1, java sets in
(1) single set (collection):
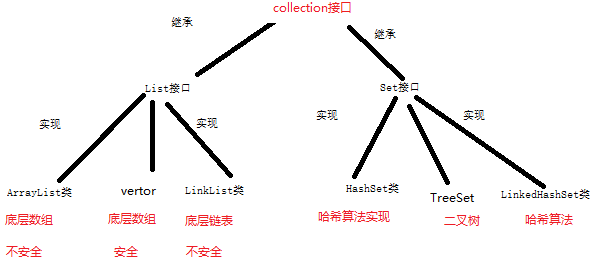
List collection: Access orderly, index, elements can be repeated
Set collections: random access, there is no index element can be repeated (according equals and hashCode judgment), that is to say if the object is to be stored in a Set must override equals and hashCode method.
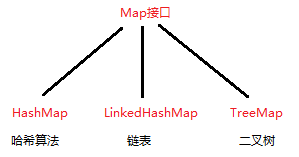
(2) Double-row set (Map):
2, the difference Arraylist and linkedList
(1) Features:
Arraylist underlying array is used: a index, query fast, slow additions, the memory array is a contiguous memory, insertion or deletion of large number of elements to be moved
LinkedList underlying list is used: the current element is divided into the pointer field and data field, a pointer field storing an address or the element, starting from the head, a query to find a low query efficiency. Does not require the insertion elements move in memory, you can just change the reference point, the insertion or deletion of high efficiency.
(2) be used:
In case of queries more, less insertion deleted: ArrayList
LinkedList: Use the query is relatively small, more insertions and deletions case
3, HashMap and HashTable distinction and connection
(1) the same point:
It can be used to store the data of key_value
(2) differences:
HashMap as the key can be null or value, but not HashTable
HashMap thread-safe, high efficiency, HashTable thread-safe, low efficiency
4, HashTable with distinction and connection ConcurrentHashMap
Using the segment, equivalent to a hashmap into a plurality of segments, each segment assigned a lock so that it can support multi-threaded access, therefore, the more efficient the case of multi-threaded.