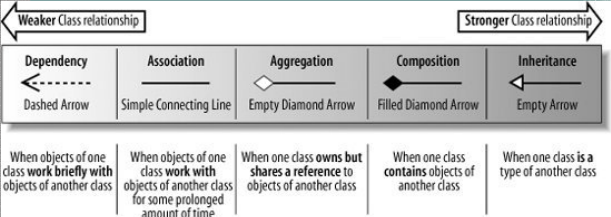
There are five types of relationships between classes:
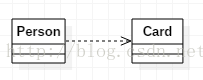
1. Dependency
One-way , which means that a class depends on the definition of another class, and changes in one class will affect the other class, which is a " use a " relationship
If A depends on B, then B behaves as A's local variables, method parameters, static method calls, etc.
- publicclass Person {
- publicvoid doSomething(){
- Card card = new Card(); //local variable
- ....
- }
- }
- publicclass Person {
- public void doSomething(Card card){ //Method parameters
- ....
- }
- }
- publicclass Person {
- publicvoid doSomething(){
- int id = Card.getId(); // static method call
- ...
- }
- }
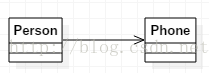
2. Association
One-way or two-way (usually we need to avoid using two-way association relationship), is a " has a " relationship, if A is unidirectionally related to B, then it can be said that A has a B, usually expressed as a global variable
- publicclass Person {
- public Phone phone;
- publicvoid setPhone(Phone phone){
- this.phone = phone;
- }
- public Phone getPhone(){
- return phone;
- }
- }
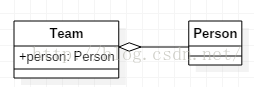
3. Aggregation
One-way, a type of association relationship, the difference between the association relationship is semantic, the two objects associated are usually equal, and the aggregation is generally unequal, there is a sense of the whole and the part, and there is little difference in implementation
Class is composed of Student, its life cycle is different, the whole does not exist, part still exists , the current Team is disbanded, the people are still there, you can also join other groups
- publicclass Team {
- public Person person;
- public Team(Person person){
- this.person = person;
- }
- }
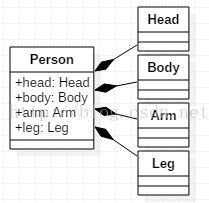
4. Composition
One-way, is a special aggregation relationship with strong dependencies
Head, Body, Arm and Leg are combined into People, and their life cycle is the same. If the whole does not exist, the parts will also die.
- publicclass Person {
- public Head head;
- public Body body;
- public Arm arm;
- public Leg leg;
- public Person(){
- head = new Head();
- body = new Body();
- arm = new Arm();
- leg = new Leg();
- }
- }
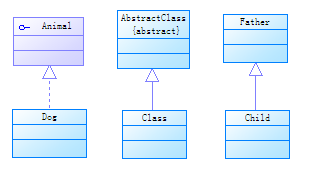
5. Inheritance
A class implements an interface, a class inherits an abstract class, and a class inherits from a parent class belongs to this relationship
It can be divided into finer points:
Realization: A class implementing an interface belongs to this relationship
Generalization: the " is a " relationship, the class inherits the abstract class, and the class inherits the parent class belongs to this relationship