一、异常概述
1.1 什么是生活的异常
男主角小明每天开车上班,正常车程1小时。但是,不出意外的话,可能会出现意外。

出现意外,即为异常情况。我们会做相应的处理。如果不处理,到不了公司。处理完了,就可以正常开车去公司。
1.2 什么是程序的异常
在使用计算机语言进行项目开发的过程中,即使程序员把代码写得 尽善尽美,在系统的运行过程中仍然会遇到一些问题,因为很多问题不是靠代码能够避免的,比如:客户输入数据的格式问题,读取文件是否存在,网络是否始终保持通畅 等等。
异常 :指的是程序在执行过程中,出现的非正常情况,如果不处理最终会导致 JVM 的非正常停止。异常指的并不是语法错误和逻辑错误。语法错了,编译不通过,不会产生字节码文件,根本不能运行。代码逻辑错误,只是没有得到想要的结果,例如:求 a 与 b 的和,你写成了 a - b
1.3 异常的抛出机制
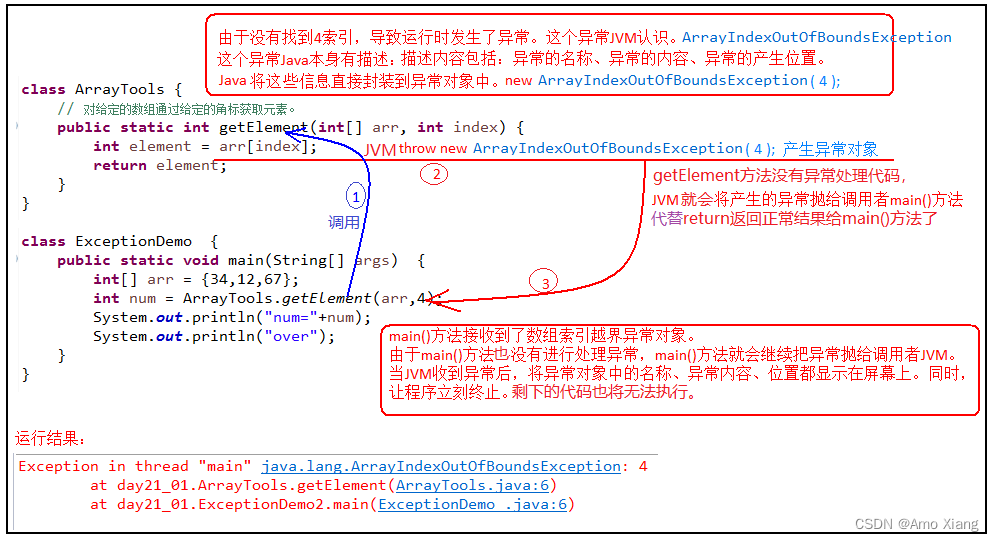
Java 中是如何表示不同的异常情况,又是如何让程序员得知,并处理异常的呢?Java 中把不同的异常用不同的类表示,一旦发生某种异常,就 创建该异常类型的对象,并且抛出(throw)。然后程序员可以捕获(catch)到这个异常对象,并处理;如果没有捕获(catch)这个异常对象,那么这个异常对象将会导致程序终止。举例:运行下面的程序,程序会产生一个数组角标越界异常 ArrayIndexOfBoundsException。我们通过图解来解析下异常产生和抛出的过程。
public class ArrayTools {
// 对给定的数组通过给定的角标获取元素。
public static int getElement(int[] arr, int index) {
int element = arr[index];
return element;
}
}
测试类
public class ExceptionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {
34, 12, 67 };
intnum = ArrayTools.getElement(arr, 4)
System.out.println("num=" + num);
System.out.println("over");
}
}
上述程序执行过程图解:
1.4 如何对待异常
对于程序出现的异常,一般有两种解决方法:一是遇到错误就终止程序的运行。另一种方法是程序员在编写程序时,就充分考虑到各种可能发生的异常和错误,极力预防和避免。实在无法避免的,要编写相应的代码进行异常的检测、以及 异常的处理,保证代码的 健壮性。
二、Java 异常体系
2.1 Throwable
java.lang.Throwable 类是 Java 程序执行过程中发生的异常事件对应的类的根父类。Throwable中的常用方法:
public void printStackTrace():打印异常的详细信息。包含了异常的类型、异常的原因、异常出现的位置、在开发和调试阶段都得使用 printStackTrace。public String getMessage():获取发生异常的原因。
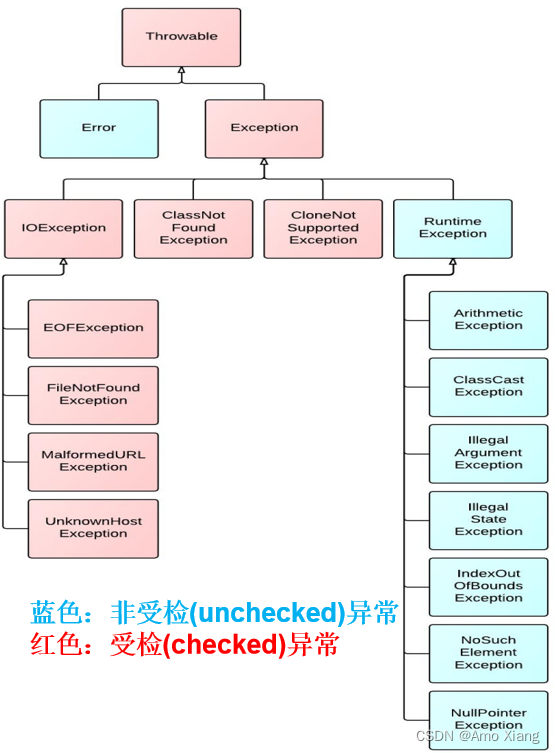
2.2 Error和Exception
Throwable 可分为两类:Error 和 Exception。分别对应着 java.lang.Error 与 java.lang.Exception 两个类。
Error: Java 虚拟机无法解决的严重问题。如:JVM 系统内部错误、资源耗尽等严重情况。一般不编写针对性的代码进行处理。例如:StackOverflowError(栈内存溢出) 和 OutOfMemoryError(堆内存溢出,简称OOM)。
Exception: 其它因编程错误或偶然的外在因素导致的一般性问题,需要使用针对性的代码进行处理,使程序继续运行。否则一旦发生异常,程序也会挂掉。例如:
- 空指针访问
- 试图读取不存在的文件
- 网络连接中断
- 数组角标越界
说明:无论是 Error 还是 Exception,还有很多子类,异常的类型非常丰富。当代码运行出现异常时,特别是我们不熟悉的异常时,不要紧张,把异常的简单类名,拷贝到 API 中去查去认识它即可。我们本文讲的异常处理,其实针对的就是 Exception。

2.3 编译时异常和运行时异常
Java 程序的执行分为编译时过程和运行时过程。有的错误只有在 运行时 才会发生。比如:除数为0,数组下标越界等。

因此,根据异常可能出现的阶段,可以将异常分为:
编译时期异常(即 checked 异常、受检异常):在代码编译阶段,编译器就能明确 警示 当前代码 可能发生(不是一定发生) xx异常,并 明确督促 程序员提前编写处理它的代码。如果程序员 没有编写 对应的异常处理代码,则编译器就会直接判定编译失败,从而不能生成字节码文件。通常,这类异常的发生不是由程序员的代码引起的,或者不是靠加简单判断就可以避免的,例如:FileNotFoundException(文件找不到异常)。
运行时期异常(即 runtime 异常、unchecked 异常、非受检异常):在代码编译阶段,编译器完全不做任何检查,无论该异常是否会发生,编译器都不给出任何提示。只有等代码运行起来并确实发生了 xx 异常,它才能被发现。通常,这类异常是由程序员的代码编写不当引起的,只要稍加判断,或者细心检查就可以避免。
java.lang.RuntimeException 类及它的子类都是运行时异常。比如:ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 数组下标越界异常,ClassCastException 类型转换异常。
三、常见的错误和异常
3.1 Error
最常见的就是 VirtualMachineError,它有两个经典的子类:StackOverflowError、OutOfMemoryError。
