
[Press] Since the Citibank report in March this year listed RWA as the most explosive innovation direction in the next ten years, the popularity of RWA in the Web3 circle has continued to rise. Especially in Hong Kong and Singapore, RWA is regarded as one of the breakthroughs that have the opportunity to lead the world in the Web3 field. RWA is one of the main battlefields of ERC-3525. I have been paying close attention to it. I have read a lot of articles, written some, and participated in more related seminars. However, I have always felt that the information and opinions are fragmented and not systematic enough. .
Spinach is a rising star in the field of industry research and has published many influential reports before. We got to know each other because we were both in Melbourne. A few months ago, he expressed his intention to join SFT Labs and work with me to promote the ERC-3525 ecological incubation. For me, it's quite stressful. Young people are talented, will their future be delayed by staying with me? However, he said that after independent and prudent analysis and research, he truly believed in the underlying logic, technical advantages and application potential of ERC-3525, and also recognized the culture of our team. Joining us was a major risk for him after careful consideration. invest. I'm glad that he can use this way of thinking to plan his own life course at such a young age. Recalling that when I was his age, I still had my foot in the watermelon rind when it came to choosing an industry and a life path. While sighing, I am very happy that the Web3 industry can not only attract talents, but also accelerate the thinking growth of talents. I am also determined to contribute to the development of the industry. It provides a good training environment.
In the past few months, as the research leader, Spinach has not only participated in the incubation of major projects in SFT Labs, but also continued to leverage his advantages to conduct in-depth research on the industry and rapidly improve in both knowledge and practice. With our support, he mainly used his spare time to write this long panoramic RWA research report with our close partner Annabella from the zCloak team, which not only systematically sorted out the ins and outs of the relevant fields, but also provided A well-founded analysis of future trends was conducted. Many of these contents also reflect and inspire the ERC-3525 ecosystem and the strategies and tactics of SFT Labs.
According to Citibank’s forecast, RWA’s annual compound revenue share will reach 75% by the end of 2027. However, this growth is not linear or exponential, but is linear, that is, after a certain turning point, there is almost explosive growth. For this prospect, it is unrealistic to operate on the right side. You must enter the market in advance on the left side, study hard, actively participate, and wait patiently. ERC-3525 was born for this, and SFT Labs is also actively planning for this. This report is SFT Labs sharing some ideas of RWA fellow travelers, hoping that many years later it will prove our foresight, just like the "What is Same as the article "Digital Assets".
With the author's permission, I am reprinting this long research report in full here. Interested friends can follow his official account.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Limited to personal knowledge, the contents of this article are all personal opinions. If you have any questions, please point them out for discussion.
Word count: This research report exceeds 28,000 words and covers a wide range of topics. Please read patiently.
Core ideas:
Crypto’s RWA logic mainly revolves around how to transfer the income rights of assets that generate income (such as the income rights of U.S. bonds, fixed income, stocks, etc.) to the chain. Put off-chain assets on the chain to mortgage loans to obtain the liquidity of on-chain assets, and move various real-life assets onto the chain for transactions (such as sand, minerals, real estate, gold, etc.), reflecting the crypto world’s unilateral demand for real-world assets, and there are many obstacles in terms of compliance
The future key development direction of Real World Asset Tokenization will be a system based on the Permission Chain promoted by traditional financial institutions, regulatory agencies, central banks and other authoritative institutions. A new financial system using DeFi technology, and to realize this system requires a computational system (blockchain technology) + non-computational system (such as legal system) + on-chain identity System and privacy protection technology + on-chain legal currency (CBDC, tokenized deposits, legal stablecoins) + complete infrastructure (low-threshold wallets, oracles, cross-chain technology, etc.)
Blockchain is the first technical means to effectively support the digitization of contracts after the development of computers and networks. So it can be said that the blockchain is essentially a digital contract platform, and the contract is the basic expression form of the asset. Token is the contract. After forming the digital carrier of assets, the blockchain has therefore become the digital expression/tokenized expression of assets, that is, the ideal infrastructure for digital assets/tokenized assets
As a distributed system jointly maintained by multiple parties, blockchain supports the creation, verification, storage, circulation and execution of digital contracts and other related operations, solving the problem of transmitting trust. And as a "computational system", blockchain can satisfy human beings' demands for "repeatable processes and testable results", Therefore, DeFi has become It has created a "computational" innovation in the financial system, replacing the "computational" part of financial activities. Automatic execution can reduce costs and increase efficiency while also achieving programmability. , but the "non-computational" part, that is, the part based on human cognition, cannot be replaced by blockchain. Therefore, the current DeFi system does not cover credit, and unsecured lending based on credit has not yet been implemented in the current DeFi system. , the reasons for this phenomenon include the current lack of an identity system that expresses "relational identity" in the blockchain and the lack of a legal system to protect the rights and interests of both parties
In the traditional financial system, the significance of Real World Asset Tokenization is to create digital numbers of real world assets (such as stocks, financial derivatives, currencies, equity, etc.) on the blockchain. Representation,extends the benefits of distributed ledger technology to enable exchange and settlement across a wide range of asset classes
Financial institutions further improve efficiency by adopting DeFi technology.Use smart contracts to replace the "calculation" links in traditional finance and automatically execute various financial transactions according to predetermined rules and conditions. Transactions,enhancing programmable features. This not only reduces labor costs, but in certain situations, it can give enterprises new possibilities, especially providing innovative solutions to financing problems for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMSE). Opening a door with great potential for the financial system
With the increasing attention and recognition of blockchain and tokenization technology in the traditional financial field and governments of various countries, and the continuous improvement of blockchain infrastructure technology, Blockchain is on the road to integrating with traditional world architecture and solving real pain points in real-world application scenarios, providing practical solutions for actual scenarios, rather than being limited to a "parallel world" that is separated from the real world< /span>
In the future permissioned chain structure with multiple different jurisdictions and regulatory systems, cross-chain technology is particularly important to solve the problems of interoperability and liquidity fragmentation. In the future, on-chain tokenized assets will exist on public blockchains and regulated permissioned chains operated by financial institutions, and any cross-chain protocol like CCIP can be used to Tokenized assets on the blockchain are connected to achieve interoperability and realize the interoperability of thousands of chains
Currently,many countries around the world are actively promoting blockchain-related legal and regulatory frameworks. At the same time, blockchain infrastructure, such as wallets, cross-chain protocols, oracles, various middleware, etc., are being rapidly improved, and the central bank’s digital currency CBDC is also constantly being implemented and can express more complex assets. Types of token standards are also constantly emerging, such as ERC-3525. Coupled with the development of privacy protection technology, especially the continued development of zero-knowledge proof technology, and the increasing maturity of on-chain identity systems, we seem to be in the midst of a large-scale adoption of blockchain technology. On the eve of application
Table of contents
1. Introduction to the background of asset tokenization
RWA from a Crypto perspective
RWA from the perspective of TradFi
2. Starting from the first principles of blockchain, what problems does blockchain solve?
Blockchain is the ideal infrastructure for tokenized expression of assets
Blockchain satisfies human demands for “computability”
DeFi is a “computational” financial innovation
3. Asset Tokenization: Transformative Effect on the Traditional Financial System
Establish a credible global payment platform, reduce costs and increase efficiency
Programmability and transparency
4. What else is needed to realize asset tokenization Mass Adoption?
Complete legal system guarantee and permission chain
Identity system and privacy protection
On-chain fiat currency
·Oracles and cross-chain protocols
·Low threshold wallet
5. Future Outlook
1. Introduction to the background of asset tokenization
Asset tokenization refers to the process of expressing assets in the form of tokens on a programmable blockchain platform. Generally, assets that can be tokenized are divided into tangible assets (real estate, collections) goods, etc.) and intangible assets (financial assets, carbon credits, etc.), this technology transfers assets recorded on the traditional ledger system to a shared programmable ledger platform [1]. It is a disruptive innovation for the traditional financial system and will even affect the entire future financial and monetary system of mankind.
First of all, the author would like to mention an observed phenomenon: "There are two groups with completely different views on RWA asset tokenization." The author calls them Crypto's RWA and TradFi's RWA, and the RWA described in this article is RWA from a TradFi perspective.
RWA from a Crypto perspective
First, let’s talk about Crypto’s RWA:Crypto’s RWA is what the author calls it the Crypto world’s unilateral demand for the rate of return on real-world financial assets, the main background is that in the context of the Federal Reserve's continuous interest rate hikes and balance sheet reduction, high interest rates have significantly affected the valuation of the risk market, and the balance sheet reduction has significantly drained the liquidity of the crypto market, resulting in a continuous decline in the yield of the DeFi market. At this time The risk-free rate of return on U.S. bonds, which is as high as about 5%, has become popular in the crypto market. The most popular one is MakerDAO’s massive purchase of U.S. bonds this year. As of September 20, 2023, MakerDAO has purchased more than 2.9 billion Real-world assets such as U.S. Treasuries.
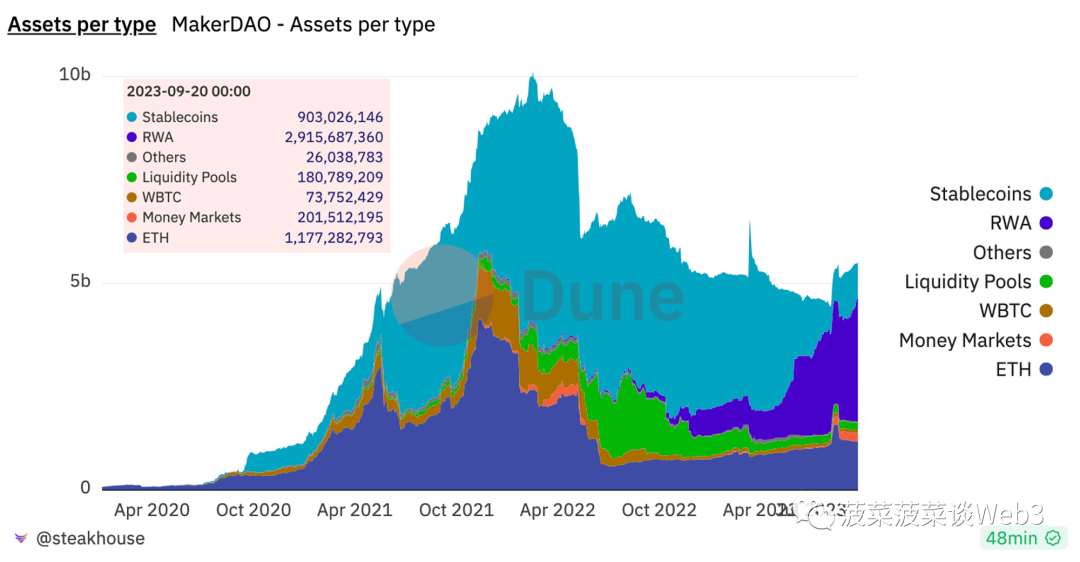
Data source: https://dune.com/steakhouse/makerdao
The significance of MakerDAO's purchase of US dollar treasury bonds is that DAI can use the ability of external credit to diversify the assets behind it, and the long-term additional income brought by US treasury bonds can help DAI Stabilizing its own exchange rate, increasing the flexibility of issuance, and incorporating US Treasury bonds into the balance sheet can reduce DAI's dependence on USDC and reduce single-point risks [2]. Not only that, since all the income from U.S. debt will flow into MakerDAO’s treasury, MakerDAO has recently increased the demand for DAI by sharing part of the income from its U.S. debt and raising the interest rate of DAI to 8% [3].
MakerDAO’s approach is obviously not replicable for all projects. With the skyrocketing price of MRK tokens and the market’s heightened sentiment towards the RWA concept,except for some larger projects In addition to the compliant RWA public chain projects, various RWA concept projects emerge in endlessly, and various assets in the real world are tried their best to be moved to the blockchain for token sale, There are some rather outrageous properties among them, resulting in a mixed bag across the RWA circuit.
In the author’s opinion,Crypto’s RWA logic mainly revolves around how to convert the income rights of assets that generate income (such as the income rights of U.S. bonds, fixed income, stocks, etc.) Transfer to the chain, put off-chain assets on the chain to mortgage loans to obtain the liquidity of on-chain assets, and move various real-life assets onto the chain for trading (such as sand and gravel , minerals, real estate, gold, etc.).
So we can find that Crypto’s RWA reflects the crypto world’s unilateral demand for real-world assets, which still has many obstacles in terms of compliance. MakerDAO’s approach is practical The above shows that the MakerDAO team deposits and withdraws funds through compliance channels (such as Coinbase, Circle), and purchases U.S. Treasury bonds through formal channels to obtain its income, rather than selling these income on the chain. It is worth noting that the so-called RWA U.S. debt actually on the chain is not the U.S. Treasury bond itself, but its income rights, and this process also involves converting the legal currency income generated by the U.S. Treasury bonds into the chain. The step of adding assets increases operational complexity and frictional costs.
The rapid rise of the RWA concept cannot be attributed solely to MakerDAO. In fact, a research report titled "Money, Tokens and Games" released by Citibank from the traditional financial community also aroused strong reactions in the industry. This report reveals the strong interest of many traditional financial institutions in RWA, and also stimulates the enthusiasm of a large number of speculators in the market. They have spread the news that major financial institutions are about to join this field, thus further increasing market expectations and speculation.
RWA from the perspective of TradFi
If you look at RWA from the perspective of Crypto, it mainly expresses the unilateral demand of the crypto world for the return on assets of the traditional financial world. If you look at this logic from the perspective of traditional finance, the size of the crypto market is basically tiny compared to the trillion-scale market of traditional finance. Regardless of Whether it is U.S. debt or any other financial asset, if it is for an additional sales channel on the blockchain, it is not necessary. From the visual market size comparison chart below, we can see the size difference between the encryption market and the traditional financial market.
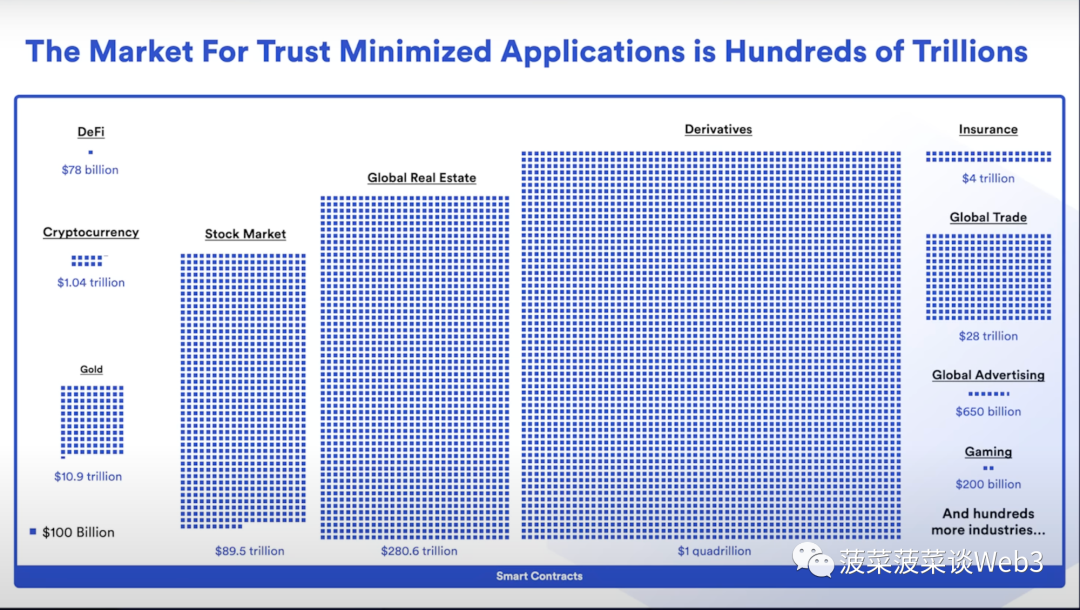
So from the perspective of traditional finance (TradFi), RWA is a two-way journey between traditional finance and decentralized finance (DeFi). For the traditional financial world, DeFi financial services based on automatic execution of smart contracts are an innovative financial technology tool. RWA in the traditional financial field is more concerned about how to combine DeFi technology to realize the tokenization of assets to empower the traditional financial system, reduce costs, improve efficiency, and solve the pain points of traditional finance. . The focus is on the benefits that tokenization brings to the traditional financial system, rather than just finding a new channel to sell assets.
The author believes that it is necessary to distinguish the logic of RWA. Because the underlying logic and implementation paths of RWA from different perspectives are quite different. First of all, when it comes to choosing the type of blockchain, the two have different implementation paths. The RWA of traditional finance is based on the permission chain (Permission Chain), while the RWA of the encryption world is based on the public chain (Public Chain).
Due to the public chain’s characteristics of no access requirements, decentralization, and anonymity, crypto-finance RWA will not only face greater compliance obstacles for project parties, but also for users when encountering adverse events such as Rug. There is no legal protection of rights and interests, not to mention that the rampant hacking activities have high requirements on users’ security awareness.Therefore, the public chain may not be suitable for the issuance and tokenization of a large number of real-world assets. trade.
The permission chain based on traditional financial RWA provides basic prerequisites for legal compliance in different countries and regions. At the same time, KYC on the chain and the establishment of an on-chain identity system are the key to realizing RWA. The necessary prerequisite is that institutions that own assets can legally issue/trade tokenized assets under the premise of legal system protection. The difference from Crypto's RWA is that the assets issued by on-chain institutions can be native on-chain assets. Rather than mapping to assets that already exist off the chain, the potential for change brought by RWA of this native on-chain financial asset will be huge.
To summarize the core point of this article, the author believes that the future development direction of Real World Asset Tokenization will be promoted and established by authoritative institutions such as traditional financial institutions, regulatory agencies, and central banks. A new financial system using DeFi technology on the permissioned chain,To realize this system requires a computational system (blockchain technology) + non-computational system (such as law system) + on-chain identity system (DID, VC) + on-chain legal currency (CBDC, tokenized deposits, legal stablecoins) + complete infrastructure (low-threshold wallets, oracles, cross-chain technology, etc.).
The following content of this article will start from the first principles of blockchain, lead readers to elaborate on the principles of each link mentioned by the author, and cite practical application cases to support the author's views.
2. Starting from the first principles of blockchain, what problems does blockchain solve?
Blockchain is the ideal infrastructure for tokenized expression of assets
Before discussing the first principles of blockchain, we need to have a clear understanding of the essence of blockchain. Teacher Meng Yan said in "What are Digital Assets?" "[4] has a very comprehensive discussion on the definition of digital assets and the essence of blockchain. The article mentions: **Writing and paper as a technology are considered to be one of the most important inventions of mankind. Human civilization has been an immeasurable boost, and its impact is likely to exceed that of all other technologies combined. **Their application scenarios are mainly concentrated in the two application areas of information dissemination and supporting contracts/instructions.
In the application field of information dissemination, through written records, knowledge and information can be copied, edited, and disseminated at low cost, which promotes the widespread transmission of knowledge and the popularization of ideas. In the application fields that support contracts/instructions, text can also record and convey various instructions. For example, ancient emperors sent military orders and intelligence through documents, the bureaucracy conveyed instructions through text, and business activities also A contract can be written to record the agreed matters, form a consensus or even legal provisions, and preserve evidence to facilitate future supervision and arbitration.
There are clear differences between these two application scenarios. In the field of information dissemination, what people pursue is the convenience of low-cost, lossless copying and editing; while in the transmission of contracts and instructions, authenticity, non-repudiation and non-tampering are regarded as as a more important attribute. In order to meet these needs, people have developed a variety of complex anti-counterfeiting printing technologies, and handwritten signatures and other verification methods are still widely used to ensure the reliability of information.
When the Internet was born and humans entered the digital age, the Internet, as a modern information transmission system, greatly met the needs of information dissemination scenarios. The Internet can realize fast, low-cost, lossless and convenient transmission of information, providing unprecedented possibilities for the sharing of global knowledge and information. At this time, the transmission and sharing of information has become easier and faster than ever. Whether it is academic knowledge or daily information, it can be quickly spread and shared around the world, which has greatly promoted the The progress and development of human society.
However, the Internet has encountered difficulties when dealing with contract/command systems, especially in scenarios involving authority and trust, such as corporate operations, government decision-making, and military command, where the credibility of information has become extremely important. It's important. In these situations, simply relying on information transmitted through the Internet may lead to significant risks and losses due to insufficient credibility. This is because the Internet mainly develops around the first application scenario of information dissemination, emphasizing the rapid, widespread and convenient transmission of information, but often ignores the authenticity and accuracy of information.
In this context, people try to make up for this shortcoming through centralized decision-making and trusting third parties, which has become the main means to achieve trusted information transmission. However, a centralized power structure can lead to the concentration and abuse of power, making information transfer opaque and unfair. The intervention of trusting a third party may bring more security risks and trust crises, because the third party itself may also become an untrustworthy information source.
Therefore, the emergence of blockchain technology provides a new solution for processing contracts and instruction systems. Blockchain, as a decentralized, transparent and non-tamperable distributed ledger, can ensure the authenticity and reliability of information, which means that people no longer need to rely on A centralized institution or third party to establish trust. This innovative technology brings new perspectives and solutions to the problem of information transmission in contracts and instruction systems, making the authenticity, integrity and consistency of information possible without the need for a central authority. Guaranteed under the premise of chemical verification.
If the Internet is the digital upgrade of text-paper technology in the information dissemination scenario, then the blockchain is undoubtedly supporting the digital upgrade of text-paper technology in the contract/instruction scenario. Therefore, we can comprehensively identify the blockchain as a distributed system jointly maintained by multiple parties, which supports the creation, verification, storage, circulation and execution of digital contracts and other related operations. It can be said that blockchain is the first technical means to effectively support the digitization of contracts after the development of computers and networks. Therefore, since the blockchain is essentially a platform for digital contracts, and the contract is the basic expression form of assets[4], Token is the digital carrier of assets after the contract is formed, and the blockchain has therefore become the ideal infrastructure for digital expression/tokenized expression of assets, that is, digital assets/tokenized assets.
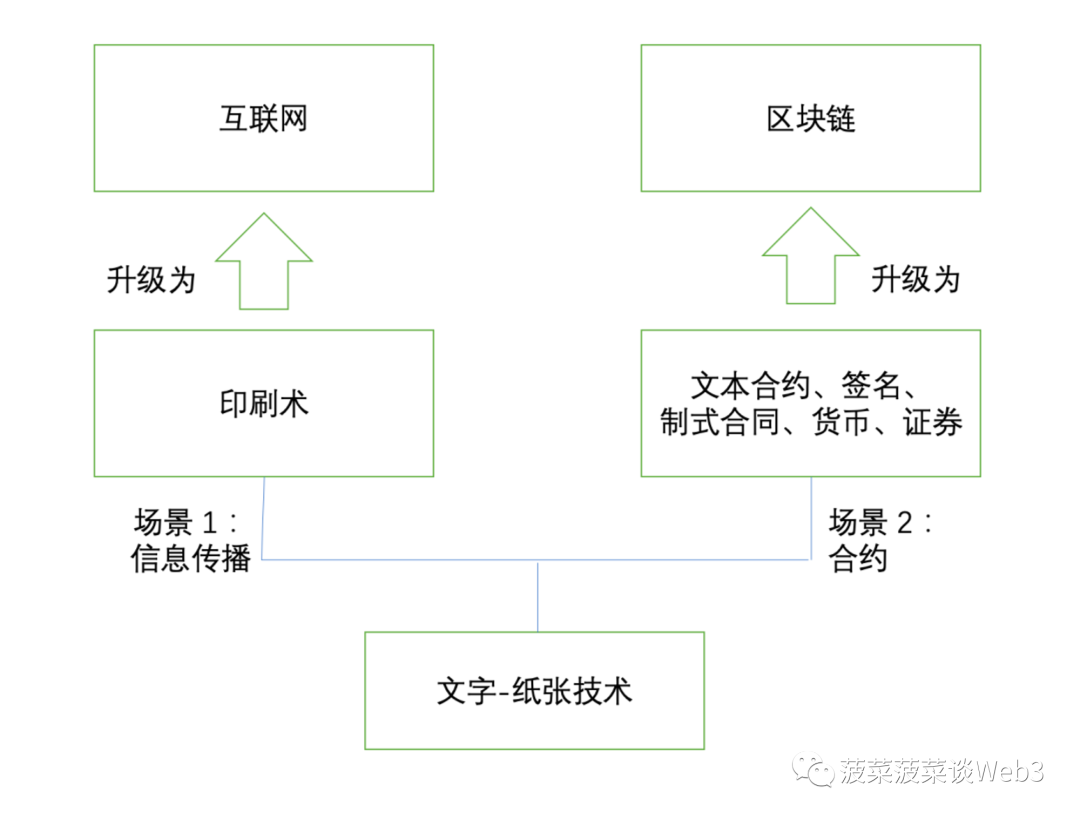
Image source: https://www.defidaonews.com/article/653729
Blockchain satisfies human demands for “computability”
Blockchain provides humans with an infrastructure that can tokenize assets, and smart contracts are the most basic form of digital asset expression, and Ethereum’s Turing completeness provides smart contracts with the ability to express a variety of Different types of asset forms have led to the emergence of token standards such as Fungible Tokens (FT), Non-Fungible Tokens (NFT), and Semi-Fungible Tokens (SFT).
Some people may ask, why can only blockchain realize the digital expression of assets? Because the blockchain solves the problem of "computability" while ensuring that it is not manipulated, that is, "the process is repeatable and the results can be verified", the author also refers to "the process is repeatable and the results can be verified"** It is considered to be the first principle of the blockchain, because the operating mechanism of the blockchain is based on this: when a node records a transaction, many other nodes will re-execute the recording process (the process is repeatable); if the declared result If it is consistent with the result of the node's self-verification, then it will be regarded as a "fait accompli" in the blockchain world and be permanently recorded [5].
When we look at what problems blockchain can solve,breaking the problem into "computational systems" and "non-computational systems" will help us understand it more clearly. Insight into the essence, the problems that blockchain can solve are "computational system" problems, that is, transactions based on "repeatable processes and testable results", while "non-computational systems" It includes those matters that cannot achieve "repeatable process and testable results", such as matters affected by human cognition. Because, if human cognition, thinking and judgment are all "processes repeatable and results testable", then aren't humans just a group of robots that only respond to the same stimulus?
Since ancient times,human beings have always had the computational pursuit of “repeatable processes and testable results.” However, due to the insufficient development of science and technology, humans can only use the body and cognition to simulate this "calculation" process, such as counting stones or recording with knots, the most primitive means. , in ancient times, the Chinese invented tools such as arithmetic and abacus to meet the growing demand for "calculation" at that time. However, because people make mistakes,human beings cannot realize it well. The process can be repeated and the results can be verified." But with the birth of computers, the process of "repeatable processes and testable results" can be solidified in the computer program, and tools that meet the "computational" demands continue to iterate. Upgrading has also made a qualitative leap in human productivity and has become an important driving force for the development of science, technology and society.
However, in a centralized "computational system" like the Internet, when human subjective consciousness interferes with this "computational system", the "process can be repeated and the results can be verified" will become ineffective. For example, hackers can By tampering with the program to produce different output results, it affects the reliability and authenticity of information transmission, thus hindering the transmission and construction of trust.
With the birth of blockchain,a new tool that meets the demands of "computing" was born, that is, when the computing system of blockchain is decentralized Afterwards, it becomes more difficult for human subjective consciousness to interfere with this computing system. For example, if a hacker wants to tamper with the output of a smart contract, the hacker may need to control more than 50% of the blockchain. It is only possible to tamper with nodes, and the cost-benefit of such attacks is often not proportional. Therefore, the blockchain can well satisfy human beings' demands for "computability" under non-extreme circumstances.
DeFi is a “computational” financial innovation
Since the advent of Ethereum and smart contracts,blockchain has occupied a pivotal position in the financial field with its inherent financial attributes , making finance one of its most important application scenarios. Therefore, decentralized finance (DeFi) emerged as the times require and has become the most widely used scenario in the blockchain field.
DeFi is a new financial model that relies on distributed ledger technology to provide various financial services, such as lending, investing, or exchanging crypto assets, without relying on traditional centralized financial institutions. The DeFi protocol implements these financial services with a set of smart contracts, which are programs that program traditional financial operation logic to automatically execute. Therefore, DeFi users interact not with another party when trading, but with these programs that are able to pool the assets of other DeFi users in order to maintain control of their funds [6].
Blockchain is a "computational system". We can regard DeFi, a financial system composed of smart contracts, as a "computational" innovation in the financial field. Smart contracts can replace traditional financial systems. Some links of "calculation", such as those steps in financial activities that rely on manual or mechanical "obtaining a deterministic result by repeating a process", such as clearing, settlement, transfer and some uncertain Repetitive work that relies on human cognition. In short, DeFi enables all manual and time-consuming steps in traditional financial activities to be executed by smart contracts, thereby significantly reducing the transaction costs of financial activities, eliminating settlement delays, and achieving automated execution and programmability. sex.
The corresponding concept of "computational system" is "non-computational system", which is human cognition. Blockchain is a purely computational system that can only solve computational problems, not solve them. Issues at the cognitive level, the cognitive system can be understood as the credit system in the financial system, such as the credit evaluation and risk control system in credit, although it has the same work income and bank flow, etc. Information: Different banks may have different judgments on the specific amount of credit that should be granted.
For example, the same customer may have a $10,000 line of credit at one bank and $20,000 at another bank. This difference is not based on a repeatable and verifiable calculation process, but is deeply affected by human cognition, experience and subjective judgment. Each bank has its own risk control system, but in specific credit decisions, human cognitive factors still play a decisive role. This kind of cognitive-level decision-making has the characteristics of being unrepeatable and not fully verifiable, because they incorporate human subjectivity and interpretation of non-black and white right and wrong issues.
Or debt relationships. Can the debt problem be solved by putting the debt contract on the chain and automating the repayment steps? To explore this question, we first need to analyze the debt itself. Debt is not just a contract or a form, it is a relationship based on mutual recognition and trust between people. In essence, the establishment of a debt relationship does not only rely on the formation of a contract, it relies more on human cognition.
Blockchain technology can put the "ontology" of the debt contract on the chain, and set rules for the contract through programming to automate the repayment process and debt transfer. This process is predictable and verifiable because it relies on fixed rules to ensure "repeatability of the process and verifiability of the results." However, the operation of this system does not involve the human cognitive level.
Although the "ontology" of the debt contract has been objectively confirmed and guaranteed technically, the formation, change and even termination of the debt relationship are based on human cognition. This kind of cognition cannot be programmed or chained. Human cognition is not a "repeatable and testable" process. It may change with changes in the environment, emotions, and information. When the debtor's perception changes, they may choose not to perform their debts, which is the so-called "default". Therefore, on-chain cannot solve the problem of default, because this is a cognitive problem rather than a computational problem.
Someone may ask, can’t DeFi’s lending agreement solve the problem of borrower default through smart contract liquidation? Isn’t the act of borrowing and lending on DeFi an act of a credit system? Compound General Counsel Jake Chervisnky once published an article discussing:The DeFi lending agreement itself does not exist as a loan, but an interest rate agreement[7] . To put it simply, DeFi lending itself does not generate any credit, and most DeFi lending protocols rely on the same basic mechanism to function: over-collateralization and liquidation. That is, if a borrower wants to borrow money, he first needs to pledge collateral that exceeds the borrowing amount. For example, if he pledges 100 yuan of ETH and lends 65 yuan of USDT, this kind of lending is essentially a kind of "calculation leverage." ” does not create any credit and the borrower does not rely on any promise of future payment, trust or reputation.
To briefly summarize,Blockchain, as a distributed system jointly maintained by multiple parties, supports the creation, verification, storage, circulation and execution of digital contracts and other related operations. , which solves the problem of transmitting trust. And as a "computational system", blockchain can satisfy human beings' demands for "repeatable processes and testable results", Therefore, DeFi has become It has created a "computational" innovation in the financial system, replacing the "computational" part of financial activities. Automatic execution can reduce costs and increase efficiency while also achieving programmability. , but the "non-computational" part, that is, the part based on human cognition, cannot be replaced by blockchain. Therefore, the current DeFi system does not cover credit, and unsecured lending based on credit has not yet been implemented in the current DeFi system. , the reasons for this phenomenon include the current lack of an identity system that expresses "relational identity" in the blockchain and the lack of a legal system to protect the rights and interests of both parties.
3. How disruptive is asset tokenization to traditional finance?
Financial services are based on trust and empowered by information. This trust relies on financial intermediaries maintaining the integrity of records covering ownership, liabilities, conditions and covenants, which are often dispersed across different systems or ledgers that operate independently. Institutions maintain and verify financial data so that people can trust the accuracy and completeness of that data.
Because each intermediary holds a different piece of the puzzle, the financial system requires a great deal of post-event coordination to reconcile and settle transactions ensuring the consistency of all relevant financial data. This is an extremely complex and time-consuming process. For example, in the context of cross-border transactions, the process is particularly complex due to the need to comply with different regulations and standards in various countries, as well as the involvement of multiple different financial institutions and platforms, making the transaction settlement cycle often longer, usually taking one to four days. In order to settle, this process increases the cost of transactions and reduces transaction efficiency [8].
Blockchain, as a distributed ledger technology, has shown great potential in solving efficiency problems prevalent in the traditional financial system. By providing a unified and shared ledger, it directly solves the problem of information fragmentation caused by multiple independent ledgers, and greatly improves the transparency, consistency and real-time update capabilities of information. The application of smart contracts further enhances this advantage, allowing transaction conditions and contracts to be encoded and automatically executed when specific conditions are met, significantly improving transaction efficiency and reducing settlement time and costs. , especially when dealing with complex multi-party or cross-border transactions.
Therefore, asset tokenization (Tokenization) is increasingly accepted by traditional finance. According to a survey report by the Bank of New York Mellon, 97% of the 271 financial institutions it interviewed It is believed that tokenization will bring a new revolution to asset management [9], which fully reflects the potential of blockchain in the financial field.

Image Source:
https://www.bnymellon.com/content/dam/bnymellon/documents/pdf/insights/migration-digital-assets-survey.pdf
Therefore, for the traditional financial system, the significance of Real World Asset Tokenization is to create digital representations of real world assets (such as stocks, financial derivatives, currencies, equity, etc.) on the blockchain , extending the benefits of distributed ledger technology to enable exchange and settlement across a wide range of asset classes.
Financial institutions further improve efficiency by adopting DeFi technology, using smart contracts to replace the "calculation" links in traditional finance, and automatically executing various types of finance according to predetermined rules and conditions. Transactions,enhancing programmable features. This not only reduces labor costs, but in certain situations, it can give enterprises new possibilities, especially providing innovative solutions to financing problems for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMSE), which opens a very rich door for the financial system. The door to potential.
In order to deeply explore the potential transformative power of tokenization on the financial system, this article will present readers with a more in-depth analysis framework:
Establish a credible global payment platform, reduce costs and increase efficiency
In all aspects of human daily life, financial activities, and trade activities, clearing and settlement are everywhere and have become a key link in maintaining economic flow. Although these two processes are very common in life, they are often not paid attention to by the public. However, they are the forces behind ensuring the smooth progress of transactions.
In our daily shopping, paying wages, sharing bills and other activities, the process of clearing and settlement is involved. When we usually share expenses with friends, we are also carrying out a simplified clearing and settlement process - calculating the amount payable by each person, making transfers, etc. Or when we use Alipay or WeChat for electronic payment, the payment platform must go through a series of clearing processes to confirm that the payment is accurately transferred from our account to the merchant's. In the account, for the user, the money is transferred just after performing a payment action, but in fact, there are many clearing and settlement processes involved behind the simple payment action (as shown in the figure below [10]).

Image source: https://www.woshipm.com/pd/654045.html
According to the Committee on Payment and Settlement Systems (CPSS) definition of clearing and settlement, CPSS defines a clearing system asA system of systems that enables financial institutions to submit and exchange funds or securities. Program arrangement of data and files. It all starts with establishing a "net position" for the transaction participants, that is, offsetting the debts of both parties. This step is called "netting" [11].
Subsequent clearing refers to the process of exchanging, negotiating and confirming payment instructions or securities transfer instructions. Clearing occurs before settlement. Settlement refers to the process in which the seller transfers securities or other financial instruments to the buyer, and the buyer transfers funds to the seller. It is the final step of the entire transaction. The settlement system ensures that the transfer of funds and financial instruments proceeds smoothly.
Simply put, clearing is the sending, receiving, and verification of payment instructions by both parties and reaching a final consensus on the assets to be paid. Settlement is the transfer of assets based on the clearing results. Let us explain this process in depth through an example. :
Clearing
Imagine you and your friends are having dinner at a restaurant and decide to split the bill. Everyone declared the amount of their consumption, and then jointly calculated the amount that each person should pay. In this scenario:
Amount Determination: The consumption amount announced by each friend is similar to the payment instruction.
Communication and verification: Everyone informs each other about their consumption and verifies the total amount. This link is equivalent to the steps of sending, receiving and confirming payment instructions in clearing.
Total calculation: After calculating the total bill, determine the amount that each person should bear. This action is equivalent to exchanging payment information and confirming the final position to be settled (i.e. the amount each person should pay amount).
Therefore, clearing is a "verification and preparation" step where the parties confirm the amount to be paid and prepare for the next step of settlement be prepared.
Settlement
In this example, once you know how much you need to pay, the next step is to actually make the payment. Everyone pays their portion, and the total is the restaurant's total bill. at this time:
Payment: The actual amount paid per person is similar to the steps for transferring funds.
Verification: Everyone confirms that their payments are accurate, verifying that each member has paid the correct amount, similar to the steps in the settlement process that confirm that funds have been transferred correctly .
Notifications: If one friend is responsible for collecting all the money and paying the bill in one go, then when he completes the payment, he will notify others that the payment has been completed. This notification step is similar to the process for notifying parties after settlement is complete.
Therefore, Settlement refers to the actual flow of funds from one party to another and the confirmation of completion of the transaction.
It can be seen that,In the traditional financial system, clearing and settlement are a "calculative" accounting and confirmation process. All parties reach a consensus through constant checking and verification, and transfer assets on this basis. This process requires the collaboration of multiple financial departments and a lot of labor costs, and may face the risk of operational errors and credit risks.
On June 28, 1974, a remarkable bank bankruptcy event attracted widespread attention in the international financial community.The collapse of Herstatt Bank exposed the cross-border International payment credit risk and its potentially huge destructive power. On that day, several German banks conducted a series of foreign exchange transactions between German marks and US dollars. The purpose was to remit US dollars to New York, and the counterparty of the transaction was Herstatt Bank.
However,due to different time zones in Germany and the United States, the transaction settlement process encountered considerable delays. This time difference resulted in the U.S. dollars not being immediately transferred to the counterparty's bank account, but "stuck" in Herstatt Bank. In short, the expected dollar payments did not go as planned. During those critical hours, Herstatt Bank received a liquidation order from German officials.
Due to lack of ability to pay, it failed to remit the corresponding U.S. dollar payments to New York, and eventually headed toward the abyss of bankruptcy. The shock wave caused by this sudden bankruptcy caused varying degrees of losses to many German and American banks engaged in foreign exchange transactions. The occurrence of this incident also promoted the widespread application of real-time gross settlement systems in the field of cross-border payments and the establishment of the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision[12] , This shows the importance of settlement and clearing in the international financial market.
Blockchain relies on the characteristics of its distributed ledger and the non-tamperability and traceability of data to provide an atomic settlement (Atomic Settlement) transaction method through smart contracts , when one party pays a certain asset to another party, the other party will also pay the corresponding asset to the payer at the same time, eliminating the risks and costs caused by clearing and settlement, while real-time settlement brings a huge improvement in transaction efficiency.
By integrating blockchain technology into cross-border payment settlement, we reveal its far-reaching significance:It builds an efficient point-to-point payment network, easing the traditional cross-border Issues with long clearing times in payment methods. By eliminating the intervention of third-party institutions, it has achieved around-the-clock payment, instant collection, and easy cash withdrawal, and successfully met the convenience needs of cross-border e-commerce payment and settlement services. In addition, it creates a globally integrated cross-border payment trust platform at a lower cost, mitigating the financial risks caused by cross-border payment fraud [13].
Projeto Mariana is a collaboration between the Bank for International Settlements (BISIH), the Bank of France, the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) and the Swiss National Bank. A test report was released on September 28, 2023, and the plan successfully verified the technical feasibility of using automated market makers (AMM) for international cross-border transactions and settlement of the tokenized central bank digital currency CBDC [14].
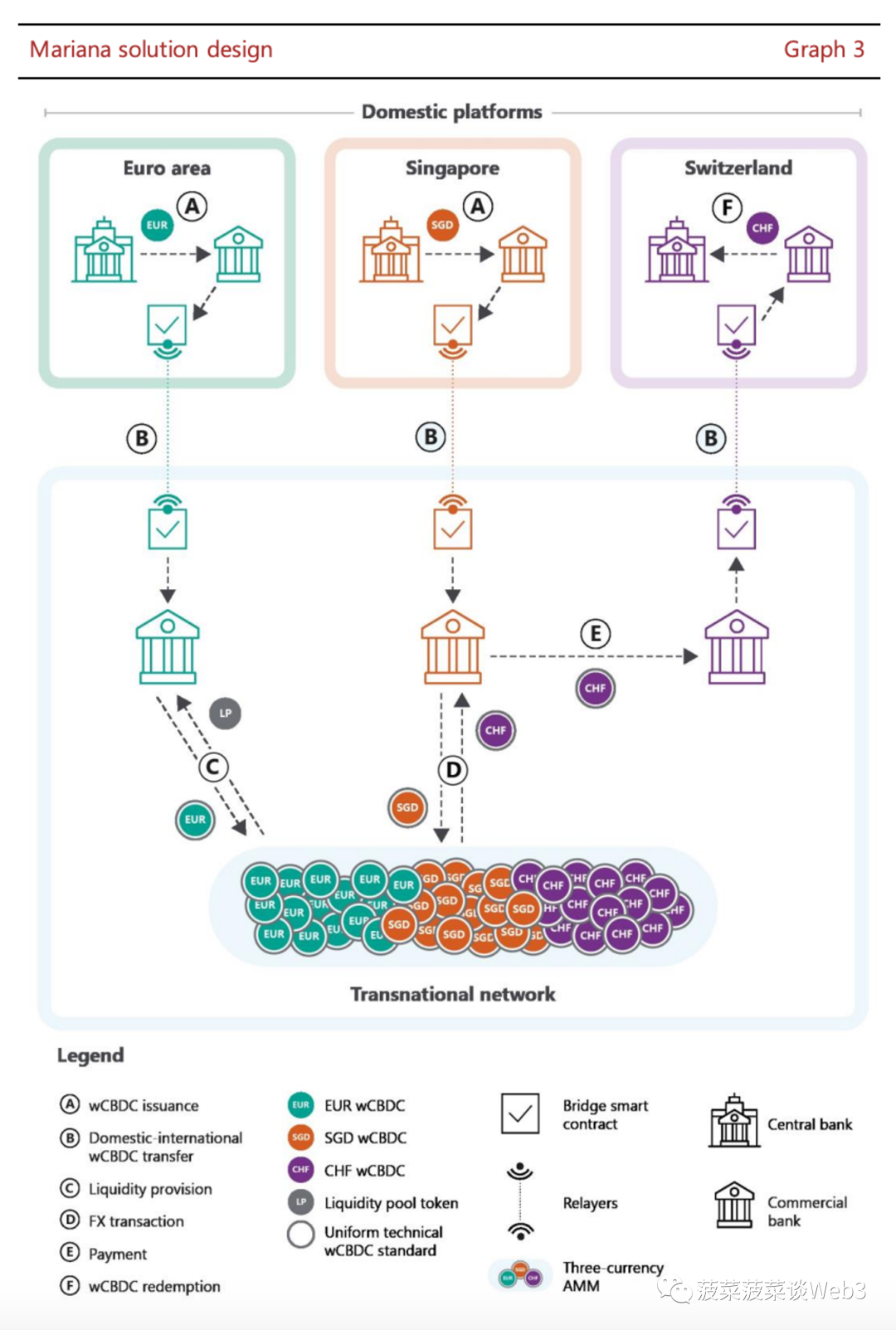
Image source: https://www.bis.org/publ/othp75.htm
In general,payment behavior in the traditional financial system is often accompanied by cumbersome clearing and settlement processes,not only incurs additional costs, It also suffers from inefficiencies due to settlement delays, while also facing issues such as human error, credit risk and strict time window restrictions. And using blockchain and DeFi technology provides an effective solution.
Through blockchain technology, the transaction process can be optimized and intermediate links can be reduced, thereby significantly reducing related costs. This technology avoids the long waiting time of traditional financial settlement and realizes true round-the-clock market operation, especially in cross-border payments, which greatly improves the processing speed and accuracy. More importantly, as transaction costs decrease, indirect profit improvements may far exceed direct cost savings, thereby promoting the vitality and efficiency of financial markets on a broader level.
Programmability and transparency
For the traditional financial system,The programmability and transparency of real-world asset tokenization will bring about disruptive changes. We can take financial derivatives as an example. To illustrate the disruption brought about by programmability and transparency, Financial Derivatives is an extremely large market in the traditional financial market, with an estimated nominal value exceeding 100 billion U.S. dollar [15], where the types of derivatives markets are large and complex, including different types of contracts in equities, fixed income, foreign exchange, credit, interest rates, commodities and other markets. These types of contracts include options (plain calls and puts as well as exotic options), warrants, futures, forwards, swaps, etc.
It is the huge potential of the leverage effect of financial derivatives that enables them to create an asset scale that far exceeds the value of the underlying assets dozens of times. Among them, the 2008 financial crisis is a classic case of a global financial disaster triggered by financial derivatives. During the crisis, banks packaged a series of mortgages into a special financial product—Mortgage-Backed Securities (MBS)—and sold them to investors. For banks, this approach can transfer the original loan risk, generate cash flow by selling these packaged mortgage loans, and earn interest rate differentials. For banks, the issuance of each loan has almost become the creation of a profit, which creates great risks.
The movie "The Big Short" vividly demonstrates this phenomenon:When a housing loan means a profit and the risk has nothing to do with the bank, the bank tends to do nothing. Create mortgage contracts endlessly. When all the home buyers with good credit are exhausted, banks tend to find other individuals with poor credit to continue the game. A person without any collateral can even use the name of his dog Get a loan at a bank. These “subprime loans[16]” of poor quality became the trigger for the subsequent financial tsunami.
Against the background of continued rise in U.S. real estate prices and low interest rates and loose monetary policy, banks have continued to issue subprime loans, and Wall Street financial institutions have also invented a variety of financial derivatives, such as collateralized debt obligations (CDOs). ), which is a financial instrument that packages various MBS; and synthetic CDO, which packages various CDOs and credit default swaps (CDS).
Eventually, there were so many and so complex financial derivatives that it became impossible to trace the physical assets behind them. In addition, a large number of subprime loans were mixed into financial derivatives rated as "low risk". Due to the distortion of ratings, high-risk assets only had to pay extremely low premiums. These layers of stacked and packaged derivatives were sold to a variety of brokers and investors. The leverage ratio of the entire financial system soared rapidly and became precarious.
Subsequently, the United States began to raise interest rates, and the increase in loan interest led to a large number of borrowers defaulting. This problem first appeared in the subprime loan market, but because subprime loans were packaged in asset-backed securities (ABS), MBS , and even among CDOs, this problem quickly spread to the entire financial market. Many seemingly high-grade, low-risk financial derivatives were suddenly exposed to huge default risks, and investors had almost no idea of the actual risks of these derivatives. Market confidence was severely hit, and the financial market suffered a massive sell-off, which became an important trigger for the outbreak of the financial crisis in 2008. All this stems from the chaos, opacity and overly complex structural system of the financial market.
This shows how important transparency is for complex financial derivatives. We can imagine that if the technology of tokenization had been used before 2008, investors could easily penetrate and understand the underlying assets, and perhaps this would not have happened. Such a financial crisis. Not only that, tokenizing financial derivatives can also improve the efficiency of multiple stages of the asset securitization process, such as the servicing, financing, and structuring (i.e., grading) stages [17].
For example, uses the semi-homogenized token standard ERC-3525 to package assets in the asset securitization process. The digital container feature of ERC-3525 can package non-standard assets It has become a standard asset that can be divided into combinations. Use smart contracts to stratify it (prioritize the mezzanine and then the inferior), and also program the cash flow of the asset to reduce operation and third Third-party costs greatly improve asset transparency and settlement certainty.
When using blockchain, the monitoring role of regulators can be partly assumed by the platform. When key information, such as seller submissions, past records, and updates are visible to all key stakeholders on the blockchain platform, single-sided governance de facto becomes multi-party governance. That is to say, any party has the right to analyze data and detect anomalies, and this timely information disclosure can reduce transaction costs in financial markets [17].
In order to further understand the benefits that programmability and transparency bring to the traditional financial system,Among them, Australian startup Unizon was selected into the Australian Central Bank's CBDC pilot project based on ERC-3525. The "Digital Invoice Tokenization" project is a very good case[18],In supply chain finance, Factoring of accounts receivable is a common business model. It allows companies to sell accounts receivable to a third party (usually a factoring company) at a certain discount to obtain the necessary financing and improve their cash flow situation.
However, due to the problem of falsification of bills, small and medium-sized enterprises generally lack sufficient credit support.Investors are unable to carry out reasonable risk control on a large number of small and medium-sized enterprises. As a result, small and medium-sized enterprises generally face financing problems in reality. If small and medium-sized enterprises cannot accept delayed payment of accounts, it will be difficult to receive orders from large enterprises. However, accepting orders from large enterprises will lead to tight liquidity of enterprises and increase cash. Risk of flow breakage.
By tokenizing the bill, we can use private key signature to add a confirmation step in the bill issuance process. Once confirmed, the ticket will be generated with the confirmation signatures of both parties, ensuring that the ticket is generated in a confirmed state by both parties. Considering that account arrears are actually equivalent to a form of loan provided by the seller to the buyer, if the issue of bill authenticity can be effectively solved, the seller can rely on the buyer's creditworthiness to use this account receivable at a certain discount rate. Sold to a factoring agency to receive discounted payments.
Tokenize payment notes in a “digital invoice tokenization” scenario thanks to the cash flow programmability of tokenization using ERC-3525. Create a pair of accounts through ERC-3525: payment account (Payable) and accounts receivable account (Receivable). The two accounts form a payment channel that is bound to each other similar to quantum entanglement. As long as the buyer remits money to the payment account, the funds will be automatically distributed to the accounts receivable account through smart contracts. This means that no matter how many shares the accounts receivable is split into, no matter whose hands it ends up in, it will eventually be transferred to the accounts receivable account according to a predetermined proportion. This is extremely costly and difficult to do in the traditional financial system. Implemented operations, using tokenization technology can greatly increase the liquidity and composability of supply chain financial factoring business and reduce operating costs.
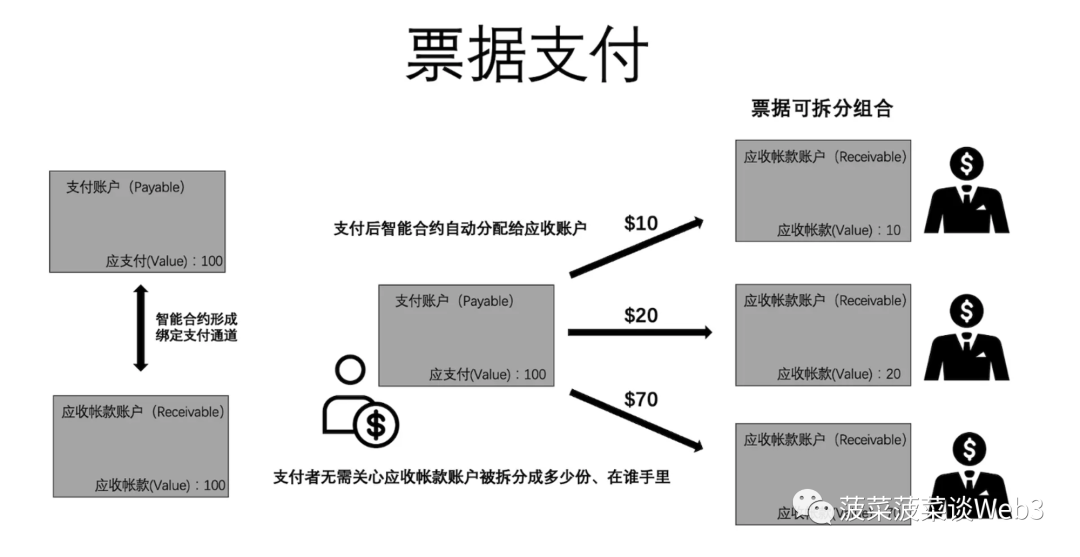
Image Source:
https://mirror.xyz/bocaibocai.eth/q3s_DhjFj6DETb5xX1NRirr7St1e2xha6uG9x3V2D-A
To summarize, the programmability and transparency of tokenization have a huge impact on the traditional financial system.The transparency brought by the use of blockchain platforms can not only reduce The problems of financial risks and information asymmetry in the traditional financial system,and the programmability of tokenization also open a door for us, making many things that are difficult to achieve in the traditional financial system Operations are possible, greatly reducing the cost of requiring manual intervention and third-party involvement. This not only greatly enhances the liquidity and composability of financial services, but also creates room for innovation, potentially giving birth to unprecedented types of financial products.
4. What else is needed to realize asset tokenization Mass Adoption?
Tokenization has undoubtedly brought revolutionary innovations to the traditional financial system, but if we want this innovation to be truly applied in real application scenarios, we still face many challenges and difficulties. Listed below are some of the key factors that need to be considered to achieve large-scale adoption of asset tokenization:
Complete legal system guarantee and permission chain
As a purely "computational system", blockchain can only solve people's demands for "computational" things (reducing friction costs, programmability, traceability gender, etc.), while demands for confirmation of relationship rights, judgments of right and wrong, and protection of rights and interests require a set of non-computing systems based on cognition, such as a complete legal supervision system, because the legal and supervisory systems cannot rely on an inherent set of Programs are used to execute the law. The execution and determination of laws, as well as the determination and control of risks are all based on human cognition.This is exactly what the public blockchain cannot satisfy. a>Not to mention the rampant hackers and frequent security incidents in the public chain ecosystem. When a user’s wallet is stolen on the public chain, it is almost impossible to recover the assets and there is nowhere to protect the rights and interests. The open and anonymous public chain Characteristics also make regulations and laws difficult to enforce.
The application scenarios of real-life asset tokenization in the traditional financial field involve a large number of asset issuance, transactions and other operations.For financial institutions that control core assets, compliance and security are the main demands.Imagine if a financial institution issued hundreds of millions of dollars of tokenized financial assets on the public chain, but all the assets were stolen by a North Korean hacker organization , in this case neither the asset losses can be recovered nor the perpetrators can be legally punished, which is obviously unacceptable.
The financial industry therefore relies on a range of legal safeguards to protect investors from fraud and abuse, combat financial crime and cyber wrongdoing, maintain investor privacy, ensure that industry participants meet certain minimum standards, and Provide a recourse mechanism when problems arise. Therefore, only the permission chain can satisfy both the requirements of "computability" and "non-computation". We can imagine that in the future, every country and region may have Different legal supervision systems, and each region will have a permission chain that complies with the legal supervision system of the region to carry the tokenized real assets.
Identity system and privacy protection
Relational identity vs contractual identity
If the blockchain hopes to be closely integrated with the real world and achieve large-scale applications, a complete on-chain identity system is the key. For a long time, blockchain has made it difficult to reveal the true identity of wallet holders due to its anonymous nature, and a system lacking identity authentication naturally has difficulty establishing credit. Credit is a product of human social cognition, and it relies on deep social connections between people. In fact, the blockchain world has always lacked a "relational identity" system based on interpersonal relationships. This system is not a simple identity label, but a complex structure that reflects the various roles and relationships of individuals in the social network.
As early as more than 150 years ago, the ancient British jurist Henry Maine inspired people to think deeply about the nature of identity[30]. He proposed that there are two major categories of identity: one is "relational identity", which originates from an individual's role in society and interpersonal relationships, such as being a father, having the nationality of a certain country, or The identity is civil servant, military personnel, etc. This identity is a reflection of social attributes, emphasizing a person's position in the social structure and his or her relationship with others.
Another type of identity is the "contractual identity" system based on "contract execution", such as contracts in the form of labor agreements, company organizational structures, and contract terms. In the blockchain field, this can be compared to the "identity" attribute composed of smart contract interactions, such as the balance of the wallet, the history of interaction with the smart contract, and the state generated by the smart contract.
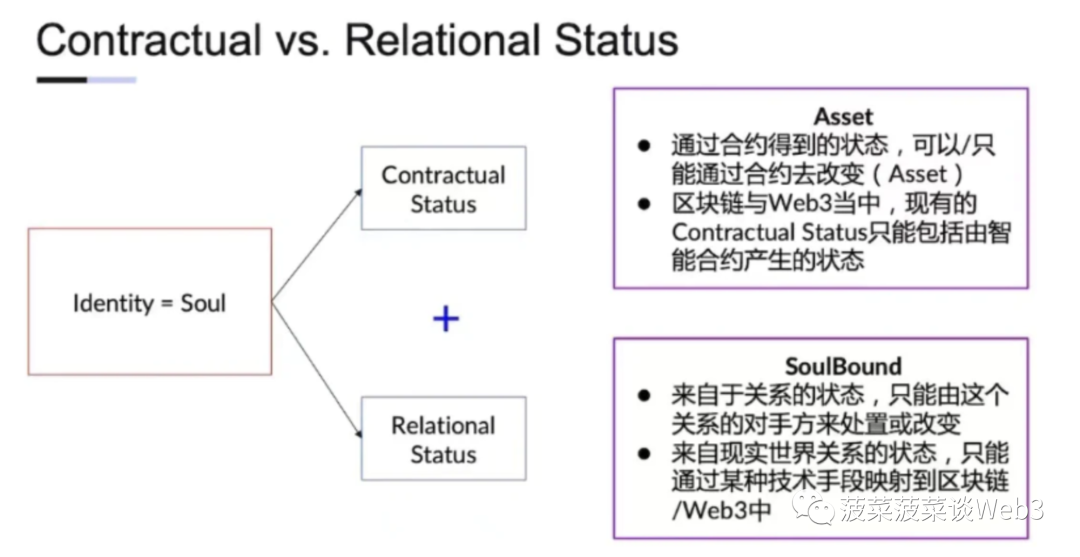
Image Source:
For many years, blockchain has been essentially a purely “computational system” in which only “contractual identities” exist. Specifically, the information on the chain is limited to unnamed wallet addresses, their balances, transaction history and other data. Although people try to use these data elements to build a "relational identity" system on the chain, because this contract-based identity system lacks the ability to express social interpersonal relationships, it cannot fully capture or replicate what "relational identity" covers. social dimensions and human interaction.
This limitation is an important factor hindering the development of the blockchain field, especially decentralized finance (DeFi), such as the lack of a credit-based unsecured lending system. Purely contract-based identity authentication cannot capture an individual’s credibility and trust. This is because credit is based on complex human social relationships, not just the history of smart contracts or account balances. In order to realize such a credit system, not only a technical solution is needed, but also a mechanism that can understand and reflect the complex network of relationships in human society.
Currently, the status quo of the identity system in the blockchain world is far from meeting the large-scale application conditions required to support the tokenization of real-world assets. In addition to the "contractual identity" system,blockchain also needs a "relational identity" system that can carry people's social relationships and credit systems, because in human society, credit is based on deep based on multi-dimensional social interaction. It is not an attribute that an individual can unilaterally attribute to himself, but is jointly shaped by the individual's behavior, reputation and recognition from others in the social network. More importantly, this kind of credit system often requires certification and endorsement by authoritative third-party institutions to ensure its credibility and authority. For example, in the real world, identity certificates and related documents issued by the government or other authoritative institutions are important signs of an individual's identity and credibility.
To summarize, If the blockchain is to be combined with the real world to achieve large-scale applications, the identity system needs to combine the "relational identity" system and the "contractual identity" system. To realize the "relational identity" system, it is necessary to introduce authoritative third parties (such as government agencies, regulatory agencies, etc.) who can verify individual social relationships and credibility to assign and certify identities on the chain. , endorsement and other operations also require technical innovation to ensure the security, privacy and non-tamperability of identity data.
W3C standard DID+VC identity system
To achieve large-scale application and implementation of asset tokenization in the real world,technically, an optimal solution to an identity scheme is needed to achieve data autonomy and privacy. A dynamic balance of protection, regulatory compliance, and interoperability. The DID+VC system under the W3C standard may be part of the answer to this unsolved problem.
To realize the tokenization of real-world assets and promote large-scale applications, a comprehensive identity solution is urgently needed at the technical level. This solution needs to find a balance between data sovereignty, privacy protection, regulatory compliance, and interoperability. dynamic equilibrium. The W3C's Decentralized Identifiers (DID) and Verifiable Credentials (VC) systems may provide partial solutions to this complex problem.
In the development of digital identity, we have witnessed several important stages of transformation: from centralized identity management, where identity information is completely controlled by a single authority; to federated identity authentication, which allows users’ identity data to It has a certain degree of portability and can achieve cross-platform login, such as one-click login through WeChat and Google accounts; then to a decentralized identity system based on authorization and permission, as demonstrated by OpenID; and finally develops to autonomy Rights Identity (SSI), in this model, the ownership and control of data truly return to the hands of individuals. Although this mechanism, such as the zkID decentralized identity system launched by zCloak Network, Not yet widely adopted.
Currently, the on-chain identity system has enhanced the anonymity and openness of identity to a certain extent by utilizing the cryptographic mechanism built into the blockchain. However, since different ecosystems and application systems often use closed or relatively independent data systems, users' identity information is still fragmented and stored in isolated systems that are difficult to interoperate with. Therefore, a key next step is to break down these silos and build an identity verification ecosystem that ensures personal data autonomy and privacy, meets regulatory requirements, and is broadly interoperable. This requires not only technological innovation, but also in-depth cooperation among all stakeholders and support from policymakers.
W3C (World Wide Web Consortium), an organization responsible for developing international Internet standards such as HTML and CSS, launched the first decentralized identity identifier (DID) in 2022. : Decentralized Identifier), and the detailed definition and standard framework of Verifiable Digital Credential (VC: Verifiable Credential) was released in 2019.
In the W3C specification, DID is defined as a string that is guaranteed to be globally unique, highly available, parsable, and cryptographically verifiable (for example, did:example:123). This identifier can be used to identify any form of entity, whether it is a person, organization, or object. Each DID is generated based on a specific algorithm and is independently controlled by its owner rather than authorized by a single authority.
DID can be parsed into a DID document, which contains the authorization key (Authentication Key), the agreement key (Agreement Key), the delegation key (Delegation Key), the verification key (Assertion Key), and the Information such as service endpoints that interact with DID entities. These keys are similar to the different types of documents we use to sign in different life scenarios, such as confidentiality agreements, power of attorney or authorization letters, etc.
VC, a verifiable digital certificate matching DID, is actually an endorsement statement of certain attributes issued by one DID to another DID, aiming to verify DID The identity, capabilities or qualifications of the subject. For example, a VC can be a digital certificate issued by an organization, government department, or commercial entity, generated and verified through cryptographic methods to confirm that the owner possesses certain attributes and that these attributes are Believable. VC can contain various information and data types, such as ID, type, timestamp, etc., and supports multiple settings for the certificate status, including valid, expired, invalidated, frozen, etc., to reflect the issuer's statement on the validity of the certificate. .
In the VC ecosystem, the W3C standard defines three roles:Issuer (issuer/attester), holder (holder/claimer) and verifier (verifier) ). These roles jointly participate in the circulation of a certificate: the issuer verifies and issues the certificate to the holder, the holder decides how and to which verifiers to display these certificates, and the verifier confirms the information they need to verify, thereby completing the entire verification process. .
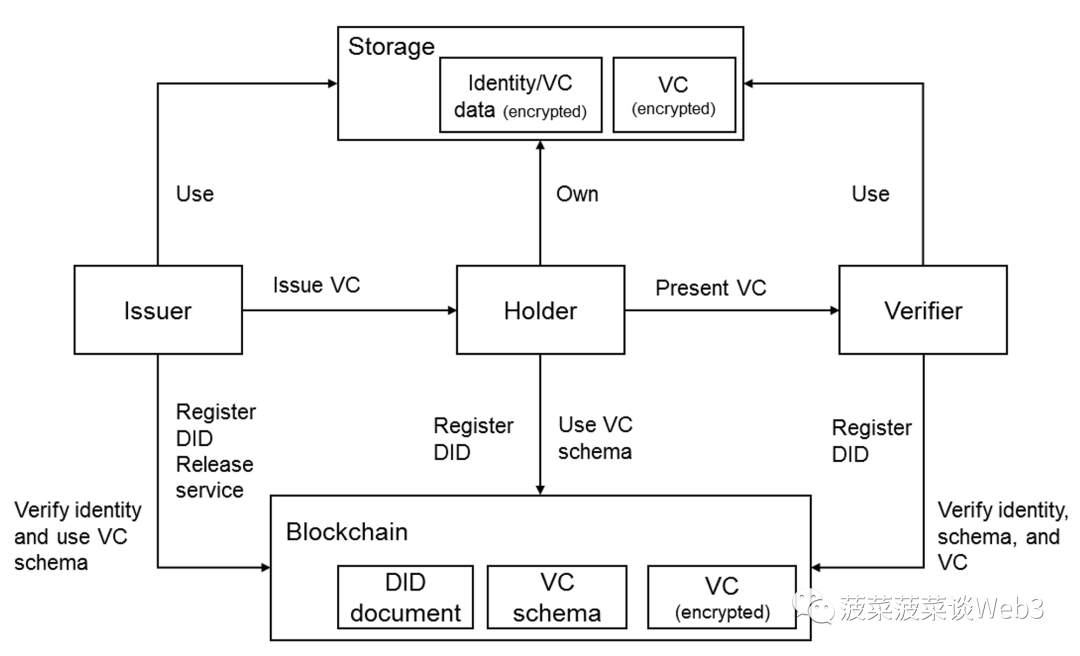
Image Source:
https://support.huaweicloud.com/intl/en-us/devg-bcs/bcs_devg_4005.html
On this basis, multiple projects and R&D teams have integrated privacy protection technologies beyond traditional cryptography into identity authentication systems, including the widely watched zero-knowledge proof (ZKP: Zero Knowledge Proof) in the Web3 field. )technology. Zero-knowledge proof is a unique method that allows one party (the prover) to verify to another party (the verifier) that it does know certain information without revealing any specific information about the information. content.
To illustrate with a simple metaphor, suppose Alice wants to prove to Bob that she knows how to restore a Rubik's Cube in a specific chaotic state, but does not want to reveal the specific recovery steps. In this case, Alice can use an opaque box to solve the Rubik's Cube without letting Bob see the specific steps. All she has to do is remove the solved Rubik's Cube from the box to prove she has mastered the technique, but the exact steps remain a secret. The same is true for the technical principle of zero-knowledge proof, which can encrypt the true content of the information in the "box" and prove a certain fact at the same time.
ZKP technology is particularly useful in digital identity verification scenarios because it allows individuals to prove themselves without exposing private details. Often, identity verification may require the disclosure of large amounts of personal information, which, once collected and analyzed by multiple parties, may pose a threat to personal privacy. However, systems using ZKP technology, such as zkID developed by zCloak, combine DID and VC to provide users with richer privacy protection options.
Through the zkID system, users can flexibly control the amount of information they are willing to share during the verification process after receiving a VC with the digital signature of the issuer. Users can choose the granularity of displaying information, such as ZKP Disclosure, Digest Disclosure, Selective Disclosure or Full Disclosure. ). Especially through zero-knowledge proof disclosure, users can display information under the "minimum knowledge principle" and only feedback "eligible" or "unqualified" results without revealing any specific private information.
For example, users can prove to relevant institutions that they have valid visas, loan qualifications, voting rights, or meet transaction specifications by simply displaying local data results that have been certified by zero-knowledge. In this process, the user's private data is always stored and processed on their local device without revealing any specific content, ensuring that the right to use the data is completely in the hands of the user.
To summarize, in the process of promoting large-scale application of real-world asset tokenization, privacy protection and compliance of identity verification have become an indispensable cornerstone. By adopting a DID and VC authentication system based on W3C standards and integrating zero-knowledge proof (ZKP) technology, we are able to meet compliance requirements while ensuring identity privacy on the chain. This not only provides implementation guidelines for a "perfect legal system", but is also a potential key link in resolving the gap between on-chain and off-chain and balancing privacy and regulatory needs.
On-chain fiat currency
Blockchain applications essentially solve trust issues, and in the business field, 99% of application scenarios that need to be related to trust issues involve dealing with money [19], Therefore, if real-world asset tokenization is to be applied on a large scale, legal currency on the chain is necessary, and the tokenized currency on the chain itself is actually a real-world asset token. For tokenized application scenarios, only by introducing central bank digital currency CBDC, tokenized deposits and compliant stablecoins can the greatest potential of real-world asset tokenization be unleashed.
The blockchain world currently lacks the monetary trust anchor provided by central banks[20]. Although stablecoins have sprung up to fill this vacuum by mapping fiat currencies, stablecoins have continued to suffer amid crypto market shocks in the past. The fact that price decoupling occurs shows that stablecoins cannot replace the role of legal currency on the blockchain. In essence, stablecoins are just "vouchers" for off-chain legal currencies on the blockchain. That is, stablecoins are not legal currencies themselves. Even when the collateral of the stablecoin issuer is fully sufficient, stablecoins may cause price deviations due to market panic. If If the Token on the chain is the "ontology" of legal currency, there will be no price de-anchoring.
Compared with the current stable currency system, the use of tokenized legal currency is not only more convenient and easier to obtain, but its application scenarios are also more significant, and it also provides greater programmable space for financial innovation. First of all, the legal currency on the chain, combined with the alliance chain structure regulated by national laws, can be directly integrated with the payment scenarios in our daily lives. It can be seamlessly integrated into our daily lives, whether it is salary payment, business activities or other aspects. This means that people can acquire on-chain fiat currency directly through their regular activities, bypassing some of the complex and time-consuming steps in the current crypto system, such as the need to obtain gas fees before using wallets and stablecoins.
In the 2023 annual report of the Bank for International Settlements, known as the “central bank of central banks” “A Blueprint for the Future Monetary System: Improving the Old ", enabling new ones" mentioned in the chapter that tokenization has the potential to have a revolutionary impact on the existing monetary system, and tokenization is exploring unprecedented opportunities for the current system. This vision describes a new type of financial market infrastructure - a "unified ledger" that integrates central bank digital currency (CBDC), tokenized deposits and tokenized claims on other financial and real assets. together.
The unified ledger has two key advantages. First, it provides a unified platform where broader emergency response measures and financial transactions can be seamlessly integrated and automated. This allows transactions to be synchronized and settled instantly. In contrast to the world of cryptocurrencies, settlement using central bank currency ensures the uniqueness of the currency and the finality of payments. Second, by concentrating everything in one place, new types of contingent contracts (contracts that rely on a specific situation or condition to take effect) will be created that are more efficient by solving problems related to information and incentives. Serve the public interest well[20].
In order to help readers further understand the importance of legal currency on the chain, the author will further elaborate. First, explain the definitions and differences of CBDC, tokenized deposits, and legal stablecoins that will be used on a large scale in the future:
Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC): A digital base currency (Base Money) directly issued by the central bank. Whenever a transaction involving CBDC occurs, it is directly reflected as a change on the central bank’s balance sheet and can be stored on the blockchain platform as a tokenized form.
Tokenised Deposits: Deposits are a form of money created by commercial banks based on credit, that is, credit money. Whenever a relevant transaction occurs, It will directly lead to changes in the balance sheets of commercial banks, and tokenized deposits are tokenized expressions on the blockchain.
Legal Stablecoin: Legal stablecoins here refer to stablecoins issued by legally regulated institutions, such as ANZ, the third largest bank in Australia. Whenever a relevant transaction occurs for the issued Australian dollar stable currency A$DC, since the stable currency is a bearer instrument, it will not be reflected in the balance sheet changes of the issuing institution, but will occur in the wallets of different people. transfer.
If you want to further understand the difference between base currency, credit currency and the process of currency creation, you can read another article by the author: "MakerDAO from a currency perspective: Understanding the deep meaning of the introduction of RWA U.S. debt assets", let us take a closer look Explain what application scenarios on-chain legal currency can bring:
Programmable digital currency:
One of the advantages of tokenization is programmability. For tokenized legal currency, programmable currency will open a door to great imagination,For example, the Monetary Authority of Singapore, MAS, released a technical white paper on Purpose-Bound Currency (PBM) in 2023. This is a technology that uses "wrapper contract" technology to retain the homogeneity properties of the digital currency itself without programming it. A digital currency standard that can programmable currency usage purposes. For more details, you can read the PBM white paper. The core point is to use a "packaging contract" to wrap and manage universal digital currency, and put the payment logic in this "packaging contract" to manage the digital currency in it. Corresponding to different application scenarios, we can choose different "packaging contracts" to constrain and manage the packaged digital currency, thereby programming the payment process and conditions. However, these packaged digital currencies themselves are unified, neutral, free, and homogeneous. Once the conditions are met, the payee can withdraw the digital currency from the package and restore the "unconditional" nature of the digital currency itself [21 ].
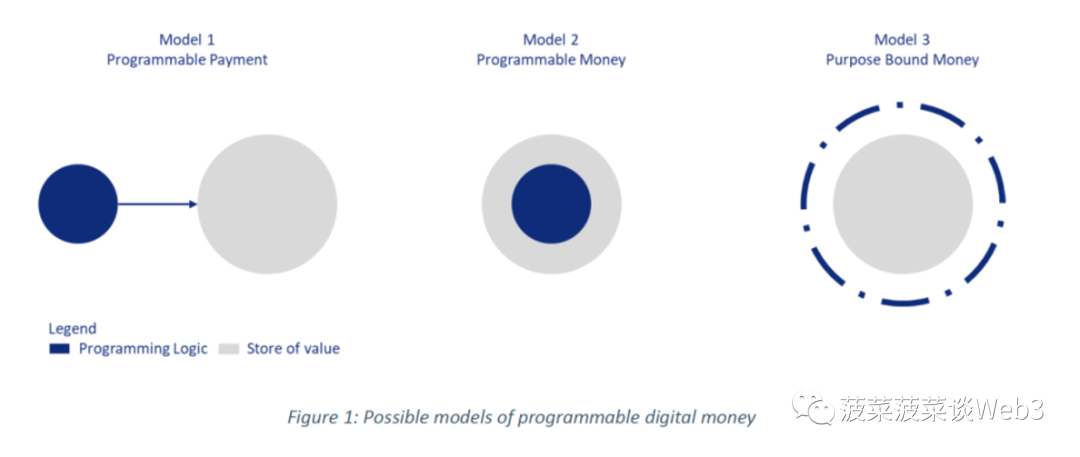
To put it simply, after using PBM technology to program currency, the currency can be used for special purposes and automatically return to a homogeneous currency form after the conditions are met. For example, in order to stimulate a certain market, such as the peach market, the government may release special funds to the public, which can only be used to purchase peaches. Alternatively, parents can set up a fund lock for their child to ensure only a certain amount is unlocked each month to regulate spending. However, the technology could be controversial because while it provides governments with more precise means of monetary control, it also means greater regulatory authority, potentially resulting in a loss of privacy and freedom.
Real world application scenarios:
In the past, blockchain technology encountered many obstacles in actual industrial applications, resulting in some blockchain projects that did not involve Tokens merely becoming expensive and inefficient database systems,Even a blockchain with Token will not be able to realize its true potential due to legal supervision and barriers on and off the chain, and the lack of legal currency on the chain is one of the reasons. We can use a RWA case as an example.
The Crypto world may wish to see some RWA projects trying to tokenize the rent income rights in the real world and sell their shares on the blockchain. To achieve such an operation, there will be barriers on and off the chain. Obstacles, for example, tenants pay rent using off-chain legal currency. The project team needs to convert the tenant’s rent into stable currency on the chain, and then distribute the rental income to investors who hold shares., not to mention compliance supervision issues, such as how to deal with disputes? How to deal with the project side running away? Not to mention the friction costs incurred by converting off-chain currencies into on-chain stablecoins, investors also have the problem of opaque information as to whether tenants actually pay rent
If it is established under a permissioned chain system with on-chain legal currency and legal supervision, tenants can naturally directly use the on-chain legal currency to pay to the corresponding smart contract,The smart contract will automatically distribute the shares of the income-rights financial product to all investors holding shares, and using token standards like ERC-3525, the issuer can easily distribute a variety of non-standard rent The income rights assets are packaged into a standardized financial product, and its transparency can also allow investors to know whether the tenant has actually paid the rent. The issuer can even repackage many such financial products to form one financial product. product.
To summarize,The popularity of on-chain legal currency, especially the widespread application of CBDC, will inject strong impetus into the large-scale application of real-world asset tokenization. This not only creates practical scenarios for the application of tokenization technology in our daily lives and various industries, but also brings broader development prospects and possibilities, which may It has a significant impact on all aspects of people’s daily lives.
Oracles and cross-chain protocols
Although the application of blockchain and tokenization technology has revolutionary potential, due to the operating mechanism of the blockchain, that is, each node must perform deterministic operations, that is, for the same input data, all Nodes will get the same output. Each node will face uncertain operations when acquiring and processing external data. This kind of uncertain operation may cause data inconsistency between nodes, thus affecting the consensus process. Therefore, the blockchain itself cannot actively obtain data from the outside. This is also called an "oracle." Question"[22].
Most of the potential application scenarios of smart contracts can only be realized by connecting off-chain data and systems. For example, in the financial field, smart contracts need to rely on price data from the external market when executing; in the insurance industry, smart contracts need to make judgments based on Internet of Things and network data when processing claims. Smart contracts in trade finance require access to relevant documents and digital signatures to confirm and execute loan operations. In addition, there are many smart contracts that require fiat currency interaction with traditional payment networks during settlement. A large amount of necessary data is generated off-chain, and these data cannot be directly transmitted to the chain [23].
In addition,Since the blockchain itself is an isolated island, this has brought about the fragmentation of users, assets, liquidity, applications, and data. To realize the real world For the large-scale application of asset tokenization, it is extremely important to connect blockchains to each other. Only by reconnecting the "islands" into a "continent" can the true potential of the blockchain be unleashed, To realize the interoperability of thousands of chains, whether it is an oracle or a cross-chain bridge, it is essentially responsible for the transmission of information between the blockchain and the outside world. As the leader of the oracle machine track, Chainlink will play a major role in the tokenization of real-world assets in the future. plays an extremely critical role in large-scale applications.
Chainlink launched two blockbuster functions, Chainlink Function and CCIP respectively in 2023. The author believes that it is a milestone for the large-scale application of real-world asset tokenization, because as more and more financial institutions to explore application scenarios involving tokenized assets and believe in the long-term value of blockchain technology and/or digital assets. However, since central banks or financial institutions in different regions will issue their own central bank digital currencies or financial assets on different private chains/permissioned chains in the future,this will lead to a global blockchain platform Very fragmented, making tokenized assets and related services isolated between different blockchains, and interoperability between these blockchains cannot be achieved, so this cross- On-chain communication issues limit the application of tokenized assets, making them inaccessible and illiquid, and complicating the integration process for financial institutions [25].
To achieve large-scale application, people need to be able to freely use these tokenized currencies to purchase assets on other blockchain ecosystems. Although there are many cross-chain protocols on the market, there have been frequent incidents in the past. Security accidents have made cross-chain protocols become high-risk security areas, causing countless asset losses. Such a "dangerous bridge" is obviously unable to carry out the mission of connecting "isolated islands" into a "mainland". Therefore, the security of cross-chain protocols has become people’s primary need, and the CCIP launched by Chainlink may change this pattern and become a universal interoperability layer that will be widely adopted in the future (Note: The author chose The reason for Chainlink is that Chainlink has the strongest ties to the traditional financial world).
CCIP is an abstraction layer and cross-chain messaging protocol that enables existing infrastructure to connect to the blockchain and instruct smart contracts to send arbitrary data and enable token transfers between public and private blockchains. In simple terms, CCIP It can link any blockchain together (such as permissioned chain and public chain) to solve the interoperability and liquidity fragmentation problems caused by blockchain islands.

Image Source:
https://zh.chain.link/resources/cross-chain-tokenized-asset-settlement
CCIP provides financial institutions with a way to meet customer needs without requiring significant modifications to existing infrastructure [26]. Financial institutions do not need to make modifications to legacy systems. This enables financial institutions to interact directly with tokenized assets in existing infrastructure, such as through Swift messages, APIs, mainframes and other traditional formats. Financial institutions can use on-chain CBDC through CCIP to directly interact with any blockchain. interact with any protocol.
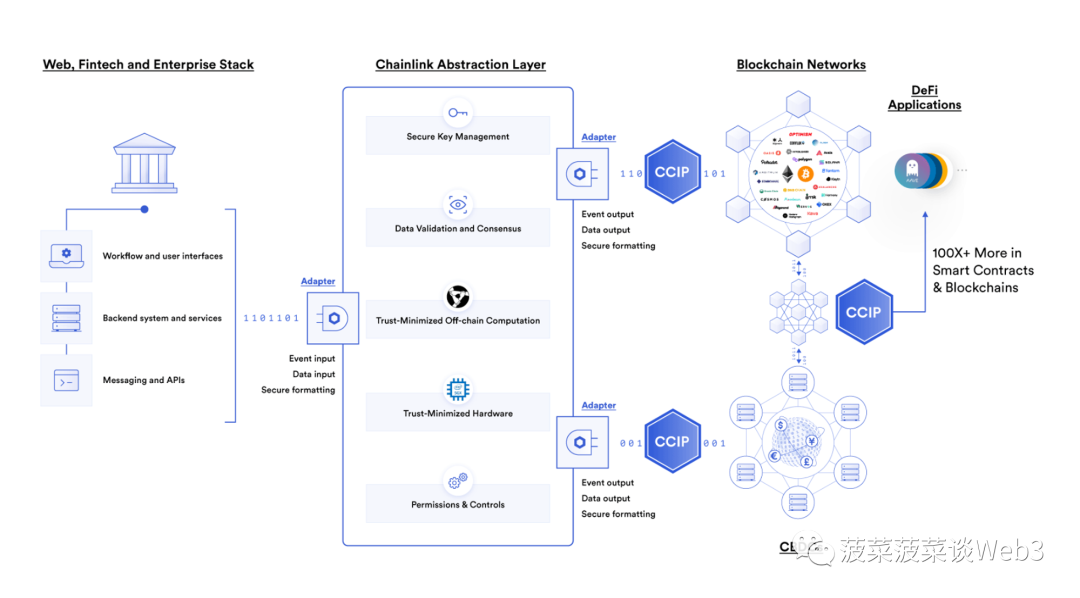
Image Source:
https://blog.chain.link/tokenization-for-capital-markets/#post-title
On August 31, 2023, the international funds settlement system SWIFT released a report [27]. SWIFT cooperated with a number of major financial institutions to conduct experiments, including Australia and New Zealand Bank (ANZ), BNP Paribas, Bank of New York Mellon, Citibank, Several major financial institutions including Clearstream, Euroclear, Lloyds Banking Group, SIX Digital Exchange and Depository Trust & Clearing Corporation (DTCC) conducted experiments. Using Chainlink’s CCIP to securely connect the Swift network to the Ethereum Sepolia network enables full interoperability between source and target chains, successfully enabling cross-chain interoperability across multiple jurisdictions and blockchains.
Image Source:
https://blog.chain.link/tokenization-for-capital-markets/#post-title
In addition, Chainlink has also reached a cooperation with Australia and New Zealand Bank (ANZ) to participate in a comprehensive case study of CCIP, and plans to deploy CCIP applications in legal stablecoins issued by ANZ to promote the adoption of institutional participants. Tokenized assets, and published a case study [25] demonstrating how financial institutions can leverage Chainlink CCIP to provide customers with the ability to trade and settle tokenized assets on public and private blockchains. From this, we can foresee that in the future, on-chain tokenized assets will exist on public blockchains and regulated permissioned chains operated by financial institutions, and CCIP can Tokenized assets on any blockchain are connected to achieve interoperability and interoperability among thousands of chains.
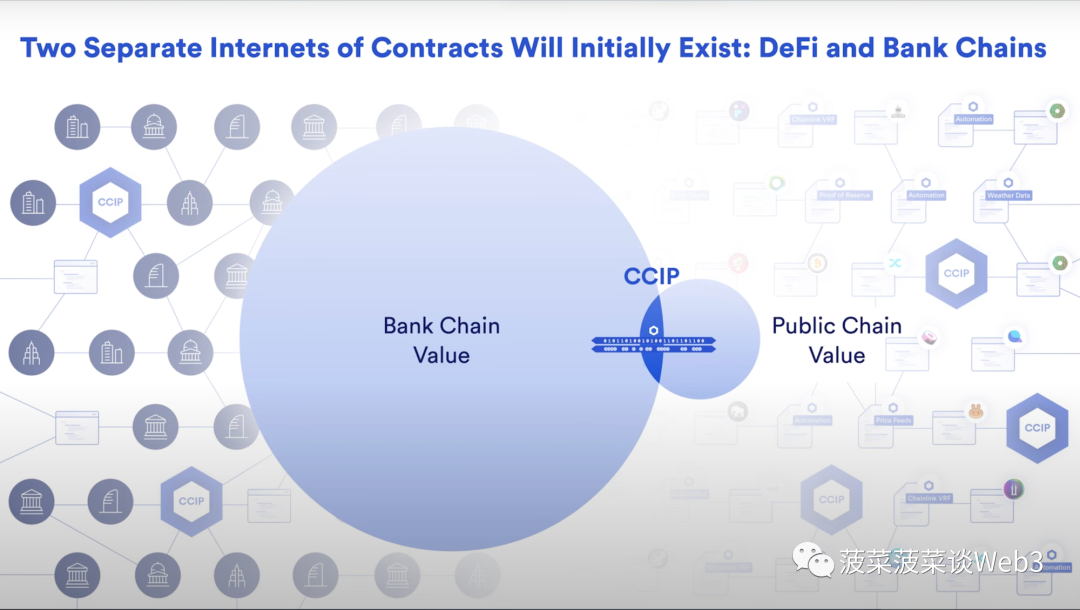
Image Source:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YBfkANJSvJ0&t=167s
For blockchain and smart contracts to realize greater potential, in addition to achieving interoperability between blockchains, the link with the real world is also extremely important In the past, the main application scenario of oracles was price feeding services, which reliably transmitted real-world price information to the chain through a specific data supply chain to provide necessary trigger conditions or parameters for smart contracts. In 2023, with the launch of Chainlink Function, smart contracts can be linked to any API in the world to trigger conditions or transmit information, and can use Chainlink's decentralized oracle network for customized calculations.
Whether it is CCIP or Function, Chainlink’s decentralized oracle network DON plays an extremely important role. It aims to ensure data security and Reliability and tamper resistance. This design reduces the risk of single points of failure and makes it more difficult to manipulate data, so decentralized oracles can provide a higher degree of trust and reliability in critical application scenarios.
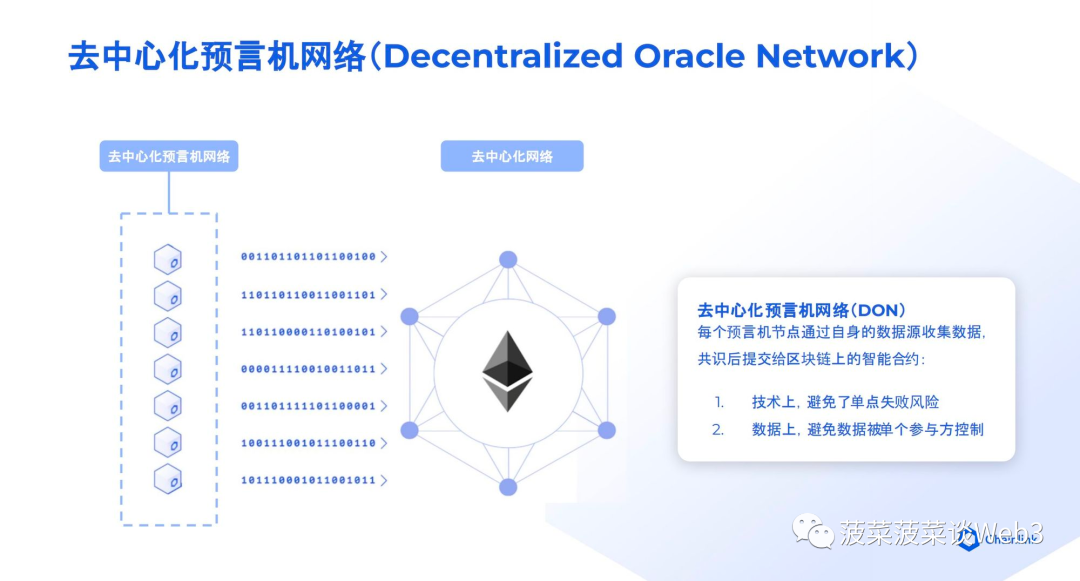
Image source: https://research.web3caff.com/zh/archives/8102?ref=W3110
Chainlink Function implements custom operations on the DON level of the decentralized oracle network. In fact, it can be called decentralized off-chain operations, minimizing trust.It Combining the characteristics of centralized off-chain operations with on-chain operations bridges the gap between centralized off-chain and on-chain operations.According to the official statement, oracle operations can enable transmission to The data of smart contracts can maintain security, reliability and difficulty in tampering, while also having the advantages of centralized off-chain computing, achieving high performance, low cost and scalability. Therefore, compared to pure on-chain computing and centralized server computing, Chainlink Function can allow smart contracts to implement functions that were previously difficult or inefficient, providing a lot of room for imagination.

Image source: https://research.web3caff.com/zh/archives/8102?ref=W3110
Through Chainlink Function, smart contracts can be linked to any device API in the real world, such as when an emergency event occurs on the chain, such as when a DeFi position is in danger of being liquidated. The contract automatically sends an email to remind the user through the Chainlink Function link mailbox API; when the plane is delayed, the insurance smart contract on the chain is automatically triggered through the Chainlink Function; the status of the RWA assets on the chain is updated through the Function by real-time monitoring of the status of off-chain assets; or A case of integration with the Internet of Things implemented by AWS IoT Core [28], which is used to monitor the price of stablecoins through Chainlink Data Feeds, and then uses Chainlink Automation to monitor the Chainlink data source that reports the price of stablecoins. If stablecoin decoupling is detected , it starts and calls the Chainlink Function to send an alarm to AWS IoT core, thereby triggering alarms on IoT devices in the real world.
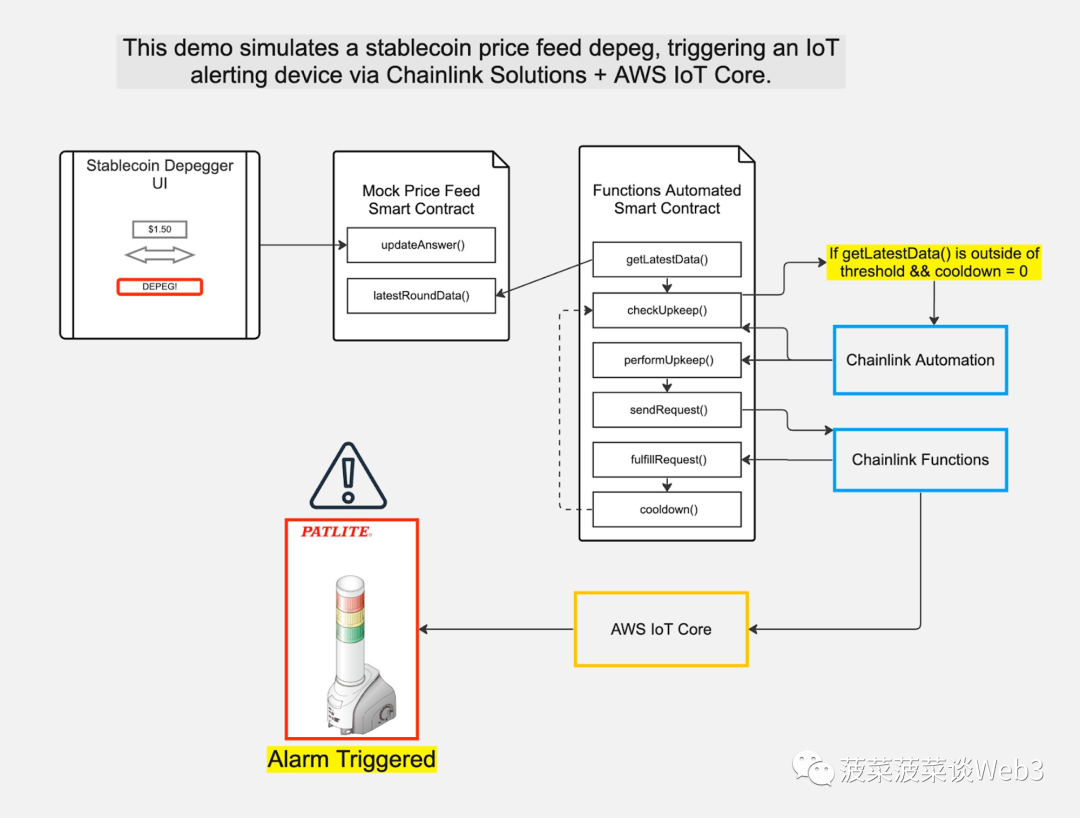
Image Source:
https://blog.chain.link/ways-to-use-chainlink-functions/#amazon_web_services_(aws)__connecting_to_iot_devices_using_aws_iot_core
To summarize, in the future permissioned chain structure with many different jurisdictions and regulatory systems, cross-chain technology is particularly important to solve the problems of interoperability and liquidity fragmentation, With the emergence of a new generation of more secure cross-chain protocols like Chainlink CCIP and the continuous exploration of the traditional financial world, it has laid the foundation for the security and large-scale application of the interconnection pattern of tokenized assets in the future, and the prediction The continuous improvement of machine functions such as the launch of Chainlink Function also opens a very imaginative door to future application scenarios that are combined with the real world.
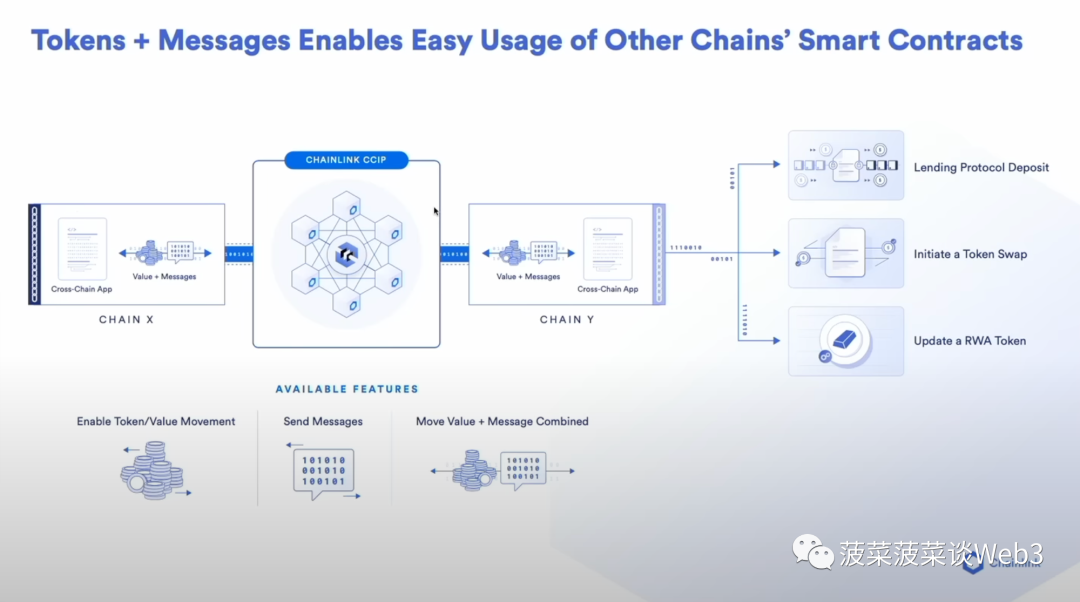
Image source: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8qqy-8Oi8ww&t=24s
Low threshold wallet
As the entrance and pass to Web3, the wallet not only assumes the function of managing assets in the traditional sense in the Web3 world, it is also an essential tool in the Web3 world, carrying the ability to interact with the blockchain and smart contracts. mission, but the current threshold for using the wallet is too high for new users to learn. Coupled with the rampant hackers and frequent asset thefts, many people are shut out. Only by lowering the wallet threshold can bring Bring more fresh blood to promote large-scale application and ecological explosion.
Currently, blockchain and wallets have a high level of awareness for the general public. The high threshold of cognition coupled with the complexity in using wallets, such as private key-based management, constitute important factors that hinder the large-scale promotion of Web3. For example, when users create a wallet, the preservation and management of private keys becomes a huge challenge. Most people have no concept of private key management, and it is easy to lose or leak private keys, leading to permanent loss of assets. Therefore, low-threshold wallets have become an important part of promoting large-scale application of blockchain.
The existing wallet system is mainly divided into two types: EOA Externally Owned Accounts and CA Contract Account. The difference between the two is EOA Externally Owned Accounts The account wallet is a wallet controlled by a key pair of private key and public key. It basically only has the functions of receiving, holding, sending Tokens and interacting with smart contracts. It does not have programmable functions. And gas fees are required to execute each transaction. There is no cost to create an externally owned account type wallet, but it can only be created by generating a private key.
The CA contract account type wallet refers to a wallet that exists in the form of a smart contract. It is not controlled by a private key and does not have a private key. Instead, it writes code in the form of a smart contract to implement various functionsIt requires an external account wallet to call and pay. Gas fee and passive transaction initiation [29]. The contract account wallet itself cannot actively initiate transactions., such as multi-signature wallets, safes, faucets and other functions. Common uses are multi-signature wallets, which require multiple external account wallet authorizations to conduct transactions. They are usually used for enterprise wallet management. . Creating a contract account wallet requires gas fees to create.
Both wallet account types have their own advantages, disadvantages and limitations.EOA externally owned accounts can only be generated according to the method of generating key pairs. They are not programmable and require It can only be operated if you have Gas fee, and the private key cannot be retrieved if it is lost. However, compared with the CA contract account type,Although the CA contract account type can automatically It is possible to define logic to achieve more functions, but the CA contract account type cannot actively initiate transactions and needs to be called by an externally owned account of EOA, and generating a wallet of the CA contract account type requires additional Cost, these two wallet account types currently cannot solve the problem of complex wallet usage experience.
Currently, existing wallet solutions include MPC wallets, smart contract wallets, managed wallets, etc., but the ERC-4337 Account Abstraction wallet is regarded as the ultimate form to achieve large-scale application of wallets, which combines EOA The advantages of wallets and CA wallets are that while being programmable, they can also greatly reduce the threshold for use, such as supporting functions such as logging in and using the wallet like Web2, gas payment, social recovery, aggregation wallet and other functions.
However, the mechanism of account abstraction has its own complexity, which causes large-scale applications to still face some challenges. However, in any case, lowering the user threshold is always a priority. Whether it is account abstraction or other types of wallets, simplifying the user experience is crucial. A wallet with a low threshold and easy use is undoubtedly the key infrastructure to promote the blockchain towards large-scale application.
5. Future Outlook
The foreseeable trend is that with the increasing attention and recognition of blockchain and tokenization technology in the traditional financial field and governments of various countries, as well as the continuous improvement of blockchain infrastructure technology, Blockchain is on the road to integrating with the traditional world architecture and solving real pain points in real-world application scenarios, providing practical solutions for actual scenarios, rather than being limited to a "blockchain" that is isolated from the real world. "Parallel World".
Although many people pursue the so-called "blockchain revolution", in the current industry environment, there are many projects in the name of decentralization, but in fact they are highly centralized, but most people don't care. This is like the "elephant in the room". Therefore,The author believes that this ideology should be weakened during the application of blockchain in real-world scenarios, and decentralization should not be forced in environments where it is not applicable.
Real World Asset Tokenization will be the killer application that leads the blockchain to tens of trillions of scale. Its potential will likely affect the entire human financial and monetary system. By transforming reality into The world's assets are tokenized and expressed using tokens on the blockchain platform. A market that can greatly improve efficiency, reduce costs, and operate 24 hours a day can be realized. Programmability, automatic execution, transparency, traceability, composability, privacy protection, empowering enterprises, global mobility, solving trust issues, identity autonomy, and potential new application scenarios, etc.
For the Crypto world at this stage, the logic of RWA is a unilateral demand for real-world asset return rates. In actual operations, there are challenges such as regulatory compliance and on-chain and off-chain barriers. The huge potential is demonstrated in the traditional financial world of TradFi. RWA’s logic for TradFi is to go in both directions. The traditional financial world needs blockchain and DeFi technology as a new financial technology tool. Empower the traditional financial system and solve the pain points of traditional finance.
To realize the large-scale application of real-world asset tokenization, legal regulatory compliance is one of the necessary prerequisites. Most of the core assets that need to be tokenized are in the hands of traditional financial institutions, and for institutions Compliance is a necessary prerequisite, and a series of legal safeguards are needed to protect investors from fraud and abuse, combat financial crime and online misconduct, maintain investor privacy, and ensure Industry participants meet certain minimum standards and provide a recourse mechanism when problems arise. With the protection of the legal system, the use of permissioned/private chains can effectively enforce laws and regulations in different jurisdictions. demands.
In order to achieve effective supervision, the concept of "relational identity" that can carry social relationships and credit systems plays a crucial role in the on-chain identity system. The combination of this identity system and privacy protection technology is the key to granting and managing digital identities under the authorization and supervision of government and regulatory agencies. Within this framework, W3C's DID (Decentralized Identifier) and VC (Verifiable Credential) technologies can play an important role. These standards provide a way for individuals and entities to control their own identity information while ensuring the integrity and verifiability of the information. Incorporating zero-knowledge proof technology in the future also provides new possibilities for enhancing user privacy, security, compliance and transparency.
In order to meet the supervision and asset risk management requirements of regulatory agencies and financial institutions,the future will be a multi-chain structure, so the interaction between blockchains Operability and the security of information transmission are particularly important. With the gradual improvement of new generation cross-chain technologies such as CCIP launched by Chainlink, coupled with its cooperation with traditional financial institutions, we can see A solid foundation is being laid for the future multi-chain landscape and the large-scale application of real-world asset tokenization.
If blockchain and smart contracts are to be widely used in real-world scenarios, tokenized legal currencies on the chain such as CBDC and tokenized deposits are also indispensable. Different from the current stable currency system, stable currency is not the currency itself, but an on-chain "voucher" of the currency, and it is difficult to be widely used in real business activities. For example, merchants typically will not accept stablecoins as a means of payment when making daily purchases or visiting convenience stores. Although some credit cards currently allow users to pay directly with crypto assets, the high fees make them impractical in daily payment activities.
With the popularization of central bank digital currency CBDC, the continued development of tokenization technology and the lowering of wallet usage thresholds, we can foresee a picture in the future: people can easily own and manage their own tokenized assets, through wallet and leverage on-chain fiat currencies to seamlessly complete transactions in your daily life. On-chain legal currency opens a new door for the promotion of tokenization technology in practical application scenarios, giving it a wider application space and practical value.
Currently,many countries around the world are actively promoting blockchain-related legal and regulatory frameworks. At the same time, blockchain infrastructure, such as wallets, cross-chain protocols, oracles, various middleware, etc., are being rapidly improved, and the central bank’s digital currency CBDC is also constantly improving. For practical applications, token standards that can express more complex asset types are also constantly emerging, such as ERC-3525. Coupled with the development of privacy protection technology, especially the continued development of zero-knowledge proof technology, and the increasing maturity of on-chain identity systems, we It seems that we are on the eve of the large-scale application of blockchain technology.
Reference:
[1]https://www.bis.org/publ/bisbull72.htm
[2]https://mirror.xyz/bocaibocai.eth/i2W73H6Uvk97e-cZzZJMoVXjBRNNgu8QiaCwpW8vKz8
[3]https://mirror.xyz/bocaibocai.eth/wCUwqHxlB55Qk9NoQEsPnj0Te7HdCPLjRp3acZjjgK8
[4]https://www.defidaonews.com/article/653729
[5]https://wenli.substack.com/p/defi
[6]https://www.bis.org/publ/work1066.htm
[7]https://bankless.ghost.io/defi-lending-doesnt-exist-yet/#/portal/signup
[8]https://www.oliverwymanforum.com/future-of-money/2022/Nov/institutional-defi.html#the-value-of-inst-design
[9]https://www.bnymellon.com/content/dam/bnymellon/documents/pdf/insights/migration-digital-assets-survey.pdf
[10]https://www.woshipm.com/pd/654045.html
[11]https://www.weiyangx.com/351961.html
[12]https://www.finlaw.pku.edu.cn/flyxjr/gk_hljryfl_20181025180041616718/2016_jrfy_20181029112516067070/zdsyq3y/239896.htm
[13] https://www.cyzone.cn/article/584647.html
[14]https://www.bis.org/publ/othp75.htm
[15]https://www.investopedia.com/ask/answers/052715/how-big-derivatives-market.asp
[16]https://mirror.xyz/bocaibocai.eth/q3s_DhjFj6DETb5xX1NRirr7St1e2xha6uG9x3V2D-A
[17]https://www.bis.org/publ/work1116.htm
[18]https://foresightnews.pro/article/detail/28192
[19]https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Advoy5E86nPhE20Dqm6paw
[20]https://www.bis.org/publ/arpdf/ar2023e3.htm
[21]https://foresightnews.pro/article/detail/36732
[22]https://research.web3caff.com/zh/archives/8102?ref=W3110
[23]https://blog.chain.link/what-is-the-blockchain-oracle-problem-zh/
[24]https://research.web3caff.com/zh/archives/11605?login=success&ref=W3110
[25]https://zh.chain.link/resources/cross-chain-tokenized-asset-settlement
[26]https://blog.chain.link/tokenization-for-capital-markets/#post-title
[27]https://www.swift.com/zh-hans/node/309229
[28]https://blog.chain.link/ways-to-use-chainlink-functions/#amazon_web_services_(aws)__connecting_to_iot_devices_using_aws_iot_core
[29]https://mirror.xyz/bocaibocai.eth/-wDOG6BqzqusFD8Y9BaQ0tMeRTRXhCpHf6mqBI8TqL0
[30]https://www.techflowpost.com/article/detail_10541.html