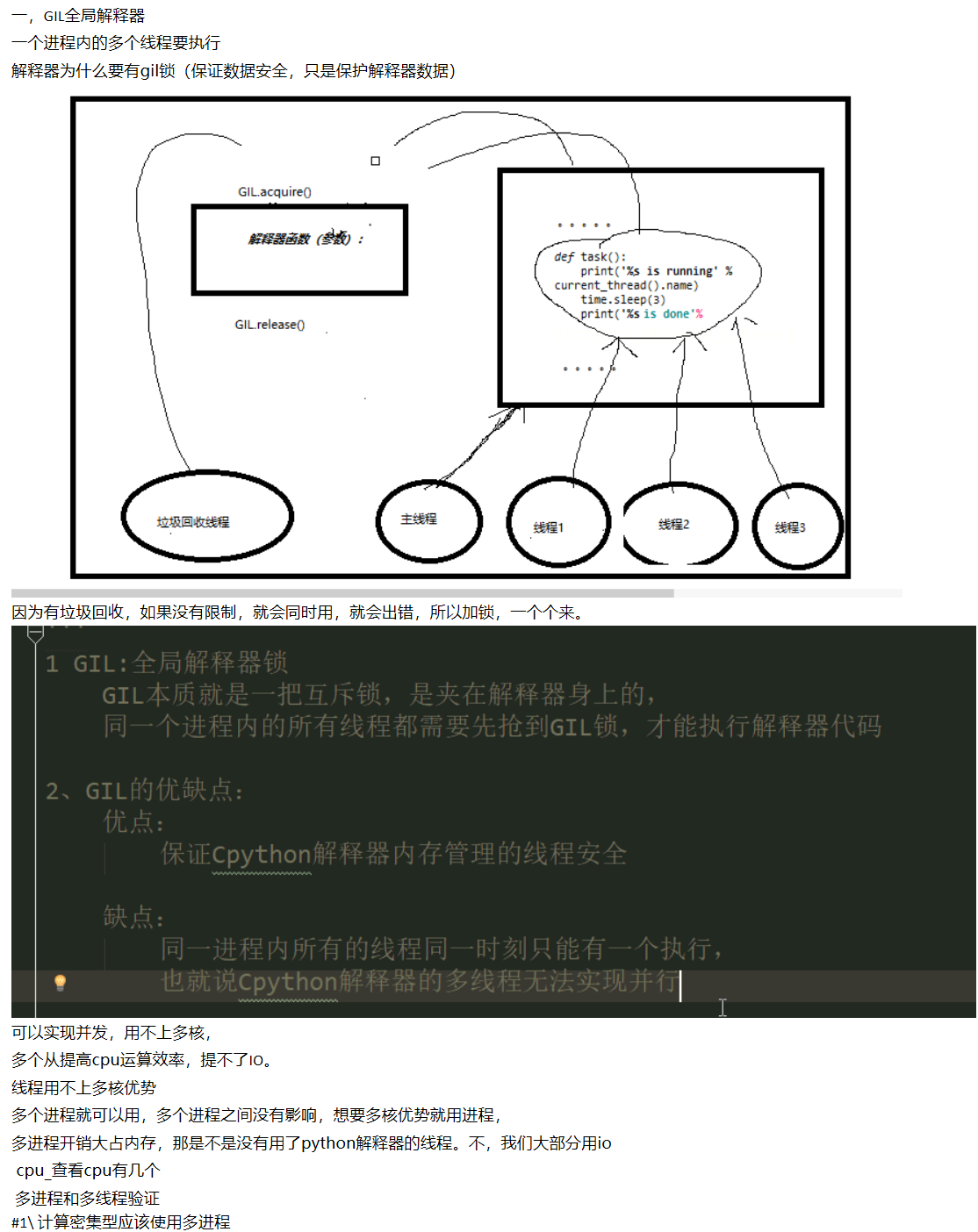
# 1\ Computationally intensive should use multiprocessing # from multiprocessing import Process # from threading import Thread # # import time # # import os # # print(os.cpu_count()) # # def task1(): # res=0 # for i in range(1,100000000): # res+=i # # def task2(): # res=0 # for i in range(1,100000000): # res+=i # # def task3(): # res=0 # for i in range(1,100000000): # res+=i # # def task4(): # res=0 # for i in range(1,100000000): # res+=i # # if __name__ == '__main__': # # p1=Process(target=task1) # # p2=Process(target=task2) # # p3=Process(target=task3) # # p4=Process(target=task4) # # p1=Thread(target=task1) # p2=Thread(target=task2) # p3=Thread(target=task3) # p4=Thread(target=task4) # start_time=time.time() # p1.start() # p2.start() # p3.start() # p4.start() # p1.join() # p2.join() # p3.join() # p4.join() # stop_time=time.time() # print(stop_time - start_time) # 2\ IO intensive should use multithreading from multiprocessing import Process from threading import Thread import time def task1(): time.sleep(3) def task2(): time.sleep(3) def task3(): time.sleep(3) def task4(): time.sleep(3) if __name__ == '__main__': # p1=Process(target=task1) # p2=Process(target=task2) # p3=Process(target=task3) # p4=Process(target=task4) # p1=Thread(target=task1) # p2=Thread(target=task2) # p3=Thread(target=task3) # p4=Thread(target=task4) # start_time=time.time() # p1.start() # p2.start() # p3.start() # p4.start() # p1.join() # p2.join() # p3.join() # p4.join() # stop_time=time.time() # print(stop_time - start_time) #3.138049364089966 p_l=[] start_time=time.time() for i in range(500): p=Thread(target=task1) p_l.append(p) p.start() for p in p_l: p.join() print(time.time() - start_time)

