公共チェーンブロックチェーン・トランザクションごとに達成
ブロック鎖の目的は、そのような私たちはブロック鎖上の例えば汎用取引ビットコインを達成する我々の共通のビットコイン取引として、安全で信頼性の高いストレージ取引、することができます。単純なデータ構造とよくチェーンブロックチェーンの完了時に、これに基づいてトランザクションのこのセクションのブロック鎖部分を達成します。公共チェーンを実現
取引メカニズム
それが作成されると、誰もがそれを修正または削除して行くことはできません、このセクションでは、取引の基本的な枠組みになるブロック鎖、トランザクションでは、特定のトランザクションの詳細は後述します。
UTXOトランザクションモデルで使用されているアカウントのモデルの一般的な概念、異なる例えばビット通貨、。私たちが必要とする情報は、間接的に利用者の残高情報を含め、各トランザクションに含まれています。
各トランザクションについて、あなたはチャンネルに想像することができ、左チャンネルが入力された情報の数を持って、チャネルの右端には、出力情報の数があるでしょう。0(入力情報は、金銭のやり取りから来ていると表し、トランザクションはゼロ以上の通貨源であってもよい意味してもユーザ源が存在しないため、特別な場合、すなわち、掘削、鉱山であるので、入力がありません情報)。出力情報を意味することはトランザクションの後、デジタル通貨の動きがなくなっていることを表しています。このように、金融取引情報の入力及び出力の数は、デジタルマネーの源の合計出力の和に等しいデジタルお金と同等であるべきです。想像することは困難ではない、伝統的なアカウントのモデルに比べて、UTXOユーザアカウントの残高のモデルは、トランザクションレコードの出力部です。
簡単な例を与えるために、コインを仮定は、Bに以下の処理を少しを支払います:
- 自分の取引を見つけるために、現在、既存のトランザクション情報、取引出力点を表示し、トータルバランスに含ま
- 現在のトランザクションの出力を決定するための独自のデジタル情報の十分なお金があります
- バランスが不十分である、バランスのヒント情報不足
- ときに十分なバランス、新しいトランザクション、すなわちUTXO
- 、バランスの消費者UTXOユーザーの一部の出力(全ての消費者のユーザーの残高は限りライン上に十分なように、する必要はありません)、およびユーザーのバランスは中UTXO前に、従来の出力に記録されているので、新しいトランザクションを入力し、彼ら特定の取引の出力前に。
- ユーザの数がトランザクションのために必要なバランスを見つけるときに等しくない、ユーザーは再び出力お金自身の残りの部分を、変更が等しい入力と出力の取引を確保するためにできること
だから我々は、当社の継続的な取引情報を運んでいる間通貨は、明確な目的地があり、取引におけるお金のソースに簡単な契約を実装しました。
その後、我々はコードを結合しますので、このロジックは、以下の鮮明な画像になりUTXOモデルの簡単な説明です:
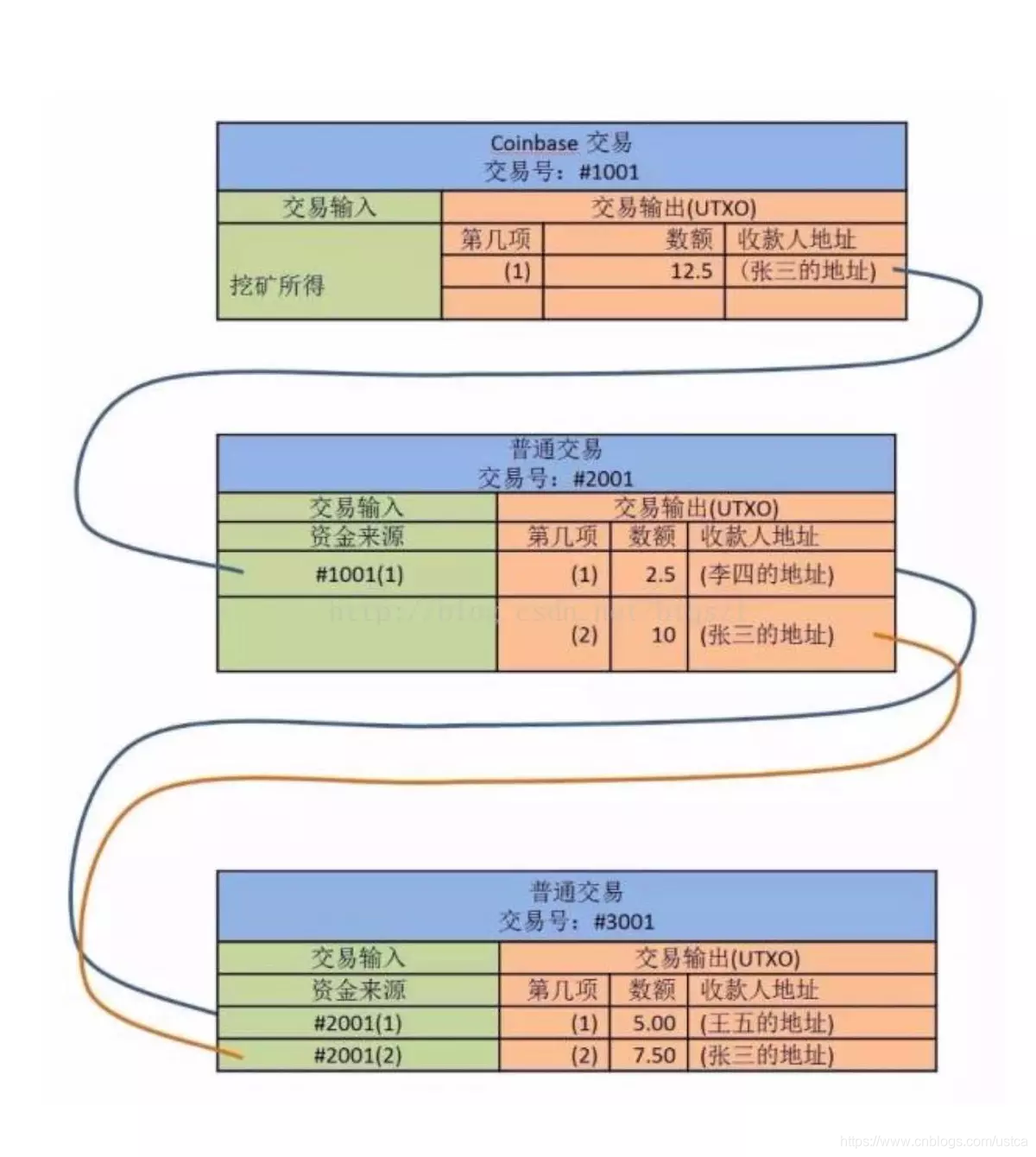
Coinbase取引は鉱山労働者が新たな鉱山を掘る表しトランザクションの特別な種類の、新しい役割であります鉱石を発掘し、追加点ウェル鎖マイニング鉱夫を出力します。
この例が示すように、12.5張マイニングビットクレジット、次いで、それらのクレジットが10ビットを残り、ジョン・ドウに2.5を支払う王ウー、7.5ビットを残り張最終クレジット2.5ビットZhangsanlisiクレジットの支払い、ジョン・ドウのバランスは、掘削鉱石を着座12.5クレジットの合計に等しい残りの5ビットキング5枚のコインを、空乏化されます。
コーディング
よくコードの実装は、チェーンの前に完了していると比較すると、トランザクションのブロック鎖は、ビジネスロジックを実装するために使用transaction.goファイルを作成する必要があります。ファイルの残りのコードは、それが取引メカニズムを添加した後の微調整となります。
transaction.go
次はtransaction.goコードです:
package main
import (
"bytes"
"crypto/sha256"
"encoding/gob"
"encoding/hex"
"fmt"
"log"
)
const subsidy = 10
// Transaction represents a Bitcoin transaction
type Transaction struct {
ID []byte
Vin []TXInput
Vout []TXOutput
}
// IsCoinbase checks whether the transaction is coinbase
func (tx Transaction) IsCoinbase() bool {
return len(tx.Vin) == 1 && len(tx.Vin[0].Txid) == 0 && tx.Vin[0].Vout == -1
}
// SetID sets ID of a transaction
func (tx *Transaction) SetID() {
var encoded bytes.Buffer
var hash [32]byte
enc := gob.NewEncoder(&encoded)
err := enc.Encode(tx)
if err != nil {
log.Panic(err)
}
hash = sha256.Sum256(encoded.Bytes())
tx.ID = hash[:]
}
// TXInput represents a transaction input
type TXInput struct {
Txid []byte
Vout int
ScriptSig string
}
// TXOutput represents a transaction output
type TXOutput struct {
Value int
ScriptPubKey string
}
// CanUnlockOutputWith checks whether the address initiated the transaction
func (in *TXInput) CanUnlockOutputWith(unlockingData string) bool {
return in.ScriptSig == unlockingData
}
// CanBeUnlockedWith checks if the output can be unlocked with the provided data
func (out *TXOutput) CanBeUnlockedWith(unlockingData string) bool {
return out.ScriptPubKey == unlockingData
}
// NewCoinbaseTX creates a new coinbase transaction
func NewCoinbaseTX(to, data string) *Transaction {
if data == "" {
data = fmt.Sprintf("Reward to '%s'", to)
}
txin := TXInput{[]byte{}, -1, data}
txout := TXOutput{subsidy, to}
tx := Transaction{nil, []TXInput{txin}, []TXOutput{txout}}
tx.SetID()
return &tx
}
// NewUTXOTransaction creates a new transaction
func NewUTXOTransaction(from, to string, amount int, bc *Blockchain) *Transaction {
var inputs []TXInput
var outputs []TXOutput
acc, validOutputs := bc.FindSpendableOutputs(from, amount)
if acc < amount {
log.Panic("ERROR: Not enough funds")
}
// Build a list of inputs
for txid, outs := range validOutputs {
txID, err := hex.DecodeString(txid)
if err != nil {
log.Panic(err)
}
for _, out := range outs {
input := TXInput{txID, out, from}
inputs = append(inputs, input)
}
}
// Build a list of outputs
outputs = append(outputs, TXOutput{amount, to})
if acc > amount {
outputs = append(outputs, TXOutput{acc - amount, from}) // a change
}
tx := Transaction{nil, inputs, outputs}
tx.SetID()
return &tx
}コードは、主に次のものが含まれます。
- 現在のトランザクションを含むID(トランザクションIDが必要)トランザクション構造、入力アレイと出力アレイ
- IsCoinbase関数は、現在のトランザクションがCoinbaseトランザクション(マイニングトランザクション)であるか否かを決定するために使用されます
- トランザクションIDを設定するSETID機能
- TXInput構造を含むストリップトランザクションID入力、アドレス出力との取引量
- 出力現在のトランザクションを備えた金額アドレスTXOutput構造
- 取引記録を提供するかどうかを判断するためのアドレスCanUnlockOutputWith機能は、入力されたアドレスに一致しています
- トランザクションの出力アドレスに一致するレコードを提供するかどうかを判断するためにCanBeUnlockedWith機能アドレス
- 採掘契約を作成するNewCoinbaseTX機能
- NewUTXOTransaction機能は、新しいトランザクションを作成し、
关于TXInput与TXOutput中地址的问题,因为目前还没有实现区块链中的地址,所以本节涉及的地址直接用字符串代替,验证地址也只是进行了字符串对比。地址是必要的,它标注了当前的余额属于谁,这里因为刚实现交易机制,还没有引入真正的地址机制,所以是存在漏洞的,用户只要知道有哪些用户就可以直接往自己地址转钱,在下一节会实现地址机制进行完善。
block.go
在transaction.go中实现了交易的结构体,如何创建一条新的交易,以及简单的交易对象判断。在其余文件中,block.go文件做了一些改动,主要是将原本的data字符串换成了Transaction交易。同样的,下一节中我们会将本节的地址字符串换成相应机制的地址,以下是改动后的block.go文件:
package main
import (
"bytes"
"crypto/sha256"
"encoding/gob"
"log"
"time"
)
// Block keeps block headers
type Block struct {
Timestamp int64
Transactions []*Transaction
PrevBlockHash []byte
Hash []byte
Nonce int
}
// Serialize serializes the block
func (b *Block) Serialize() []byte {
var result bytes.Buffer
encoder := gob.NewEncoder(&result)
err := encoder.Encode(b)
if err != nil {
log.Panic(err)
}
return result.Bytes()
}
// HashTransactions returns a hash of the transactions in the block
func (b *Block) HashTransactions() []byte {
var txHashes [][]byte
var txHash [32]byte
for _, tx := range b.Transactions {
txHashes = append(txHashes, tx.ID)
}
txHash = sha256.Sum256(bytes.Join(txHashes, []byte{}))
return txHash[:]
}
// NewBlock creates and returns Block
func NewBlock(transactions []*Transaction, prevBlockHash []byte) *Block {
block := &Block{time.Now().Unix(), transactions, prevBlockHash, []byte{}, 0}
pow := NewProofOfWork(block)
nonce, hash := pow.Run()
block.Hash = hash[:]
block.Nonce = nonce
return block
}
// NewGenesisBlock creates and returns genesis Block
func NewGenesisBlock(coinbase *Transaction) *Block {
return NewBlock([]*Transaction{coinbase}, []byte{})
}
// DeserializeBlock deserializes a block
func DeserializeBlock(d []byte) *Block {
var block Block
decoder := gob.NewDecoder(bytes.NewReader(d))
err := decoder.Decode(&block)
if err != nil {
log.Panic(err)
}
return &block
}添加了HashTransactions函数,用来将交易转换成哈希值,其余函数随结构体中Data->Transactions的变动相应调整。
blockchain.go
在blockchain.go中,涉及到寻找用户余额(未花费交易输出)操作,需要多做一些调整:
package main
import (
"encoding/hex"
"fmt"
"log"
"os"
"bolt-master"
)
const dbFile = "blockchain.db"
const blocksBucket = "blocks"
const genesisCoinbaseData = "The Times 03/Jan/2009 Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks"
// Blockchain implements interactions with a DB
type Blockchain struct {
tip []byte
db *bolt.DB
}
// BlockchainIterator is used to iterate over blockchain blocks
type BlockchainIterator struct {
currentHash []byte
db *bolt.DB
}
// MineBlock mines a new block with the provided transactions
func (bc *Blockchain) MineBlock(transactions []*Transaction) {
var lastHash []byte
err := bc.db.View(func(tx *bolt.Tx) error {
b := tx.Bucket([]byte(blocksBucket))
lastHash = b.Get([]byte("l"))
return nil
})
if err != nil {
log.Panic(err)
}
newBlock := NewBlock(transactions, lastHash)
err = bc.db.Update(func(tx *bolt.Tx) error {
b := tx.Bucket([]byte(blocksBucket))
err := b.Put(newBlock.Hash, newBlock.Serialize())
if err != nil {
log.Panic(err)
}
err = b.Put([]byte("l"), newBlock.Hash)
if err != nil {
log.Panic(err)
}
bc.tip = newBlock.Hash
return nil
})
}
// FindUnspentTransactions returns a list of transactions containing unspent outputs
func (bc *Blockchain) FindUnspentTransactions(address string) []Transaction {
var unspentTXs []Transaction
spentTXOs := make(map[string][]int)
bci := bc.Iterator()
for {
block := bci.Next()
for _, tx := range block.Transactions {
txID := hex.EncodeToString(tx.ID)
Outputs:
for outIdx, out := range tx.Vout {
// Was the output spent?
if spentTXOs[txID] != nil {
for _, spentOut := range spentTXOs[txID] {
if spentOut == outIdx {
continue Outputs
}
}
}
if out.CanBeUnlockedWith(address) {
unspentTXs = append(unspentTXs, *tx)
}
}
if tx.IsCoinbase() == false {
for _, in := range tx.Vin {
if in.CanUnlockOutputWith(address) {
inTxID := hex.EncodeToString(in.Txid)
spentTXOs[inTxID] = append(spentTXOs[inTxID], in.Vout)
}
}
}
}
if len(block.PrevBlockHash) == 0 {
break
}
}
return unspentTXs
}
// FindUTXO finds and returns all unspent transaction outputs
func (bc *Blockchain) FindUTXO(address string) []TXOutput {
var UTXOs []TXOutput
unspentTransactions := bc.FindUnspentTransactions(address)
for _, tx := range unspentTransactions {
for _, out := range tx.Vout {
if out.CanBeUnlockedWith(address) {
UTXOs = append(UTXOs, out)
}
}
}
return UTXOs
}
// FindSpendableOutputs finds and returns unspent outputs to reference in inputs
func (bc *Blockchain) FindSpendableOutputs(address string, amount int) (int, map[string][]int) {
unspentOutputs := make(map[string][]int)
unspentTXs := bc.FindUnspentTransactions(address)
accumulated := 0
Work:
for _, tx := range unspentTXs {
txID := hex.EncodeToString(tx.ID)
for outIdx, out := range tx.Vout {
if out.CanBeUnlockedWith(address) && accumulated < amount {
accumulated += out.Value
unspentOutputs[txID] = append(unspentOutputs[txID], outIdx)
if accumulated >= amount {
break Work
}
}
}
}
return accumulated, unspentOutputs
}
// Iterator returns a BlockchainIterat
func (bc *Blockchain) Iterator() *BlockchainIterator {
bci := &BlockchainIterator{bc.tip, bc.db}
return bci
}
// Next returns next block starting from the tip
func (i *BlockchainIterator) Next() *Block {
var block *Block
err := i.db.View(func(tx *bolt.Tx) error {
b := tx.Bucket([]byte(blocksBucket))
encodedBlock := b.Get(i.currentHash)
block = DeserializeBlock(encodedBlock)
return nil
})
if err != nil {
log.Panic(err)
}
i.currentHash = block.PrevBlockHash
return block
}
func dbExists() bool {
if _, err := os.Stat(dbFile); os.IsNotExist(err) {
return false
}
return true
}
// NewBlockchain creates a new Blockchain with genesis Block
func NewBlockchain(address string) *Blockchain {
if dbExists() == false {
fmt.Println("No existing blockchain found. Create one first.")
os.Exit(1)
}
var tip []byte
db, err := bolt.Open(dbFile, 0600, nil)
if err != nil {
log.Panic(err)
}
err = db.Update(func(tx *bolt.Tx) error {
b := tx.Bucket([]byte(blocksBucket))
tip = b.Get([]byte("l"))
return nil
})
if err != nil {
log.Panic(err)
}
bc := Blockchain{tip, db}
return &bc
}
// CreateBlockchain creates a new blockchain DB
func CreateBlockchain(address string) *Blockchain {
if dbExists() {
fmt.Println("Blockchain already exists.")
os.Exit(1)
}
var tip []byte
db, err := bolt.Open(dbFile, 0600, nil)
if err != nil {
log.Panic(err)
}
err = db.Update(func(tx *bolt.Tx) error {
cbtx := NewCoinbaseTX(address, genesisCoinbaseData)
genesis := NewGenesisBlock(cbtx)
b, err := tx.CreateBucket([]byte(blocksBucket))
if err != nil {
log.Panic(err)
}
err = b.Put(genesis.Hash, genesis.Serialize())
if err != nil {
log.Panic(err)
}
err = b.Put([]byte("l"), genesis.Hash)
if err != nil {
log.Panic(err)
}
tip = genesis.Hash
return nil
})
if err != nil {
log.Panic(err)
}
bc := Blockchain{tip, db}
return &bc
}代码的主要变动是新增了三个关于交易的函数:
- FindUnspendTransactions遍历公链,寻找交易信息中没有被使用过输出的交易,即未被花费过的余额。当一条交易中的余额被其他交易用做过输入,该余额也就不在具有余额的属性,不能再次被交易
- FindUTXO在内部调用了FindUnspendTransactions函数,与FindUnspendTransactions不同的是它用于查询用户的余额信息,即所有有效未花费余额的总和
- FindSpendableOutputs在内部调用了FindUnspendTransactions函数,用于找出哪些余额是可用的
其次,原本的Addblock被改成了更具体的Mineblock挖矿函数,新增了Createblockchain函数和dbExists函数,用来判断数据库是否存在,只有当数据库中没有公链时才能创建新的区块链。
proofofwork.go
データprepareDataはHashTransactionsを置き換えるだけproofofworkファイル、無印刷部分のデータマイニングでは、次のように完全なコードをproofofwork.go:
package main
import (
"bytes"
"crypto/sha256"
"fmt"
"math"
"math/big"
)
var (
maxNonce = math.MaxInt64
)
const targetBits = 24
// ProofOfWork represents a proof-of-work
type ProofOfWork struct {
block *Block
target *big.Int
}
// NewProofOfWork builds and returns a ProofOfWork
func NewProofOfWork(b *Block) *ProofOfWork {
target := big.NewInt(1)
target.Lsh(target, uint(256-targetBits))
pow := &ProofOfWork{b, target}
return pow
}
func (pow *ProofOfWork) prepareData(nonce int) []byte {
data := bytes.Join(
[][]byte{
pow.block.PrevBlockHash,
pow.block.HashTransactions(),
IntToHex(pow.block.Timestamp),
IntToHex(int64(targetBits)),
IntToHex(int64(nonce)),
},
[]byte{},
)
return data
}
// Run performs a proof-of-work
func (pow *ProofOfWork) Run() (int, []byte) {
var hashInt big.Int
var hash [32]byte
nonce := 0
fmt.Printf("Mining a new block")
for nonce < maxNonce {
data := pow.prepareData(nonce)
hash = sha256.Sum256(data)
// fmt.Printf("\r%x", hash)
hashInt.SetBytes(hash[:])
if hashInt.Cmp(pow.target) == -1 {
break
} else {
nonce++
}
}
// fmt.Print("\n\n")
return nonce, hash[:]
}
// Validate validates block's PoW
func (pow *ProofOfWork) Validate() bool {
var hashInt big.Int
data := pow.prepareData(pow.block.Nonce)
hash := sha256.Sum256(data)
hashInt.SetBytes(hash[:])
isValid := hashInt.Cmp(pow.target) == -1
return isValid
}cli.go
ビジネスロジックの基礎となるいくつかの変更を使用してファイルをcli.goし、適切な変更を行い、変動は主に、コマンドラインを実装するために使用される、チェーンは、論理ブロックを含みません。
package main
import (
"flag"
"fmt"
"log"
"os"
"strconv"
)
// CLI responsible for processing command line arguments
type CLI struct{}
func (cli *CLI) createBlockchain(address string) {
bc := CreateBlockchain(address)
bc.db.Close()
fmt.Println("Done!")
}
func (cli *CLI) getBalance(address string) {
bc := NewBlockchain(address)
defer bc.db.Close()
balance := 0
UTXOs := bc.FindUTXO(address)
for _, out := range UTXOs {
balance += out.Value
}
fmt.Printf("Balance of '%s': %d\n", address, balance)
}
func (cli *CLI) printUsage() {
fmt.Println("Usage:")
fmt.Println(" getbalance -address ADDRESS - Get balance of ADDRESS")
fmt.Println(" createblockchain -address ADDRESS - Create a blockchain and send genesis block reward to ADDRESS")
fmt.Println(" printchain - Print all the blocks of the blockchain")
fmt.Println(" send -from FROM -to TO -amount AMOUNT - Send AMOUNT of coins from FROM address to TO")
}
func (cli *CLI) validateArgs() {
if len(os.Args) < 2 {
cli.printUsage()
os.Exit(1)
}
}
func (cli *CLI) printChain() {
// TODO: Fix this
bc := NewBlockchain("")
defer bc.db.Close()
bci := bc.Iterator()
for {
block := bci.Next()
fmt.Printf("Prev. hash: %x\n", block.PrevBlockHash)
fmt.Printf("Hash: %x\n", block.Hash)
pow := NewProofOfWork(block)
fmt.Printf("PoW: %s\n", strconv.FormatBool(pow.Validate()))
fmt.Println()
if len(block.PrevBlockHash) == 0 {
break
}
}
}
func (cli *CLI) send(from, to string, amount int) {
bc := NewBlockchain(from)
defer bc.db.Close()
tx := NewUTXOTransaction(from, to, amount, bc)
bc.MineBlock([]*Transaction{tx})
fmt.Println("Success!")
}
// Run parses command line arguments and processes commands
func (cli *CLI) Run() {
cli.validateArgs()
getBalanceCmd := flag.NewFlagSet("getbalance", flag.ExitOnError)
createBlockchainCmd := flag.NewFlagSet("createblockchain", flag.ExitOnError)
sendCmd := flag.NewFlagSet("send", flag.ExitOnError)
printChainCmd := flag.NewFlagSet("printchain", flag.ExitOnError)
getBalanceAddress := getBalanceCmd.String("address", "", "The address to get balance for")
createBlockchainAddress := createBlockchainCmd.String("address", "", "The address to send genesis block reward to")
sendFrom := sendCmd.String("from", "", "Source wallet address")
sendTo := sendCmd.String("to", "", "Destination wallet address")
sendAmount := sendCmd.Int("amount", 0, "Amount to send")
switch os.Args[1] {
case "getbalance":
err := getBalanceCmd.Parse(os.Args[2:])
if err != nil {
log.Panic(err)
}
case "createblockchain":
err := createBlockchainCmd.Parse(os.Args[2:])
if err != nil {
log.Panic(err)
}
case "printchain":
err := printChainCmd.Parse(os.Args[2:])
if err != nil {
log.Panic(err)
}
case "send":
err := sendCmd.Parse(os.Args[2:])
if err != nil {
log.Panic(err)
}
default:
cli.printUsage()
os.Exit(1)
}
if getBalanceCmd.Parsed() {
if *getBalanceAddress == "" {
getBalanceCmd.Usage()
os.Exit(1)
}
cli.getBalance(*getBalanceAddress)
}
if createBlockchainCmd.Parsed() {
if *createBlockchainAddress == "" {
createBlockchainCmd.Usage()
os.Exit(1)
}
cli.createBlockchain(*createBlockchainAddress)
}
if printChainCmd.Parsed() {
cli.printChain()
}
if sendCmd.Parsed() {
if *sendFrom == "" || *sendTo == "" || *sendAmount <= 0 {
sendCmd.Usage()
os.Exit(1)
}
cli.send(*sendFrom, *sendTo, *sendAmount)
}
}main.go
main.goでは、我々はすべて、これだけ次のコードをCLIオブジェクト、新しいブロック操作の元々古いmain.goの作成を操作する必要があり、また、ロジックのcli.goを配置します。
package main
func main() {
bc := NewBlockchain()
defer bc.db.Close()
cli := CLI{bc}
cli.Run()
}utils.go
導入された新しいユーティリティ機能しない、utils.goはそのままファイル。