Reprinted from: https://blog.csdn.net/hguisu/article/details/38385371
Foreword:
Philosophers often think about questions: "Who am I?" "Where do I come from?" "Where do I go? Not just philosophers, I think everyone has their own understanding of these three questions.
If we want to become architects, we have to face three big problems ourselves:
Identify yourself: Who am I? Where?
How to be a good architect: what do I do?
How to Build an Architect Body of Knowledge: How Do I Do It?
Here is the methodology of doing things: goal (what I want to do), method (plan) (what should I do), execution/action
Two definitions of software industry architect
• A
system
architect is a person who needs to control both the whole and local bottlenecks and provide solutions according to specific business scenarios. Specifically, it is a technician who confirms and evaluates system requirements, gives development specifications, builds the core framework for system implementation, clarifies technical details, and clears up major difficulties. The main focus is on the "technical realization" of the system. Therefore, he
/
she should be a master of specific development platforms, languages, and tools, and can immediately provide the most appropriate solutions for common application scenarios. the cost of functional requirements. The system architect is responsible for designing the overall structure of the system. Every detail from the requirements to the design must be considered, and the entire project should be grasped to make the designed project as efficient as possible, easy to develop, easy to maintain, and simple to upgrade.
•
Architect is an emerging profession in the software industry. The job responsibility is to convert the customer's requirements into a standardized development plan and text during the development of a software project, formulate the overall structure of the project, and guide the entire development team to complete the project. plan. The main task of the architect is not to engage in the writing of specific software programs, but to engage in higher-level development framework work. He must be very knowledgeable about development techniques and needs to have good organizational management skills
.
The difference between the Internet and conventional enterprises in the software industry
• Internet project (flexible and extensible)
• Profit direction: oriented by products and services, attracting users with products, and mining profit models from them
• Iterative frequency: rapid iteration, rapid product presentation , and continuous product update to meet business development and user needs
• Business complexity: Due to the entire Internet, the greater the complexity, the fewer people who use it
• The waterfall approach is not suitable for the Internet, and the architect's way of doing things is also different from enterprise architecture
• Enterprise projects ( partial accumulation reusability)
• Profitable direction: technical services are demand-oriented, generally serving internal and partners
• Iterative frequency: oriented by customer needs, generally the cycle is very long
• Business complexity: customer demand-oriented, generally complex business logic
• Suitable for waterfall flow and spiral model
Internal direction of the architect
• System architect:
server load
, reliability, scaling, scaling, database slicing, caching applications
• Application architect:
understand business, sort out models, design patterns, interfaces, data
interaction
Architects are not omnipotent
• Good at communication, not necessarily technically strong
•擅长展望的,不见得细节完善
•擅长攻关的,不见得会规划
•擅长设计的,不见得会实现
•擅长理论的,不见得能落地
•擅长推动的,不见得细节可控
•擅长总结的,不见得会创新
•不擅长的事情怎么办?很多方法能解决!!
架构师具备的素质
• 精通某项技术,能够从本质上类比,触类旁通其他技术
• 对等所有技术,只有合适和不合适,没有喜欢和不喜欢。
• 视野开阔,了解不同技术的优缺点。知道使用某项开源技术实现某项业务需求,能够辨别重复造轮子。
• 精通设计模式,但又不泛用。
• 把系统拆分成多个子系统或模块。模块之间尽量松耦合,使得原先串行的开发任务变得可以并行发展。
• 能清楚系统的瓶颈在什么地方, 不断定位技术难度,开发进度,性能,内存等个方面的瓶颈。不断调整骨干力量解决瓶颈,在
风险爆发之前消除隐患。
• 能做好前瞻性设计,预判到需求可能产生的变化。
互联网团队特点
•努力目标:产品做得好,技术玩的欢
•迭代快,效率高,业务逻辑清晰明了,扩展强,
•迭代次数过多,需要定期整理迭代代码整理精华及总结。
•一个人精力有限,不能面面俱到
•高手凤毛麟角,即使有,也因为精力有限也只能解决几个问题
•产品是一个整体,技术团队也是一个整体,所有细节的优秀才会成为一个优秀的产品,优秀的团队
架构是要靠团队做出来的
•保持和架构的沟通,架构通过团队的沟通总结出方向
•队员经常提出自己碰到的问题,并分享给大家,思维碰撞促进发展
•产品经常提出设想和规划,能够使得架构符合未来发展需求
•运维经常提出隐患及分析,能使得架构快速拆分模块
•定期做总结归纳以此分析问题,解决问题
•团队成长、就是每个人的成长、每个人成长眼界自然增长
•团队的成功、就是产品的成功,产品的成功就是公司的成功
公司的成功可以给你加光环,但光环不代表自己的能力代表经历
架构师职责:会做什么?
•方向规划:有想法和技术展望目标,制定短期目标
•架构设计:集思广益来设计,归类总结,根据讨论结果制定规范。设计不仅仅是技术相关(业务流程,业务方向,模块划分组合,框架设计,流程纰漏等),设计出来还是需要实施的。
•技术攻关:疑难技术点攻关,将问题集中化解决,提供平台化解决方案以及选型决策。
•解决疑难问题:发现各类型问题(不仅仅是技术),通过规范,演讲,绘图等方式解决隐患。
•互动沟通:部门之间沟通,开发之间沟通,产品之间沟通,市场沟通,沟通后产出图形化文档及设计。
•关注点:秩序,统一,规范,稳定,高效
在知乎(https://www.zhihu.com/question/19558112)这么回答:
架构师是一个既需要掌控整体又需要洞悉局部瓶颈并依据具体的业务场景给出解决方案的团队领导型人物。架构师不是一个人,他需要建立高效的体系,带领团队去攻城略地,在规定的时间内完成项目。
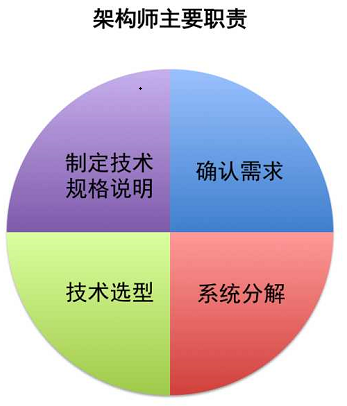
架构师主要做些什么:
1 确认需求
架构师要懂得用户需求,理解用户真正想要什么,这使得架构师必须要和分析人员不断沟通,反复确认需求规格说明书,以此来保证他精准清楚用户需求。
项目经理刘先生在受访时说:「架构师会与很多人沟通,例如开发人员,例如我们项目经理,有时甚至是用户本身。架构设计的目的很明确,目的是什么呢?挖掘用户需求。」
2 系统分解
在架构师认可需求规格说明书后,架构师已明确用户需求是是什么,这时候便看架构师的分解能力了。
通过100offer入职的全栈技术架构师周先生从「纵向分解」和「横向分解」和我们说明了系统分解是什么——
「一般分为纵向分解和横向分解,纵向分解是将整个系统分层,从而将整体系统分解成下一级的子系统与组件。横向分解是在系统分解成不同的逻辑层或服务后,对逻辑层进行分块,确定层与层之间的关系。」
3 技术选型
在系统分解后,架构师会最终形成软件整体架构,接下来,架构师的职责是技术选型。
「前端到底用瘦客户端还是富客户端呢?数据库是用MySQL还是MSSQL又或是Oracle呢?」架构师张先生在接受采访时说,「在了解用户需求后,分解完系统后,技术选型是非常重要的环节,提出各个方向,我再进行评估。不过,很多人都以为架构师是有决定权的,其实不是,架构师没有拍版的权力,决定由项目经理来做。 」
架构师在技术选型阶段会提供参考信息给项目经理,项目经理再从预算、进度、人力、资源等各方面情况来权衡,最终确认。
4 制定技术规格说明
如前文调查显示,架构师在项目开发过程中是「灵魂人物」,并且要具备协调组织能力和懂得人员分工。
在制定技术规格说明阶段,架构师要协调起所有的开发人员,架构师通常会用技术规格说明书与开发人员保持沟通,让开发人员能从各个视角去观测、理解他们负责的模块或者子系统,确保开发人员能够按照架构意图实现各项功能。
架构师团队内做的事情
•
沟通能力:各个方面都要了解,人人想法及规划都要知道,了解产品思想,用了什么方法实现的
•
组织能力:组织推动各种技术的改进及功能的完善
•
谈判代表:左右两难的时候的调解人
•
设计模块及业务:通过图形化设计发现开发后才会发现的业务问题
•
成本规划:通过过往经验评估成本及步伐
•
愿望收集:不断收集建议及愿望,一步步实现
•
传播
布道
:不断参与行业交流,提高理论及技术知识科普分享团队
互联网常见架构优化项
•目的:通过各种方式,强化产品运行速度及效率及体验等
•缩短开发周期,归类设计减少重复造轮子
•工具化所有环节,数据归类所有数据
•优化服务器利用率,减少服务器资源浪费
•强化服务器稳定性,设计完善的服务器监视预警
•图形化文档管理关键点,缩短产品及业务的成熟时间,规范业务模块间的关系。
•拆解复杂业务及任务,组合高依赖业务,减少开发细节模糊点
如何成长为架构师?
•行业动态要了解,时刻关注技术更新
•开发时先设计然后在做,做好后总结
•关注公司业务动态,结合产品观察
•关注系统运维及相关技术
•关注业务划分技巧及目的
•清晰化自己掌握的技术的用途
•多沟通
开发的发展的几条路
•偏管理:
做项目管理、总监、
CTO
•偏技术:
做架构、技术专家、领域专家
例子:如何做好业务完善设计?

例子:如何做好技术设计及设计沟通?

设计中注意要点
•问题拆解,明确知道关键点是那些,围绕核心思想进行设计
•避免过度设计,现在需要多少就做多少
•灵活及扩展性越强的模块越容易复杂
•相互依赖过多的模块要合并
•相互依赖模块之间要做隔离为以后升级适配留路
•隔离不仅仅隔离依赖还需要隔离适配临界点(如第三方接口)
•系统单点要备份,监控
•层级多了会以性能及效率为代价,少了则不好维护,掌握平衡即可
•不能过分追求一个极致,谁也不能预测业务下一步
•不知道所有业务场景慎重设计,应以整体产品方向为设计依据
开发如何更好的沟通?
•发现问题,分析问题原因时
•阐述所有相关信息,碰到什么问题,目前情况什么样,并做演示
•通过输入,输出判断结果分析原因
•通过图形化讨论更好理解
•术语不是所有人都知道其意义,不如白话沟通
•有不知道的地方,及时拉所有相关人加入讨论分析
•代码如果没有注释,只能知道动了那些数据
架构总结:
1、架构不是设计出来,是进化优化出来的。