1. Antecedentes
Para utilizar el marco de red OpenPCDet y tomar prestados los métodos de procesamiento de datos existentes del conjunto de datos de Kitti, necesitamos organizar y clasificar nuestros datos anotados en carpetas y archivos para facilitar el preprocesamiento y la carga. Por ejemplo, los datos de Kitti están organizados de la siguiente manera:
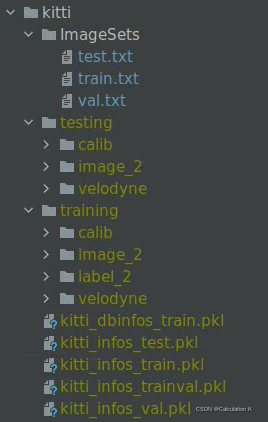
Pero, por lo general, nuestros conjuntos de datos etiquetados generalmente incluyen dos partes (tome la nube de puntos como ejemplo, las imágenes son similares, excepto por la calibración conjunta): una son los datos originales, incluidos los datos originales de la nube de puntos LIDAR, principalmente en formato PCD, que almacena cada uno Las coordenadas tridimensionales del punto y la intensidad de reflexión correspondiente. La segunda parte es la información de la etiqueta confirmada manualmente, que puede incluir identificación del objetivo, categoría, coordenadas (x, y, z), tamaño (largo, ancho, alto), ángulo de rumbo y otra información, que puede ser csv, txt, etc. .formatear archivo.
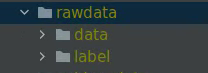
Por lo tanto, necesitamos organizar manualmente nuestro propio conjunto de datos y convertirlo a un formato similar a Kitti. Aquí escribimos un script para organizar automáticamente los datos de acuerdo con la proporción preestablecida de conjunto de entrenamiento, conjunto de verificación y conjunto de prueba.
2. Idea general
1. Lea los archivos de datos en el directorio de trabajo y genere una lista y el número total de archivos de datos.
2. Divida aleatoriamente los índices de cada conjunto de datos según la proporción.
3. Cree una estructura de directorio y copie los archivos correspondientes al índice a la ruta especificada.
3. Implementación específica
import os
import numpy as np
import math
import random
import shutil
from progress.bar import Bar
def Data_PreProcess(rawpath, train_perce, val_perce, test_perce, label_form='txt', data_form='pcd2bin'):
# 1 读取路径下数据文件,并与标签文件名比对,匹配成功生成数据列表和标签列表,以及无标签数据列表
# 2、按预设比例生成各个数据集索引列表
# 3、创建各个数据集文件夹,根据格式要求,重组数据
label_num = 0
data_num = 0
for dir_name in os.listdir(rawpath):
if dir_name == 'label':
label_names = os.listdir(rawpath + 'label/')
label_names.sort()
label_num = len(label_names)
print("=====label==========")
print("Label_nums: ", label_num)
print("Firstlabel: ", label_names[0])
print("Lastlabel : ", label_names[label_num - 1])
elif dir_name == 'data':
data_names = os.listdir(rawpath + 'data/')
data_names.sort()
data_num = len(data_names)
print("=====data==========")
print("data_nums: ", data_num)
print("Firstdata: ", data_names[0])
print("Lastdata : ", data_names[data_num - 1])
else:
continue
if data_num == 0:
print("\nError! can not find 'data' in ", rawpath)
if label_num == 0:
print("\nError! can not find 'label' in ", rawpath)
if data_num != label_num:
print("\nWarning! data_num!=label_num ")
# 检查数据与标签名是否一致
j = 0
for i in range(len(label_names)):
templabel = label_names[i][:-4]
tempdata = data_names[i][:-4]
if templabel != tempdata:
print("label and data not match", templabel, tempdata, i)
j = j + 1
print(" not match num :", j)
# 按比例分配数据集
# 训练集 /和(验证+测试)
train_data, traindata_index, other_data, other_index = DataSplit(data_names, train_perce)
if test_perce == 0 and train_perce + val_perce == 1:
val_data = other_data
valdata_index = other_index
else:
# 再次划分 验证集和测试集
percent = val_perce / (val_perce + test_perce) * 1.0
val_data, valdata_index, test_data, test_index = DataSplit(other_data, percent)
print("=====Spil Set==========")
print("train_num: ", len(train_data))
print("Val_num : ", len(val_data))
print("test_num : ", len(test_data))
# 将分配好的数据配置 写入“dataSets”目录下的 train.txt val.txt test.txt
# 创建目录结构
pre_root_path = rawpath + 'DataGroup/'
DataSets_Path = pre_root_path + '/DataSets'
traindata_Path = pre_root_path + '/training/data'
trainlabel_Path = pre_root_path + '/training/label'
testdata_Path = pre_root_path + '/testing/data'
testlabel_Path = pre_root_path + '/testing/label'
if not os.path.exists(DataSets_Path):
os.makedirs(DataSets_Path)
if not os.path.exists(traindata_Path):
os.makedirs(traindata_Path)
if not os.path.exists(trainlabel_Path):
os.makedirs(trainlabel_Path)
if not os.path.exists(testdata_Path):
os.makedirs(testdata_Path)
if not os.path.exists(testlabel_Path):
os.makedirs(testlabel_Path)
# 创建数据分配文本:
train_filename = DataSets_Path + '/train.txt'
val_filename = DataSets_Path + '/val.txt'
test_filename = DataSets_Path + '/test.txt'
train_cluster = []
test_cluster = []
train_file = open(train_filename, 'w')
for i in train_data:
index = i.rfind('.')
