学习大纲
- Collection
- List
- 数组和链表
- List子类
- JDK5新特性
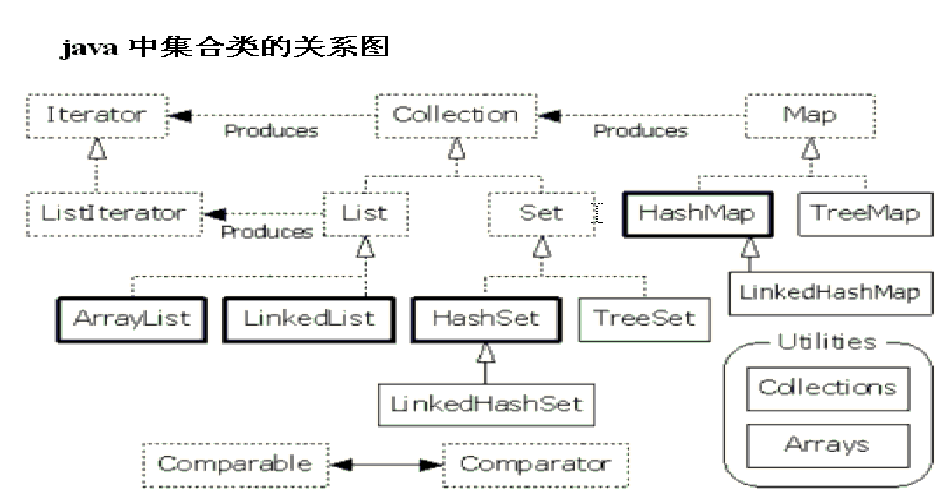
今天我们主要讲Collection和List。
正式讲课之前,我们先来搞明白三个小问题:
1. 为什么需要集合类?
很多情况下,我们需要对一组对象进行操作。而且很可能事先并不知道到底有多少个对象。为了解决这个问题呢,Java 就提供了集合类供我们使用。
很多情况下,我们需要对一组对象进行操作。而且很可能事先并不知道到底有多少个对象。为了解决这个问题呢,Java 就提供了集合类供我们使用。
2. 集合类的特点
a. 只能存储引用数据类型
b. 可以自动地调整自己的大小
a. 只能存储引用数据类型
b. 可以自动地调整自己的大小
3. 数组和集合类都是容器,它们有何不同?
a. 数组可以存储基本数据类型的数据,集合不可以。
b. 数组的长度是固定的,集合可以自动调整自己的大小。
c. 数组的效率高,相对来说集合效率比较低。
d. 数组没有API,集合有丰富的API。
a. 数组可以存储基本数据类型的数据,集合不可以。
b. 数组的长度是固定的,集合可以自动调整自己的大小。
c. 数组的效率高,相对来说集合效率比较低。
d. 数组没有API,集合有丰富的API。
Collection
- Collection 概述
Collection 层次结构中的根接口。Collection 表示一组对象,这些对象也称为 collection 的元素。一些 collection 允许有重复的元素,而另一些则不允许。一些 collection 是有序的,而另一些则是无序的。
- 特点
b. 只能存储引用数据类型
Collection 的含义大家应该清楚了,那么它应该包含哪些 API 呢?
- Collection接口的API
增:
boolean add(E e)
boolean addAll(Collection c)
删:
void clear()
boolean remove(Object o)
boolean removeAll(Collection c)
boolean retainAll(Collection c)
查:
boolean contains(Object o)
boolean containsAll(Collection c)
获取集合的属性:
boolean isEmpty()
int size()
遍历:
Object[] toArray()
Iterator<E> iterator()
boolean add(E e)
boolean addAll(Collection c)
删:
void clear()
boolean remove(Object o)
boolean removeAll(Collection c)
boolean retainAll(Collection c)
查:
boolean contains(Object o)
boolean containsAll(Collection c)
获取集合的属性:
boolean isEmpty()
int size()
遍历:
Object[] toArray()
Iterator<E> iterator()
1 public class CollectionDemo1 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Collection c = new ArrayList(10); 4 for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) { 5 c.add(i); 6 } 7 System.out.println(c); 8 System.out.println(c.size()); 9 } 10 }
- 自动装箱和自动拆箱(JDK5)
1 /* 自动装箱和自动拆箱(JDK5) 2 * 基本数据类型 引用数据类型 3 * byte Byte 4 * short Short 5 * int Integer 6 * long Long 7 * float Float 8 * double Double 9 * char Character 10 * boolean Boolean 11 * 自动装箱:基本数据类型转换成对应的引用数据类型 12 * 自动拆箱:引用数据类型转换成对应的基本数据类型 13 * 14 */ 15 public class CollectionDemo2 { 16 public static void main(String[] args) { 17 /*int intValue = 10; 18 Integer integer = Integer.valueOf(intValue); 19 int i = integer.intValue();*/ 20 21 int intValue = 10; 22 // 自动装箱 23 Integer integer = intValue; 24 // 自动拆性 25 int i = integer; 26 } 27 }
API:
boolean add(E e)
boolean remove(Object o)
void clear()
boolean contains(Object o)
boolean isEmpty()
int size()
1 package com.cskaoyan.collection; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Collection; 5 6 /* 7 API: 8 boolean add(E e) 9 boolean remove(Object o) 10 void clear() 11 boolean contains(Object o) 12 boolean isEmpty() 13 int size() 14 15 */ 16 public class CollectionDemo3 { 17 public static void main(String[] args) { 18 // boolean add(E e) 19 Collection c = new ArrayList(); 20 c.add("hello"); 21 c.add("world"); 22 c.add("java"); 23 24 /*System.out.println(c); 25 System.out.println(c.add("java")); // ? 26 System.out.println(c); 27 28 /*Collection c = new HashSet(); 29 System.out.println(c.add("hello")); 30 System.out.println(c.add("world")); 31 System.out.println(c.add("java")); 32 System.out.println(c); 33 System.out.println(c.add("java")); 34 System.out.println(c);*/ 35 36 // boolean remove(Object o) 37 /*System.out.println(c.remove("java")); // true 38 System.out.println(c); 39 System.out.println(c.remove("database")); // false 40 System.out.println(c);*/ 41 42 /*c.add("javase"); 43 c.add("java"); 44 System.out.println(c.remove("java")); 45 System.out.println(c);*/ 46 47 // int size() , void clear() 48 /* System.out.println(c.size()); 49 c.clear(); 50 System.out.println(c.size());*/ 51 52 // boolean empty() 判空:判断集合中是否有元素 53 /*c = null; 54 System.out.println(c.isEmpty()); // ?*/ 55 /*c.clear(); 56 System.out.println(c.isEmpty());*/ 57 58 // boolean contains(Object o) 59 /*System.out.println(c.contains("java")); 60 System.out.println(c.contains("database"));*/ 61 } 62 }
