Funktion implementieren
Passen Sie das MyBatis-Plugin an, um die Fehlerursache, SQL-Parameter und die vollständige SQL-Anweisung auszugeben, wenn eine Ausnahme auftritt, wenn MyBatis SQL ausführt. In der täglichen Entwicklung können wir über die Mybatis-Konfiguration festlegen, ob SQL ausgegeben werden soll, aber die Menge der ausgegebenen Protokolle für alle normal ausgeführten SQL-Anweisungen ist zu groß, daher implementieren wir hier nur die SQL-Anweisungen, die ausgeführt werden, wenn eine Ausnahme auftritt. Das SQL-Framework für die Protokollausgabe stellt SQL nur Platzhalter und entsprechende Parameter zur Verfügung. Wenn Sie dieses SQL testen und ausführen möchten, müssen Sie es manuell selbst spleißen. Um die Effizienz zu verbessern, wird das SQL daher analysiert und in den Plug eingefügt -in. Durch Ersetzen der Symbole kann die endgültige Ausgabe-SQL-Anweisung direkt in der Datenbank ausgeführt werden.
Derzeit ist die Implementierung für abnormale Situationen vorgesehen. Dies kann je nach Bedarf geändert und erweitert werden, z. B. das Drucken aller ausgeführten SQL-Anweisungen oder das Hinzufügen von Statistiken zur Ausführungszeit auf dieser Basis usw.
Plug-in-Entwicklung
Abhängigkeiten hinzufügen
compileOnly 'org.projectlombok:lombok:1.18.26'
compileOnly 'org.slf4j:slf4j-api:2.0.5'
compileOnly 'org.slf4j:slf4j-simple:2.0.5'
compileOnly 'org.mybatis:mybatis:3.2.3'
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.text.DateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.Properties;
import org.apache.ibatis.executor.Executor;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.BoundSql;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.MappedStatement;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.ParameterMapping;
import org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Interceptor;
import org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Intercepts;
import org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Invocation;
import org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Plugin;
import org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Signature;
import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.MetaObject;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.ResultHandler;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.RowBounds;
import org.apache.ibatis.type.TypeHandlerRegistry;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
/**
* 拦截执行SQL发生异常的场景,并将执行错误,执行SQL和参数打印出来
* 拦截Executor里面的query和update方法
*
* @author zhangyu
* @date 2023/6/19
*/
@Intercepts({
@Signature(method = "query", type = Executor.class, args = {
MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class}),
@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "update", args = {
MappedStatement.class, Object.class})})
public class PrintExceptionSqlInterceptor implements Interceptor {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(PrintExceptionSqlInterceptor.class);
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// 获取执行方法的MappedStatement参数
MappedStatement mappedStatement = (MappedStatement) invocation.getArgs()[0];
Object parameter = null;
if (invocation.getArgs().length > 1) {
parameter = invocation.getArgs()[1];
}
String sqlId = mappedStatement.getId();
BoundSql boundSql = mappedStatement.getBoundSql(parameter);
Configuration configuration = mappedStatement.getConfiguration();
Object response;
try {
response = invocation.proceed();
} catch (Exception e) {
// 输出SQL异常信息
LOGGER.error("SQL ErrorException:", e);
LOGGER.info("SQL Parameters: {}", boundSql.getParameterObject());
LOGGER.info("Execute SqlId: {}", sqlId);
LOGGER.info("Completely Execute SQL: {}", getFullSql(configuration, boundSql));
// 根据源异常类型进行返回
if (e instanceof InvocationTargetException) {
throw new InvocationTargetException(e);
} else if (e instanceof IllegalAccessException) {
throw new IllegalAccessException(e.getMessage());
} else {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
return response;
}
/**
* 通过该方法决定要返回的对象是目标对象还是对应的代理
* 不要想的太复杂,一般就两种情况:
* <p>
* 1. return target; 直接返回目标对象,相当于当前Interceptor没起作用,不会调用上面的intercept()方法
* 2. return Plugin.wrap(target, this); 返回代理对象,会调用上面的intercept()方法
*
* @param target 目标对象
* @return 目标对象或者代理对象
*/
@Override
public Object plugin(Object target) {
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
/**
* 用于获取在Configuration初始化当前的Interceptor时时候设置的一些参数
*
* @param properties Properties参数
*/
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
}
/**
* 转义正则特殊字符 ($()*+.[]?\^{}
* \\需要第一个替换,否则replace方法替换时会有逻辑bug
*/
private static String makeQueryStringAllRegExp(String str) {
if (str != null && !"".equals(str)) {
return str.replace("\\", "\\\\")
.replace("*", "\\*")
.replace("+", "\\+")
.replace("|", "\\|")
.replace("{", "\\{")
.replace("}", "\\}")
.replace("(", "\\(")
.replace(")", "\\)")
.replace("^", "\\^")
.replace("$", "\\$")
.replace("[", "\\[")
.replace("]", "\\]")
.replace("?", "\\?")
.replace(",", "\\,")
.replace(".", "\\.")
