一、视图组件的使用
在我们自己书写视图类时需要不断书写重复冗余的代码,看起来十分繁琐不简洁易见,当然rest_framework中的视图组件帮我们做到了一些必要的步骤,使我们节省了编写冗余代码的时间。
1.视图组件的导入
from rest_framework import generics # generics.GenericAPIView 里面封装了APIView from rest_framework.mixins import ( ListModelMixin, # ListModelMixin表示get请求,获取全部数据 CreateModelMixin, # CreateModelMixin表示post请求,添加数据 DestroyModelMixin, # DestroyModelMixin表示delete请求,删除数据 UpdateModelMixin, # UpdataModelMixin表示put请求,修改数据 RetrieveModelMixin # RetrieveModelMixin表示get请求,获取单条数据 )
2.视图组件的使用
# 视图组件优化第一版 class BookListView(ListModelMixin, CreateModelMixin, generics.GenericAPIView): ''' 使用组件的步骤: 1.获取queryset对象 2.绑定序列化类 ''' queryset = Book.objects.all() serializer_class = BookSerializer def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs): return self.list(request, *args, **kwargs) def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs): return self.create(request, *args, **kwargs) class BookFilterView(RetrieveModelMixin, DestroyModelMixin, UpdateModelMixin, generics.GenericAPIView): queryset = Book.objects.all() serializer_class = BookSerializer def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs): # print(self.kwargs) {'pk': '1'} return self.retrieve(request, *args, **kwargs) def delete(self, request, *args, **kwargs): return self.destroy(request, *args, **kwargs) def put(self, request, *args, **kwargs): return self.update(request, *args, **kwargs)
是不是觉得视图组件帮我们做到了很多麻烦的事,还没完下面是改进版,
# 第二版本 class BookView(generics.ListCreateAPIView): queryset = Book.objects.all() serializer_class = BookSerializer class BookFilterView(generics.RetrieveUpdateDestroyAPIView): queryset = Book.objects.all() serializer_class = BookSerializer
不用我们自己写每个请求的方法了,去看看源码:其实是源码帮我们写了 我们要写的了。
class ListCreateAPIView(mixins.ListModelMixin, mixins.CreateModelMixin, GenericAPIView): """ Concrete view for listing a queryset or creating a model instance. """ def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs): return self.list(request, *args, **kwargs) def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs): return self.create(request, *args, **kwargs) class RetrieveUpdateAPIView(mixins.RetrieveModelMixin, mixins.UpdateModelMixin, GenericAPIView): """ Concrete view for retrieving, updating a model instance. """ def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs): return self.retrieve(request, *args, **kwargs) def put(self, request, *args, **kwargs): return self.update(request, *args, **kwargs) def patch(self, request, *args, **kwargs): return self.partial_update(request, *args, **kwargs)
但是,我们还是要写两个这个:
queryset = Book.objects.all()
serializer_class = BookSerializer
最终版本:
在使用时需要注意url中需要对每个请求类型声明
url:
re_path(r'book/$', views.BookView.as_view({ 'get': 'list', 'post': 'create' })), re_path(r'book/(?P<pk>\d+)/$', views.BookView.as_view({ 'get': 'retrieve', 'put': 'update', 'delete': 'destroy' })) # 注:在使用ModelViewSet时需要在as_view()中声明请求对应的视图方法,如:get请求对应list ( ListModelMixin ) ]
导入与使用:
from rest_framework.viewsets import ModelViewSet #ModelViewSet 里面既封装了mixins又封装了generics中的方法
# 终极版 class BookView(ModelViewSet): queryset = Book.objects.all() serializer_class = BookSerializer
只需要导入ModelViewSet就可以解决我们麻烦的冗余代码,看看源码怎么帮我们解决的:
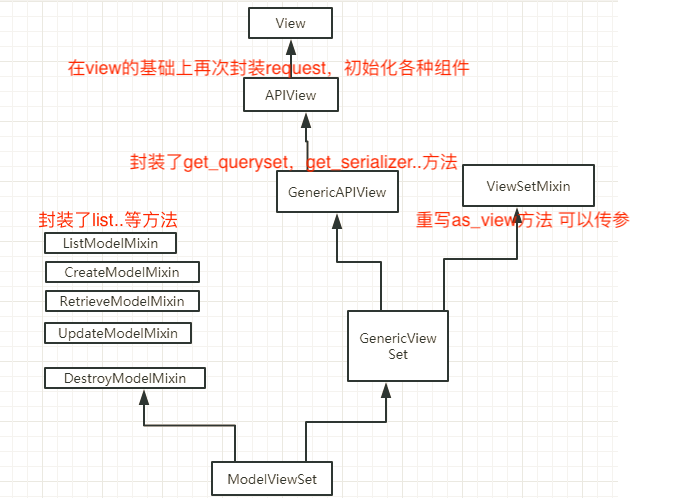
第一步: ModelViewSet类, 继承了放有具体执行每种操作的类(list, create, update, destroy, retrieve)
class ModelViewSet(mixins.CreateModelMixin, mixins.RetrieveModelMixin, mixins.UpdateModelMixin, mixins.DestroyModelMixin, mixins.ListModelMixin, GenericViewSet): """ A viewset that provides default `create()`, `retrieve()`, `update()`, `partial_update()`, `destroy()` and `list()` actions. """ pass