boolean addAll(Collection c)
boolean removeAll(Collection c)
boolean containsAll(Collection c)
boolean retainAll(Collection c)
1 package com.cskaoyan.collection; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Collection; 5 import java.util.HashSet; 6 7 /* 8 boolean addAll(Collection c) 9 如果集合发生了改变返回true, 否则返回false 10 boolean removeAll(Collection c) 11 如果集合发生了改变返回true, 否则返回false 12 boolean retainAll(Collection c) 13 如果集合发生了改变返回true, 否则返回false 14 15 boolean containsAll(Collection c) 16 如何包含集合c中所有的元素返回true, 否则返回false 17 */ 18 public class CollectionDemo4 { 19 public static void main(String[] args) { 20 Collection c = new ArrayList(); 21 c.add("hello"); 22 c.add("world"); 23 c.add("java"); 24 25 Collection c1 = new ArrayList(); 26 c1.add("beijing"); 27 c1.add("shenzhen"); 28 c1.add("wuhan"); 29 /* System.out.println(c.addAll(c1)); // true 30 31 System.out.println(c); 32 System.out.println(c1);*/ 33 34 // boolean removeAll(Collection c) 35 /*System.out.println(c.removeAll(c1)); // false 36 System.out.println(c); 37 System.out.println(c1);*/ 38 39 /* c1.add("java"); 40 System.out.println(c.removeAll(c1)); 41 System.out.println(c);*/ 42 43 44 /*c.add("java"); 45 c.add("java"); 46 c1.add("java"); 47 System.out.println(c); 48 System.out.println(c1); 49 System.out.println(c.removeAll(c1)); // true 50 System.out.println(c);*/ 51 52 // boolean retainAll(Collection c) 53 /*System.out.println(c.retainAll(c1)); // true 54 System.out.println(c); //[] 55 System.out.println(c1);*/ 56 57 /*c.clear(); 58 c.add("beijing"); 59 c.add("wuhan"); 60 System.out.println(c.retainAll(c1)); //false 61 System.out.println(c); 62 System.out.println(c1);*/ 63 64 /*c.clear(); 65 c.add("beijing"); 66 c.add("beijing"); 67 c.add("beijing"); 68 c.add("java"); 69 System.out.println(c.retainAll(c1)); // true 70 System.out.println(c); 71 System.out.println(c1);*/ 72 73 // boolean containsAll(Collection c) 74 System.out.println(c.containsAll(c1)); // false 75 76 c.add("beijing"); 77 c.add("wuhan"); 78 System.out.println(c.containsAll(c1)); // false 79 80 c.add("shenzhen"); 81 System.out.println(c.containsAll(c1)); // true 82 83 c1.add("beijing"); 84 c1.add("beijing"); 85 c1.add("beijing"); 86 System.out.println(c.containsAll(c1)); // true 87 } 88 }
Object[] toArray()
将集合转换成数组
将集合转换成数组
1 package com.cskaoyan.collection;
2
3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Arrays; 5 import java.util.Collection; 6 7 /* 8 遍历: 9 Object[] toArray() 10 Iterator<E> iterator() 11 12 小结: 13 数组长度:arr.length 14 字符串长度:s.length() 15 集合的大小:c.size() 16 */ 17 public class CollectionDemo5 { 18 public static void main(String[] args) { 19 Collection c = new ArrayList(); 20 c.add("hello"); 21 c.add("world"); 22 c.add("java"); 23 24 /*Object[] arr = c.toArray(); 25 for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { 26 String s = (String) arr[i]; 27 System.out.println(s); 28 }*/ 29 30 Object[] arr = c.toArray(); 31 for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { 32 String s = (String) arr[i]; 33 // s.toUpperCase(); 34 if ("java".equals(s)) arr[i] = "javaSE"; 35 } 36 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); 37 System.out.println(c); // c会发生改变吗? 38 } 39 }
Iterator iterator()
迭代器,集合的专用遍历方式
迭代器,集合的专用遍历方式
Iterator接口
它是对集合进行迭代的迭代器
依赖于集合对象存在
boolean hasNext()
E next()
void remove()
Iterator 接口原理
我们用过了 Iterator 的 API,发现我们是通过集合的 iterator() 方法获取 Iterator 接口对象的,它肯定是 Iterator 的子类对象,那它具体是什么类型的呢?
为什么Iterator接口要定义成一个接口?而不是一个类?

看看源码是如何实现的。

ArrayList迭代器示意图
1 package com.cskaoyan.collection; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Collection; 5 import java.util.Iterator; 6 7 /* 8 Iterator<E> iterator() 9 10 Iterable接口 11 Iterator<T> iterator() 12 13 Iterator接口 14 boolean hasNext() 15 E next() 16 void remove() 17 */ 18 public class CollectionDemo6 { 19 public static void main(String[] args) { 20 Collection c = new ArrayList(); 21 c.add("hello"); 22 c.add("world"); 23 c.add("java"); 24 25 /*Iterator it = c.iterator(); 26 System.out.println(it.next()); 27 System.out.println(it.next()); 28 System.out.println(it.next()); 29 System.out.println(it.next()); // NoSuchElementException*/ 30 31 /*Iterator it = c.iterator(); 32 while (it.hasNext()) { 33 String s = (String) it.next(); 34 System.out.println(s); 35 }*/ 36 37 // void remove() 删除最近返回的元素 38 // 例子:删除"java" 39 /*Iterator it = c.iterator(); 40 while (it.hasNext()) { 41 String s = (String) it.next(); 42 if ("java".equals(s)) it.remove(); 43 } 44 45 System.out.println(c);*/ 46 47 /*c.remove("java"); 48 System.out.println(c);*/ 49 50 51 Iterator it = c.iterator(); 52 while (it.hasNext()) { 53 String s = (String) it.next(); //ConcurrentModificationException 54 if ("java".equals(s)) c.remove(s); 55 } 56 57 System.out.println(c); //可以删除"java"吗? 58 } 59 }
ConcurrentModificationException
现象
原因

并发修改异常
注意事项
1. 用迭代器对集合遍历的时候,不要使用集合的API对集合进行修改
2. 使用集合对象的时候,不要使用while循环,可以使用for循环,最好使用foreach循环。
1. 用迭代器对集合遍历的时候,不要使用集合的API对集合进行修改
2. 使用集合对象的时候,不要使用while循环,可以使用for循环,最好使用foreach循环。
1 package com.cskaoyan.collection; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Collection; 5 import java.util.Iterator; 6 /* 7 注意事项: 8 a. 用集合的API修改集合的结构,所有的迭代器会失效 9 用迭代器的API修改集合的结构,其它迭代器会失效 10 b. 用迭代器遍历集合的时候,不要使用while循环,可以使用for循环,最好使用foreach循环 11 */ 12 public class CollectionDemo7 { 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 Collection c = new ArrayList(); 15 c.add("hello"); 16 c.add("world"); 17 c.add("java"); 18 19 /*Iterator it1 = c.iterator(); 20 while (it1.hasNext()) { 21 String s = (String) it1.next(); 22 System.out.println(s); 23 }*/ 24 for(Iterator it = c.iterator(); it.hasNext(); ) { 25 String s = (String) it.next(); 26 System.out.println(s); 27 } 28 // ... 茫茫多代码 29 30 /*Iterator it2 = c.iterator(); 31 while (it2.hasNext()) { 32 String s = (String) it2.next(); 33 if ("java".equals(s)) it1.remove(); 34 }*/ 35 36 for(Iterator it = c.iterator(); it.hasNext(); ) { 37 String s = (String) it.next(); 38 if ("java".equals(s)) it.remove(); 39 } 40 System.out.println(c); 41 } 42 }
List
- List接口概述
有序的 collection(也称为序列)。此接口的用户可以对列表中每个元素的插入位置进行精确地控制。
用户可以根据元素的整数索引(在列表中的位置)访问元素,并搜索列表中的元素。
与 set 不同,列表通常允许重复的元素。更确切地讲,列表通常允许满足 e1.equals(e2) 的元素对 e1 和 e2,并且如果列表本身允许 null 元素的话,通常它们允许多个 null 元素。
- List接口API
增:
void add(int index, E element)
boolean addAll(int index, Collection c)
删:
E remove(int index)
改:
E set(int index, E element)
查:
E get(int index)
int indexOf(Object o)
int lastIndexOf(Object o)
void add(int index, E element)
boolean addAll(int index, Collection c)
删:
E remove(int index)
改:
E set(int index, E element)
查:
E get(int index)
int indexOf(Object o)
int lastIndexOf(Object o)
获取子串:
List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) 包左不包右
List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) 包左不包右
遍历:
ListIterator<E> listIterator()
ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index)
ListIterator<E> listIterator()
ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index)
void add(int index,E element)
E remove(int index)
E get(int index)
E set(int index,E element)
ListIterator listIterator()
boolean hasPrevious()
E previous()
1 package com.cskaoyan.list; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Collection; 5 import java.util.List; 6 7 /* 8 List: 9 概述:有序的 collection(也称为序列)。此接口的用户可以对列表中每个元素的插入位置进行精确地控制。 10 用户可以根据元素的整数索引(在列表中的位置)访问元素,并搜索列表中的元素。 11 与 set 不同,列表通常允许重复的元素。更确切地讲,列表通常允许满足 e1.equals(e2) 的元素对 e1 和 e2,并且如果列表本身允许 null 元素的话,通常它们允许多个 null 元素。 12 13 API: 14 增: 15 void add(int index, E element) 16 boolean addAll(int index, Collection c) 17 删: 18 E remove(int index) 19 改: 20 E set(int index, E element) 21 查: 22 E get(int index) 23 int indexOf(Object o) 24 int lastIndexOf(Object o) 25 26 获取子串: 27 List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) 包左不包右 28 29 遍历: 30 ListIterator<E> listIterator() 31 ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) 32 */ 33 public class ListDemo1 { 34 public static void main(String[] args) { 35 // void add(int index, E element) 36 List list = new ArrayList(); 37 list.add("hello"); 38 list.add("world"); 39 list.add("java"); 40 // System.out.println(list); 41 42 // void add(int index, E element) index范围:[0, size()] 43 44 // list.add(0, "刘亦菲"); 45 // list.add(1, "刘亦菲"); 46 // list.add(list.size(), "刘亦菲"); 47 // list.add(-1, "刘亦菲"); // IndexOutOfBoundsException 48 // list.add(list.size() + 1, "刘亦菲"); 49 // System.out.println(list); 50 51 // boolean addAll(int index, Collection c) index范围:[0, size()] 52 /* Collection c = new ArrayList(); 53 c.add("Allen"); 54 c.add("Beyonce"); 55 c.add("Cindy");*/ 56 57 // list.addAll(0, c); 58 // list.addAll(1, c); 59 // list.addAll(list.size(), c); 60 // list.addAll(-1, c); 61 /*list.addAll(list.size() + 1, c); 62 System.out.println(list); //[ hello, Allen, Beyonce, Cindy, world, java] 63 System.out.println(c); 64 System.out.println(list.size());*/ 65 66 /*list.add(0, c); 67 System.out.println(list); 68 System.out.println(list.size()); // 4*/ 69 70 // E remove(int index) index范围:[0, size() - 1] 71 // System.out.println(list.remove(-1)); 72 // System.out.println(list.remove(list.size())); 73 // System.out.println(list.remove(1)); 74 // System.out.println(list); 75 76 // E set(int index, E element) index范围:[0, size() - 1] 77 /*System.out.println(list.set(2, "javaSE")); 78 System.out.println(list);*/ 79 80 // E get(int index) index范围:[0, size()-1] 81 // System.out.println(list.get(1)); // world 82 83 // int indexOf(Object o) 84 // 获取第一个与指定对象o相等元素的索引,如何不存在这样的元素,那么返回-1 85 /*list.add("hello"); 86 System.out.println(list.indexOf("hello")); 87 System.out.println(list.indexOf("wuhan"));*/ 88 89 // int lastIndexOf(Object o) 90 // 获取最后一个与指定对象o相等元素的索引,如何不存在这样的元素,那么返回-1 91 list.add("hello"); 92 System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf("hello")); // 3 93 System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf("wuhan")); // -1 94 } 95 }