.replace("&", "\\&");
}
return str;
}
/**
* 获取参数对应的string值
*
* @param obj 参数对应的值
* @return string
*/
private static String getParameterValue(Object obj) {
String value;
if (obj instanceof String) {
value = "'" + obj + "'";
} else if (obj instanceof Date) {
DateFormat formatter =
DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormat.DEFAULT, DateFormat.DEFAULT, Locale.CHINA);
value = "'" + formatter.format(obj) + "'";
} else {
if (obj != null) {
value = obj.toString();
} else {
value = "";
}
}
// 对特殊字符进行转义,方便之后处理替换
return value != null ? makeQueryStringAllRegExp(value) : "";
}
/**
* 获取完整的执行SQL
*/
public static String getFullSql(Configuration configuration, BoundSql boundSql) {
try {
return parseAndExtractFullSql(configuration, boundSql);
} catch (Exception e) {
// 如果解析失败返回原始SQL
return boundSql.getSql();
}
}
/**
* 组装完整的sql语句并把把对应的参数都代入到sql语句里面
*
* @param configuration Configuration
* @param boundSql BoundSql
* @return sql完整语句
*/
private static String parseAndExtractFullSql(Configuration configuration, BoundSql boundSql) {
// 获取mapper里面方法上的参数
Object sqlParameter = boundSql.getParameterObject();
// sql语句里面需要的参数
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
// sql原始语句(?还没有替换成我们具体的参数)
String sql = boundSql.getSql().replaceAll("[\\s]+", " ");
if (!parameterMappings.isEmpty() && sqlParameter != null) {
// sql语句里面的?替换成真实的参数
TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry();
if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(sqlParameter.getClass())) {
sql = sql.replaceFirst("\\?", getParameterValue(sqlParameter));
} else {
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(sqlParameter);
for (ParameterMapping parameterMapping : parameterMappings) {
// 按顺序把?替换成对应的值
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
if (metaObject.hasGetter(propertyName)) {
Object obj = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
sql = sql.replaceFirst("\\?", getParameterValue(obj));
} else if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) {
Object obj = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
sql = sql.replaceFirst("\\?", getParameterValue(obj));
}
}
}
}
return sql;
}
}
JAR-Komponenten ausgeben und verwenden
(1) Methode 1: Manuelle Registrierung
Die manuelle Registrierungsmethode erfordert eine manuelle Registrierung nach Einführung der aktuellen Komponentenabhängigkeiten. Diese Methode wird derzeit bevorzugt. Im Allgemeinen können wir mehrere Mybatis-Plug-Ins in einer JAR-Komponente unterbringen, aber für den Aufrufer müssen diese nicht unbedingt auf das aktuelle Projekt angewendet werden, sodass er die Registrierung entsprechend seinen Anforderungen konfigurieren kann.
@Configuration
public class MyBatisConfig {
@Autowired
private List<SqlSessionFactory> sqlSessionFactoryList;
@PostConstruct
public void addMyInterceptor() {
for (SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory : sqlSessionFactoryList) {
sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration().addInterceptor(new PrintExceptionSqlInterceptor());
}
}
}
(2) Methode 2: Automatische Konfiguration
Wenn Sie möchten, dass der Benutzer die Abhängigkeiten der aktuellen Komponente einführt und sie ohne Konfiguration direkt verwendet, können Sie die automatische Konfiguration verwenden.
Fügen Sie Abhängigkeiten im Zusammenhang mit der automatischen Konfiguration hinzu und legen Sie den Umfang der Abhängigkeiten auf „compileOnly“ fest
compileOnly (
"org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-autoconfigure:2.0.5.RELEASE",
"org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-configuration-processor:2.0.5.RELEASE"
)
Erstellen Sie eine Autokonfigurationsklasse
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnClass;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnProperty;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnWebApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnWebApplication
@ConditionalOnClass({
PrintExceptionSqlInterceptor.class})
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "mybatis-plugin", name = "enabled", havingValue = "true", matchIfMissing = true)
public class MyBatisPluginAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
public PrintExceptionSqlInterceptor yourInterceptor() {
return new PrintExceptionSqlInterceptor();
}
}
Datei META-INF/spring.factories erstellen
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=Benutzerdefinierter Konfigurationsklassenpfad
prüfen
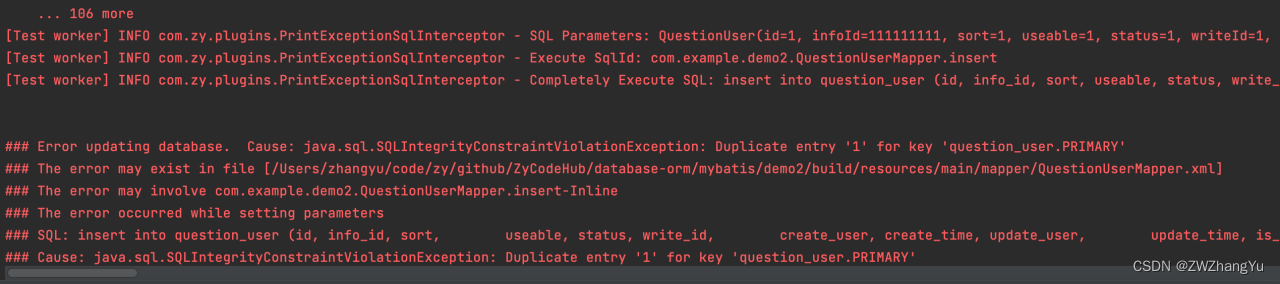
SQL Parameters: QuestionUser(id=1, infoId=111111111, sort=1, useable=1, status=1, writeId=1, createUser=1, createTime=Sun Jun 18 14:15:51 CST 2023, updateUser=1, updateTime=Sun Jun 18 14:15:51 CST 2023, isDeleted=0)
Execute SqlId: com.example.demo2.QuestionUserMapper.insert
Completely Execute SQL: insert into question_user (id, info_id, sort, useable, status, write_id, create_user, create_time, update_user, update_time, is_deleted) values (1, 111111111, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, '2023-6-18 14:15:51', 1, '2023-6-18 14:15:51', 0)
Aktuelle Testszenarien umfassen: Hinzufügen, Löschen, Ändern und Abfragen einzelner Tabellen, Operationen mit mehreren Tabellenparametern, Batch-SQL-Operationen, Kartenparameter, Entitätsklassenparameter usw.
Code
https://github.com/zwzhangyu/ZyCodeHub/tree/main/database-orm/mybatis