import org.junit.Test;
public class TestStackOverflowError {
@Test
public void test01(){
//StackOverflowError
recursion();
}
public void recursion(){
//递归方法
recursion();
}
}
import org.junit.Test;
public class TestOutOfMemoryError {
@Test
public void test02(){
//OutOfMemoryError
//方式一:
int[] arr = new int[Integer.MAX_VALUE];
}
@Test
public void test03(){
//OutOfMemoryError
//方式二:
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
while(true){
s.append("AmoXiang");
}
}
}
3.2 运行时异常
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TestRuntimeException {
@Test
public void test01(){
//NullPointerException
int[][] arr = new int[3][];
System.out.println(arr[0].length);
}
@Test
public void test02(){
//ClassCastException
Object obj = 15;
String str = (String) obj;
}
@Test
public void test03(){
//ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
int[] arr = new int[5];
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
@Test
public void test04(){
//InputMismatchException
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入一个整数:");//输入非整数
int num = input.nextInt();
input.close();
}
@Test
public void test05(){
int a = 1;
int b = 0;
//ArithmeticException
System.out.println(a/b);
}
}
3.3 编译时异常
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class TestCheckedException {
@Test
public void test06() {
Thread.sleep(1000);//休眠1秒 InterruptedException
}
@Test
public void test07(){
Class c = Class.forName("java.lang.String");//ClassNotFoundException
}
@Test
public void test08() {
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("...."); //SQLException
}
@Test
public void test09() {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("我的Java秘籍.txt"); //FileNotFoundException
}
@Test
public void test10() {
File file = new File("我的Java秘籍.txt");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);//FileNotFoundException
int b = fis.read();//IOException
while(b != -1){
System.out.print((char)b);
b = fis.read();//IOException
}
fis.close();//IOException
}
}
四、异常的处理
4.1 异常处理概述
在编写程序时,经常要在可能出现错误的地方加上检测的代码,如进行 x/y 运算时,要 检测分母为0,数据为空,输入的不是数据而是字符 等。过多的 if-else 分支会导致程序的 代码加长、臃肿,可读性差,程序员需要花很大的精力 堵漏洞。因此采用异常处理机制。
Java异常处理: Java 采用的异常处理机制,是 将异常处理的程序代码集中在一起,与正常的程序代码分开,使得程序简洁、优雅,并易于维护。
Java异常处理的方式:
方式一:try-catch-finally
方式二:throws + 异常类型

4.2 方式1:捕获异常(try-catch-finally)
Java 提供了异常处理的 抓抛模型。
- 前面提到,Java 程序的执行过程中如出现异常,会生成一个异常类对象,该异常对象将被提交给 Java 运行时系统,这个过程称为
抛出(throw)异常。 - 如果一个方法内抛出异常,该异常对象会被抛给调用者方法中处理。如果异常没有在调用者方法中处理,它继续被抛给这个调用方法的上层方法。这个过程将一直继续下去,直到异常被处理。这一过程称为
捕获(catch)异常。 - 如果一个异常回到 main() 方法,并且 main() 也不处理,则程序运行终止。
4.2.1 try-catch-finally基本格式
捕获异常语法如下:
try{
...... //可能产生异常的代码
}
catch( 异常类型1 e ){
...... //当产生异常类型1型异常时的处置措施
}
catch( 异常类型2 e ){
...... //当产生异常类型2型异常时的处置措施
}
finally{
...... //无论是否发生异常,都无条件执行的语句
}
1、整体执行过程: 当某段代码可能发生异常,不管这个异常是编译时异常(受检异常)还是运行时异常(非受检异常),我们都可以使用 try 块将它括起来,并在 try 块下面编写 catch 分支尝试捕获对应的异常对象。
- 如果在程序运行时,try 块中的代码没有发生异常,那么 catch 所有的分支都不执行。
- 如果在程序运行时,try 块中的代码发生了异常,根据异常对象的类型,将从上到下选择第一个匹配的 catch 分支执行。此时 try 中发生异常的语句下面的代码将不执行,而整个 try…catch 之后的代码可以继续运行。
- 如果在程序运行时,try 块中的代码发生了异常,但是所有 catch 分支都无法匹配(捕获)这个异常,那么 JVM 将会终止当前方法的执行,并把异常对象
抛给调用者。如果调用者不处理,程序就挂了。

2、try 捕获异常的第一步是用 try{…}语句块 选定捕获异常的范围,将可能出现异常的业务逻辑代码放在 try 语句块中。
3、catch(Exceptiontype e) catch 分支,分为两个部分,catch() 中编写异常类型和异常参数名, {} 中编写如果发生了这个异常,要做什么处理的代码。如果明确知道产生的是何种异常,可以用该异常类作为 catch 的参数;也可以用其父类作为 catch 的参数。比如:可以用 ArithmeticException 类作为参数的地方,就可以用 RuntimeException 类作为参数,或者用所有异常的父类 Exception 类作为参数。但不能是与 ArithmeticException 类无关的异常,如 NullPointerException(catch 中的语句将不会执行)。每个 try 语句块可以伴随一个或多个 catch 语句,用于处理可能产生的不同类型的异常对象。如果有多个 catch 分支,并且多个异常类型有父子类关系,必须保证小的子异常类型在上,大的父异常类型在下。否则,报错。catch中常用异常处理的方式:
public String getMessage():获取异常的描述信息,返回字符串public void printStackTrace():打印异常的跟踪栈信息并输出到控制台。包含了异常的类型、异常的原因、还包括异常出现的位置,在开发和调试阶段,都得使用 printStackTrace()。

4.2.2 使用举例
举例1:
public class IndexOutExp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String friends[] = {
"lisa", "bily", "kessy" };
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println(friends[i]);
}
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("index err");
}
System.out.println("\nthis is the end");
}
}
举例2:
public class DivideZero1 {
int x;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int y;
DivideZero1 c = new DivideZero1();
try {
y = 3 / c.x;
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("divide by zero error!");
}
System.out.println("program ends ok!");
}
}
举例3:
@Test
public void test1(){
try{
String str1 = "atguigu.com";
str1 = null;
System.out.println(str1.charAt(0));
}catch(NullPointerException e){
//异常的处理方式1
System.out.println("不好意思,亲~出现了小问题,正在加紧解决...");
}catch(ClassCastException e){
//异常的处理方式2
System.out.println("出现了类型转换的异常");
}catch(RuntimeException e){
//异常的处理方式3
System.out.println("出现了运行时异常");
}
//此处的代码,在异常被处理了以后,是可以正常执行的
System.out.println("hello");
}
4.2.3 finally使用及举例
 因为异常会引发程序跳转,从而会导致有些语句执行不到。而程序中有一些特定的代码无论异常是否发生,都需要执行。例如,数据库连接、输入流输出流、Socket 连接、Lock 锁的关闭等,这样的代码通常就会放到 finally 块中。所以,我们通常将一定要被执行的代码声明在 finally 中。唯一的例外,使用 System.exit(0) 来终止当前正在运行的 Java 虚拟机。不论在 try 代码块中是否发生了异常事件, catch 语句是否执行,catch 语句是否有异常,catch 语句中是否有 return,finally 块中的语句都会被执行。finally 语句和 catch 语句是可选的,但 finally 不能单独使用。
因为异常会引发程序跳转,从而会导致有些语句执行不到。而程序中有一些特定的代码无论异常是否发生,都需要执行。例如,数据库连接、输入流输出流、Socket 连接、Lock 锁的关闭等,这样的代码通常就会放到 finally 块中。所以,我们通常将一定要被执行的代码声明在 finally 中。唯一的例外,使用 System.exit(0) 来终止当前正在运行的 Java 虚拟机。不论在 try 代码块中是否发生了异常事件, catch 语句是否执行,catch 语句是否有异常,catch 语句中是否有 return,finally 块中的语句都会被执行。finally 语句和 catch 语句是可选的,但 finally 不能单独使用。
try{
}finally{
}
举例1:确保资源关闭
package com.atguigu.keyword;
import java.util.InputMismatchException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TestFinally {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
try {
System.out.print("请输入第一个整数:");
int a = input.nextInt();
System.out.print("请输入第二个整数:");
int b = input.nextInt();
int result = a/b;
System.out.println(a + "/" + b +"=" + result);
} catch (InputMismatchException e) {
System.out.println("数字格式不正确,请输入两个整数");
}catch (ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println("第二个整数不能为0");
} finally {
System.out.println("程序结束,释放资源");
input.close();
}
}
@Test
public void test1(){
FileInputStream fis = null;
try{
File file = new File("hello1.txt");
fis = new FileInputStream(file);//FileNotFoundException
int b = fis.read();//IOException
while(b != -1){
System.out.print((char)b);
b = fis.read();//IOException
}
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try {
if(fis != null)
fis.close();//IOException
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
举例2:从 try 回来
public class FinallyTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int result = test("12");
System.out.println(result);
}
public static int test(String str){
try{
Integer.parseInt(str);
return 1;
}catch(NumberFormatException e){
return -1;
}finally{
System.out.println("test结束");
}
}
}
举例3:从 catch 回来
public class FinallyTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int result = test("a");
System.out.println(result);
}
public static int test(String str) {
try {
Integer.parseInt(str);
return 1;
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
return -1;
} finally {
System.out.println("test结束");
}
}
}
举例4:从 finally 回来
public class FinallyTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int result = test("a");
System.out.println(result);
}
public static int test(String str) {
try {
Integer.parseInt(str);
return 1;
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
return -1;
} finally {
System.out.println("test结束");
return 0;
}
}
}
笔试题:
public class ExceptionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int result = test();
System.out.println(result); //100
}
public static int test(){
int i = 100;
try {
return i;
} finally {
i++;
}
}
}
笔试题:final、finally、finalize有什么区别?
4.2.4 练习
编写一个类 ExceptionTest,在 main 方法中使用 try、catch、finally,要求:
- 在 try 块中,编写被零除的代码。
- 在 catch 块中,捕获被零除所产生的异常,并且打印异常信息
- 在 finally 块中,打印一条语句。
4.2.5 异常处理的体会
前面使用的异常都是 RuntimeException类 或是它的 子类,这些类的异常的特点是:即使没有使用 try 和 catch 捕获,Java 自己也能捕获,并且编译通过(但运行时会发生异常使得程序运行终止)。所以,对于这类异常,可以不作处理,因为这类异常很普遍,若全处理可能会对程序的可读性和运行效率产生影响。如果抛出的异常是 IOException 等类型的 非运行时异常,则必须捕获,否则 编译错误。也就是说,我们必须处理编译时异常,将异常进行捕捉,转化为运行时异常。
4.3 方式2:声明抛出异常类型(throws)
如果在编写方法体的代码时,某句代码可能发生某个 编译时异常,不处理编译不通过,但是在当前方法体中可能 不适合处理 或 无法给出合理的处理方式,则此方法应 显示地 声明抛出异常,表明该方法将不对这些异常进行处理,而由该方法的调用者负责处理。

具体方式:在方法声明中用 throws语句 可以声明抛出异常的列表,throws 后面的异常类型可以是方法中产生的异常类型,也可以是它的父类。
4.3.1 throws基本格式
声明异常格式:
修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(参数) throws 异常类名1,异常类名2…{
}
在 throws 后面可以写多个异常类型,用逗号隔开。举例:
public void readFile(String file) throws FileNotFoundException,IOException {
...
// 读文件的操作可能产生FileNotFoundException或IOException类型的异常
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
//...
}
4.3.2 throws 使用举例
举例:针对于编译时异常
package com.atguigu.keyword;
public class TestThrowsCheckedException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("上课.....");
try {
afterClass();//换到这里处理异常
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("准备提前上课");
}
System.out.println("上课.....");
}
public static void afterClass() throws InterruptedException {
for(int i=10; i>=1; i--){
Thread.sleep(1000);//本来应该在这里处理异常
System.out.println("距离上课还有:" + i + "分钟");
}
}
}
举例:针对于运行时异常: throws 后面也可以写运行时异常类型,只是运行时异常类型,写或不写对于编译器和程序执行来说都没有任何区别。如果写了,唯一的区别就是调用者调用该方法后,使用 try…catch 结构时,IDEA 可以获得更多的信息,需要添加哪种 catch 分支。
package com.atguigu.keyword;
import java.util.InputMismatchException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TestThrowsRuntimeException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
try {
System.out.print("请输入第一个整数:");
int a = input.nextInt();
System.out.print("请输入第二个整数:");
int b = input.nextInt();
int result = divide(a,b);
System.out.println(a + "/" + b +"=" + result);
} catch (ArithmeticException | InputMismatchException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
input.close();
}
}
public static int divide(int a, int b)throws ArithmeticException{
return a/b;
}
}
4.3.3 方法重写中throws的要求
方法重写时,对于方法签名是有严格要求的。复习:
① 方法名必须相同
② 形参列表必须相同
③ 返回值类型
- 基本数据类型和 void:必须相同
- 引用数据类型:<=
④ 权限修饰符:>=,而且要求父类被重写方法在子类中是可见的
⑤ 不能是 static,final 修饰的方法
此外,对于 throws 异常列表要求:如果父类被重写方法的方法签名后面没有 throws 编译时异常类型,那么重写方法时,方法签名后面也不能出现 throws 编译时异常类型。如果父类被重写方法的方法签名后面有 throws 编译时异常类型,那么重写方法时,throws 的编译时异常类型必须 <= 被重写方法 throws 的编译时异常类型,或者不 throws 编译时异常。方法重写,对于 throws 运行时异常类型 没有要求。
package com.atguigu.keyword;
import java.io.IOException;
class Father{
public void method()throws Exception{
System.out.println("Father.method");
}
}
class Son extends Father{
@Override
public void method() throws IOException,ClassCastException {
System.out.println("Son.method");
}
}
4.4 两种异常处理方式的选择
前提:对于异常,使用相应的处理方式。此时的异常,主要指的是编译时异常。如果程序代码中,涉及到资源的调用(流、数据库连接、网络连接等),则必须考虑使用 try-catch-finally 来处理,保证不出现内存泄漏。如果父类被重写的方法没有 throws 异常类型,则子类重写的方法中如果出现异常,只能考虑使用 try-catch-finally 进行处理,不能 throws。开发中,方法 a 中依次调用了方法 b,c,d 等方法,方法 b,c,d 之间是递进关系。此时,如果方法 b,c,d 中有异常,我们通常选择使用 throws,而方法 a 中通常选择使用 try-catch-finally。
五、手动抛出异常对象:throw
Java 中异常对象的生成有两种方式:由虚拟机 自动生成:程序运行过程中,虚拟机检测到程序发生了问题,那么针对当前代码,就会在后台自动创建一个对应异常类的实例对象并抛出。由开发人员 手动创建:new 异常类型([实参列表]);,如果创建好的异常对象不抛出对程序没有任何影响,和创建一个普通对象一样,但是一旦 throw 抛出,就会对程序运行产生影响了。
5.1 使用格式
throw new 异常类名(参数);
throw 语句抛出的异常对象,和 JVM 自动创建和抛出的异常对象一样。如果是编译时异常类型的对象,同样需要使用 throws 或者 try…catch 处理,否则编译不通过。如果是运行时异常类型的对象,编译器不提示。可以抛出的异常必须是 Throwable 或其子类的实例。下面的语句在编译时将会产生语法错误:
throw new String("want to throw");
5.2 使用注意点:
无论是编译时异常类型的对象,还是运行时异常类型的对象,如果没有被 try…catch 合理的处理,都会导致程序崩溃。throw 语句会导致程序执行流程被改变,throw 语句是明确抛出一个异常对象,因此它 下面的代码将不会执行。如果当前方法没有 try…catch 处理这个异常对象,throw 语句就会 代替return语句 提前终止当前方法的执行,并返回一个异常对象给调用者。
package com.atguigu.keyword;
public class TestThrow {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
System.out.println(max(4,2,31,1));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
System.out.println(max(4));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
System.out.println(max());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static int max(int... nums){
if(nums == null || nums.length==0){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("没有传入任何整数,无法获取最大值");
}
int max = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
if(nums[i] > max){
max = nums[i];
}
}
return max;
}
}
六、自定义异常
6.1 为什么需要自定义异常类
Java 中不同的异常类,分别表示着某一种具体的异常情况。那么在开发中总是有些异常情况是核心类库中没有定义好的,此时我们需要根据自己业务的异常情况来定义异常类。例如年龄负数问题,考试成绩负数问题,某员工已在团队中等。
6.2 如何自定义异常类
① 要继承一个异常类型
自定义一个编译时异常类型:自定义类继承 java.lang.Exception
自定义一个运行时异常类型:自定义类继承 java.lang.RuntimeException
② 建议大家提供至少两个构造器,一个是无参构造,一个是(String message)构造器。
③ 自定义异常需要提供 serialVersionUID
6.3 注意点
① 自定义的异常只能通过 throw 抛出。
② 自定义异常最重要的是异常类的名字和 message 属性。当异常出现时,可以根据名字判断异常类型。比如:TeamException("成员已满,无法添加"); 、 TeamException("该员工已是某团队成员");
③ 自定义异常对象只能手动抛出。抛出后由 try…catch 处理,也可以甩锅 throws 给调用者处理。
6.4 举例
举例1:
class MyException extends Exception {
static final long serialVersionUID = 23423423435L;
private int idnumber;
public MyException(String message, int id) {
super(message);
this.idnumber = id;
}
public int getId() {
return idnumber;
}
}
public class MyExpTest {
public void regist(int num) throws MyException {
if (num < 0)
throw new MyException("人数为负值,不合理", 3);
else
System.out.println("登记人数" + num);
}
public void manager() {
try {
regist(100);
} catch (MyException e) {
System.out.print("登记失败,出错种类" + e.getId());
}
System.out.print("本次登记操作结束");
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
MyExpTest t = new MyExpTest();
t.manager();
}
}
举例2:
package com.atguigu.define;
//自定义异常:
public class NotTriangleException extends Exception{
static final long serialVersionUID = 13465653435L;
public NotTriangleException() {
}
public NotTriangleException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
package com.atguigu.define;
