A full set of operations research knowledge points
Chapter 3 Decision
1. Decision
Narrow sense: decision-making is to choose some alternative options.
Broad sense: including clarifying the purpose of the decision-making project, seeking feasible options, making decisions among the feasible options, and summarizing and evaluating the results of the selected options after implementation
Second, the classification of decisions
Classified according to different decision-making methods
(1) Routine decision-making : repetitive decision-making of routine decision-making examples. For example, a family or canteen intends to buy food; a car driver decides to overtake while driving.
(2) Special-type decision-making : Special-type decision-making is a decision on a new problem that is specific and has no precedent to follow. For example: a student who is about to graduate from high school needs to apply for a university major, and a factory plans to introduce a certain type of new equipment.
According to the plan and control relationship
(1) Planned decision-making : national or organizational policies and comparisons. Long-term plan
(2) Controlling decision : It is a decision that needs to be made in the process of implementing policies or implementing plans. Including the decision to implement the policy or implementation plan and the decision when the policy or plan is adjusted according to the actual situation.
Planned decisions are mostly special decisions, and control decisions are special and conventional

Answer: C
3. Decision-making procedures
- Determining the goal , determining the goal is the premise of decision
- Draw up multiple feasible solutions . Drawing up a feasible plan is the key to scientific decision-making
- Predict the natural state that may occur, calculate the income value (loss value) of different scenarios in different natural states , and compile a decision-making income table (loss table). The decision income table is also called the decision matrix.
- Based on the decision-making income table, different decision-making standards are used for decision-making analysis and the optimal plan is selected.
4. Decision-making in different environments
- Decision-making under certain conditions : There is only one natural state. The
so-called natural state refers to a future state that is beyond the control of the decision maker - Decision-making under uncertainty : There is more than one natural state, and the decision maker does not understand other states, or even fully understands how to assign probability to the natural state.
- Decision under risk conditions : There are more than one natural state, but the decision maker has the information to assign a probability value to each possible state.

Answer: D
Five, decision-making under uncertain conditions
It has the following characteristics:
(1) There is a clear decision-making goal
(2) Two or more feasible schemes can be drawn up for comparison and selection .
(3) There is more than one natural state
(4) It is possible to predict or estimate the profit loss value of different feasible schemes in different natural states.
Six, the largest and largest decision-making criteria
Also known as the optimist 's decision-making standard, when making decisions, only consider the best natural state that will occur in the future, that is, set the probability of the best natural state as 1, and the probability of other states as 0.
Its decision-making procedure is: first select a maximum return value from each scheme, and then select a scheme with the largest return value as an alternative from the different schemes represented by these maximum return values, also known as
Take big
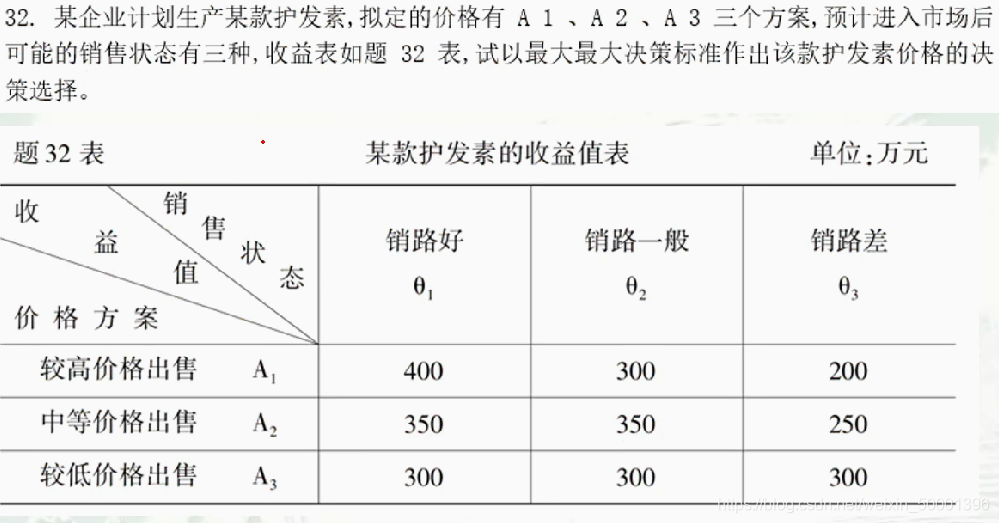

7. Maximum and Minimum Regret Decision-making Criteria
Also known as the decision-making standard of conservatives, when making decisions, only consider the best natural state that will occur in the future, that is, set the probability of the best natural state as 1, and position the probability of other states as 0.
Its decision-making procedure is: first select a minimum return value from each scheme, and then select a scheme with the largest return value as an alternative from the different schemes represented by these minimum return values, which is also called pessimistic Ideological decision criteria
Small, medium and large
8. The minimum and maximum regret value decision-making criteria
Regret value: In the decision-making process, when a certain natural state may appear, the decision-maker did not choose the best option due to a decision error, but chose other options, so he would feel regret. The difference between the two options is called Regret value
Its decision-making procedure is: first transform the income statement into a regret value table, based on regret index,
Big and small

9. Realistic decision-making standards
Also known as the eclectic decision-making standard , it sets the probability of the best state in the future as a, the probability of the worst state as 1-a, and the probability of other intermediate states as 0, that is, considering the two situations.
His decision-making procedure is: Calculate the compromise value of each plan, and choose the plan corresponding to the largest profit value after the compromise as the alternative plan.
The calculation formula is:

10. Decision-making under risk conditions
Decision analysis is generally called in the case of statistical decision making or random decision making , mainly based on a number of different takes natural state that can occur decisions rates. Therefore, in accordance with criteria are the expected value criterion
-
Features
(1) There is a clear decision goal
(2) There are multiple feasible solutions
(3) There are multiple natural states, and each natural state can estimate its probability value
(4) Different feasible solutions in different states The loss of revenue can be calculated quantitatively. The standard for decision-making in risky situations is mainly the expected value standard.

Answer B

Answer: B
Answer: D

Answer: A -
Maximum expected return standard Make
decisions under risky conditions. Generally, the most commonly used decision-making standard is the expected profit standard, also known as the Bayesian standard.
The expected profit standard is used to make decisions. The usual steps are as follows:
(1) Determine the probability value
(2) Calculation The conditional profit calculation formula is as follows:
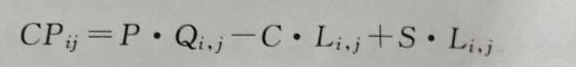
(3) Calculate the expected profit of each plan and select the optimal plan.
The expected profit of each program can be calculated as follows:
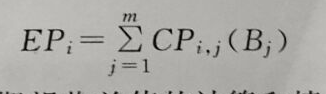
(4) The calculation of the maximum expected return value with accurate information and the calculation of the intelligence value. -
The minimum expected loss value standard
This is a standard corresponding to the maximum expected return value standard. It is the optimal solution to choose the solution with the smallest expected loss value.
The simulation calculation is as follows:



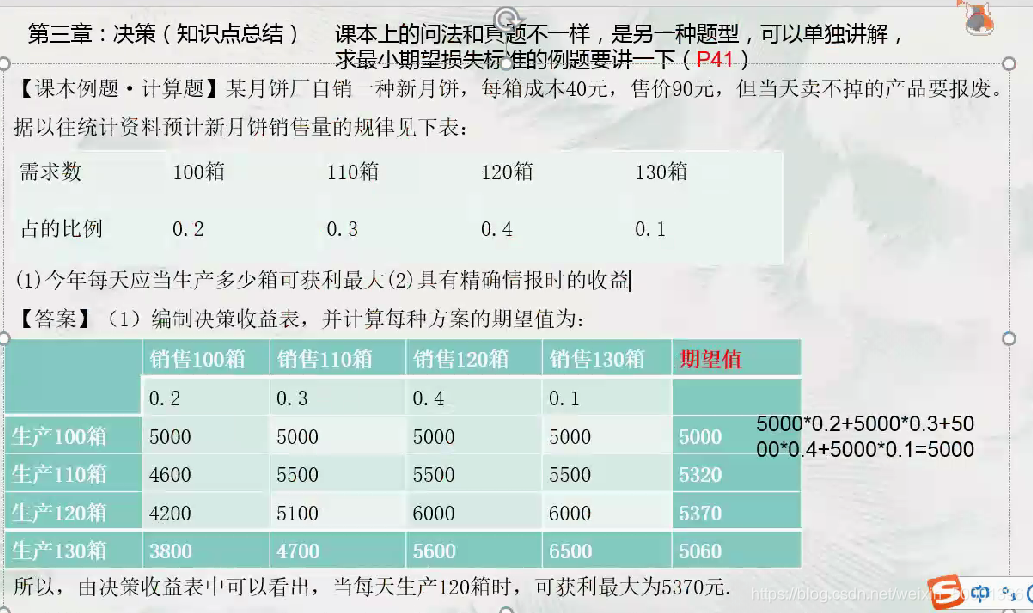
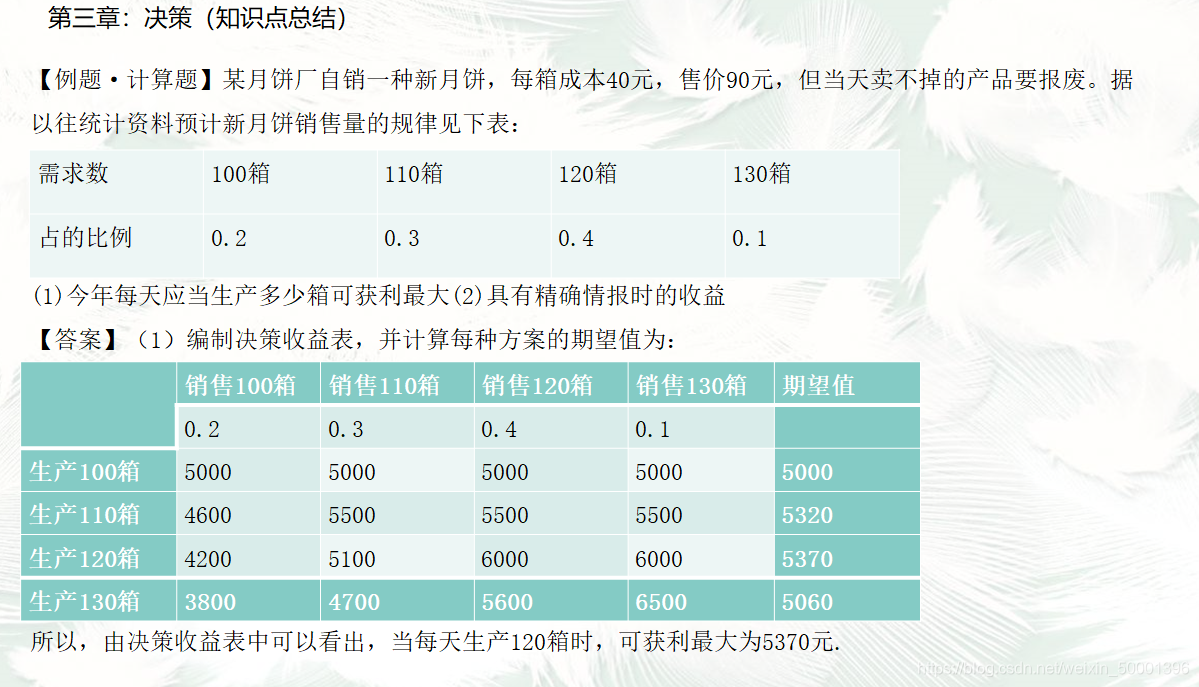
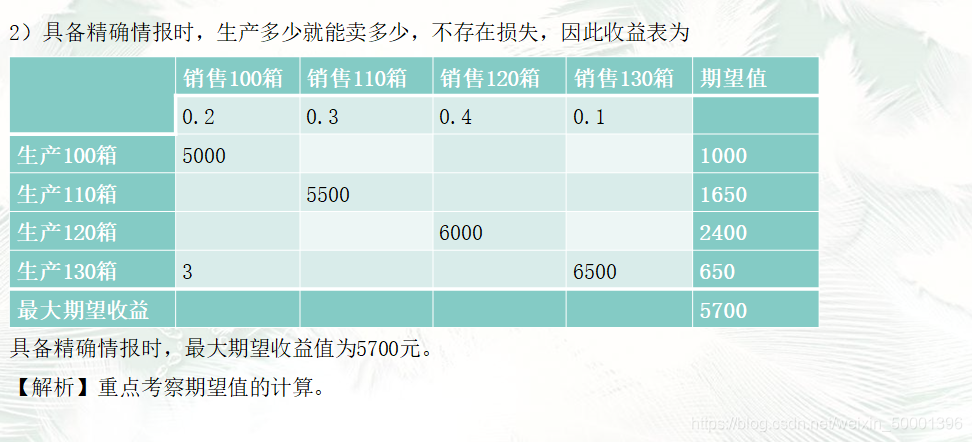
11. Decision tree
Decision income table is an important tool for single-stage decision-making in expected income decision-making standards. In addition, decision trees can not only solve single-stage decision-making problems, but also solve multi-stage sequential decision problems that are difficult to express in income tables.
The square node is the decision node, and the branch that it leads out is called the plan branch. The
circle node is the state node, and the branch that leads out is called the state branch.
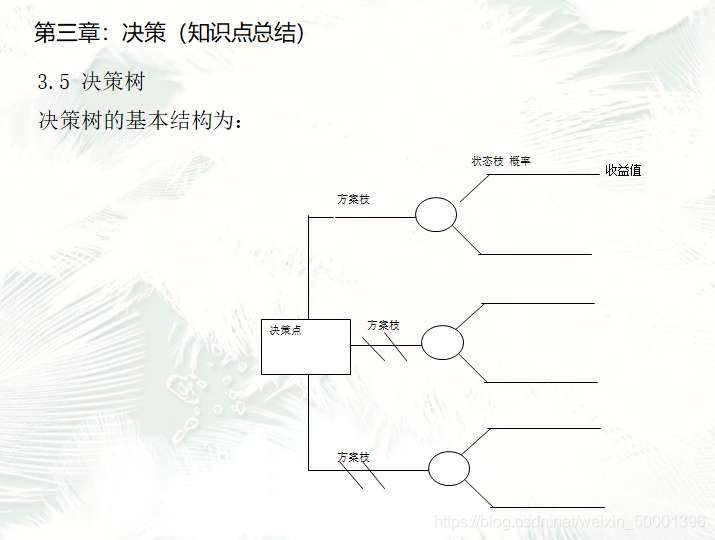
Twelve, the advantages of decision trees
- It constitutes the decision-making process, enabling decision-makers to approach decision-making in a sequential and methodical manner.
- It requires decision makers to test all possible outcomes, and to test the unifying and undesirable meanings.
- It conveys the decision-making process to others in a very concise way, explaining every hypothesis about the future.
- By focusing on each fiscal figure, probability, and prioritized assumptions-one at a time, in order to discuss various options in groups.
- It can be used with a computer to simulate a variety of different combinations of assumptions.