1. Dirección de descarga del artículo:
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2104.00680.pdf
2. Dirección de descarga del código:
https://github.com/zju3dv/LoFTR
3. Cree un nuevo entorno virtual de Python y actívelo.
conda create -n LoFTR python=3.7
source activate LoFTR4. Instale las bibliotecas necesarias.
pip install torch==1.6.0 einops yacs kornia opencv-python matplotlib5. Descargue bibliotecas adicionales
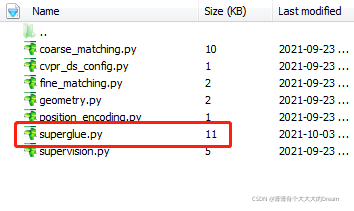
En la siguiente URL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/magicleap/SuperGluePretrainedNetwork/master/models/superglue.py
Descargar superglue.py
Luego colóquelo en la ruta src/loftr/utils
6. Descargue el modelo previamente entrenado
Enlace: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1dwUDx6A9lRMBkCSowLIz5Q
Código de extracción: jlcl
Colocar en la ruta:weights/outdoor_ds.ckpt
7. Demostración en ejecución
1) Agregue la variable de entorno de la ruta del proyecto:
export PYTHONPATH=$PYTHONPATH:/home1/users/XXX/Codes/LoFTR-master/2) Cree un nuevo mydemo.py y escriba el siguiente código:
import os
os.chdir("..")
from copy import deepcopy
# import os
# os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "0"
import torch
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.cm as cm
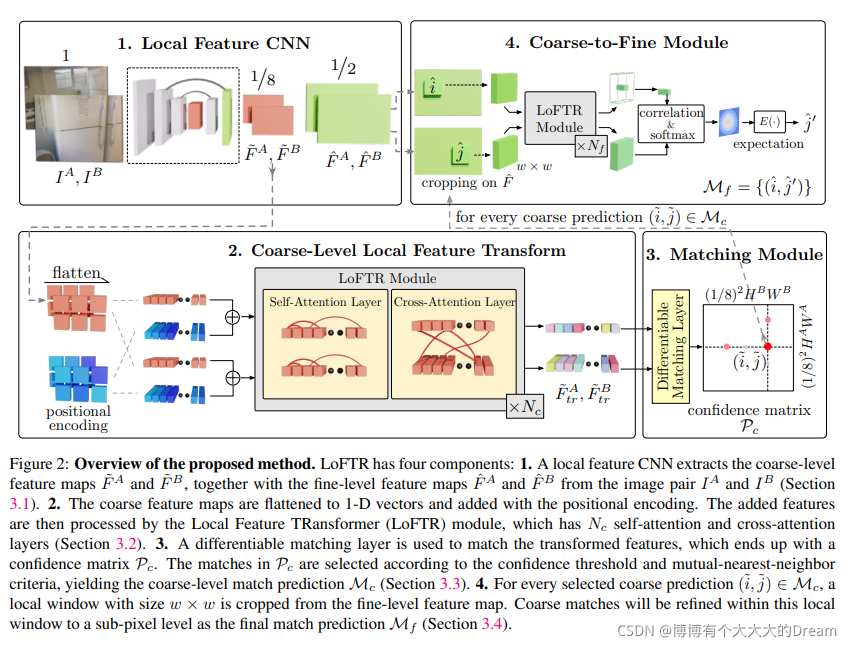
from src.utils.plotting import make_matching_figure
from src.loftr import LoFTR, default_cfg
# The default config uses dual-softmax.
# The outdoor and indoor models share the same config.
# You can change the default values like thr and coarse_match_type.
matcher = LoFTR(config=default_cfg)
matcher.load_state_dict(torch.load("/home1/users/XXX/Codes/LoFTR-master/weights/outdoor_ds.ckpt")['state_dict'])
matcher = matcher.eval().cuda()
default_cfg['coarse']
# Load example images
img0_pth = "/home1/users/XXX/Codes/LoFTR-master/assets/phototourism_sample_images/united_states_capitol_26757027_6717084061.jpg"
img1_pth = "/home1/users/XXX/Codes/LoFTR-master/assets/phototourism_sample_images/united_states_capitol_98169888_3347710852.jpg"
img0_raw = cv2.imread(img0_pth, cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
img1_raw = cv2.imread(img1_pth, cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
img0_raw = cv2.resize(img0_raw, (img0_raw.shape[1]//8*8, img0_raw.shape[0]//8*8)) # input size shuold be divisible by 8
img1_raw = cv2.resize(img1_raw, (img1_raw.shape[1]//8*8, img1_raw.shape[0]//8*8))
img0 = torch.from_numpy(img0_raw)[None][None].cuda() / 255.
img1 = torch.from_numpy(img1_raw)[None][None].cuda() / 255.
batch = {'image0': img0, 'image1': img1}
# Inference with LoFTR and get prediction
with torch.no_grad():
matcher(batch)
mkpts0 = batch['mkpts0_f'].cpu().numpy()
mkpts1 = batch['mkpts1_f'].cpu().numpy()
mconf = batch['mconf'].cpu().numpy()
# Draw
color = cm.jet(mconf)
text = [
'LoFTR',
'Matches: {}'.format(len(mkpts0)),
]
fig = make_matching_figure(img0_raw, img1_raw, mkpts0, mkpts1, color, text=text,path="LoFTR-master/LoFTR-colab-demo.pdf")
3) Ejecute python mydemo.py para obtener el resultado: