1.base64
Utilice la herramienta para descifrar base64 directamente

2 César
Use herramientas para descifrar y encontrar que el desplazamiento es 12

3.Morse
Piense en 1 como y 0 como.

Convertir a minúsculas
4. Codificación mixta
Primera decodificación base64:
LzExOS8xMDEvMTA4Lzk5LzExMS8xMDkvMTAxLzExNi8xMTEvOTcvMTE2LzExNi85Ny85OS8xMDcvOTcvMTEwLzEwMC8xMDAvMTAxLzEwMi8xMDEvMTEwLzk5LzEwMS8xMTkvMTExLzExNC8xMDgvMTAw
Luego convierta el Unicode decodificado a ASCII, o póngalo directamente en el archivo html para abrir
LzExOS8xMDEvMTA4Lzk5LzExMS8xMDkvMTAxLzExNi8xMTEvOTcvMTE2LzExNi85Ny85OS8xMDcvOTcvMTEwLzEwMC8xMDAvMTAxLzEwMi8xMDEvMTEwLzk5LzEwMS8xMTkvMTExLzExNC8xMDgvMTAw
Luego realiza un descifrado en base64
/119/101/108/99/111/109/101/116/111/97/116/116/97/99/107/97/110/100/100/101/102/101/110/99/101/119/111/114/108/100
Finalmente, ASCII se convierte en una cadena

5. Cifrado de energía
Se dice que el cifrado de potencia no es el caso. Aquí consideramos directamente el 0 como un separador y sumamos los números en cada grupo, y los números resultantes se mapean según el alfabeto.
s=['88421','122','48','2244','4','142242','248','122']
flag=''
x=0
a={
1:"A",2:'B',3:'C',4:'D',5:'E',6:'F',7:'G',8:'H',9:'I',10:'J',11:'K',12:'L',13:'M',14:'N',15:'O',16:'P',17:'Q',18:'R',19:'S',20:'T',21:'U',22:'V',23:'W',24:'X',25:'Y',26:'Z'}
for i in range(8):
for j in range(len(s[i])):
x+=int(s[i][j])
flag+=a[x]
x=0
print(flag)
#WELLDONE
Obtenga el resultado: BIEN HECHO
6.Railfence
Contraseña de la cerca: el
número es 5

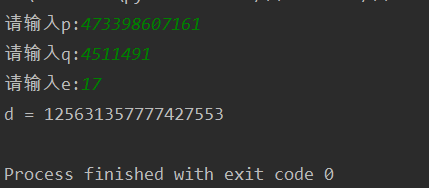
7.easy_RSA
Dado p, q, e, encuentre d
def exgcd(a, n):
if n == 0:
return 1, 0
else:
x, y = exgcd(n, a % n)
x, y = y, x - (a // n) * y
return x, y
def getReverse(a, n):
re, y = exgcd(a, n)
while(re < 0):
re += n
return re
if __name__ == "__main__":
p = int(input("请输入p:"))
q = int(input("请输入q:"))
e = int(input("请输入e:"))
d = getReverse(e, (p - 1)*(q - 1))
print('d = ' + str(d))
8. Más que Morse
Descifrado de tocino después del descifrado de Moss
may_be_have_another_decodehhhhaaaaabaabbbaabbaaaaaaaabaababaaaaaaabbabaaabbaaabbaabaaaababaabaaabbabaaabaaabaababbaabbbabaaabababbaaabbababaaabaabaaaaabba
Tomar decodificar
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding=utf -*-
import re
table ={
'a': 'aaaaa', 'b': 'aaaab', 'c': 'aaaba', 'd': 'aaabb', 'e': 'aabaa', 'f': 'aabab', 'g': 'aabba',
'h': 'aabbb', 'i': 'abaaa', 'j': 'abaab', 'k': 'ababa', 'l': 'ababb', 'm': 'abbaa', 'n': 'abbab',
'o': 'abbba', 'p': 'abbbb', 'q': 'baaaa', 'r': 'baaab', 's': 'baaba', 't': 'baabb', 'u': 'babaa',
'v': 'babab', 'w': 'babba', 'x': 'babbb', 'y': 'bbaaa', 'z': 'bbaab'}
def bacon(cipher):
msg = ''
codes = re.findall(r'.{5}', cipher)
for code in codes:
if code == '':
msg += ' '
else:
UNCODE = dict(map(lambda t: (t[1], t[0]), table.items()))
msg += UNCODE[code]
return msg
if __name__ == '__main__':
cipher = 'aaaaabaabbbaabbaaaaaaaabaababaaaaaaabbabaaabbaaabbaabaaaababaabaaabbabaaabaaabaababbaabbbabaaabababbaaabbabaaabaabaabaaaabbabbaabbaabaabaaabaabaabaababaabbabaaaabbabaabba'
plaintext = bacon(cipher)
print(plaintext)
9.fácil desafío
pyc en código py
https://tool.lu/pyc/
Descifrar:
import base64
def decode1(ans):
s = ''
for i in ans:
x=(ord(i)-25)^36
s += chr(x)
return s
def decode2(ans):
s = ''
for i in ans:
i=i^36
x=i-36
s += chr(x)
return s
def decode3(ans):
return base64.b32decode(ans)
final= 'UC7KOWVXWVNKNIC2XCXKHKK2W5NLBKNOUOSK3LNNVWW3E==='
flag=decode1(decode2(decode3(final)))
print(flag)
10.Normal_RSA
Utilice OpenSSL de kali para extraer la información del archivo pem
openssl rsa -pubin -text -modulus -in warmup -in pubkey.pem
El módulo aquí es la representación hexadecimal de n de RSA
Convierta hexadecimal a decimal, luego descomponga números grandes:
http://www.factordb.com/
275127860351348928173285174381581152299
319576316814478949870590164193048041239
Use rsatool.py para generar una clave privada, e toma 65537
python rsatool.py -o private.pem -e 65537 -p 275127860351348928173285174381581152299 -q 319576316814478949870590164193048041239
Luego use OpenSSL para descifrar flag.enc
openssl rsautl -decrypt -in flag.enc -inkey private.pem
11. Cifrado de máquina rotativa
Rotación de violencia directa, saque el valor de cada rotación y luego pruebe las banderas una por una
import re
sss='1: <ZWAXJGDLUBVIQHKYPNTCRMOSFE<2: <KPBELNACZDTRXMJQOYHGVSFUWI<3: <BDMAIZVRNSJUWFHTEQGYXPLOCK<4: <RPLNDVHGFCUKTEBSXQYIZMJWAO<5: <IHFRLABEUOTSGJVDKCPMNZQWXY<6: <AMKGHIWPNYCJBFZDRUSLOQXVET<7: <GWTHSPYBXIZULVKMRAFDCEONJQ<8: <NOZUTWDCVRJLXKISEFAPMYGHBQ<9: <XPLTDSRFHENYVUBMCQWAOIKZGJ<10: <UDNAJFBOWTGVRSCZQKELMXYIHP<11: <MNBVCXZQWERTPOIUYALSKDJFHG<12: <LVNCMXZPQOWEIURYTASBKJDFHG<13: <JZQAWSXCDERFVBGTYHNUMKILOP<'
m='NFQKSEVOQOFNP'
#将sss转化成列表,正则表达式,re.S在此模式下"."的匹配不受限制,可匹配所有字符
content=re.findall(r'<(.*?)<',sss,re.S)
iv=[2,3,7,5,13,12,9,1,8,10,4,11,6]
print(content)
lll=[]
for i in range(13):
index=content[iv[i]-1].index(m[i])
lll.append(index)
print(lll)
for i in range(0,26):
flag=""
for j in range(13):
flag+=content[iv[j]-1][(lll[j]+i)%26]
print(flag.lower())
12.easy_ECC
Problema matemático difícil, sin estudio en profundidad, aquí está el valor para proporcionar el código, si necesita saber más, consulte https://bbs.pediy.com/thread-253672.htm
import collections
def inverse_mod(k, p):
"""Returns the inverse of k modulo p.
This function returns the only integer x such that (x * k) % p == 1.
k must be non-zero and p must be a prime.
"""
if k == 0:
raise ZeroDivisionError('division by zero')
if k < 0:
# k ** -1 = p - (-k) ** -1 (mod p)
return p - inverse_mod(-k, p)
# Extended Euclidean algorithm.
s, old_s = 0, 1
t, old_t = 1, 0
r, old_r = p, k
while r != 0:
quotient = old_r // r
old_r, r = r, old_r - quotient * r
old_s, s = s, old_s - quotient * s
old_t, t = t, old_t - quotient * t
gcd, x, y = old_r, old_s, old_t
assert gcd == 1
assert (k * x) % p == 1
return x % p
# Functions that work on curve points #########################################
def is_on_curve(point):
"""Returns True if the given point lies on the elliptic curve."""
if point is None:
# None represents the point at infinity.
return True
x, y = point
return (y * y - x * x * x - curve.a * x - curve.b) % curve.p == 0
def point_neg(point):
"""Returns -point."""
assert is_on_curve(point)
if point is None:
# -0 = 0
return None
x, y = point
result = (x, -y % curve.p)
assert is_on_curve(result)
return result
def point_add(point1, point2):
"""Returns the result of point1 + point2 according to the group law."""
assert is_on_curve(point1)
assert is_on_curve(point2)
if point1 is None:
# 0 + point2 = point2
return point2
if point2 is None:
# point1 + 0 = point1
return point1
x1, y1 = point1
x2, y2 = point2
if x1 == x2 and y1 != y2:
# point1 + (-point1) = 0
return None
if x1 == x2:
# This is the case point1 == point2.
m = (3 * x1 * x1 + curve.a) * inverse_mod(2 * y1, curve.p)
else:
# This is the case point1 != point2.
m = (y1 - y2) * inverse_mod(x1 - x2, curve.p)
x3 = m * m - x1 - x2
y3 = y1 + m * (x3 - x1)
result = (x3 % curve.p,
-y3 % curve.p)
assert is_on_curve(result)
return result
def scalar_mult(k, point):
"""Returns k * point computed using the double and point_add algorithm."""
assert is_on_curve(point)
if k < 0:
# k * point = -k * (-point)
return scalar_mult(-k, point_neg(point))
result = None
addend = point
while k:
if k & 1:
# Add.
result = point_add(result, addend)
# Double.
addend = point_add(addend, addend)
k >>= 1
assert is_on_curve(result)
return result
# Keypair generation and ECDHE ################################################
def make_keypair():
"""Generates a random private-public key pair."""
private_key = curve.n
public_key = scalar_mult(private_key, curve.g)
return private_key, public_key
EllipticCurve = collections.namedtuple('EllipticCurve', 'name p a b g n h')
curve = EllipticCurve(
'secp256k1',
# Field characteristic.
p=15424654874903,
# Curve coefficients.
a=16546484,
b=4548674875,
# Base point.
g=(6478678675,5636379357093),
# Subgroup order.
n=546768,
# Subgroup cofactor.
h=1,
)
private_key, public_key = make_keypair()
print("private key:", hex(private_key))
print("public key: (0x{:x}, 0x{:x})".format(*public_key))
print("x + y = " + str(public_key[0] + public_key[1]))
Bienvenido a seguir la cuenta oficial para obtener más información:
