One-way circular linked list
Changing the pointer end of the interrupt node in the singly-linked list with a null pointer to point to the head node will make the entire singly-linked list form a loop. This kind of singly-linked list with detailed head and tail is called a single-loop linked list, or circular linked list for short;
Schematic diagram:
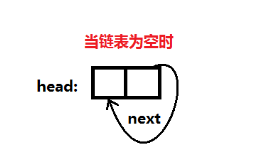
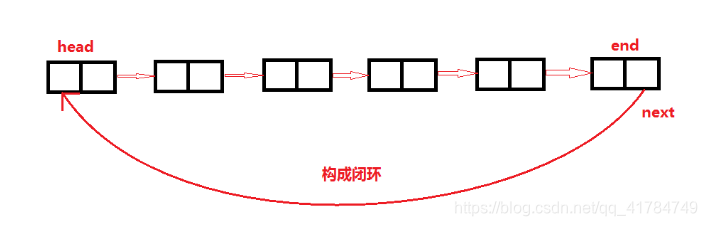
Note:
①There is no NULL pointer in the circular linked list. When it comes to traversal operations, its termination condition is no longer to judge whether p or p->next is empty like a non-cyclic linked list, but to judge whether they are equal to a specified pointer, such as a head pointer or a tail pointer.
②In a singly linked list, starting from a known node, only that node and its subsequent nodes can be visited, and other nodes before the node cannot be found. In a single-cycle linked list, all nodes in the list can be accessed from any node. This advantage makes certain operations easy to implement on a single-cycle linked list.
Josephu question
Josephu’s question is: suppose n people with numbers 1, 2, ... n sit in a circle, and the person with number k (1<=k<=n) is agreed to start counting from 1, and the person who counts to m goes out. , Its next digit starts counting from 1, and the person who counts to m goes out again, and so on, until everyone goes out, thus generating a sequence of dequeue numbers.
Tip:
Use a circular linked list without a leading node to deal with Josephu's problem : first form a single circular linked list with n nodes, and then count from 1 from the k node, and when it reaches m, the corresponding node is from the linked list Delete from the list, and then count from 1 again from the next node of the deleted node, until the last node is deleted from the linked list and the algorithm ends.
Code:
Define the structure of the linked list node as follows:
// 创建一个Boy类,表示一个节点
class Boy {
private int no;// 编号
private Boy next; // 指向下一个节点,默认null
public Boy(int no) {
this.no = no; }
public int getNo() {
return no; }
public void setNo(int no) {
this.no = no; }
public Boy getNext() {
return next; }
public void setNext(Boy next) {
this.next = next; }
}
Construct a circular linked list
Enter nums to form a circular linked list of nums nodes
// 添加小孩节点,构建成一个环形的链表
public void addBoy(int nums) {
// nums 做一个数据校验
if (nums < 1) {
System.out.println("nums的值不正确");
return;
}
Boy curBoy = null; // 辅助指针,帮助构建环形链表
// 使用for来创建我们的环形链表
for (int i = 1; i <= nums; i++) {
// 根据编号,创建小孩节点
Boy boy = new Boy(i);
// 如果是第一个小孩
if (i == 1) {
first = boy;
first.setNext(first); // 构成环
curBoy = first; // 让curBoy指向第一个小孩
} else {
curBoy.setNext(boy);//
boy.setNext(first);//
curBoy = boy;
}
}
}
According to the user's input, calculate the order in which the child goes out of the circle
/**
*
* @param startNo
* 表示从第几个小孩开始数数
* @param countNum
* 表示数几下
* @param nums
* 表示最初有多少小孩在圈中
*/
public void countBoy(int startNo, int countNum, int nums) {
// 先对数据进行校验
if (first == null || startNo < 1 || startNo > nums) {
System.out.println("参数输入有误, 请重新输入");
return;
}
// 创建要给辅助指针,帮助完成小孩出圈
Boy helper = first;
// 需求创建一个辅助指针(变量) helper , 事先应该指向环形链表的最后这个节点
while (true) {
if (helper.getNext() == first) {
// 说明helper指向最后小孩节点
break;
}
helper = helper.getNext();
}
//小孩报数前,先让 first 和 helper 移动 k - 1次
for(int j = 0; j < startNo - 1; j++) {
first = first.getNext();
helper = helper.getNext();
}
//当小孩报数时,让first 和 helper 指针同时 的移动 m - 1 次, 然后出圈
//这里是一个循环操作,知道圈中只有一个节点
while(true) {
if(helper == first) {
//说明圈中只有一个节点
break;
}
//让 first 和 helper 指针同时 的移动 countNum - 1
for(int j = 0; j < countNum - 1; j++) {
first = first.getNext();
helper = helper.getNext();
}
//这时first指向的节点,就是要出圈的小孩节点
System.out.printf("小孩%d出圈\n", first.getNo());
//这时将first指向的小孩节点出圈
first = first.getNext();
helper.setNext(first); //
}
System.out.printf("最后留在圈中的小孩编号%d \n", first.getNo());
}
Complete code
public class Josephu {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 测试一把看看构建环形链表,和遍历是否ok
CircleSingleLinkedList circleSingleLinkedList = new CircleSingleLinkedList();
//circleSingleLinkedList.addBoys(5);// 加入5个小孩节点
Boy b1 = new Boy(1);
Boy b2 = new Boy(2);
Boy b3 = new Boy(3);
Boy b4 = new Boy(4);
Boy b5 = new Boy(5);
circleSingleLinkedList.addBoy(b2);
circleSingleLinkedList.addBoy(b1);
circleSingleLinkedList.addBoy(b5);
circleSingleLinkedList.addBoy(b4);
circleSingleLinkedList.addBoy(b3);
circleSingleLinkedList.showBoy();
circleSingleLinkedList.delete(1);
System.out.println("删除节点1");
circleSingleLinkedList.showBoy();
circleSingleLinkedList.delete(3);
System.out.println("删除节点3");
circleSingleLinkedList.showBoy();
circleSingleLinkedList.delete(5);
System.out.println("删除节点5");
circleSingleLinkedList.showBoy();
//测试一把小孩出圈是否正确
// circleSingleLinkedList.countBoy(1, 2, 5); // 2->4->1->5->3
//String str = "7*2*2-5+1-5+3-3";
}
}
// 创建一个环形的单向链表
class CircleSingleLinkedList {
// 创建一个first节点,当前没有编号
private Boy first = null;
// 添加小孩节点,构建成一个环形的链表
public void addBoys(int nums) {
// nums 做一个数据校验
if (nums < 1) {
System.out.println("nums的值不正确");
return;
}
Boy curBoy = null; // 辅助指针,帮助构建环形链表
// 使用for来创建我们的环形链表
for (int i = 1; i <= nums; i++) {
// 根据编号,创建小孩节点
Boy boy = new Boy(i);
// 如果是第一个小孩
if (i == 1) {
first = boy;
first.setNext(first); // 构成环
curBoy = first; // 让curBoy指向第一个小孩
} else {
curBoy.setNext(boy);//
boy.setNext(first);//
curBoy = boy;
}
}
}
//添加单个节点 按递增序插入
public void addBoy( Boy boy){
if(first ==null){
//如果第一个节点为空,即链表为空
first = boy;
first.setNext(first);
return;
}
else{
boolean flag = false; // flag标志添加的编号是否存在,默认为false
Boy curBoy = first; // 辅助指针,
while (true){
if (first.getNo() > boy.getNo()){
//插入到左端,即插入到first的前面
boy.setNext(curBoy);
curBoy.setNext(boy);
first = boy;
break;//插入完成直接返回
}
if (curBoy !=first && curBoy.getNext() == first){
//说明链表已经遍历完,则新节点插入到原理链表的最后
curBoy.setNext(boy);
boy.setNext(first);
break;
}
if(curBoy.getNext().getNo() > boy.getNo()){
//找到待插入的位置
boy.setNext(curBoy.getNext());//插入方式与普通单链表的方式相同
curBoy.setNext(boy);
break;
}
if (curBoy.getNext().getNo() == boy.getNo()){
System.out.println("待插入结点已经存在,不能重复插入");
break;
}
curBoy = curBoy.getNext();//后移
}
}
}
//移除环形链表中的某个节点
public void delete(int no){
Boy curBoy = first;
if (first.getNo() == no){
//删除的是第一个节点
//如果链表中只有一个节点
if(first.getNext() ==first){
first =null;//将first置为空即可
}
else {
//找到链表的最后一个节点
curBoy = curBoy.getNext();
while (curBoy.getNext() != first){
curBoy = curBoy.getNext();
}
curBoy.setNext(first.getNext());//将最后一个节点指向first的下一个节点
first = first.getNext();//将first后移一位
}
return;
}
//遍历链表,找到待删除的点
boolean flag = false;//判断是否找到了待删除节点
while (true){
if (curBoy.getNext().getNo() == no){
//找到
//判断待删除节点是不是链表的最后一个节点
if (curBoy.getNext().getNext() ==first){
//是
curBoy.setNext(first);
}else {
//否
curBoy.setNext(curBoy.getNext().getNext());
}
flag=true;
break;
}
if (curBoy.getNext()==first){
//遍历完
break;
}
curBoy = curBoy.getNext();
}
if (flag ==false){
System.out.printf("未找到待删除节点 %d",no);
}
}
// 遍历当前的环形链表
public void showBoy() {
// 判断链表是否为空
if (first == null) {
System.out.println("没有任何小孩~~");
return;
}
// 因为first不能动,因此我们仍然使用一个辅助指针完成遍历
Boy curBoy = first;
while (true) {
System.out.printf("小孩的编号 %d \n", curBoy.getNo());
if (curBoy.getNext() == first) {
// 说明已经遍历完毕
break;
}
curBoy = curBoy.getNext(); // curBoy后移
}
}
// 根据用户的输入,计算出小孩出圈的顺序
/**
*
* @param startNo
* 表示从第几个小孩开始数数
* @param countNum
* 表示数几下
* @param nums
* 表示最初有多少小孩在圈中
*/
public void countBoy(int startNo, int countNum, int nums) {
// 先对数据进行校验
if (first == null || startNo < 1 || startNo > nums) {
System.out.println("参数输入有误, 请重新输入");
return;
}
// 创建要给辅助指针,帮助完成小孩出圈
Boy helper = first;
// 需求创建一个辅助指针(变量) helper , 事先应该指向环形链表的最后这个节点
while (true) {
if (helper.getNext() == first) {
// 说明helper指向最后小孩节点
break;
}
helper = helper.getNext();
}
//小孩报数前,先让 first 和 helper 移动 k - 1次
for(int j = 0; j < startNo - 1; j++) {
first = first.getNext();
helper = helper.getNext();
}
//当小孩报数时,让first 和 helper 指针同时 的移动 m - 1 次, 然后出圈
//这里是一个循环操作,知道圈中只有一个节点
while(true) {
if(helper == first) {
//说明圈中只有一个节点
break;
}
//让 first 和 helper 指针同时 的移动 countNum - 1
for(int j = 0; j < countNum - 1; j++) {
first = first.getNext();
helper = helper.getNext();
}
//这时first指向的节点,就是要出圈的小孩节点
System.out.printf("小孩%d出圈\n", first.getNo());
//这时将first指向的小孩节点出圈
first = first.getNext();
helper.setNext(first); //
}
System.out.printf("最后留在圈中的小孩编号%d \n", first.getNo());
}
}
// 创建一个Boy类,表示一个节点
class Boy {
private int no;// 编号
private Boy next; // 指向下一个节点,默认null
public Boy(int no) {
this.no = no; }
public int getNo() {
return no; }
public void setNo(int no) {
this.no = no; }
public Boy getNext() {
return next; }
public void setNext(Boy next) {
this.next = next; }
}