系列文章目录
【JavaScript】Promise(零) —— 准备工作(实例对象、函数对象、回调函数分类、捕获抛出错误)
【JavaScript】Promise(一) —— 理解和使用(是什么、怎么使用、与 Ajax 配合使用、涉及的API)
【JavaScript】Promise(二) —— 几个关键问题
文章目录
一、几个关键问题
1. 如何改变一个 Promise 实例的状态
- 执行 resolve(value):如果当前是 pending 就会变为 fulfilled。
- 执行 reject(reason):如果当前是 pending 就会变为 rejected。
- 执行器函数 (executor) 抛出异常:如果当前是 pending 就会变为 rejected。
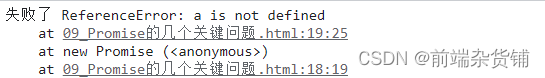
引擎抛异常:
const p = new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
console.log(a); //引擎抛异常
})
p.then(
value => {
console.log('成功了', value);},
reason => {
console.log('失败了', reason);}
)
编码抛异常:
const p = new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
throw -100 //编码抛异常
})
p.then(
value => {
console.log('成功了', value);},
reason => {
console.log('失败了', reason);}
)

2. 改变 Promise 实例的状态和指定回调函数谁先谁后?
- 如果先指定的回调,那当状态发生改变时,回调函数就会调用,得到数据。
- 如果先改变的状态,那当指定回调时,回调函数就会调用,得到数据。
先指定回调,后改变状态:
const p = new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
resolve(100)
}, 1000)
})
p.then(
value => {
console.log('成功了', value);},
reason => {
console.log('失败了', reason);}
)

先改状态,后指定回调:
const p = new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
resolve('a')
})
setTimeout(()=>{
p.then(
value => {
console.log('成功了', value);},
reason => {
console.log('失败了', reason);}
)
}, 1000)

3. Promise实例.then返回的是一个【新的Promise实例】,它的值和状态由什么决定?
- 简单表达:由 then 所指定的回调函数执行的结果决定。
- 详细表达:
(1)如果 then 所指定的回调返回的是非 Promise 值 a,那么【新Promise实例】状态为:成功(fulfilled),成功的 value 为 a。
(2)如果 then 所指定的回调返回的是一个 Promise 实例 p,那么【新Promise实例】的状态、值,都与 p 一致。
(3)如果then所指定的回调抛出异常:那么【新Promise实例】状态为 rejected,reason 为抛出的那个异常。
const p = new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
resolve('a')
}, 1000)
})
const x = p.then(
value => {
console.log('成功了1', value); return 900},
reason => {
console.log('失败了1', reason);}
)
x.then(
value => {
console.log('成功了2', value);},
reason => {
console.log('失败了2', reason);}
)

then的链式调用:
const p = new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
resolve('a')
}, 1000)
})
p.then(
value => {
console.log('成功了1', value); return Promise.reject('b')},
reason => {
console.log('失败了1', reason);}
).then(
value => {
console.log('成功了2', value); return true},
reason => {
console.log('失败了2', reason); return 100}
).then(
value => {
console.log('成功了3', value); throw 900},
reason => {
console.log('失败了3', reason); return false}
).then(
value => {
console.log('成功了4', value); return 200},
reason => {
console.log('失败了4', reason);}
)

4. Promise如何串连多个异步任务?
通过 then 的链式调用
实例:发送三次请求,每次请求成功后再发下一次请求。
// 封装ajax请求
function sendAjax(url) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// 实例xhr
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
// 绑定监听
xhr.onreadystatechange = () => {
if (xhr.readyState === 4) {
if (xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) {
resolve(xhr.response);
} else {
reject('请求出了点问题');
}
}
}
xhr.open('GET', url)
xhr.responseType = 'json'
xhr.send()
})
}
// 发送第1次请求
sendAjax('https://api.apiopen.top/api/sentences')
.then(
value => {
console.log('第1次请求成功了', value);
return sendAjax('https://api.apiopen.top/api/sentences')
},
reason => {
console.log('第1次请求失败了', reason);
}
)
.then(
value => {
console.log('第2次请求成功了', value);
return sendAjax('https://api.apiopen.top/api/sentences')
},
reason => {
console.log('第2次请求失败了', reason);
}
)
.then(
value => {
console.log('第3次请求成功了', value);
},
reason => {
console.log('第3次请求失败了', reason);
}
)
then的链式调用,依次请求成功:
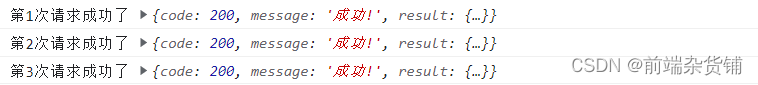
5. 中断 promise 链
- 当使用 promise 的 then 链式调用时,在中间中断,不再调用后面的回调函数。
- 办法:在失败的回调函数中返回一个 pendding 状态的 Promise 实例。
在失败的回调中返回 pendding 状态的 Promise 实例
return new Promise(() => {
})
实例:
// 封装ajax请求
function sendAjax(url) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// 实例xhr
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
// 绑定监听
xhr.onreadystatechange = () => {
if (xhr.readyState === 4) {
if (xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) {
resolve(xhr.response);
} else {
reject('请求出了点问题');
}
}
}
xhr.open('GET', url)
xhr.responseType = 'json'
xhr.send()
})
}
// 发送第1次请求
sendAjax('https://api.apiopen.top/api/sentences')
.then(
value => {
console.log('第1次请求成功了', value);
return sendAjax('https://api.apiopen.top/api/sentences2')
},
reason => {
console.log('第1次请求失败了', reason);
return new Promise(() => {
})
}
)
.then(
value => {
console.log('第2次请求成功了', value);
return sendAjax('https://api.apiopen.top/api/sentences')
},
reason => {
console.log('第2次请求失败了', reason);
return new Promise(() => {
})
}
)
.then(
value => {
console.log('第3次请求成功了', value);},
reason => {
console.log('第3次请求失败了', reason);
return new Promise(() => {
})
}
)

6. promise 的错误穿透
- 当使用 promise 的 then 链式调用时,可以在最后用 catch 指定一个失败的回调
- 前面任何操作出了错误,都会传到最后失败的回调中处理了
- 如果不存在 then 的链式调用,就不需要考虑 then 的错误穿透
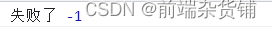
使用定时器:
const p = new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
reject(-1)
}, 500)
})
p.then(
value => {
console.log('成功了1', value);}
)
.then(
value => {
console.log('成功了2', value);}
)
.catch(
reason => {
console.log('失败了', reason);}
)
发送 Ajax 请求:
// 封装ajax请求
function sendAjax(url, index) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// 实例xhr
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
// 绑定监听
xhr.onreadystatechange = () => {
if (xhr.readyState === 4) {
if (xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) {
resolve(xhr.response);
} else {
reject(`第${
index}次请求出了点问题`);
}
}
}
xhr.open('GET', url)
xhr.responseType = 'json'
xhr.send()
})
}
sendAjax('https://api.apiopen.top/api/sentences', 1)
.then(
value => {
console.log('第1次请求成功了', value);
return sendAjax('https://api.apiopen.top/api/sentences2', 2)
},
)
.then(
value => {
console.log('第2次请求成功了', value);
return sendAjax('https://api.apiopen.top/api/sentences', 3)
},
)
.then(
value => {
console.log('第3次请求成功了', value);
},
)
.catch(
reason => {
console.log('失败了', reason);
}
)

不积跬步无以至千里,不积小流无以成江海
点个关注不迷路,持续更新中…