public class Triangle {
private double a;
private double b;
private double c;
public Triangle(double a, double b, double c) throws NotTriangleException {
if(a<=0 || b<=0 || c<=0){
throw new NotTriangleException("三角形的边长必须是正数");
}
if(a+b<=c || b+c<=a || a+c<=b){
throw new NotTriangleException(a+"," + b +"," + c +"不能构造三角形,三角形任意两边之后必须大于第三边");
}
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
this.c = c;
}
public double getA() {
return a;
}
public void setA(double a) throws NotTriangleException{
if(a<=0){
throw new NotTriangleException("三角形的边长必须是正数");
}
if(a+b<=c || b+c<=a || a+c<=b){
throw new NotTriangleException(a+"," + b +"," + c +"不能构造三角形,三角形任意两边之后必须大于第三边");
}
this.a = a;
}
public double getB() {
return b;
}
public void setB(double b) throws NotTriangleException {
if(b<=0){
throw new NotTriangleException("三角形的边长必须是正数");
}
if(a+b<=c || b+c<=a || a+c<=b){
throw new NotTriangleException(a+"," + b +"," + c +"不能构造三角形,三角形任意两边之后必须大于第三边");
}
this.b = b;
}
public double getC() {
return c;
}
public void setC(double c) throws NotTriangleException {
if(c<=0){
throw new NotTriangleException("三角形的边长必须是正数");
}
if(a+b<=c || b+c<=a || a+c<=b){
throw new NotTriangleException(a+"," + b +"," + c +"不能构造三角形,三角形任意两边之后必须大于第三边");
}
this.c = c;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Triangle{" +
"a=" + a +
", b=" + b +
", c=" + c +
'}';
}
}
package com.atguigu.define;
public class TestTriangle {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Triangle t = null;
try {
t = new Triangle(2,2,3);
System.out.println("三角形创建成功:");
System.out.println(t);
} catch (NotTriangleException e) {
System.err.println("三角形创建失败");
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if(t != null) {
t.setA(1);
}
System.out.println("三角形边长修改成功");
} catch (NotTriangleException e) {
System.out.println("三角形边长修改失败");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
七、练习
练习1:
public class ReturnExceptionDemo {
static void methodA() {
try {
System.out.println("进入方法A");
throw new RuntimeException("制造异常");
}finally {
System.out.println("用A方法的finally");
}
}
static void methodB() {
try {
System.out.println("进入方法B");
return;
} finally {
System.out.println("调用B方法的finally");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
methodA();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
methodB();
}
}
练习2: 从键盘接收学生成绩,成绩必须在 0~100 之间。自定义成绩无效异常。编写方法接收成绩并返回该成绩,如果输入无效,则抛出自定义异常。
八、小结与小悟
8.1 小结:异常处理5个关键字

类比:上游排污,下游治污
8.2 感悟
小哲理: 世界上最遥远的 距离,是我在 if 里你在 else 里,似乎一直相伴又永远分离;世界上最痴心的 等待,是我当 case 你是 switch,或许永远都选不上自己;世界上最真情的 相依,是你在 try 我在 catch。无论你发神马脾气,我都默默承受,静静处理。到那时,再来期待我们的 finally。
至此今天的学习就到此结束了,笔者在这里声明,笔者写文章只是为了学习交流,以及让更多学习Java语言的读者少走一些弯路,节省时间,并不用做其他用途,如有侵权,联系博主删除即可。感谢您阅读本篇博文,希望本文能成为您编程路上的领航者。祝您阅读愉快!

好书不厌读百回,熟读课思子自知。而我想要成为全场最靓的仔,就必须坚持通过学习来获取更多知识,用知识改变命运,用博客见证成长,用行动证明我在努力。
如果我的博客对你有帮助、如果你喜欢我的博客内容,请点赞、评论、收藏一键三连哦!听说点赞的人运气不会太差,每一天都会元气满满呦!如果实在要白嫖的话,那祝你开心每一天,欢迎常来我博客看看。
编码不易,大家的支持就是我坚持下去的动力。点赞后不要忘了关注我哦!