DNS Domain Name System
When two hosts communicate, they need to know the IP address of the other party, but for users, it is difficult to remember a long list of IP addresses. In order to facilitate memory, a domain name system appears, such as www.baidu.com. The ip address is 110.242.68.4. The domain name system DNS is to convert host names on the Internet into IP addresses. The domain name system is a distributed database system. The resolution of domain names to IP addresses is done by many domain name server programs distributed on the Internet.
The domain name system structure of the Internet is divided into: top-level domain name (.com), second-level domain name (baidu), third-level domain name (www), etc. Although the domain name structure is divided in this way, the division of DNS servers is based on "zones." As a unit, each domain name server only has jurisdiction over a part of the domain name system. The domain name servers can be divided into the following four different types:
- Root domain name server: The root domain name server is the highest-level DNS server, and all root domain name servers know the domain names and IP addresses of all top-level domain name services
- Top-level domain name server: Manage second-level domain names
- Authority domain name server: responsible for the domain name of a zone
- Local domain name server: query the server that arrives first
DNS resolution process
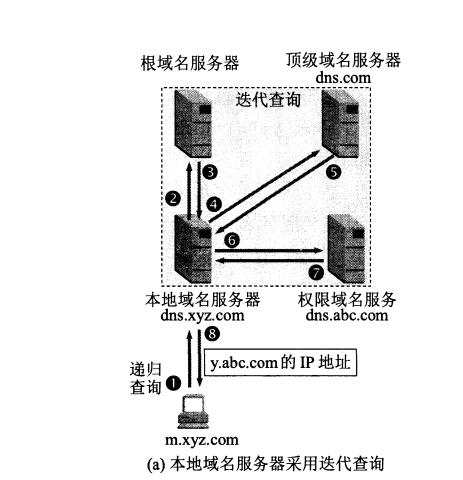
As shown in the figure above, assuming that the host m.xyz.com needs to know the ip address of y.abc.com, analyze the DNS resolution process:
- First, the host m.xyz.com first initiates a recursive query to the local domain name server (equivalent to the local domain name server returning to the host is ip or an error)
- Recursive query: The result of the recursive query is the desired ip address, which is equivalent to the agent, and the prime minister makes a whole query
- Iterative query: the query result returns the address of the next server, that is, it does not return the final result
- The local domain name server adopts iterative query, and first queries the root domain name server
- The root domain name server tells the local domain name server the location of the top-level domain name server for the next query
- The top-level domain name server tells the local domain name server the location of the authorized domain name server for the next query
- The authority domain name server tells the local domain name server the required ip address
- The local domain name server finally tells the host m.xyz.com the result of the query
These messages are all UDP messages, and in order to improve the efficiency of DNS query, there is a cache on the local browser, and it must be cached on the host. At the same time, a high-speed cache is also used on the domain name server.
DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
DHCP is a dynamic host configuration protocol. It is a local area network protocol that uses UDP to work. Two commonly used ports: 67 (DHCP server port) and 68 (DHCP client port). Use DHCP to dynamically obtain IP addresses and management addresses. Wait, to put it simply, DHCP is a protocol that does not require account passwords and can automatically assign information such as IP addresses to the intranet.
DHCP working process
- First, the DHCP client broadcasts a Discover message with a source address of 0.0.0.0:68 and a destination address of 225.225.225.225:67. If the client and the DHCP server are not in the same subnet, they need to be relayed
- After receiving the Discover message, the DHCP server sends an Offer message to the client. The message contains all the information needed by the client. Because there may be many DHCP servers, the corresponding client will also receive many offers, so the client is also required. Confirm message
- After receiving the Offer message, the DHCP client selects the information of a certain server and sends a Request request to the DHCP server.
After that, the DHCP client selects the information of a certain server and sends a Request request to the DHCP server. - The DHCP service area sends an ACK message, the client can use the information provided to it