Chapter 4 Network Layer
- 4.1_ Two services provided by the network layer
- 4.2_Network Protocol
- Three-level directory
4.1_ Two services provided by the network layer
Background:
In the field of computer networks,Network layerShould go toTransport layerWhat kind of service is provided ("Connection-oriented" or "connectionless") Has caused a long-term controversy.
ControversialsubstanceThat is: in computer communication,Reliable deliveryWho should be responsible?The internetstill isEnd system?
(1) Virtual circuit service
The idea of telecommunications network:
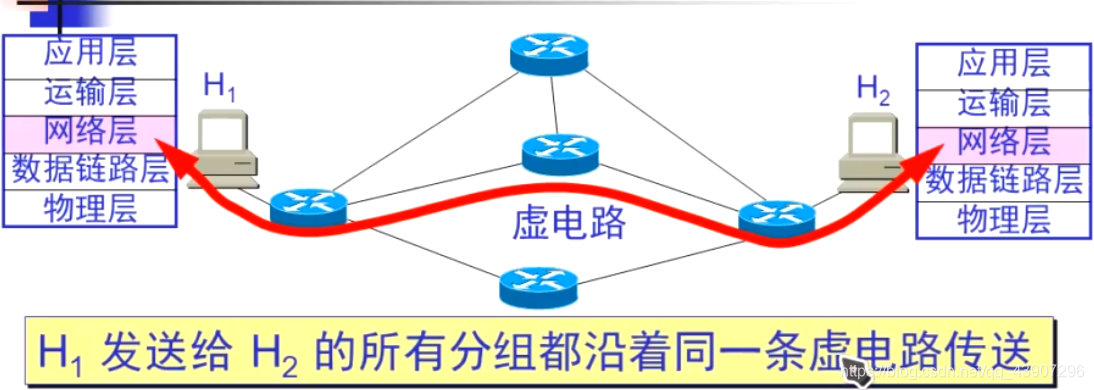
virtual circuit is justA piece of logic On the connection, whileNot really established a physical connection。
(2) Datagram service
The idea of the Internet:
only provide at the network layer upwardsSimple and flexible、Connectionless、Best effort deliveryofDatagram service。
no connection: When the network is sending packetsNo need to establish a connection first. EveryPackets (i.e. IP datagrams) are sent independently, Has nothing to do with the grouping before and after it (no numbering).
Best effort delivery: The network layer does not provide promises of service quality. That is, the transmitted packets may be wrong, lost, repeated, and out of sequence (reaching the end point out of order), and of course, the time limit for packet transmission is not guaranteed.Reliable transmissionbyThe transport layer in the host of the networkResponsible (including error handling, flow control, etc.)
4.2_Network Protocol
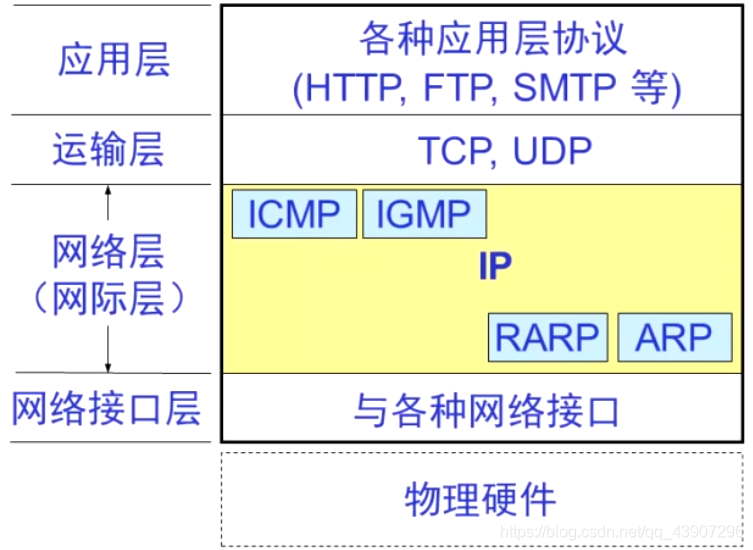
The Internet Protocol IP is one of the two most important protocols in the TCP/IP system. There are four other protocols used in conjunction with the IP protocol:
Address Resolution Protocol ARP (Address Resolution Protocol)
Reverse Address Resolution Protocol RARP (Reverse Address Resolution Protocol)
Internet Control Message Protocol ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol)
Internet Group Management Protocol IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol)
The IP protocol and supporting protocols of the Internet layer:
4.2.1_Virtual interconnection network
The meaning of virtual interconnection network: the
so-called virtual interconnection network isLogical interconnection network, It means that the heterogeneity of various interconnected physical networks originally exists objectively, but we useIP protocolYou can make theseDifferent performanceThe network looks from usersSeems to be a unified network,useIP protocol virtual interconnection networkcanReferred to as IP network. useBenefits of virtual interconnection networkYes: When the hosts on the Internet communicate, it is as if they are communicating on a network, and the heterogeneous details of the interconnected networks are invisible.
E.g:

4.2.2_ Classified IP address
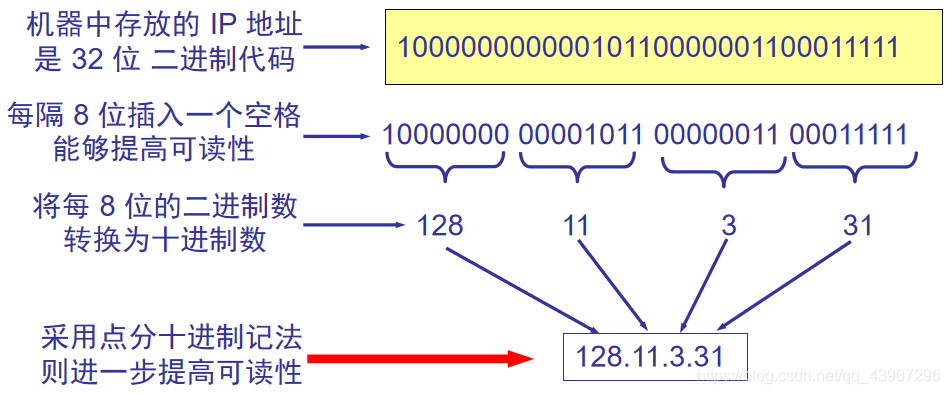
The IP address is for everyone connected to the InternetHost(orrouter) Assign one inThe world is uniqueof32nd placeThe identifier.
The development of IP address addressing method
Classified IP address: The most basic addressing method. The corresponding standard protocol was adopted in 1981.
Division of subnets: An improvement to classified IP addresses, the standard [RFC 950] was passed in 1985.
SupernetRelatively new unclassified addressing method. It was promoted and applied soon after it was proposed in 1993.
Dotted decimal notation:
(1) Classified IP address
Each type of address consists of two fixed-length fields, one of which is the network number. net-id, which identifies the network to which the host (or router) is connected, and the other field is the host number host-id, which identifies the host (or router).
IP address::= {<network number>, <host number>} The classification basis is How many digits does the network number and host number occupy
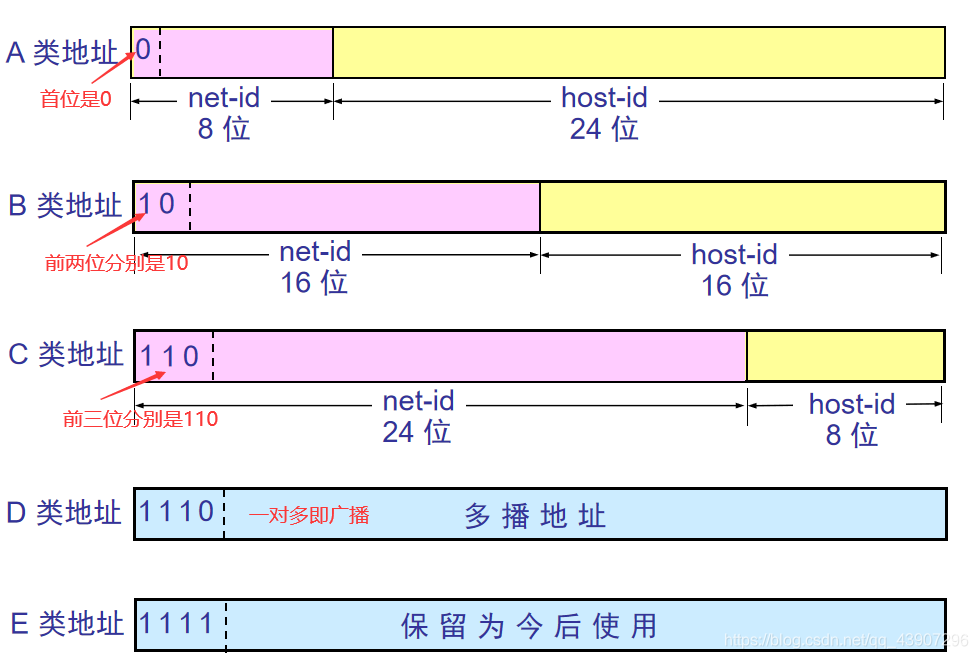
Three classification methods
①Class A
Network number
Assignable network number: 126=2 7 -2 (Because the first digit is fixed at 1, only 7 digits are available)
All zerosOn behalf of this network,127representativeLoopback test
Host number
Maximum number of hosts per network: 224-2
All zerosOn behalf of theThe network where the host is located,All 1Indicates that on this networkAll hosts.
Class A addresses account for 50% of the total IP space
②Class B
Network number
Assignable network number: 2 14 -1
Network address 128.0.0.0 cannot be assigned
Host number
The number of hosts contained in each class B network: 2 16 -2
All zeros and all 1s are unavailable.
Class B addresses account for 25% of the total IP space.
