1, the list format:
namesList = ['xiaoWang','xiaoZhang','xiaoHua']C than an array of powerful local language that elements in the list can be different types of
testList = [1, 'a']
2, print list
nameList=['jack1','jack2','jack3'] print(nameList[0]) print(nameList[1]) print(nameList[2])
result:
jack1
jack2
jack3
3, circular list traversal
① using a for loop
② use a while loop
. 1 # for loop Printing List 2 ageList = [12, 14, ] . 3 for Age in ageList: . 4 Print (Age, End = " " ) . 6 # the while loop to print a listing . 7 I = 0 . 8 the while I < len (ageList) : . 9 Print (ageList [I], End = " " ) 10 I +. 1 =
Print Results:
12 14 17
4, a list of related operations
① add elements ( "add" append, extend, insert)
append: You can add elements to the list by append
1 # increase the append 2 NAME_LIST = [ " Xiao Ming " , " Mike " , " Wang " ] 3 name = the INPUT ( " Please enter the name you want to add: " ) 4 name_List.append (name) 5 for name in NAME_LIST: . 6 Print (name, End = " " )
Print Results:

extend: one by one can add another set of the elements extend through to the list
1 # 增 extend 2 a=[1,2] 3 b=[3,4] 4 b.append(a) 5 for i in b: 6 print(i,end=" ") 7 print( ) 8 b.extend(a) 9 for i in b: 10 print(i,end=" ")
Print Results:
insert
insert (index, object) is inserted into the specified position in front of the element object index
1 # 增 insert 2 arr1=[1,2,3] 3 arr1.insert(2,'a') 4 for i in arr1: 5 print(i,end=" ")
Print Results:
1 2 a 3
② modify an element ( "change")
Modify elements of time, to determine which element is to be modified by the subscript, and then to make changes
1 # 改 2 list1=['a','b','1','d'] 3 list1[2]='c' 4 for i in list1: 5 print(i,end=" ")
Print Results:
a b c d
Find ③ element ( "check" in, not in, index, count)
The so-called lookup, is to look at the specified element exists
Python find common method is as follows:
in (there is), if there is then the result is true, otherwise false
not in (does not exist), if not present then the result is true, otherwise false
index: find the index
count: Find the number of occurrences
1 # to check in, not in 2 NAME_LIST = [ " Mike " , " Zhang " , " Wang " ] 3 find_name the INPUT = ( " Please enter the name you want to find: " ) 4 IF find_name in NAME_LIST: 5 Print ( " find the name you're looking for " ) 6 the else : 7 Print ( " not finding what you're looking for the name " ) 8 9 Print () 10 11 # 查 index count 12 str=['a','c','b','d','c'] 13 print(str.index('b',0,3)) # 2 14 print(str.index('c')) # 1 15 print(str.count('c')) # 2
④ remove elements ( "delete" del, pop, remove)
Common delete method list elements are:
del: delete according to index
pop: Removes the last element
remove: remove as value elements
1 # deletion del 2 MOVIE_NAME = [ ' spirited away ' , ' Zha ' , ' weather son ' , ' Chinatown Holmes ' ] . 3 del MOVIE_NAME [1 ] . 4 for I in MOVIE_NAME: . 5 Print (I)
Print Results:
Spirited Away
Weather son
Chinatown Holmes
1 # puncturing POP 2 film_name = [ ' spirited away ' , ' Zha ' , ' weather son ' , ' Chinatown Holmes ' ] . 3 film_name.pop () . 4 for I in film_name: . 5 Print (I)
Print Results:
Spirited Away
Rebels
Weather son
1 # 删 remove 2 a=[1,2,3,4,5] 3 a.remove(3) 4 for i in a: 5 print(i)
Print Results:
1 2 4 5
⑤ sort (sort, reverse)
sort the list is rearranged in a specific order, the default is small to large, reverse = True parameters can be changed to reverse, descending order. reverse method is to list Retrograde
1 # 排序 2 p=[1,7,3,9,0,3] 3 p.sort() 4 for i in p: 5 print(i,end=" ") # 0 1 3 3 7 9
6 print() 7 p.sort(reverse=True) 8 for i in p: 9 print(i, end=" ") #9 7 3 3 1 0
10 print() 11 p.reverse() 12 for i in p: 13 print(i,end=" ") # 0 1 3 3 7 9
⑥ nested list
A list of the elements is a list, then this is a nested list
school_names = [['北京大学','清华大学'],
['南开大学','天津大学','天津师范大学'],
['山东大学','中国海洋大学']]
application:
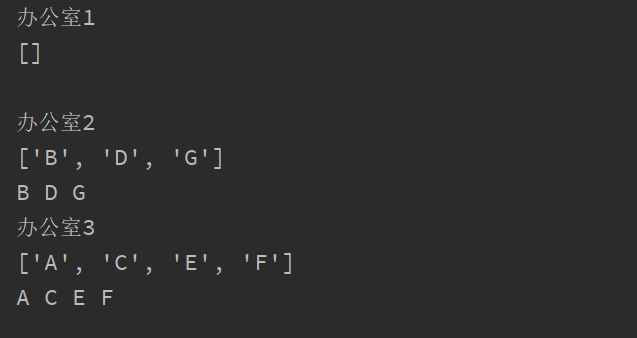
A school, there are three offices, there are eight teachers awaiting distribution station, write procedures, were randomly assigned to complete
. 1 Import Random 2 Office = [[], [], []] # three offices . 3 Teachers = [ ' A ' , ' B ' , ' C ' , ' D ' , ' E ' , ' F. ' , ' G ' ] # 8 teacher . 4 . 5 for teacher in teachers: . 6 index the random.randint = (0,2 ) . 7 Office [index] .append (teacher) . 8 9 i=1 10 for tmp in office: 11 print("办公室%d" % i) 12 i += 1 13 print(tmp) 14 for j in tmp: 15 print( j,end=" ") 16 print()