Article Directory
1. Structure
1.1 C structure and C++ structure
The structure in C++ is an extension of the C structure, adding some new usages and differences when using attributes

:
struct Human
{
char name[15];
int age;
};
typedef struct Human human_; C语言中取别名
struct Human tom; C语言中使用
Human tom; C语言别名使用/C++中使用
Fundamental: The
structure in the C language is a collection of different types of elements, and does not involve the algorithm for processing data
. The structure in C++ not only contains data but also encapsulates different methods of processing data.
1.2 C++ structure and C++ class
- The default permissions of internal members are different
struct student1 成员默认public属性
{
int age;
};
class student2 成员默认private属性
{
int age;
};
- Different default permissions under inheritance
struct human
{
int age;
}
struct student : human 默认public继承属性
{
int Stu_ID;
}
student tom;
tom.age = 19; 在class下会报错,class默认private属性
- Use of templates
定义一个模板:
template <class T> 或者 template <typename T>,但不能是:struct
1.3 Structure memory alignment
Purpose: In order to improve the efficiency of program operation, the CPU needs to access unaligned memory twice, while aligned memory access only needs one time
. The address of the CPU access must meet an integer multiple of 4. Memory alignment is a sacrifice of space in exchange for efficiency Plan
Alignment rules:
- The first element does not need to be aligned
- Other members are aligned to integer multiples of their own type
- If the default alignment number is specified, it will be aligned to the address with the smaller value of its own type and the default alignment number
- Total size: an integer multiple of the maximum number of alignments
struct A // 24
{
char a;
double b;
char c;
};
struct B // 12
{
char a;
int b;
char c;
};
struct C // 8
{
char a;
char b;
int c;
};
struct D // 16
{
double a;
char b;
int c;
};
struct E // 32
{
char a;
struct D b;
double c;
};
Second, position
1.1 What is a position?
- Bit segment is a kind of data compression, without considering efficiency, paying attention to space usage, so there is no need for memory alignment
- Bit segments are used in TCP/IP headers
struct A
{
char a : 3;
char b : 4;
char c : 5;
char d : 4;
};
int main()
{
A a = {
0 }; // 初始化,防止里面是随机值
a.a = 10;
a.b = 12;
a.c = 3;
a.d = 4;
cout << sizeof(struct A) << endl;
return 0;
}

1.2 The use of bit segment in TCP/IP protocol header
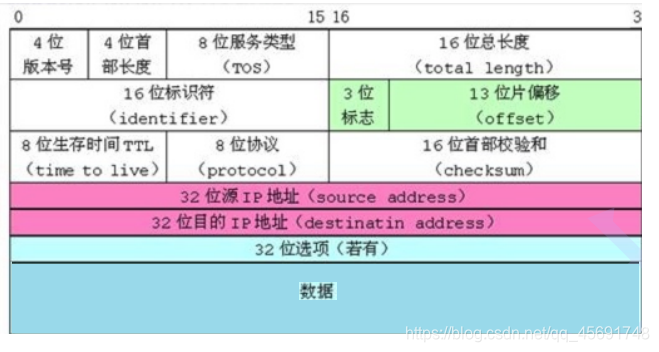
struct
{
unsigned int vison : 4;
unsigned int handler lend : 4
unsigned int TOS : 8
unsigned int total length : 16
};
Three, joint
The members of the union share the same space, so the union is also called a union
union Un
{
char c;
int i;
};
//联合变量的定义
union Un un;
//计算连个变量的大小
printf("%d\n", sizeof(un));
un.i = 1
if (un.c)
printf("小端\n");
else
printf("大端\n");