前言:
Zookeeper的响应之所以快,一部分原因与它的节点数据都加载到内存有关。避免了每次节点查询都到磁盘中查询。
而本文介绍的ZKDatabase,就是作为Zookeeper的内存数据库而存在。
我们主要来看下它是如何在启动时加载数据,在事务执行时同步变更,又如何将数据同步到快照日志中的。
1.ZKDatabase的基本结构
/**
* This class maintains the in memory database of zookeeper
* server states that includes the sessions, datatree and the
* committed logs. It is booted up after reading the logs
* and snapshots from the disk.
*/
public class ZKDatabase {
// 本文中主要分析dataTree这个属性,这个就是内存中节点存放对象
protected DataTree dataTree;
protected ConcurrentHashMap<Long, Integer> sessionsWithTimeouts;
protected FileTxnSnapLog snapLog;
public ZKDatabase(FileTxnSnapLog snapLog) {
dataTree = new DataTree();
sessionsWithTimeouts = new ConcurrentHashMap<Long, Integer>();
this.snapLog = snapLog;
}
}ZKDatabase实现数据的内存加载主要通过DataTree来实现。我们来看下DataTree的结构
1.1 DataTree
/**
* This class maintains the tree data structure. It doesn't have any networking
* or client connection code in it so that it can be tested in a stand alone
* way.
* <p>
* The tree maintains two parallel data structures: a hashtable that maps from
* full paths to DataNodes and a tree of DataNodes. All accesses to a path is
* through the hashtable. The tree is traversed only when serializing to disk.
*/
public class DataTree {
// 所有节点对应的map集合
private final ConcurrentHashMap<String, DataNode> nodes = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, DataNode>();
// 临时节点对应的map集合
private final Map<Long, HashSet<String>> ephemerals = new ConcurrentHashMap<Long, HashSet<String>>();
}很容易看到,节点信息在Zookeeper服务端中以Map形式存放在nodes中,key就是path,value就是DataNode。再来看下DataNode的基本信息
1.2 DataNode
public class DataNode implements Record {
// 父节点
DataNode parent;
// 节点data信息
byte data[];
// acl权限信息
Long acl;
// 节点stat 信息
public StatPersisted stat;
// 子节点集合
private Set<String> children = null;
DataNode() {
}
public DataNode(DataNode parent, byte data[], Long acl, StatPersisted stat) {
this.parent = parent;
this.data = data;
this.acl = acl;
this.stat = stat;
}
}DataNode基本包含了一个节点的所有信息,stat信息则存放在Statpersisted对象中。
总结:通过对ZKDatabase结构的分析,我们知道节点的信息都存放在DataTree中,以map形式存放,节点信息存放在DataNode中
2.Zookeeper服务端启动时加载快照数据到ZKDatabase中
在之前分析Zookeeper服务端单机版启动过程中,曾经直接跳过一个知识点,就是在启动时加载快照数据到内存中,也就是以下代码
public class NIOServerCnxnFactory extends ServerCnxnFactory implements Runnable {
public void startup(ZooKeeperServer zks) throws IOException,
InterruptedException {
...
// 加载数据到内存中,这里我们先知道有这个操作,后续分析事务日志时再一起说明下
zks.startdata();
...
}
}就是这句ZookeeperServer.startdata(),就将快照数据加载到内存中,我们一起来看下。
2.1 ZookeeperServer.startdata()
public class ZooKeeperServer implements SessionExpirer, ServerStats.Provider {
public void startdata()
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//check to see if zkDb is not null
if (zkDb == null) {
// 创建ZKDatabase
zkDb = new ZKDatabase(this.txnLogFactory);
}
if (!zkDb.isInitialized()) {
// 初始化加载数据
loadData();
}
}
public void loadData() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// 后续再分析这个问题
if(zkDb.isInitialized()){
setZxid(zkDb.getDataTreeLastProcessedZxid());
}
else {
// 重点在这里,直接调用loadDataBase()方法,直接看2.2
setZxid(zkDb.loadDataBase());
}
...
