1PyTorchのセマンティックセグメンテーションの組み込みモデル
torchvisionライブラリの下のmodels\segmentationディレクトリで、segmentation.Pyファイルを見つけます。このファイルには、PyTorchの組み込みのセマンティックセグメンテーションモデルが格納されています。
2MaskR-セマンティックセグメンテーション用のCNN組み込みモデル
2.1コードロジックの簡単な説明
COCO 2017データセットの事前トレーニング済みモデルdceplabv3_resnet101_cocoをメモリにロードし、このモデルを使用して画像のセマンティックセグメンテーションを実行します。
2.2コードの実装:MaskR-CNN組み込みモデルはセマンティックセグメンテーションを実装します
Maskrcnn_resent_Semantic_Segmentation.py
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
from torchvision import models
from torchvision import transforms
import os
os.environ["KMP_DUPLICATE_LIB_OK"]="TRUE"
# 获取模型,如果本地没有缓存,则下载
model = models.segmentation.deeplabv3_resnet101(pretrained=True) # 调用内置模型,并使用预训练权重进行初始化。
model.eval() # 不然报错 Expected more than 1 value per channel when training, got input size torch.Size
# 在图片的数据输入网络之前,对图片进行预处理
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize(256), # 将图片尺寸调整为256×256
transforms.CenterCrop(224), # 中心裁剪成224×224
transforms.ToTensor(), # 转换成张量归一化到[0,1]
transforms.Normalize( # 使用均值,方差标准化
mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
)
])
def preimg(img): # 定义图片预处理函数
if img.mode == 'RGBA': # 兼容RGBA图片
ch = 4
print('ch', ch)
a = np.asarray(img)[:, :, :3]
img = Image.fromarray(a)
return img
# 加载要预测的图片
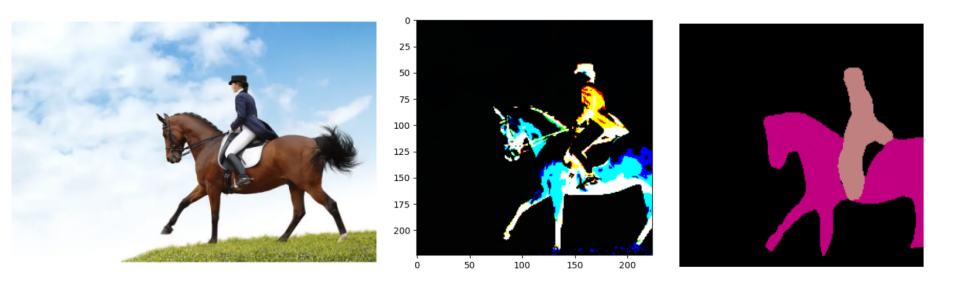
img = Image.open('./models_2/mask.jpg') # 将图片输入模型,进行预测。
# 模型预测的输出是一个OrderedDict结构。deeplabv3_resnet101模型的图片输入尺寸是[224,224],输出形状是[1,21,224,224],代表20+1(背景)个类别。
plt.imshow(img)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show() # 显示加载图片
im = preimg(img)
# 对输入数据进行维度扩展,成为NCHW
inputimg = transform(im).unsqueeze(0)
# 显示用transform转化后的图片
tt = np.transpose(inputimg.detach().numpy()[0],(1,2,0))
plt.imshow(tt.astype('uint8')) # 不然报错:Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers)
plt.show()
output = model(inputimg) # 将图片输入模型
print("输出结果的形状:",output['out'].shape)
# 去掉批次维度,提取结果。使用argmax函数在每个像素点的21个分类中选出概率值最大的索引,为预测结果。
output = torch.argmax(output['out'].squeeze(), dim=0).detach().cpu().numpy()
resultclass = set(list(output.flat))
print("所发现的分类:",resultclass)
# 所发现的分类.{0,13,15}
# 模型从图中识别出了两个类别的内容。索引值13和15分别对应分类名称“马”和“人”。
def decode_segmap(image,nc=21): # 对图片中的每个像素点根据其所属类别进行染色。不同的类别显示不同的颜色。
label_colors = np.array([(0, 0, 0), # 定义每个分类对应的颜色
(128, 0, 0), (0, 128, 0), (128, 128, 0), (0, 0, 128), (128, 0, 128),
(0, 128, 128), (128, 128, 128), (64, 0, 0), (192, 0, 0), (64, 128, 0),
(192, 128, 0), (64, 0, 128), (192, 0, 128), (64, 128, 128), (192, 128, 128),
(0, 64, 0), (128, 64, 0), (0, 192, 0), (128, 192, 0), (0, 64, 128)])
r = np.zeros_like(image).astype(np.uint8) # 初始化RGB
g = np.zeros_like(image).astype(np.uint8)
b = np.zeros_like(image).astype(np.uint8)
for l in range(0, nc): # 根据预测结果进行染色
idx = image == l
print("idx:",idx)
r[idx] = label_colors[l, 0]
g[idx] = label_colors[l, 1]
b[idx] = label_colors[l, 2]
return np.stack([r, g, b], axis=2) # 返回结果
rgb = decode_segmap(output)
img = Image.fromarray(rgb)
plt.axis('off') # 显示模型的可视化结果
print("快完了")
plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()