JSON
JSON的概念
- JSON :javascript object notation
- JSON 是存储和交换文本信息的语法,类似 XML。但是json比xml更小、更快、更容易解析。
- JSON 独立于语言:JSON 使用 Javascript语法来描述数据对象,但是 JSON 仍然独立于语言和平台。JSON 解析器和 JSON 库支持许多不同的编程语言。 目前非常多的动态(PHP,JSP,.NET)编程语言都支持JSON。
- JSON适用于进行数据交互的场景,如网站前台与后台之间的数据交互。
JSON的语法
- json的语法是Javascript的语法子集。
- 数据在名称/值对中
- 数据由逗号 , 分隔
- 使用斜杆 ** 来转义字符
- 大括号 {} 保存对象
- 中括号 [] 保存数组,数组可以包含多个对象
- json 的数据结构
- 1.大括号{ }保存的的对象是一个无序的名称/值对的合集。一个对象以左括号 { 开始, 右括号 } 结束。每个"键"后跟一个冒号 :,名称/值对使用逗号 , 分隔。
- **数组:**中括号 [] 保存的数组是值(value)的有序集合。一个数组以左中括号 [ 开始, 右中括号 ] 结束,值之间使用逗号 , 分隔。
json的书写格式
JSON 数据的书写格式是:
key : value
JSON 值可以是:
- 数字(整数或浮点数)
- 字符串(在双引号中)
- 逻辑值(true 或 false)
- 数组(在中括号中)
- 对象(在大括号中)
- null
JSON 对象:JSON 对象在大括号 {} 中书写。下面就是一个json对象。
{
"id": 41,
"name": "重庆",
"weather_id": "CN101040100"
}
JSON 数组:JSON 数组在中括号 [] 中书写,数组可包含多个对象。
下面的例子是对象city是包含四个对象的数组。
{
"city":[
{
"id": 41, "name": "重庆", "weather_id": "CN101040100"},
{
"id": 42, "name": "永川", "weather_id": "CN101040200"},
{
"id": 43, "name": "合川", "weather_id": "CN101040300"},
{
"id": 44, "name": "南川", "weather_id": "CN101040400"}
]
}
Android 中解析json数据的方法
1.JsonObject
使用JSONObject解析JSON数据,这是Android中最基本的数据解析方式。谷歌官方提供的解析json数据的方法。
Android中提供的Json解析类
- JSONObject: Json对象,可以完成Json字符串与Java对象的相互转换
- JSONArray: Json数组,可以完成Json字符串与Java集合或对象的相互转换
- JSONStringer: Json文本构建类,这个类可以帮助快速和便捷的创建JSON text, 每个JSONStringer实体只能对应创建一个JSON text
- JSONTokener:Json解析类
- JSONException:Json异常
下面使用代码实例进行分析:
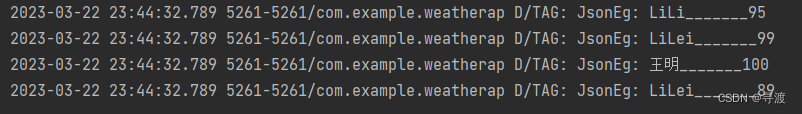
1.使用JSONArray类解析JSON数据的主要逻辑代码
[{
"name":"LiLi","score":"95"},{
"name":"LiLei","score":"99"},{
"name":"王明","score":"100"},{
"name":"LiLei","score":"89"}]
注意:因为""有申明字符串的意思我们初始化的是一个String字符串,所以在对象中需要用\对"进行转义,否则会造成String字符串提前结束的问题.
public static void JsonEg(){
String json="[{\"name\":\"LiLi\",\"score\":\"95\"},{\"name\":\"LiLei\",\"score\":\"99\"},{\"name\":\"王明\",\"score\":\"100\"},{\"name\":\"LiLei\",\"score\":\"89\"}]";
try {
JSONArray jsonArray=new JSONArray(json);
for (int i=0;i<jsonArray.length();i++){
JSONObject object=jsonArray.getJSONObject(i);
String name=object.optString("name");
int score=object.optInt("score");
Log.d("TAG", "JsonEg: "+name+"_______"+score);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}

optString和getString区别:
optString(“key”)如果为空返回 “” ,不报异常。优点:并不会应为key值使程序错误
getString(“key”)如果为空,返回空指针异常。
2.jsonObject对象解析
{
"user":{
"name":"alex",
"age":"18",
"isMan":true
}
}
public class OrgJSONTest {
public static String json = "{\"user\":{\"name\":\"alex\",\"age\":\"18\",\"isMan\":true}}";
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
JSONObject obj = new JSONObject(json);//最外层的JSONObject对象
JSONObject user = obj.getJSONObject("user");//通过user字段获取其所包含的JSONObject对象
String name = user.getString("name");//通过name字段获取其所包含的字符串
System.out.println(name);
} catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
打印结果:
alex
3.创建一个json数据,将json数据解析并且打印。
{
"cat":"it",
"languages":[
{
"id":1,"ide":"Eclipse","name":"Java"},
{
"id":2,"ide":"XCode","name":"Swift"},
{
"id":3,"ide":"Visual Studio","name":"C#"}
]
}
具体代码:
activity_main.xml代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context="com.oak.d4_json.MainActivity">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="创建"
android:id="@+id/bt_create"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="读取"
android:id="@+id/bt_read"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/tv"/>
</LinearLayout>
MainActivity.java代码:
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import org.json.JSONArray;
import org.json.JSONException;
import org.json.JSONObject;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private Button bt_create;//声明创建按钮组件变量
private Button bt_read;//声明读取按钮组件变量
private File file;//声明一个文件对象
private TextView tv;//声明TextView组件变量
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
bt_create = (Button) findViewById(R.id.bt_create);//获取到创建按钮组件
bt_read = (Button) findViewById(R.id.bt_read);//获取到读取按钮组件
tv = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv);//获取到TextView组件
file = new File(getFilesDir(),"Test.json");//获取到应用在内部的私有文件夹下对应的Test.json文件
bt_create.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
try {