from socket import * from threading import Thread from concurrent.futures import ProcessPoolExecutor,ThreadPoolExecutor tpool=ThreadPoolExecutor(3) def communicate(conn,client_addr): while True: #communication loop try : data = conn.recv(1024) if not data: break conn.send(data.upper()) except ConnectionResetError: break conn.close() def server(): server = socket (AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM) server.bind(('127.0.0.1',8080)) server.listen(5) while True: # 链接循环 conn,client_addr=server.accept() print(client_addr) # t=Thread(target=communicate,args=(conn,client_addr)) # t.start() tpool.submit(communicate,conn,client_addr) server.close() if __name__ == '__main__': server() Kefuduan from socket import * client = socket (AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM) client.connect(('127.0.0.1',8080)) while True: msg=input('>>>: ').strip() if not msg:continue client.send(msg.encode('utf-8')) data=client.recv(1024) print(data.decode('utf-8')) client.close()

from concurrent.futures import ProcessPoolExecutor,ThreadPoolExecutor import time,os,random def task(x): print('%s 接客 '%os.getpid()) time.sleep(random.randint(2,5)) return x**2 if __name__ == '__main__': p =ProcessPoolExecutor(max_workers=2) # = The number of processes opened by default is the number of cpu cores for i in range(20 ): p.submit(task,i) Thread Pool from concurrent .futures import ProcessPoolExecutor,ThreadPoolExecutor import time,os,random def task(x): print('%s 接客 '%os.getpid()) time.sleep(random.randint(2,5)) return x**2 if __name__ == '__main__': p=ThreadPoolExecutor() for i in range(20): p.submit(task,i)

from concurrent.futures import ProcessPoolExecutor,ThreadPoolExecutor import time,os,random def task(x): print ( ' %s pick up ' % x) time.sleep(random.randint(1,3)) return x**2 if __name__ == ' __main__ ' : #Asynchronous call # p=ThreadPoolExecutor(4) # The number of threads that are enabled by default is the number of cpu cores*5 # # # alex, Wu Peiqi, Yang Li, Wu Chenyu, Zhang San # # obj_l =[] # for i in range(10): # obj=p.submit(task,i) # obj_l.append(obj) # # # p.close() # # p.join() # p.shutdown( wait=True) # # print(obj_l[3].result()) # print('main') #Synchronous call p=ThreadPoolExecutor(4) #The number of threads enabled by default is the number of cpu cores*5 for i in range(10): res=p.submit(task,i).result() print ( ' main ' ) close() join() does not allow submission of old thread pools to it
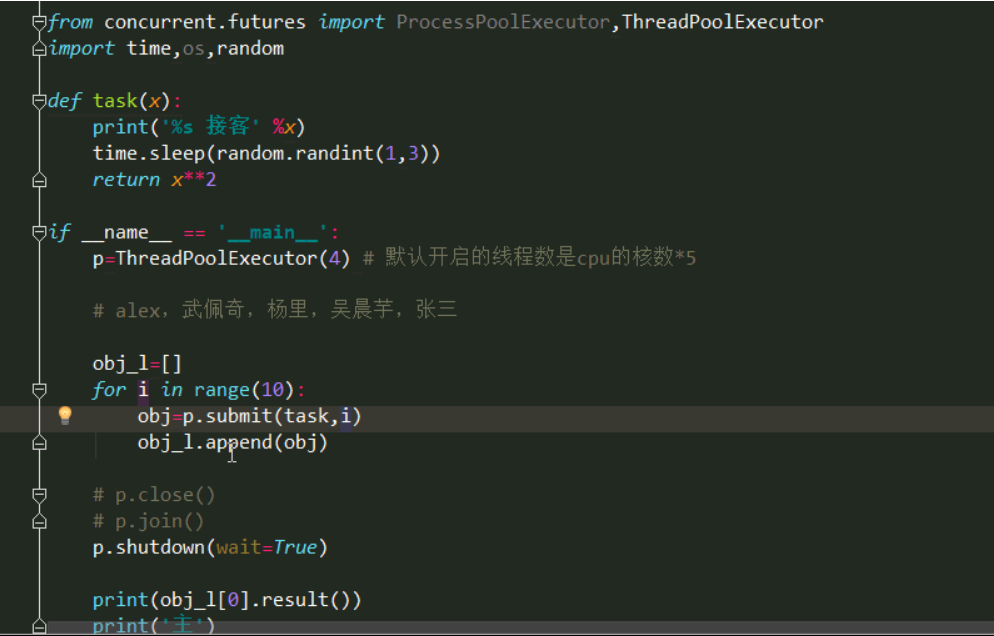
get the result