第二步:GenericViewSet, 这个类啥都没看,继续看父类
class GenericViewSet(ViewSetMixin, generics.GenericAPIView): """ The GenericViewSet class does not provide any actions by default, but does include the base set of generic view behavior, such as the `get_object` and `get_queryset` methods. """ pass
第三步: ViewSetMixin
class ViewSetMixin(object): """ This is the magic. Overrides `.as_view()` so that it takes an `actions` keyword that performs the binding of HTTP methods to actions on the Resource. For example, to create a concrete view binding the 'GET' and 'POST' methods to the 'list' and 'create' actions... view = MyViewSet.as_view({'get': 'list', 'post': 'create'}) """ @classonlymethod def as_view(cls, actions=None, **initkwargs): """ Because of the way class based views create a closure around the instantiated view, we need to totally reimplement `.as_view`, and slightly modify the view function that is created and returned. """ # The suffix initkwarg is reserved for displaying the viewset type. # eg. 'List' or 'Instance'. cls.suffix = None # The detail initkwarg is reserved for introspecting the viewset type. cls.detail = None # Setting a basename allows a view to reverse its action urls. This # value is provided by the router through the initkwargs. cls.basename = None # actions must not be empty if not actions: raise TypeError("The `actions` argument must be provided when " "calling `.as_view()` on a ViewSet. For example " "`.as_view({'get': 'list'})`") # sanitize keyword arguments for key in initkwargs: if key in cls.http_method_names: raise TypeError("You tried to pass in the %s method name as a " "keyword argument to %s(). Don't do that." % (key, cls.__name__)) if not hasattr(cls, key): raise TypeError("%s() received an invalid keyword %r" % ( cls.__name__, key)) def view(request, *args, **kwargs): self = cls(**initkwargs) # We also store the mapping of request methods to actions, # so that we can later set the action attribute. # eg. `self.action = 'list'` on an incoming GET request. self.action_map = actions # Bind methods to actions # This is the bit that's different to a standard view for method, action in actions.items(): # actions ---> {"get": "list", "post": "create"} {"put": "update", "delete": "destroy", "get": "retrieve"} handler = getattr(self, action) # 第一种get请求 self.list = getattr(self, list) 第二种 get请求 self.retrieve = getattr(self, retrieve) setattr(self, method, handler) # 第一种get请求 self.get = self.list 第二种get请求 self.get = self.retrieve if hasattr(self, 'get') and not hasattr(self, 'head'): self.head = self.get self.request = request self.args = args self.kwargs = kwargs # And continue as usual return self.dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs) # take name and docstring from class update_wrapper(view, cls, updated=()) # and possible attributes set by decorators # like csrf_exempt from dispatch update_wrapper(view, cls.dispatch, assigned=()) # We need to set these on the view function, so that breadcrumb # generation can pick out these bits of information from a # resolved URL. view.cls = cls view.initkwargs = initkwargs view.suffix = initkwargs.get('suffix', None) view.actions = actions return csrf_exempt(view)
这个类里面有as_view(cls, actions=None, **initkwargs)方法, 也就是我们的url里面写的as_view({"get": "list", "post": "create"}),执行的是这个类中的as_view()方法,而不是APIView种的as_view()方法了!
把那个参数字典传给actions,在放回的view函数中,把每种请求要执行的那种方法 setattr()设置了(看代码中注释);
然后当用户来访问时,执行那个view函数,正常执行dispatch()方法,根据请求方式分发到每种请求的方法中,这次这个方法,是使用setattr()方法设置给self的,没有具体写,也就能正常执行每种方法了。