介绍
LiveData 是一款基于观察者模式的可感知生命周期的核心组件。LiveData 为界面代码 (Observer)的监视对象
(Observable),当 LiveData 所持有的数据改变时,它会通知相应的界面代码进行更新。同时,LiveData 持有
界面代码 Lifecycle 的引用,这意味着它会在界面代码(LifecycleOwner)的生命周期处于 started 或 resumed
时作出相应更新,而在 LifecycleOwner 被销毁时停止更新。通过 LiveData,开发者可以方便地构建安全性更高、
性能更好的高响应度用户界面 .
https://developer.android.google.cn/topic/libraries/architecture/livedata.html
使用必知
推荐在 ViewModel , 而不是在 Activity / Fragment 中保存 LiveData 对象
- 防止 Activity / Fragment 过于臃肿, 这些 UI 控制器只负责显示数据, 而不负责保存数据.
- 将 LiveData 实例与 Activity / Fragment 实例分离, 使得 LiveData 对象在 Activity / Fragment 实例销毁时仍能保存数据.
观察/订阅 LiveData 对象的最佳时机是 onCreate() 方法中
- 防止因 Activity / Fragment 的 onStart() / onResume() 多次回调, 导致 LiveData 多次被 observe
- 确保 Activity / Fragment 一旦变成活跃状态,就有可展示的数据
LiveData 使用
一般按照以下步骤:
-
在 ViewModel 类中, 创建 LiveData 的实例, 用来保存指定类型的数据.
/** * 实现每隔一秒钟,调用 postValue() 设置一次数据 */ // step1 public class TimerViewModel extends ViewModel { private static final String TAG = "TimerViewModel"; private static final int ONE_SECOND = 1000; private MutableLiveData<Long> mutableLiveData = new MutableLiveData<>(); private final Long initTime; public TimerViewModel() { initTime = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime(); new Timer().schedule(new TimerTask() { @Override public void run() { long num = (SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - initTime) / 1000; // setValue()会抛出异常 : Cannot invoke setValue on a background thread mutableLiveData.postValue(num); } }, ONE_SECOND, ONE_SECOND); } public MutableLiveData<Long> getMutableLiveData() { return mutableLiveData; } /** * 当 Activity 或 Fragment 销毁时,会回调该方法 */ @Override protected void onCleared() { super.onCleared(); Log.e(TAG, "onCleared: "); } } -
在 Activity / Fragment 创建 Observer 对象, 实现 onChanged() 方法, 当 LiveData 对象中保存的数据发生改变时会回调 onChanged() 方法, 我们可以在该方法中进行更新 UI 操作.
// step2 Observer<Long> observer = new Observer<Long>() { @Override public void onChanged(@Nullable Long aLong) { textView.setText(String.valueOf(aLong)); } }; -
使用 LiveData 对象的 observe(LifecycleOwner owner, Observer observer) 方法, 将 Observer 对象订阅到 LiveData 对象上; 也可以使用 observeForever(Observer oberver) 方法不传 LifecycleOwner 参数订阅 Observer, 这时 Observer 被认为始终处于活动状态.
public class LiveDataActivity extends AppCompatActivity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_live_data); textView = findViewById(R.id.tv_title); // step2 Observer<Long> observer = new Observer<Long>() { @Override public void onChanged(@Nullable Long aLong) { textView.setText(String.valueOf(aLong)); } }; // step3 timerViewModel = ViewModelProviders.of(this).get(TimerViewModel.class); timerViewModel.getMutableLiveData().observe(this, observer); } }
LiveData 更新数据
MutableLiveData 类提供了两个公开方法: setValue(T) 和 postValue(T) , 如果需要更新 LiveData 对象存储的数据, 必须需要使用这两个方法.
public void click(View view) {
timerViewModel.getMutableLiveData().postValue(100L);
}
setValue(T) 和 postValue(T) 区别 :
setValue(T) 必须在主线程中调用 , 而 postValue(T) 既可以在主线程中调用, 也可以在子线程中调用 .
LiveData 扩展
需求: 在 Activity 处于前台 started 时 , 子线程开始计数, 并更新显示到 UI 上, 在 Activity 处于后台 paused 时, 暂停计数, 再次回到前台时,继续计数.
