@SpringBootApplication contains annotations
@Target (ElementType.TYPE) // specify the legal position written comments where @Retention (RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) // RetentionPolicy This enumeration constants describing retention strategies annotated them with the meta-annotation (@Retention ) to specify how long you want to keep together the comment @Documented // indicate this by a comment javadoc recorded by default has a similar record tool. If a type declaration is annotated documented, it notes become part of the public API. It indicates @Inherited // annotated classes inherit automatically @SpringBootConfiguration @EnableAutoConfiguration @ComponentScan (excludeFilters = {@Filter (type = FilterType.CUSTOM, = TypeExcludeFilter classes. Class ), the scanner // @Filter (type = the FilterType. the CUSTOM, = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter classes. class )}) // filter scanner
A, @ SpringBootConfiguration contains notes
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Configuration
@Configuration. 1, indicating that the annotation is a configuration class, can be used to replace the previous annotation @Configuration conventional spring.xml profile;
2, @ Configuration annotation class is automatically added to the spring container.
Two, @ EnableAutoConfiguration: the spring boot automatic configuration. (Convention over configuration)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited @AutoConfigurationPackage @Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
@AutoConfigurationPackage: The packet is put into the automatic scanning, which has an annotation
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class)
The method of its implementation:
static class Registrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, DeterminableImports { @Override public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { register(registry, new PackageImport(metadata).getPackageName()); } @Override public Set<Object> determineImports(AnnotationMetadata metadata) { return Collections.singleton(new PackageImport(metadata)); } }
metadata can acquire @SpringBootApplication annotated classes, and then get through the class package name. By this method all of the class into the package and its sub-packets contained in the container into the spring, which is why spring Boot code should be placed @SpringBootApplication annotated classes or sub-packet of the packet, in order to be spring containers the reason identified.
Wherein @EnableAutoConfiguration itself has a @Import (AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class), a method wherein:
@Override public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) { if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) { return NO_IMPORTS; } AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata = AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader .loadMetadata(this.beanClassLoader); AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = getAutoConfigurationEntry(autoConfigurationMetadata, annotationMetadata); return StringUtils.toStringArray(autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations()); }
protected AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry(AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata, AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) { if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) { return EMPTY_ENTRY; } AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata); List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes); configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations); Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes); checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions); configurations.removeAll(exclusions); configurations = filter(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata); fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions); return new AutoConfigurationEntry(configurations, exclusions); }
DEBUG can be found by LinkedList linked list data structure configurations by, third parties is dependent jar into packages, this structure allows chain deletions dependent jar package fast.
List <String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations (annotationMetadata, attributes) is how to introduce jar package it?
Enter getCandidateConfigurations:
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) { List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), getBeanClassLoader()); Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you " + "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct."); return configurations; }
Proceed to SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames:
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName(); return loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryClassName, Collections.emptyList()); }
Proceed to loadSpringFactories:
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { MultiValueMap<String, String> result = cache.get(classLoader); if (result != null) { return result; } try { Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) : ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION)); result = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>(); while (urls.hasMoreElements()) { URL url = urls.nextElement(); UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url); Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource); for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) { String factoryClassName = ((String) entry.getKey()).trim(); for (String factoryName : StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue())) { result.add(factoryClassName, factoryName.trim()); } } } cache.put(classLoader, result); return result; } catch (IOException ex) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" + FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex); } }
We can clearly see the key FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION This enumeration is to introduce jar package, continue to enter:
public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories";
Jar package eventually found by the configuration file: spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.1.13.RELEASE.jar in the META-INF / spring.factories, to declare, then use to open by @EnableAutoConfiguration.
Third, look at the specific principle of automatic assembly
In spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.1.13.RELEASE.jar in the META-INF / spring.factories in org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration example, annotation information into the class to see which:
@Configuration // configuration identified as a class, to incorporate spring containers @EnableConfigurationProperties (HttpProperties. Class ) // enter the annotation, to find the default encoding UTF_8 @ConditionalOnWebApplication (type = ConditionalOnWebApplication.Type.SERVLET) // If a servlet such type of the commencement @ConditionalOnClass (CharacterEncodingFilter. class ) // filter exists bytecode programs is established @ConditionalOnProperty (prefix = "spring.http.encoding", value = "Enabled", = matchIfMissing to true ) // when when the properties to meet the requirements, the condition is satisfied public class HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration {... }
3.1、进入@EnableConfigurationProperties(HttpProperties.class):
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.http")
/**
* Configuration properties for http encoding.
*/
Discovery provided "" spring.http "" prefix, comments, information encoding, plus Charset attribute information written to a application.properties in:
spring.http.encoding.charset=US_ASCII
It found that the agreement can be changed by this prefix.
3.2、解读@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.http.encoding", value = "enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
prefix = "spring.http.encoding", value = "enabled":前缀为spring.http.encoding,名为enabled;
matchIfMissing: said attributes is established when there is no current.
That is not configured spring.http.encoding.enabled this property in application.properties, the class effect.
Summary: i.e. when the automatic configuration class @ConditionalOnXXXX annotation conditions are met, i.e., automatic assembly effect. That may change the global automatic assembly profile @ConditionalOnProperty key from the prefix + value.
Attachment:
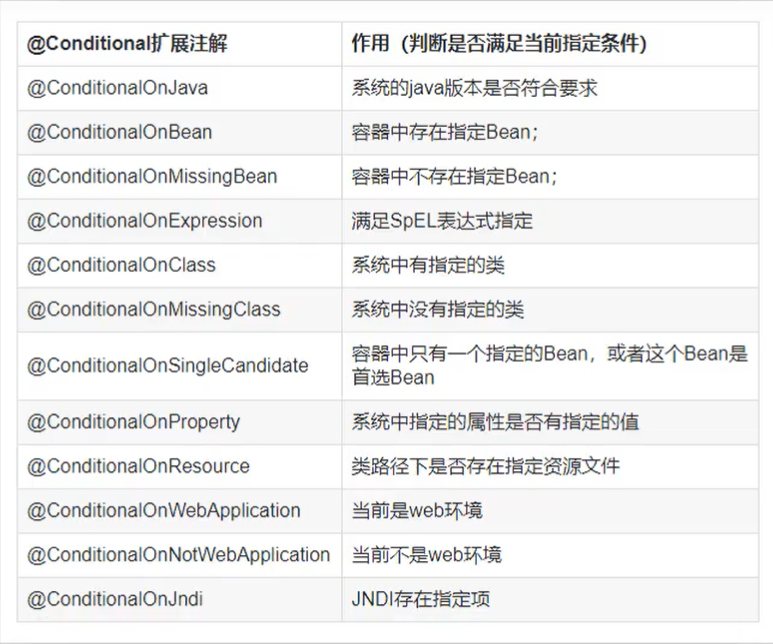
tip: Set debug = true in the global configuration file, quick access to information can be automatically fitted in the console.
Positive matches a listing showing the automatic open spring boot assembly;
Negative matches list indicates automatic assembly spring boot is not open.