to_rgb(image_A)
if image_B.mode != "RGB":
image_B = to_rgb(image_B)
# 把RGB图像转换为tensor图, 方便计算,返回字典数据
item_A = self.transform(image_A)
item_B = self.transform(image_B)
return {
"A": item_A, "B": item_B}
## 获取A,B数据的长度
def __len__(self):
return max(len(self.files_A), len(self.files_B))
#########################################################################
############################ models.py ###################################
## 定义参数初始化函数
def weights_init_normal(m):
classname = m.__class__.__name__ ## m作为一个形参,原则上可以传递很多的内容, 为了实现多实参传递,每一个moudle要给出自己的name. 所以这句话就是返回m的名字.
if classname.find("Conv") != -1: ## find():实现查找classname中是否含有Conv字符,没有返回-1;有返回0.
torch.nn.init.normal_(m.weight.data, 0.0, 0.02) ## m.weight.data表示需要初始化的权重。nn.init.normal_():表示随机初始化采用正态分布,均值为0,标准差为0.02.
if hasattr(m, "bias") and m.bias is not None: ## hasattr():用于判断m是否包含对应的属性bias, 以及bias属性是否不为空.
torch.nn.init.constant_(m.bias.data, 0.0) ## nn.init.constant_():表示将偏差定义为常量0.
elif classname.find("BatchNorm2d") != -1: ## find():实现查找classname中是否含有BatchNorm2d字符,没有返回-1;有返回0.
torch.nn.init.normal_(m.weight.data, 1.0, 0.02) ## m.weight.data表示需要初始化的权重. nn.init.normal_():表示随机初始化采用正态分布,均值为0,标准差为0.02.
torch.nn.init.constant_(m.bias.data, 0.0) ## nn.init.constant_():表示将偏差定义为常量0.
##############################
## 残差块儿ResidualBlock
##############################
class ResidualBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_features):
super(ResidualBlock, self).__init__()
self.block = nn.Sequential( ## block = [pad + conv + norm + relu + pad + conv + norm]
nn.ReflectionPad2d(1), ## ReflectionPad2d():利用输入边界的反射来填充输入张量
nn.Conv2d(in_features, in_features, 3), ## 卷积
nn.InstanceNorm2d(in_features), ## InstanceNorm2d():在图像像素上对HW做归一化,用在风格化迁移
nn.ReLU(inplace=True), ## 非线性激活
nn.ReflectionPad2d(1), ## ReflectionPad2d():利用输入边界的反射来填充输入张量
nn.Conv2d(in_features, in_features, 3), ## 卷积
nn.InstanceNorm2d(in_features), ## InstanceNorm2d():在图像像素上对HW做归一化,用在风格化迁移
)
def forward(self, x): ## 输入为 一张图像
return x + self.block(x) ## 输出为 图像加上网络的残差输出
##############################
## 生成器网络GeneratorResNet
##############################
class GeneratorResNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_shape, num_residual_blocks): ## (input_shape = (3, 256, 256), num_residual_blocks = 9)
super(GeneratorResNet, self).__init__()
channels = input_shape[0] ## 输入通道数channels = 3
## 初始化网络结构
out_features = 64 ## 输出特征数out_features = 64
model = [ ## model = [Pad + Conv + Norm + ReLU]
nn.ReflectionPad2d(channels), ## ReflectionPad2d(3):利用输入边界的反射来填充输入张量
nn.Conv2d(channels, out_features, 7), ## Conv2d(3, 64, 7)
nn.InstanceNorm2d(out_features), ## InstanceNorm2d(64):在图像像素上对HW做归一化,用在风格化迁移
nn.ReLU(inplace=True), ## 非线性激活
]
in_features = out_features ## in_features = 64
## 下采样,循环2次
for _ in range(2):
out_features *= 2 ## out_features = 128 -> 256
model += [ ## (Conv + Norm + ReLU) * 2
nn.Conv2d(in_features, out_features, 3, stride=2, padding=1),
nn.InstanceNorm2d(out_features),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
]
in_features = out_features ## in_features = 256
# 残差块儿,循环9次
for _ in range(num_residual_blocks):
model += [ResidualBlock(out_features)] ## model += [pad + conv + norm + relu + pad + conv + norm]
# 上采样两次
for _ in range(2):
out_features //= 2 ## out_features = 128 -> 64
model += [ ## model += [Upsample + conv + norm + relu]
nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2),
nn.Conv2d(in_features, out_features, 3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.InstanceNorm2d(out_features),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
]
in_features = out_features ## out_features = 64
## 网络输出层 ## model += [pad + conv + tanh]
model += [nn.ReflectionPad2d(channels), nn.Conv2d(out_features, channels, 7), nn.Tanh()] ## 将(3)的数据每一个都映射到[-1, 1]之间
self.model = nn.Sequential(*model)
def forward(self, x): ## 输入(1, 3, 256, 256)
return self.model(x) ## 输出(1, 3, 256, 256)
##############################
