The following are some basic operations of python's list and set
1. Some operations of list
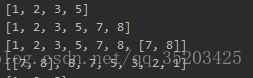
list = [1, 2, 3] list.append(5) print(list) list.extend([ 7 , 8 ]) # extend is to add the elements of the iterable object to the list in turn print (list) list.append([ 7 , 8 ]) # append is to add the incoming parameter as an element to the list print (list) list.reverse() #Elements are reversed. Note that this operation cannot be assigned to a variable. This operation is an operation on the list itself, that is, the list itself changes . # l=list.reverse() l is empty, and the reversed list is not obtained. value print (list)
Output result:
2.set basic operation
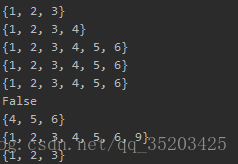
list = [1, 1, 3, 2, 3] s = set(list) print(s) s.add( 4 ) # s.add([2,3]) error, the add function can only add elements of the same type as the original set print (s) s.update([ 3 , 5 , 6 ]) # s.update(5) error, an iterable object is passed in when update updates the collection print (s) c = s.copy() #For collection copy , create a new collection cc = s print (c) print (cc) #Similar to the copy method in list print (cc is c) ss = {1, 2, 3, 9} minus = s.difference(ss) #find the difference print ( minus) union = s.union(ss) #Union print ( union ) intersection = s.intersection(ss) #Seek intersection print ( intersection)
Output result: