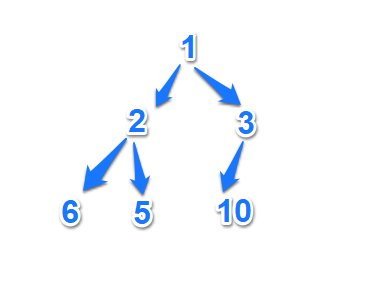
堆有大根堆和小根堆之分,这里主要实现大根堆,首先利用一个数组建立一个抽象的完全二叉树,例如
arr[]={ 1,2,3,6,5,10};
首先初始化建立一个二叉树,接着给二叉树排序成大根堆
Heap.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<windows.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int HeapDataType;
typedef struct heap
{
HeapDataType *a;
size_t size;
size_t capacity;
}heap;
void HeapInit(heap *hp, HeapDataType *_arr, size_t size)
{
assert(_arr&&size>0);
hp->a = (HeapDataType*)malloc(sizeof(HeapDataType)*size);
assert(hp->a);
hp->size = size;
hp->capacity = hp->size;
for (size_t i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
hp->a[i] = _arr[i];
}
}
void swap(HeapDataType* x, HeapDataType* y)
{
HeapDataType tmp = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = tmp;
}
//从下往上调整 插入需要
void HeapAdjustUp(heap *hp, int child)
{
assert(hp);
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child>0)
{
if (hp->a[parent] <hp->a[child])
{
HeapDataType tmp = hp->a[parent];
hp->a[parent] = hp->a[child];
hp->a[child] = tmp;
}
else
{
break;
}
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
}
//从上往下调整 在父亲节点的两子树中找到最大节点和其交换
void HeapAdjustDown(heap *hp, int root)
{
assert(hp);
size_t parent = root;
size_t child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < hp->size)
{
if ((child + 1)<hp->size && hp->a[child] < hp->a[child + 1])
{
child++;
}
if (hp->a[parent] < hp->a[child])
{
swap(&hp->a[parent], &hp->a[child]);
}
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
}
//插入元素
void HeapPush(heap *hp, HeapDataType x)
{
assert(hp);
if (hp ->size == hp->capacity)
{
hp->capacity *= 2;
hp->a = realloc(hp->a, hp->capacity * sizeof(HeapDataType));
}
hp->a[hp->size] = x;
//从上往下调整
HeapAdjustUp(hp, hp->size);
hp->size++;
}
//删除元素
void HeapPop(heap *hp)
{
assert(hp);
if (hp->size == 0)
{
return;
}
hp->a[0] = hp->a[hp->size - 1];
hp->size--;
HeapAdjustDown(hp, 0);
}
//返回元素个数
size_t Heap_Size(heap *hp)
{
assert(hp);
return hp->size;
}
//返回最大元素
HeapDataType HeapTop(heap *hp)
{
assert(hp);
return hp->a[0];
}
//堆排序 必须借助从上往下调整
void HeapSort(heap *hp)
{
assert(hp);
int root = (hp->size - 1 ) / 2; //找到最后一个非叶子节点
while (root >= 0)
{
HeapAdjustDown(hp, root);
root--;
}
}
void test()
{
heap hp;
HeapDataType arr[] = { 1,2,3,6,5,10};
size_t ret = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
HeapInit(&hp, arr, ret);
HeapSort(&hp);
HeapPush(&hp, 7);
HeapPop(&hp);
printf("最大值为: %d ", HeapTop(&hp));
printf("\n");
for (size_t i = 0; i < hp.size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", hp.a[i]);
}
}
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________
main.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Heap.h"
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}