}
}2.2 ZKDatabase.loadDataBase()
public class ZKDatabase {
protected FileTxnSnapLog snapLog;
public long loadDataBase() throws IOException {
// 直接调用FileTxnSnapLog的方法来实现
long zxid = snapLog.restore(dataTree, sessionsWithTimeouts, commitProposalPlaybackListener);
initialized = true;
return zxid;
}
}2.3 FileTxnSnapLog.restore()
public class FileTxnSnapLog {
public long restore(DataTree dt, Map<Long, Integer> sessions,
PlayBackListener listener) throws IOException {
// 调用反序列化
snapLog.deserialize(dt, sessions);
// 这里加载那些没有被更新到快照日志但是已经添加到事务日志的请求,重新将对应节点添加到DataTree中
return fastForwardFromEdits(dt, sessions, listener);
}
}2.4 FileSnap.deserialize() 最终在这里执行
public class FileSnap implements SnapShot {
public long deserialize(DataTree dt, Map<Long, Integer> sessions)
throws IOException {
// 直接从dataDir目录下获取至多100个有效的快照日志文件
List<File> snapList = findNValidSnapshots(100);
if (snapList.size() == 0) {
return -1L;
}
File snap = null;
boolean foundValid = false;
for (int i = 0; i < snapList.size(); i++) {
snap = snapList.get(i);
InputStream snapIS = null;
CheckedInputStream crcIn = null;
try {
LOG.info("Reading snapshot " + snap);
snapIS = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(snap));
// 检查checksum
crcIn = new CheckedInputStream(snapIS, new Adler32());
InputArchive ia = BinaryInputArchive.getArchive(crcIn);
// 反序列化文件
deserialize(dt,sessions, ia);
long checkSum = crcIn.getChecksum().getValue();
long val = ia.readLong("val");
if (val != checkSum) {
throw new IOException("CRC corruption in snapshot : " + snap);
}
foundValid = true;
break;
} ...
}
...
}
public void deserialize(DataTree dt, Map<Long, Integer> sessions,
InputArchive ia) throws IOException {
FileHeader header = new FileHeader();
// 反序列化头文件信息,检查魔数
header.deserialize(ia, "fileheader");
if (header.getMagic() != SNAP_MAGIC) {
throw new IOException("mismatching magic headers "
+ header.getMagic() +
" != " + FileSnap.SNAP_MAGIC);
}
// 在这里反序列化数据信息,如下
SerializeUtils.deserializeSnapshot(dt,ia,sessions);
}
}
public class SerializeUtils {
public static void deserializeSnapshot(DataTree dt,InputArchive ia,
Map<Long, Integer> sessions) throws IOException {
// session信息
int count = ia.readInt("count");
while (count > 0) {
long id = ia.readLong("id");
int to = ia.readInt("timeout");
sessions.put(id, to);
if (LOG.isTraceEnabled()) {
ZooTrace.logTraceMessage(LOG, ZooTrace.SESSION_TRACE_MASK,
"loadData --- session in archive: " + id
+ " with timeout: " + to);
}
count--;
}
// 节点信息,最终交由DataTree来执行反序列化
dt.deserialize(ia, "tree");
}
}
之前一篇文章分析快照日志生成时,我们看到了如何将DataTree的信息序列化到磁盘文件中。此时在Zookeeper服务端启动时,又执行了将文件反序列化到DataTree中,反序列化的过程不算复杂,读者可以自行阅读。
通过一个时序图来展示下整个过程:
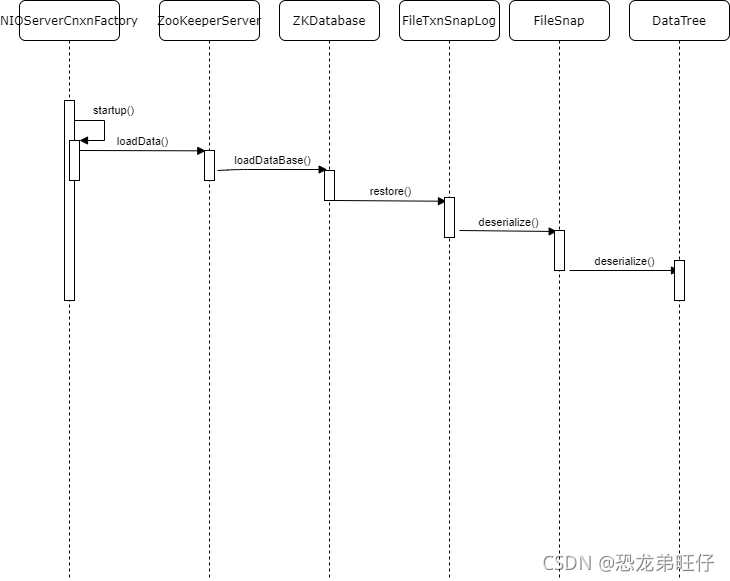
3.事务请求时对DataTree的操作
在2中我们分析了Zookeeper服务端启动时对快照日志的加载,使节点数据加载到内存中。那么在每次接收客户端请求时,实际也会对DataTree保存的节点信息发生变更。我们分析一个示例,来展示下DataTree的变更过程。
DataTree提供了一系列节点操作的方法,在这里我们就只针对createNode()方法进行分析。
3.1 FinalRequestProcessor.processRequest()
之前分析过,请求会经过三个requestProcessor,而这里分析的FinalRequestProcessor就是最后一个processor
public class FinalRequestProcessor implements RequestProcessor {
ZooKeeperServer zks;
public void processRequest(Request request) {
...