name = i[:index]
train_file.write(name + '\n')
train_cluster.append(name)
train_file.close()
val_file = open(val_filename, 'w')
for i in val_data:
index = i.rfind('.')
name = i[:index]
val_file.write(name + '\n')
train_cluster.append(name)
val_file.close()
test_file = open(test_filename, 'w')
for i in test_data:
index = i.rfind('.')
name = i[:index]
test_file.write(name + '\n')
test_cluster.append(name)
test_file.close()
# 将分配好的数据配置 写入“prepcess”目录下的 training val testing
# training copy data to
data_srcfile = rawpath + '/data/'
label_srcfile = rawpath + '/label/'
tra_data_dstpath = traindata_Path + '/'
tra_label_dstpath = trainlabel_Path + '/'
test_data_dstpath = testdata_Path + '/'
test_label_dstpath = testlabel_Path + '/'
bar = Bar('cluster train_data...', max=len(train_cluster), fill='#', suffix='%(percent)d%%')
for i in train_cluster:
if data_form=='pcd':
pcd2bin(data_srcfile + i + '.pcd', tra_data_dstpath + i + '.bin')
elif data_form == 'bin':
shutil.copy(data_srcfile + i + '.bin', tra_data_dstpath + i + '.bin') # 复制文件 到 training/data
else:
print("Unkown data form! 'bin' or 'pcd' can be read")
if label_form=='csv2txt':
#
print(1)
else:
shutil.copy(label_srcfile + i + '.csv', tra_label_dstpath + i + '.csv') # 复制文件 到 training/label
bar.next()
bar.finish()
bar = Bar('cluster test_data...', max=len(test_cluster), fill='#', suffix='%(percent)d%%')
for i in test_cluster:
if data_form == 'pcd':# 复制文件 到 testing/data
pcd2bin(data_srcfile + i + '.pcd', test_data_dstpath + i + '.bin')
elif data_form == 'bin':
shutil.copy(data_srcfile + i + '.bin', test_data_dstpath + i + '.bin')
else:
print("Unkown data form! 'bin' or 'pcd' can be read")
if label_form=='csv2txt':
#
print(1)
else:
shutil.copy(label_srcfile + i + '.csv', test_label_dstpath + i + '.csv') # 复制文件 到 testing/label
bar.next()
bar.finish()
def DataSplit(raw_data, get_precet):
# 获取数据长度,并生成相同长度索引
dataA = []
dataB = []
index_B = []
length = len(raw_data)
index_rawdata = np.arange(0, length, 1) # 连续索引
index_rawdata_copy = index_rawdata[:] # 复制一分
if get_precet < 1 and get_precet > 0:
get_num = math.floor(length * get_precet) # 向下取整 避免溢出
index_A = random.sample(range(0, length), get_num)
for j in index_A:
dataA.append(raw_data[j])
index_rawdata_copy[j] = -1
for k in index_rawdata_copy:
if k != -1:
index_B.append(k)
dataB.append(raw_data[k])
else:
print('Precentage out of range [0,1]')
return dataA, index_A, dataB, index_B
def read_pcd(filepath):
lidar = []
i=0
with open(filepath, 'r') as f:
line = f.readline().strip()
while line:
linestr = line.split(" ")
i = i + 1
if i>10:#skip pcd file head
if len(linestr) == 3:# only x,y,z
linestr_convert = list(map(float, linestr))
linestr_convert.append(0)
lidar.append(linestr_convert)
if len(linestr) == 4:# x,y,z,i
linestr_convert = list(map(float, linestr))
lidar.append(linestr_convert)
line = f.readline().strip()
return np.array(lidar)
def pcd2bin(pcd_fullname, bin_fullname):
pl = read_pcd(pcd_fullname)
pl = pl.reshape(-1, 4).astype(np.float32) # x,y,z,i
pl.tofile(bin_fullname)
if __name__ == '__main__':
Data_PreProcess("/data/OpenPCDet/data/rawdata/", 0.5, 0.3, 0.2, 'txt', 'bin')
4. La estructura del directorio final.