JSONObject root = new JSONObject();//实例一个JSONObject对象
root.put("cat","it");//对其添加一个数据
JSONArray languages = new JSONArray();//实例一个JSON数组
JSONObject lan1 = new JSONObject();//实例一个lan1的JSON对象
lan1.put("id",1);//对lan1对象添加数据
lan1.put("ide","Eclipse");//对lan1对象添加数据
lan1.put("name","Java");//对lan1对象添加数据
JSONObject lan2 = new JSONObject();//实例一个lan2的JSON对象
lan2.put("id",2);//对lan2对象添加数据
lan2.put("ide","XCode");//对lan2对象添加数据
lan2.put("name","Swift");//对lan2对象添加数据
JSONObject lan3 = new JSONObject();//实例一个lan3的JSON对象
lan3.put("id",3);//对lan3对象添加数据
lan3.put("ide","Visual Studio");//对lan3对象添加数据
lan3.put("name","C#");//对lan3对象添加数据
languages.put(0,lan1);//将lan1对象添加到JSON数组中去,角标为0
languages.put(1,lan2);//将lan2对象添加到JSON数组中去,角标为1
languages.put(2,lan3);//将lan3对象添加到JSON数组中去,角标为2
root.put("languages",languages);//然后将JSON数组添加到名为root的JSON对象中去
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);//创建一个文件输出流
fos.write(root.toString().getBytes());//将生成的JSON数据写出
fos.close();//关闭输出流
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),"创建成功!",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
} catch (JSONException | IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
bt_read.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);//获取一个文件输入流
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis);//读取文件内容
BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(isr);//将字符流放入缓存中
String line;//定义一个用来临时保存数据的变量
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();//实例化一个字符串序列化
while((line = bf.readLine()) != null){
sb.append(line);//将数据添加到字符串序列化中
}
//关闭流
fis.close();
isr.close();
bf.close();
JSONObject root = new JSONObject(sb.toString());//用JSONObject进行解析
String cat = root.getString("cat");//获取字符串类型的键值对
tv.append("cat"+"="+cat+"\n");//显示数据
tv.append("---------------"+"\n");//分割线
JSONArray array = root.getJSONArray("languages");//获取JSON数据中的数组数据
for (int i=0; i<array.length(); i++){
JSONObject object = array.getJSONObject(i);//遍历得到数组中的各个对象
int id = object.getInt("id");//获取第一个值
String ide = object.getString("ide");//获取第二个值
String name = object.getString("name");//获取第三个值
tv.append("id"+"="+id+"\n");//显示数据
tv.append("ide"+"="+ide+"\n");//显示数据
tv.append("name"+"="+name+"\n");//显示数据
tv.append("---------------"+"\n");//分割线
}
} catch (IOException | JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
}
2.GSON
使用 Gson 获取 Json 中的数据
{
"data": {
"stuID": 1111,
"passwd": "admin",
"name": "admin",
"email": "[email protected]",
"authority": "admin",
"state": 0
},
"error": 0
}
创建一个 FullBackResponse.java 文件用于处理数据。
大体的思想是,非嵌套数据使用 getting 和 setting 方法将值赋值给变量,
嵌套的数据通过上述方法赋值给一个 实体类,在实体类里面获取对应的变量值。
public class FullBackResponse {
private dataBean data;
private int error;
// Json 内嵌套的实体类
public static class dataBean{
private int stuID;
private String passwd;
private String name;
private String email;
private String authority;
private int state;
public int getStuID() {
return stuID;
}
public void setStuID(int stuID) {
this.stuID = stuID;
}
public String getPasswd() {
return passwd;
}
public void setPasswd(String passwd) {
this.passwd = passwd;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getAuthority() {
return authority;
}
public void setAuthority(String authority) {
this.authority = authority;
}
public int getState() {
return state;
}
public void setState(int state) {
this.state = state;
}
}
public dataBean getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(dataBean data) {
this.data = data;
}
public int getError() {
return error;
}
public void setError(int error) {
this.error = error;
}
}
// res 是 String 类型的 Json 数据
FullBackResponse fullBackResponse = gson.fromJson(res, FullBackResponse.class);
// 将数据赋值给变量
// 这两个是 Json 内嵌套的 实体类 里的数据
int LoginResponse_stuID = fullBackResponse.getData().getStuID();
String LoginResponse_passwd = fullBackResponse.getData().getPasswd();
// 着个不是嵌套的数据
int LoginResponse_error = fullBackResponse.getError();
Android JSON数据解析
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_53958979/article/details/125086028
Android Java 使用 Gson 获取 Json 中的数据(包含嵌套的数据)
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_17790209/article/details/126950237