ProcessTxnResult rc = null;
synchronized (zks.outstandingChanges) {
...
if (request.hdr != null) {
TxnHeader hdr = request.hdr;
Record txn = request.txn;
// 执行processTxn()方法
rc = zks.processTxn(hdr, txn);
}
}
...
}3.2 ZooKeeperServer.processTxn()
public class ZooKeeperServer implements SessionExpirer, ServerStats.Provider {
public ProcessTxnResult processTxn(TxnHeader hdr, Record txn) {
ProcessTxnResult rc;
int opCode = hdr.getType();
long sessionId = hdr.getClientId();
// 执行ZKDatabase的操作
rc = getZKDatabase().processTxn(hdr, txn);
...
return rc;
}
}3.3 ZKDatabase.processTxn()
public class ZKDatabase {
public ProcessTxnResult processTxn(TxnHeader hdr, Record txn) {
// 操作的还是DataTree
return dataTree.processTxn(hdr, txn);
}
}3.4 DataTree.processTxn()
public class DataTree {
public ProcessTxnResult processTxn(TxnHeader header, Record txn){
ProcessTxnResult rc = new ProcessTxnResult();
try {
rc.clientId = header.getClientId();
rc.cxid = header.getCxid();
rc.zxid = header.getZxid();
rc.type = header.getType();
rc.err = 0;
rc.multiResult = null;
switch (header.getType()) {
case OpCode.create:
CreateTxn createTxn = (CreateTxn) txn;
rc.path = createTxn.getPath();
// 请求create请求则直接创建节点
createNode(
createTxn.getPath(),
createTxn.getData(),
createTxn.getAcl(),
createTxn.getEphemeral() ? header.getClientId() : 0,
createTxn.getParentCVersion(),
header.getZxid(), header.getTime());
break;
...
}
}
}
public String createNode(String path, byte data[], List<ACL> acl,
long ephemeralOwner, int parentCVersion, long zxid, long time)
throws KeeperException.NoNodeException,
KeeperException.NodeExistsException {
int lastSlash = path.lastIndexOf('/');
String parentName = path.substring(0, lastSlash);
String childName = path.substring(lastSlash + 1);
// 创建节点stat信息
StatPersisted stat = new StatPersisted();
stat.setCtime(time);
stat.setMtime(time);
stat.setCzxid(zxid);
stat.setMzxid(zxid);
stat.setPzxid(zxid);
stat.setVersion(0);
stat.setAversion(0);
stat.setEphemeralOwner(ephemeralOwner);
DataNode parent = nodes.get(parentName);
if (parent == null) {
throw new KeeperException.NoNodeException();
}
synchronized (parent) {
Set<String> children = parent.getChildren();
if (children.contains(childName)) {
throw new KeeperException.NodeExistsException();
}
if (parentCVersion == -1) {
parentCVersion = parent.stat.getCversion();
parentCVersion++;
}
parent.stat.setCversion(parentCVersion);
parent.stat.setPzxid(zxid);
Long longval = aclCache.convertAcls(acl);
// 创建节点信息,添加到nodes中
DataNode child = new DataNode(parent, data, longval, stat);
parent.addChild(childName);
nodes.put(path, child);
if (ephemeralOwner != 0) {
HashSet<String> list = ephemerals.get(ephemeralOwner);
if (list == null) {
list = new HashSet<String>();
ephemerals.put(ephemeralOwner, list);
}
synchronized (list) {
list.add(path);
}
}
}
...
}
}总结:针对客户端的创建节点请求,服务端会生成一个DataNode添加到nodes中,并修改其parentNode的基本信息。代码不算复杂,笔者用时序图展示下这个过程。

4.序列化节点信息到快照文件
之前的文章中有说过快照文件的生成,具体可见快照日志的查看与分析。
总结:作为Zookeeper的内存数据库,提供了一系列的API支持节点的操作。通过与快照日志的配合使用,使得Zookeeper可以快速响应客户端的查询请求。