# Discriminator
##############################
class Discriminator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_shape):
super(Discriminator, self).__init__()
channels, height, width = input_shape ## input_shape:(3, 256, 256)
# Calculate output shape of image discriminator (PatchGAN)
self.output_shape = (1, height // 2 ** 4, width // 2 ** 4) ## output_shape = (1, 16, 16)
def discriminator_block(in_filters, out_filters, normalize=True): ## 鉴别器块儿
"""Returns downsampling layers of each discriminator block"""
layers = [nn.Conv2d(in_filters, out_filters, 4, stride=2, padding=1)] ## layer += [conv + norm + relu]
if normalize: ## 每次卷积尺寸会缩小一半,共卷积了4次
layers.append(nn.InstanceNorm2d(out_filters))
layers.append(nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True))
return layers
self.model = nn.Sequential(
*discriminator_block(channels, 64, normalize=False), ## layer += [conv(3, 64) + relu]
*discriminator_block(64, 128), ## layer += [conv(64, 128) + norm + relu]
*discriminator_block(128, 256), ## layer += [conv(128, 256) + norm + relu]
*discriminator_block(256, 512), ## layer += [conv(256, 512) + norm + relu]
nn.ZeroPad2d((1, 0, 1, 0)), ## layer += [pad]
nn.Conv2d(512, 1, 4, padding=1) ## layer += [conv(512, 1)]
)
def forward(self, img): ## 输入(1, 3, 256, 256)
return self.model(img) ## 输出(1, 1, 16, 16)
#########################################################################
############################ utils.py ###################################
## 先前生成的样本的缓冲区
class ReplayBuffer:
def __init__(self, max_size=50):
assert max_size > 0, "Empty buffer or trying to create a black hole. Be careful."
self.max_size = max_size
self.data = []
def push_and_pop(self, data): ## 放入一张图像,再从buffer里取一张出来
to_return = [] ## 确保数据的随机性,判断真假图片的鉴别器识别率
for element in data.data:
element = torch.unsqueeze(element, 0)
if len(self.data) < self.max_size: ## 最多放入50张,没满就一直添加
self.data.append(element)
to_return.append(element)
else:
if random.uniform(0, 1) > 0.5: ## 满了就1/2的概率从buffer里取,或者就用当前的输入图片
i = random.randint(0, self.max_size - 1)
to_return.append(self.data[i].clone())
self.data[i] = element
else:
to_return.append(element)
return Variable(torch.cat(to_return))
## 设置学习率为初始学习率乘以给定lr_lambda函数的值
class LambdaLR:
def __init__(self, n_epochs, offset, decay_start_epoch): ## (n_epochs = 50, offset = epoch, decay_start_epoch = 30)
assert (n_epochs - decay_start_epoch) > 0, "Decay must start before the training session ends!" ## 断言,要让n_epochs > decay_start_epoch 才可以
self.n_epochs = n_epochs
self.offset = offset
self.decay_start_epoch = decay_start_epoch
def step(self, epoch): ## return 1-max(0, epoch - 30) / (50 - 30)
return 1.0 - max(0, epoch + self.offset - self.decay_start_epoch) / (self.n_epochs - self.decay_start_epoch)
###########################################################################
############################ cycle_gan.py ###################################
## 超参数配置
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--epoch", type=int, default=0, help="epoch to start training from")
parser.add_argument("--n_epochs", type=int, default=5, help="number of epochs of training")
parser.add_argument("--dataset_name", type=str, default="dataset/facades", help="name of the dataset")## ../input/facades-dataset
parser.add_argument("--batch_size", type=int, default=1, help="size of the batches")
parser.add_argument("--lr", type=float, default=0.0003, help="adam: learning rate")
parser.add_argument("--b1", type=float, default=0.5, help="adam: decay of first order momentum of gradient")
parser.add_argument("--b2", type=float, default=0.999, help="adam: decay of first order momentum of gradient")
parser.add_argument("--decay_epoch", type=int, default=3, help="epoch from which to start lr decay")
parser.add_argument("--n_cpu", type=int, default=2, help="number of cpu threads to use during batch generation")
parser.add_argument("--img_height", type=int, default=256, help="size of image height")
parser.add_argument("--img_width", type=int, default=256, help="size of image width")
parser.add_argument("--channels", type=int, default=3, help="number of image channels")
parser.add_argument("--sample_interval", type=int, default=100, help="interval between saving generator outputs")
parser.add_argument("--checkpoint_interval", type=int, default=-1, help="interval between saving model checkpoints")
parser.add_argument("--n_residual_blocks", type=int, default=9, help="number of residual blocks in generator")
parser.add_argument("--lambda_cyc", type=float, default=10.0, help="cycle loss weight")
parser.add_argument("--lambda_id", type=float, default=5.0, help="identity loss weight")
opt = parser.parse_args()
# opt = parser.parse_args(args=[]) ## 在colab中运行时,换为此行
print(opt)
## 创建文件夹
os.makedirs("images/%s" % opt.dataset_name, exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs("save/%s" % opt.dataset_name, exist_ok=True)
## input_shape:(3, 256, 256)
input_shape = (opt.channels, opt.img_height, opt.img_width)
## 创建生成器,判别器对象
G_AB = GeneratorResNet(input_shape, opt.n_residual_blocks)
G_BA = GeneratorResNet(input_shape, opt.n_residual_blocks)
D_A = Discriminator(input_shape)
D_B = Discriminator(input_shape)
## 损失函数
## MES 二分类的交叉熵
## L1loss 相比于L2 Loss保边缘
criterion_GAN = torch.nn.MSELoss()
criterion_cycle = torch.nn.L1Loss()
criterion_identity = torch.nn.L1Loss()
## 如果有显卡,都在cuda模式中运行
if torch.cuda.is_available():
G_AB = G_AB.cuda()
G_BA = G_BA.cuda()
D_A = D_A.cuda()
D_B = D_B.cuda()
criterion_GAN.cuda()
criterion_cycle.cuda()
criterion_identity.cuda()
## 如果epoch == 0,初始化模型参数; 如果epoch == n, 载入训练到第n轮的预训练模型
if opt.epoch != 0:
# 载入训练到第n轮的预训练模型
G_AB.load_state_dict(torch.load("save/%s/G_AB_%d.pth" % (opt.dataset_name, opt.epoch)))
G_BA.load_state_dict(torch.load("save/%s/G_BA_%d.pth" % (opt.dataset_name, opt.epoch)))
D_A.load_state_dict(torch.load("save/%s/D_A_%d.pth" % (opt.dataset_name, opt.epoch)))
D_B.load_state_dict(torch.load("save/%s/D_B_%d.pth" % (opt.dataset_name, opt.epoch)))
else:
# 初始化模型参数
G_AB.apply(weights_init_normal)
G_BA.apply(weights_init_normal)
D_A.apply(weights_init_normal)
D_B.apply(weights_init_normal)
## 定义优化函数,优化函数的学习率为0.0003
optimizer_G = torch.optim.Adam(
itertools.chain(G_AB.parameters(), G_BA.parameters()), lr=opt.lr, betas=(opt.b1, opt.b2)
)
optimizer_D_A = torch.optim.Adam(D_A.parameters(), lr=opt.lr, betas=(opt.b1, opt.b2))
optimizer_D_B = torch.optim.Adam(D_B.parameters(), lr=opt.lr, betas=(opt.b1, opt.b2))
## 学习率更行进程
lr_scheduler_G = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.LambdaLR(
optimizer_G, lr_lambda=LambdaLR(opt.n_epochs, opt.epoch, opt.decay_epoch).step
)
lr_scheduler_D_A = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.LambdaLR(
optimizer_D_A, lr_lambda=LambdaLR(opt.n_epochs, opt.epoch, opt.decay_epoch).step
)
lr_scheduler_D_B = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.LambdaLR(
optimizer_D_B, lr_lambda=LambdaLR(opt.n_epochs, opt.epoch, opt.decay_epoch).step
)
## 先前生成的样本的缓冲区
fake_A_buffer = ReplayBuffer()
fake_B_buffer = ReplayBuffer()
## 图像 transformations
transforms_ = [
transforms.Resize(int(opt.img_height * 1.12)), ## 图片放大1.12倍
transforms.RandomCrop((opt.img_height, opt.img_width)), ## 随机裁剪成原来的大小
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(), ## 随机水平翻转
transforms.ToTensor(), ## 变为Tensor数据
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5)), ## 正则化
]
## Training data loader
dataloader = DataLoader( ## 改成自己存放文件的目录
ImageDataset("dataset/facades", transforms_=transforms_, unaligned=True), ## "./datasets/facades" , unaligned:设置非对其数据
batch_size=opt.batch_size, ## batch_size = 1
shuffle=True,
num_workers=opt.n_cpu,
)
## Test data loader
val_dataloader = DataLoader(
ImageDataset("dataset/facades", transforms_=transforms_, unaligned=True, mode="test"), ## "./datasets/facades"
batch_size=5,
shuffle=True,
num_workers=1,
)
## 每间隔100次打印图片
def sample_images(batches_done): ## (100/200/300/400...)
"""保存测试集中生成的样本"""
imgs = next(iter(val_dataloader)) ## 取一张图像
G_AB.eval()
G_BA.eval()
real_A = Variable(imgs["A"]).cuda() ## 取一张真A
fake_B = G_AB(real_A) ## 用真A生成假B
real_B = Variable(imgs["B"]).cuda() ## 去一张真B
fake_A = G_BA(real_B) ## 用真B生成假A
# Arange images along x-axis
## make_grid():用于把几个图像按照网格排列的方式绘制出来
real_A = make_grid(real_A, nrow=5, normalize=True)
real_B = make_grid(real_B, nrow=5, normalize=True)
fake_A = make_grid(fake_A, nrow=5, normalize=True)
fake_B = make_grid(fake_B, nrow=5, normalize=True)
# Arange images along y-axis
## 把以上图像都拼接起来,保存为一张大图片
image_grid = torch.cat((real_A, fake_B, real_B, fake_A), 1)
save_image(image_grid, "images/%s/%s.png" % (opt.dataset_name, batches_done), normalize=False)
def train():
# ----------
# Training
# ----------
prev_time = time.time() ## 开始时间
for epoch in range(opt.epoch, opt.n_epochs): ## for epoch in (0, 50)
for i, batch in enumerate(dataloader): ## batch is a dict, batch['A']:(1, 3, 256, 256), batch['B']:(1, 3, 256, 256)
# print('here is %d' % i)
## 读取数据集中的真图片
## 将tensor变成Variable放入计算图中,tensor变成variable之后才能进行反向传播求梯度
real_A = Variable(batch["A"]).cuda() ## 真图像A
real_B = Variable(batch["B"]).cuda() ## 真图像B
## 全真,全假的标签
valid = Variable(torch.ones((real_A.size(0), *D_A.output_shape)), requires_grad=False).cuda() ## 定义真实的图片label为1 ones((1, 1, 16, 16))
fake = Variable(torch.zeros((real_A.size(0), *D_A.output_shape)), requires_grad=False).cuda() ## 定义假的图片的label为0 zeros((1, 1, 16, 16))
## -----------------
## Train Generator
## 原理:目的是希望生成的假的图片被判别器判断为真的图片,
## 在此过程中,将判别器固定,将假的图片传入判别器的结果与真实的label对应,
## 反向传播更新的参数是生成网络里面的参数,
## 这样可以通过更新生成网络里面的参数,来训练网络,使得生成的图片让判别器以为是真的, 这样就达到了对抗的目的
## -----------------
G_AB.train()
G_BA.train()
## Identity loss ## A风格的图像 放在 B -> A 生成器中,生成的图像也要是 A风格
loss_id_A = criterion_identity(G_BA(real_A), real_A) ## loss_id_A就是把图像A1放入 B2A 的生成器中,那当然生成图像A2的风格也得是A风格, 要让A1,A2的差距很小
loss_id_B = criterion_identity(G_AB(real_B), real_B)
loss_identity = (loss_id_A + loss_id_B) / 2 ## Identity loss
## GAN loss
fake_B = G_AB(real_A) ## 用真图像A生成的假图像B
loss_GAN_AB = criterion_GAN(D_B(fake_B), valid) ## 用B鉴别器鉴别假图像B,训练生成器的目的就是要让鉴别器以为假的是真的,假的太接近真的让鉴别器分辨不出来
fake_A = G_BA(real_B) ## 用真图像B生成的假图像A
loss_GAN_BA = criterion_GAN(D_A(fake_A), valid) ## 用A鉴别器鉴别假图像A,训练生成器的目的就是要让鉴别器以为假的是真的,假的太接近真的让鉴别器分辨不出来
loss_GAN = (loss_GAN_AB + loss_GAN_BA) / 2 ## GAN loss
# Cycle loss 循环一致性损失
recov_A = G_BA(fake_B) ## 之前中realA 通过 A -> B 生成的假图像B,再经过 B -> A ,使得fakeB 得到的循环图像recovA,
loss_cycle_A = criterion_cycle(recov_A, real_A) ## realA和recovA的差距应该很小,以保证A,B间不仅风格有所变化,而且图片对应的的细节也可以保留