-
继承扩展 MutableLiveData ,覆盖 onActive() 和 onInactive() 方法, 根据标识是否 postValue 更新数据.
public class CountLiveData extends MutableLiveData<Integer> { private static final String TAG = "CountLiveData"; private int count; private boolean isRun = true; private final CountTask countTask; public CountLiveData() { countTask = new CountTask(); countTask.start(); } @Override protected void onActive() { super.onActive(); Log.e(TAG, "onActive: "); countTask.interrupt(); isRun = true; } @Override protected void onInactive() { super.onInactive(); Log.e(TAG, "onInactive: "); isRun = false; } private class CountTask extends Thread { @Override public void run() { super.run(); while (true) { if (!isRun) { try { Thread.sleep(Integer.MAX_VALUE); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } count++; postValue(count); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } } -
创建 ViewModel , 存储 LiveData 对象中的数据.
public class CountViewModel extends ViewModel { private static final String TAG = "CountViewModel"; CountLiveData countLiveData; public CountViewModel() { countLiveData = new CountLiveData(); } public CountLiveData getCountLiveData() { return countLiveData; } /** * Activity / Fragment 销毁时回调该方法 */ @Override protected void onCleared() { super.onCleared(); Log.e(TAG, "onCleared: "); } } -
Activity 中创建 Observer , 订阅监听 LiveData 中的数据变化 , 并更新 UI
public class LiveDataActivity extends AppCompatActivity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { // 计数 CountViewModel countViewModel = ViewModelProviders.of(this).get(CountViewModel.class); Observer<Integer> countObserver = new Observer<Integer>() { @Override public void onChanged(@Nullable Integer integer) { countTextView.setText("计数: " + String.valueOf(integer)); } }; countViewModel.getCountLiveData().observe(this, countObserver); } @Override protected void onStart() { super.onStart(); Log.e("CountLiveData", "LiveDataActivity -> onStart(): " ); } @Override protected void onResume() { super.onResume(); Log.e("CountLiveData", "LiveDataActivity -> onResume(): " ); } @Override protected void onRestart() { super.onRestart(); Log.e("CountLiveData", "LiveDataActivity -> onRestart(): " ); } @Override protected void onPause() { super.onPause(); Log.e("CountLiveData", "LiveDataActivity -> onPause(): " ); } public void click(View view) { startActivity(new Intent(this, LiveDataSecondActivity.class)); timerViewModel.getMutableLiveData().postValue(100L); } }
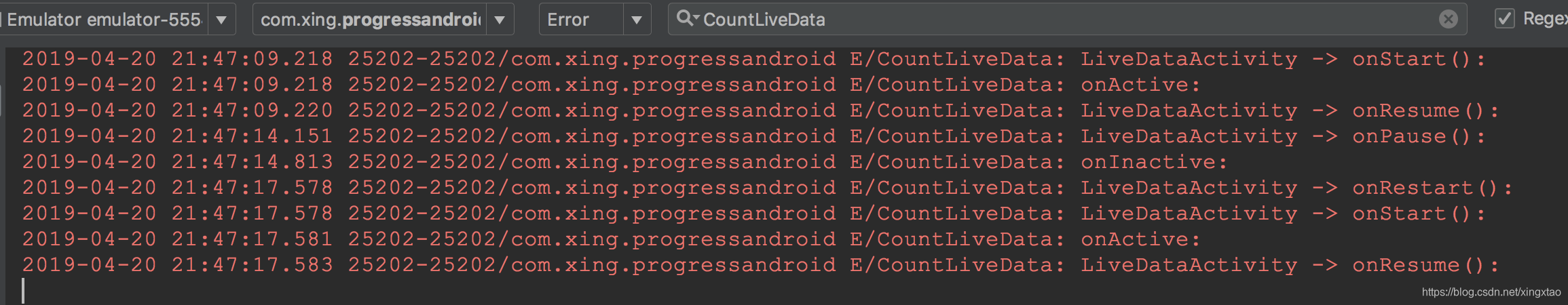
效果图

由 GIF 图可知: Activity 活跃时, 子线程每隔一秒钟 postValue() 一次数据给 observer, 当 Activity 变成不活跃时, 子线程暂停了 postValue() , 再次回到活跃状态时, 接着计数开始 postValue.