The original text comes from [Tingyun Technology Blog]: http://blog.tingyun.com/web/article/detail/1348
Summary
This article is aimed at junior network engineers and data mining engineers, involving EGP (Exterior Gateway Protocol), IGP (Interior Gateway Protocol) two types of protocols, AS (Autonomous System) composition, whois content analysis And some RPSL (Routing Policy Specification Language) syntax to understand what the hell is the ISP in the so-called operator library . Senior operation and maintenance players retreat quickly~_~
The update date of the cited data in the text is as of 2016/12/10, and some of the cited links are from the wiki, which requires **.
Anti-obfuscation statement
Before starting again, due to the difference in publication time and credibility of different books, before the main text, correct and unify the possible erroneous definitions. The EGP and IGP mentioned in this article refer to two types of protocols, not a specific one. algorithm. The earliest [RFC 827] defined a protocol called EGP, and then BGP (Border Gateway Protocol; Border Gateway Protocol), BGP4 was used to replace the algorithm, and now it is extended to BGP4+ that can support ipv6. In the category, These three algorithms belong to the EGP protocol. In addition, since the word Router is used in the new RFC document, some books translate these two types of protocols into ERP (Exterior Router Protocol) and IRP (Interior Router Protocol), Actually, they mean the same thing. In addition, all readers who have passed the intermediate qualification examination can skip to the third section to save reading time.
Chat from IGP
The specific algorithm is not discussed, the focus of this article is not here, only the idea.
There are many kinds of such protocols, such as RIP , IGRP , OSPF , IS-IS , EIGRP , which will not be translated here. It is meaningless to overemphasize Chinese. The difference between them is mainly in the algorithm implementation and the chain of the protocol. The road distance index is different, that is, the cost generated by the link distance. The simplest RIP, routers communicate with each other, each router does not know the topology of the entire network, they only report their reachable distance to other adjacent routers, exceeding and including 16 and indicating unreachable (some books). The reachable distance is defined from 0, which is used to indicate the intranet distance that does not need to pass through the router), and update each other.
OSPF and IS-IS forward routes according to the link state. In short, routers using these two protocols store the routing topology of the entire internal network, while RIP only knows part of it. Another advantage of OSPF over RIP is that it sets the cost of route propagation. That's right, adding a number to the topology line indicates whether the road is good or not. Calculate the cost before choosing.
to BGP
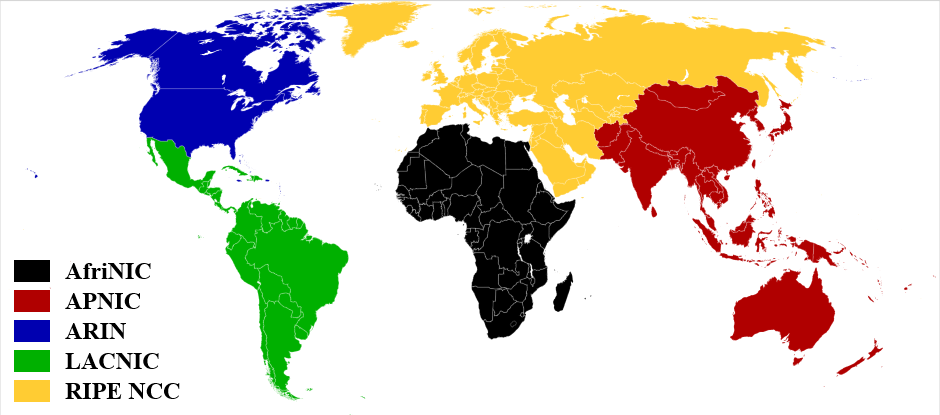
Basically the same idea as IGP, how to switch and so on is similar, make a routing table and so on, but why did you make a separate protocol, because of the scene. This involves the concept of an autonomous system, which roughly means that my own internal computers can communicate with each other, and even if I don’t communicate with the outside world, I can play online games, and I don’t have to go online. But if you want to connect to the Internet, you need to make an announcement to other networks. Who am I and whoever is on my network can correctly forward packets to other ASs. At this time, you need an ID card to express your identity, which is ASN (Autonomous System Number). If you want this number, you have to pay for it, and so does IP. Who do you buy from? Five major international organizations have contracted these things. Insert a picture to illustrate everything.
NIC means that the letters in front of the Network Information Center (Network Information Center) are Africa, Asia Pacific, Latin America and the Caribbean.
The names of the American Empire and Europe are very strange. I specially checked them and sorted them out as follows
The division method is probably based on this.
In the country, you can also apply for (buy) to the national distribution agency, CNNIC, and require you to use the AS number applied for to establish a BGP agreement with an ISP within one month, and within 3-6 months, you can establish a BGP agreement with more than two (including two ) ISPs mutually set up the BGP protocol [1] . Therefore, we can understand why Baidu (AS38365) and NetEase (AS45062) appear in the list of each ISP library.
好的,说回为什么场景不同,目前来讲,全球互联的(存在BGP服务器通报的)骨干网IP前缀路由表共有72739条,通过链路状态协议同步路由表,时间略长也不合适。除了技术上的原因,这里面涉及很多复杂的政治问题和安全问题,比如在中国内部流通的流量就没有必要从外面跑。因此在AS的边界路由器上会设置很多规则,比如,允许来自AS1的网络包进入本网络不允许AS2的进入,或者允许来自AS1的4.0.0.0/8进入本网络,或者让购买了本网络带宽的其他AS优先进入,这里的设置语法后面讲。
最终的BGP需要找到一条能通的路由,而不是一条可以最短的。因此BGP采用的是路径向量选择协议(这里指类别,区别于RIP的距离向量协议和OSPF的链路状态协议)。
AS
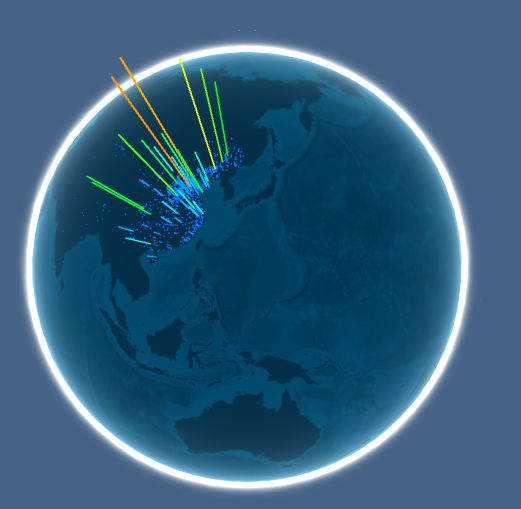
关于定义和概念我们讲了这么多,还是直观点的好,我们来看一下中国联通骨干网(AS4837)它在全国范围内的ip地理位置分布(注意,这里的骨干网并非全球骨干网,即该AS并非一个根节点,在它之上还有其他AS作为他的提供商)
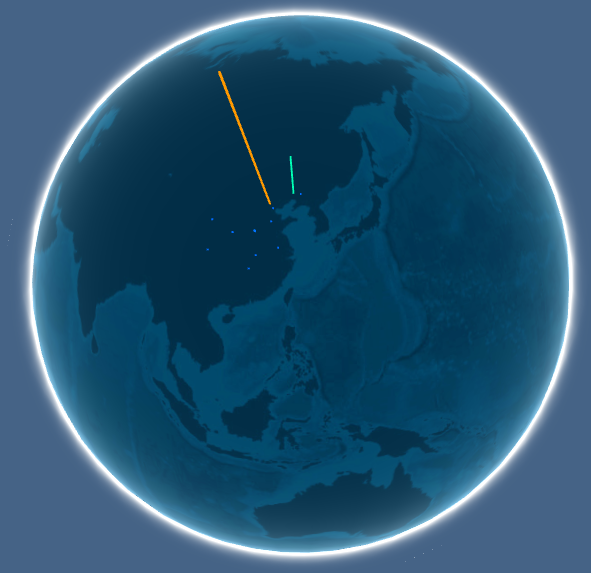
我们再来看神舟长城(AS9389)的ip地理位置分布, 神舟长城又是从中国联通购买服务(可能有些优化吧,具体的处理逻辑只能从策略上看了)。
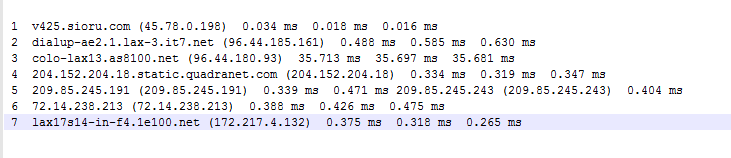
跟踪一次AS转播,以www.google.com为例,在tracerouter得到的路由追踪信息中我们可以看到
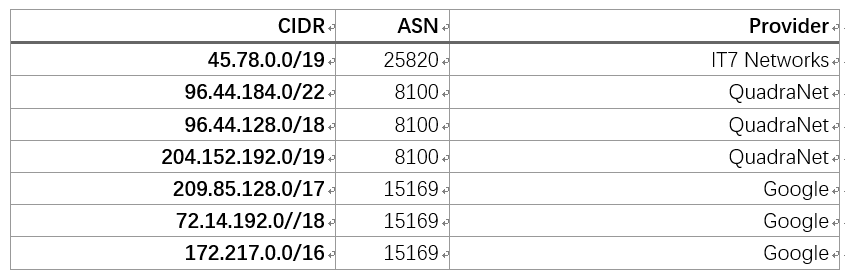
每一个ip所在的CIDR为
一段请求,经过源AS中的路由,到达自治系统的边界路由器,被转发到了AS8100,又从AS8100的一个边界被路由到了另外一个边界路由,最终进入AS15169的内部域。注意,此处的Provider并不一定是专门的运营商Internet Service Provider,有些公司为了处理多个ISP入口的流量,申请了ASN。如果在流量逻辑上和上级ISP没有太多的出入,就没有必要申请一个ASN,就算使用了BGP协议,起源域也可以使用一个私有ASN如同私有IP一样进行连接,在IANA的规定中将[64512-65534][4200000000-4294967294]保留为私有ASN用于上述情况,其他保留ASN请访问官方网站。
那所有IP都有对应的ASN嘛?不是,因为不是所有的IP都选择接入互联网,如果我接入了那我就一定有ASN嘛?是的。在一个局域网玩游戏,自己设置IP,怎么设置都行,让大家能通信就好,但是如果你要和其他局域网玩,两个局域网的管理员就得互相商量一下,怎么设置IP,怎么通信,以此来更改路由器设置。如果想和全世界玩,就得服从人家的协议了。
在某些基于多协议标签交换中为了实现VPN之间的交流,同样也可以为VPN单独申请一个ASN,以区分彼此并进行路由[2]。
Whois信息
对于ASN的whois信息可能各个数据库的存储格式都有所不同,以RIPE的数据库为例子。下面是由RPSL语言所写的中国网通AS的信息
其中import就是AS的路由表导入规则
Import语法如下
. . .
from <peering-N> [action <action-N>]
accept <filter>
意思就是说,从所有的from后米娜的peering导入符合filter规则的路由表,以上的import信息表示,接受所有来自AS701,A S11919, AS6453, AS9225, AS4134, AS4538, AS4789, AS9800, AS4799的路由表,并分别设置了100,120的优先级。
更细粒度的语法
action pref = 10;
accept { 128.9.0.0/16 }
则表示,接受来自AS2的路由128.9.0.0/16
而export的语法类似
. . .
to <peering-N> [action <action-N>]
announce <filter>
向所有符合filter的peer转发路由上面的例子之一则表示向AS4134转发AS9929,AS9812,AS9810,AS9813,AS9816,AS9819,AS17432,AS7639的路由。
对于其他路由协议,多协议路由协议,和协议间的反射路由的完整import和export语法如下:
from <peering-1> [action <action-1>]
. . .
from <peering-N> [action <action-N>]
accept <filter>
to <peering-1> [action <action-1>]
. . .
to <peering-N> [action <action-N>]
announce <filter>
详细的解释请翻阅RFC[2622]文档.
BGP劫持
因为协议的特殊性,在计算路由路线时,通常在会合路由表中的所有ip前缀进行匹配,如果满足变长掩码的需求,就会把通过该路由将数据转发,如果存在相同的IP前缀,则找到一个ip块更小的路由,既掩码最长的那一个。攻击者通常会攻击边界路由器,使将错误的或者未经使用的ip前缀散发出去,将错误的路由信息广播至上级和其他对等体的路由表中,从而达到获取本不应该接受到的路由的数据消息。
就BGP本身而言,这种攻击很难从协议上进行更改,因为设计中虽然是建立在TCP之上,但是协议本身并没有验证数据源可靠与否的设计。唯一一个难点在于,边界路由的连接必须在物理上进行端口设置,而且BGP互换报文的TTL只有1,也就是必须在1秒之内建立连接才能进行下一步操作,比如,边界路由器RA和边界路由RB如果要互设BGP,那么必须在路由器的console中设置BGP会通过哪一个物理端口。因此,这种攻击服务器中如果有人为改动的话,是很难防范的。
2014年记录到的BGP劫持曾经拦截了比特币矿机到采矿器服务器的连接,将流量转移到了攻击者自己的矿池,就简简单单看着流量就收集了在当时价值8万美刀的比特币。
参考文献
http://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc827
http://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc1105
http://docstore.mik.ua/orelly/networking/tcpip/ch07_05.htm
http://docstore.mik.ua/orelly/networking/tcpip/ch07_04.htm
http://www.cnnic.net.cn/jczyfw/ipas/assq/201206/t20120612_26541.htm