recov_B = G_AB(fake_A)
loss_cycle_B = criterion_cycle(recov_B, real_B)
loss_cycle = (loss_cycle_A + loss_cycle_B) / 2
# Total loss ## 就是上面所有的损失都加起来
loss_G = loss_GAN + opt.lambda_cyc * loss_cycle + opt.lambda_id * loss_identity
optimizer_G.zero_grad() ## 在反向传播之前,先将梯度归0
loss_G.backward() ## 将误差反向传播
optimizer_G.step() ## 更新参数
## -----------------------
## Train Discriminator A
## 分为两部分:1、真的图像判别为真;2、假的图像判别为假
## -----------------------
## 真的图像判别为真
loss_real = criterion_GAN(D_A(real_A), valid)
## 假的图像判别为假(从之前的buffer缓存中随机取一张)
fake_A_ = fake_A_buffer.push_and_pop(fake_A)
loss_fake = criterion_GAN(D_A(fake_A_.detach()), fake)
# Total loss
loss_D_A = (loss_real + loss_fake) / 2
optimizer_D_A.zero_grad() ## 在反向传播之前,先将梯度归0
loss_D_A.backward() ## 将误差反向传播
optimizer_D_A.step() ## 更新参数
## -----------------------
## Train Discriminator B
## 分为两部分:1、真的图像判别为真;2、假的图像判别为假
## -----------------------
# 真的图像判别为真
loss_real = criterion_GAN(D_B(real_B), valid)
## 假的图像判别为假(从之前的buffer缓存中随机取一张)
fake_B_ = fake_B_buffer.push_and_pop(fake_B)
loss_fake = criterion_GAN(D_B(fake_B_.detach()), fake)
# Total loss
loss_D_B = (loss_real + loss_fake) / 2
optimizer_D_B.zero_grad() ## 在反向传播之前,先将梯度归0
loss_D_B.backward() ## 将误差反向传播
optimizer_D_B.step() ## 更新参数
loss_D = (loss_D_A + loss_D_B) / 2
## ----------------------
## 打印日志Log Progress
## ----------------------
## 确定剩下的大约时间 假设当前 epoch = 5, i = 100
batches_done = epoch * len(dataloader) + i ## 已经训练了多长时间 5 * 400 + 100 次
batches_left = opt.n_epochs * len(dataloader) - batches_done ## 还剩下 50 * 400 - 2100 次
time_left = datetime.timedelta(seconds=batches_left * (time.time() - prev_time)) ## 还需要的时间 time_left = 剩下的次数 * 每次的时间
prev_time = time.time()
# Print log
sys.stdout.write(
"\r[Epoch %d/%d] [Batch %d/%d] [D loss: %f] [G loss: %f, adv: %f, cycle: %f, identity: %f] ETA: %s"
% (
epoch,
opt.n_epochs,
i,
len(dataloader),
loss_D.item(),
loss_G.item(),
loss_GAN.item(),
loss_cycle.item(),
loss_identity.item(),
time_left,
)
)
# 每训练100张就保存一组测试集中的图片
if batches_done % opt.sample_interval == 0:
sample_images(batches_done)
# 更新学习率
lr_scheduler_G.step()
lr_scheduler_D_A.step()
lr_scheduler_D_B.step()
## 训练结束后,保存模型
torch.save(G_AB.state_dict(), "save/%s/G_AB_%d.pth" % (opt.dataset_name, epoch))
torch.save(G_BA.state_dict(), "save/%s/G_BA_%d.pth" % (opt.dataset_name, epoch))
torch.save(D_A.state_dict(), "save/%s/D_A_%d.pth" % (opt.dataset_name, epoch))
torch.save(D_B.state_dict(), "save/%s/D_B_%d.pth" % (opt.dataset_name, epoch))
print("\nsave my model finished !!")
