PIM (Protocol Independent Multicast)
Introduction
- The multicast routing protocol runs between the multicast routers. The multicast routing protocol is used to establish and maintain multicast routes and establish a loop-free data transmission path from the multicast source to multiple receivers, that is, to construct the multicast distribution tree and correct 3. Forwarding multicast data packets in colleges and universities.
PIM (protocol Independent Multicast) is a typical intra-domain multicast routing protocol. It is divided into DM (Dense Mode) and SM (sparse Mode) models. - Mechanism to prevent loops: RPF (reverse path forwarding) Reverse path forwarding: mainly used in multicast environments for routing inspection of all data of multicast group addresses for multicast sources. First, the multicast routing protocol is based on the unicast routing protocol, that is, the unicast routing protocol is the bottom layer of the multicast routing protocol, and when the multicast routing table is formed, its destination address is a multicast address and the source address is a single For the multicast address, in order to ensure that the source-to-destination multicast data transmission path is reachable and smooth, the multicast router will enable the RPF function by default to check the next hop based on the unicast routing protocol to check whether the upstream interface is reachable and the most The optimal path is directly sent if it is reachable and optimal; if the RPF check fails, it is directly discarded.
- The full name of PIM is protocol independent multicast, and the Chinese name is protocol independent multicast. PIM is a typical intra-domain multicast routing protocol. In fact, there are inter-domain multicast routing protocols.
- PIM-DM is called PIM Dense Mode ((Dense Mode))
- PIM-SM is called PIM's sparse mode ((sparse Mode))
How does the router forward multicast packets

-
In the multicast routing protocol, there are several roles to understand
①Source: represents the multicast source, generally a server, such as a video-on-demand server
②Client: represents the receiver
③connects to the Source router, represents the first hop router ④connects
to the Client (receive Router), which represents the last-hop router. The router
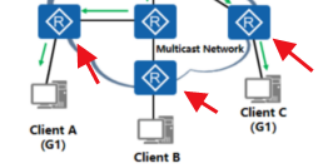
between the first-hop and last-hop routers is called the intermediate router. -
We have finished the agreement between the last-hop router and the receiver. The content is IGMP. For the receiver, it is reported to the multicast router and the receiver will join the group; for the router, it is IGMP to maintain the following group membership. However, it should be noted that IGMP is the maintenance of the relationship between the multicast router and the receiver in IPv4. It is called MLD in IPv6 (the principle and function are the same as IGMP)
-
It should be noted that on the link connecting the Source and the first-hop router, the interface of the first-hop router needs to be configured with the multicast routing protocol. If it is not configured, the router has no right to handle it, and it will not be processed or viewed. But if the interface uses the multicast routing protocol, all multicast data needs to be processed, even if I have not joined this group. But the last-hop router does not need to use PIM, IGMP / mld is enough, but for the first-hop router, there is no need to use IGMP or MID, it is enough to use the routing protocol PIM.
-
For the multicast routers between the first-hop and last-hop routers, intra-domain and inter-domain multicast routing protocols are used.
The domains include DVMRP, PIM, MOSPF, and CBT. The Mbone mentioned earlier uses the very old multicast routing protocol (DVMRP). MOSPF and CBT are not much use now. The most popular one is PIM; the
inter-domain multicast routing protocol is MBGP / MSDP (Multicast Source Discovery Protocol) [these two protocols are actually not multicast router protocols, but Use these two protocols to achieve inter-domain multicast] -
The role of intra-domain multicast routing protocol: By discovering the multicast source and constructing a multicast distribution tree, the information is delivered to the receiver. In the HCIP stage, you only need to know about PIM-DM and PIM-SM in the multicast channel protocol in the domain.

Introduction to basic concepts -
PIM routing entries are multicast routing entries established through the PIM protocol. There are two routing table entries in the PIM network: (S, G) routing table entries or (*, G) routing table entries. S indicates a multicast source, G indicates a multicast group, and * indicates any.
-
SPT (shortest path tree)
-
RPT: The multicast distribution tree with RP (Rendezvous Point) as the root and the multicast group members as leaves is called RPT (RP Tree)
-
The (S, G) routing table entry is mainly used to establish SPT in the PIM network. Applicable to PIM-DM network and PIM-SM network.
-
(*, G) The routing table entry is mainly used to establish RPT in the PIM network. Applicable to PIM-SM network.
There may be two routing entries on the PIM router. When a multicast packet with a source address of S and a group address of G is received and the RPF check is passed, it is forwarded according to the following rules: -
If there are (S, G) routing entries, the (S, G) routing entries will guide packet forwarding.
-
If there is no (S, G) routing table entry and only (*, G) routing table entry exists, then the (S, G) routing table entry is created according to the (*, G) routing table entry, and then (S, G) ) Routing table entries guide packet forwarding.
:( summary , G) represents a group knows only entries do not know the source, (S, G) represents a group that is also active entries from the client device receives a request packet when the multicast group will be formed ( , G) Entry, when receiving the source message, it will form (S, G) entry, the specific formation process of each multicast protocol has certain differences
PIM routing table entries are mainly used to guide forwarding information as follows:
multicast source address
multicast group address
upstream interface: the interface on the local router that receives multicast data.
Downstream interface: An interface that forwards multicast data.
Basic overview of PIM-DM:
[Revisit the concept of PIM first]

· Although PIM is called protocol-independent multicast, it is actually related to IGP because we will use SPT, the shortest path tree. Its irrelevance means that the basis for PIM to complete the RPF check is irrelevant to IGP.
[PIM-DM concept]
- Design Idea of PIM-DM (Dense Mode)

- First of all, we have to push to copy and send our data, but in copying and sending, we will find that there are no receivers in some branches, so we will pruning, but if there is a reception in this cut branch later In this case, you need to use a 3-minute cycle to recover the receiver in the cut branch, but because the 3-minute cycle is too long, we will use graft grafting to directly connect the branches without Waited for 3 minutes.


PIM-DM neighbor discovery

-
The Hello packet has two functions:
① Discover neighbors using the hello mechanism.
First, if we enable PIM on the RTA and RTB interfaces, the function is actually similar to OSPF. They will send PIM hello packets to each other. This hello packet is used to discover To establish and maintain the PIM neighbor relationship, the interval for sending hello packets is 30S, and the default timeout is 105 seconds.

②Use the hello packet to elect DR
. In the MA network, we need to select a DR as an IGMPv1 querier in PIM-DM, (selected in the MA network, but DR is not required in PPP or HDLC) . It must be noted here that the IGMPv1 version of the querier is elected, not v2
· RTC and RTD to elect DR, which is queried by priority. The priority here (referring to the priority carried by the hello message) defaults to 1. If the priority is consistent, the election will be conducted by IP address. The larger the priority value and the IP address, the higher the priority.
In the MA network, after PIM elects DR, there is no BDR. Therefore, the DR will be re-elected after the DR fails. -
HELLO message type:

· The time for sending hello is 30s by default, and the holdtime time is that we want to monitor whether the neighbor is normal. But some materials write 90s in the holdtime, because it is obtained for 3 * 30s, but the holdtime in Huawei equipment is 105s, 90s and 105s are actually not much different.
· By comparing the priority and IP address carried in the Hello message, the larger the better, each router elects the designated router DR for the multi-router network segment
PIM-DM builds SPT
-
Early construction of SPT

① The specific process of diffusion is as follows:
· The router will perform RPF check when receiving the multicast message.
· If the RPF check passes, create (S, G) entries and then forward the data to all downstream PIM-DM nodes. This process is called flooding. If the RPF check fails, the packet is discarded.
RPF (Reverse Path Forwarding) Purpose: To prevent duplicate packets and loops in the forwarding process of multicast packets, the router must perform RPF check. (RPF check is to prevent loops)
RPF check details:
The so-called RPF check means that the router looks for the route to the multicast source to determine whether the received multicast packet comes from the "correct" upstream interface. The outgoing interface corresponding to the route from a router to a multicast source is called the RPF interface on the router about the multicast source. After a router receives a multicast message from an interface, if it is found that the interface is not the RPF interface (upstream interface) of the corresponding multicast source, it means that the RPF check failed and the received multicast message will be throw away.

-
When flooding, the state of each interface is forward (forwarding state)
②Pruning:
-
In this picture, we know that there is no receiver in the middle RTE link, so actually sending multicast data will waste our bandwidth and resources, so we are thinking about whether there is any way to solve this problem, then this solves the problem The way is pruning
-
If the downstream node has no multicast members, it sends Prune pruning information (224.0.0.13) to the upstream node, informing the upstream node that it no longer needs to forward data to the branch. After receiving the Prune pruning message, the upstream node puts the output interface list corresponding to S and G of the corresponding interface into the Prune state. The pruning process continues until only the necessary branches are left in PIM-DM, and a Multicast source S is the root SPT.
-
Taking RTC as an example, the three ports take a number.
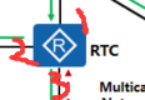
As we are in the process of flooding, the router will actually generate (S, G) entries, the inbound direction is 1 port, the outbound direction is 2 and 3 ports, the state of the outbound interface must be forward at the beginning, that is forward State, in terms of RTB and RTE, the interface at the incoming interface is actually in the forward state. But now in the case of pruning, a new state will appear, called Prune.
Question: Under what circumstances will the prune status appear?
Answer: During the pruning process, if the upstream device is not required to send multicast packets, we will change the state of the port from forward to prune. In our picture, when RTE finds that its downstream node has no receiver, it will change its port to prune state. In this case, it will prune the branch. For RTE, it will trim upstream. , Then the link between RTE and RTC will be pruned, so no multicast packets will be sent on this link. In this picture, the source tree of SPT (active tree) is formed -
But will RTC continue to prun up? In fact, it will not, because there is a receiver in the RTB downstream of the RTC. In this case, we cannot trim it.
-
After the pruning is complete, only the branches with the receiver are left. However, the pruned routers have not cleared their (S, G) entries.
The necessity of (S, G) entry: Taking RTC as an example, the (S, G) entry interface entry is prune, so we will not transmit multicast data to this interface, if not, It will cause it to spread again. -
But after being pruned, will there be new recipients in the pruned branches, then in the original way will we cause our traffic to go down? The answer is yes. If there is a receiver after the pruning and the pruned branches, how does it receive multicast information? Then in the early treatment
answer: To solve this problem, by default, the PIM-DM diffusion-prune mechanism is performed periodically, repeating every 3 minutes, that is, after the RTE inbound interface becomes prune, a timer is generated for 180s The time is counted down, and when the time is up, it will change from the prune state to the forward state, so that the multicast message transmitted by RTC can be received. If there is a receiver, it will not be pruned; if there is no receiver , The same steps as before.
Question 2: If the receiver never appears in the RTE, periodic diffusion and pruning every time is actually a waste of bandwidth and resources, so can we find a way to solve the waste of our periodic changes?
------------------------------- Status Update ----------------- -----------
Answer: Therefore, Huawei used an optimization in the later SPT establishment process, that is, although the interface became the prune state, and there is a 3-minute timer. However, when the multicast source sends multicast data to RTA, the first hop router (RTA) will periodically send to the pruned branchesStatus update information(State Refresh) In this state, the interface of prune is a 3 minute countdown, then every time state refresh is sent, prune will never time out. This period of sending status update information is actually 1 minute.
·The status update information is enabled by default on Huawei devices, but some Cisco devices actually disable the status update information. After configuring dm on Cisco, it will appear once every 3 minutes.
But what if a new recipient arrives? Then the solution is to graft, see the next blog, PIM (below)