③Class C
Network number
Assignable network number: 2 21 -1
192.0.0.0 is not available
Host number
Each network contains at most hosts: 2 8 -2
Class C addresses account for 12.5% of the total IP space
Some important features of IP addresses
① IP address is a hierarchical address structure. The benefits of dividing into two levels are:
the first: The IP address management organization assigns network numbers when assigning IP addresses, and the remaining host numbers are assigned by the unit that gets the network number. This facilitates the management of IP addresses.
second: The router only forwards packets according to the network number connected to the destination host (regardless of the destination host number), so that the number of items in the routing table can be greatly reduced, thereby reducing the storage space occupied by the routing table.
② When a host is connected to two networks at the same time , the host must have two corresponding IP addresses at the same time, and its network number net-id must be different. This kind of host is calledMultihomed host.
Due to aThe router should be connected to at least two networks(So that it can forward IP datagrams from one network to another), soA router should have at least two different IP addresses.
③ Several LANs connected by repeaters or bridges are still a network , so these LANs all have the same network number net-id.
④All the networks assigned to the network number net-id, the local area network with a small area, or the wide area network that may cover a large geographic area, are equal.
4.2.3_IP address and hardware address
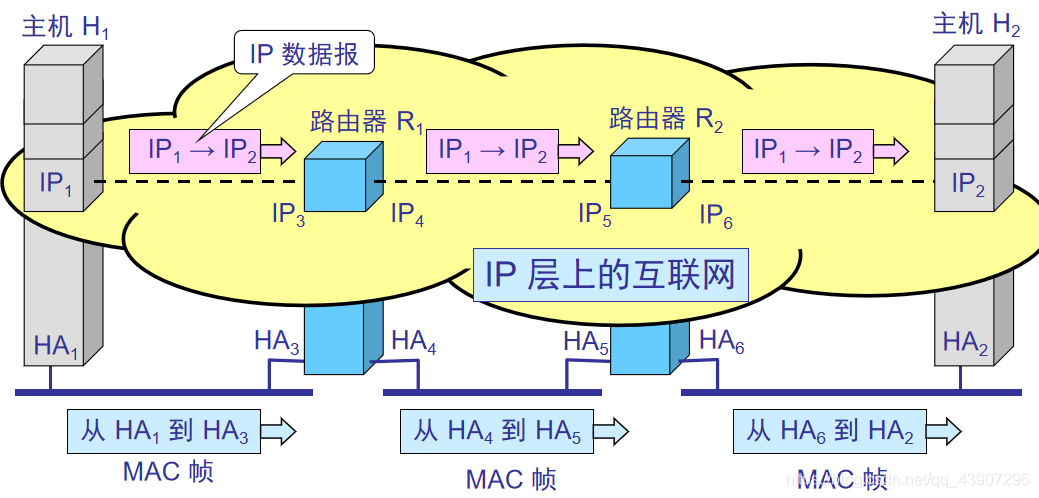
Look at the flow of data from the level of the protocol stack, look at the flow of IP datagrams from the virtual IP layer, and look at the flow of MAC frames on the link
On the Internet abstracted at the IP layerCan only see IP datagramsIP1→IP2 in the figure meansFrom source address IP1 to destination address IP2,IP addresses of the two routersandDoes not appear in IP datagramsIn the first part (and how to achieveTransfer of two adjacent pointsWhat? It is based on the source and destination addresses of the MAC frame on the data link layer)
4.2.4_Address Resolution Protocol ARP and Reverse Address Resolution Protocol RARP
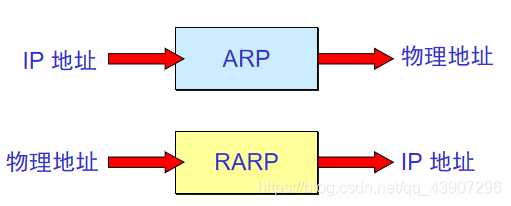
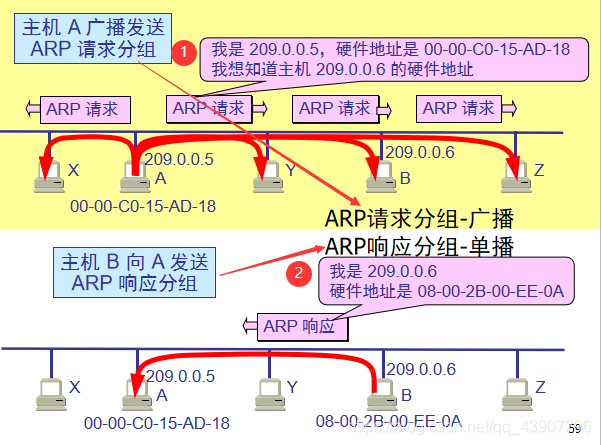
No matter what protocol is used at the network layer,Transmit data frames on the link of the actual networkTime,In the end, hardware addresses must be used.
Each host hasAn ARP cache(ARP cache), there areConnected to the local area networkofHosts and routersof IP address to hardware address mapping table.
whenHost A DesireLocal area networkOnHost B When sending an IP datagram,First in its ARP cacheCheck for the IP address of host B in.If any, You can find out its corresponding hardware address, write this hardware address into the MAC frame, and then send the MAC frame to this hardware address through the local area network.