# ## 每间隔几个epoch保存一次模型
# if opt.checkpoint_interval != -1 and epoch % opt.checkpoint_interval == 0:
# # Save model checkpoints
# torch.save(G_AB.state_dict(), "saved_models/%s/G_AB_%d.pth" % (opt.dataset_name, epoch))
# torch.save(G_BA.state_dict(), "saved_models/%s/G_BA_%d.pth" % (opt.dataset_name, epoch))
# torch.save(D_A.state_dict(), "saved_models/%s/D_A_%d.pth" % (opt.dataset_name, epoch))
# torch.save(D_B.state_dict(), "saved_models/%s/D_B_%d.pth" % (opt.dataset_name, epoch))
def test():
## 超参数设置
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--batchSize', type=int, default=2, help='size of the batches')
parser.add_argument('--dataroot', type=str, default='dataset/facades', help='root directory of the dataset')
parser.add_argument('--channels', type=int, default=3, help='number of channels of input data')
parser.add_argument('--n_residual_blocks', type=int, default=9, help='number of channels of output data')
parser.add_argument('--size', type=int, default=256, help='size of the data (squared assumed)')
parser.add_argument('--cuda', type=bool, default=True, help='use GPU computation')
parser.add_argument('--n_cpu', type=int, default=8, help='number of cpu threads to use during batch generation')
parser.add_argument('--generator_A2B', type=str, default='save/dataset/facades/G_AB_4.pth', help='A2B generator checkpoint file')
parser.add_argument('--generator_B2A', type=str, default='save/dataset/facades/G_BA_4.pth', help='B2A generator checkpoint file')
opt = parser.parse_args()
print(opt)
#################################
## test准备工作 ##
#################################
## input_shape:(3, 256, 256)
input_shape = (opt.channels, opt.size, opt.size)
## 创建生成器,判别器对象
netG_A2B = GeneratorResNet(input_shape, opt.n_residual_blocks)
netG_B2A = GeneratorResNet(input_shape, opt.n_residual_blocks)
## 使用cuda
if opt.cuda:
netG_A2B.cuda()
netG_B2A.cuda()
## 载入训练模型参数
netG_A2B.load_state_dict(torch.load(opt.generator_A2B))
netG_B2A.load_state_dict(torch.load(opt.generator_B2A))
## 设置为测试模式
netG_A2B.eval()
netG_B2A.eval()
## 创建一个tensor数组
Tensor = torch.cuda.FloatTensor if opt.cuda else torch.Tensor
input_A = Tensor(opt.batchSize, opt.channels, opt.size, opt.size)
input_B = Tensor(opt.batchSize, opt.channels, opt.size, opt.size)
'''构建测试数据集'''
transforms_ = [ transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5,0.5,0.5), (0.5,0.5,0.5)) ]
dataloader = DataLoader(ImageDataset(opt.dataroot, transforms_=transforms_, mode='test'),
batch_size=opt.batchSize, shuffle=False, num_workers=opt.n_cpu)
#################################
## test开始 ##
#################################
'''如果文件路径不存在, 则创建一个 (存放测试输出的图片)'''
if not os.path.exists('output/A'):
os.makedirs('output/A')
if not os.path.exists('output/B'):
os.makedirs('output/B')
for i, batch in enumerate(dataloader):
## 输入数据 real
real_A = Variable(input_A.copy_(batch['A']))
real_B = Variable(input_B.copy_(batch['B']))
## 通过生成器生成的 fake
fake_B = 0.5*(netG_A2B(real_A).data + 1.0)
fake_A = 0.5*(netG_B2A(real_B).data + 1.0)
## 保存图片
save_image(fake_A, 'output/A/%04d.png' % (i+1))
save_image(fake_B, 'output/B/%04d.png' % (i+1))
print('processing (%04d)-th image...' % (i))
print("测试完成")
## 函数的起始
if __name__ == '__main__':
train() ## 训练
# test() ## 测试