1. Tariff package module
Tariff package refers to the tariff standard used by customers when conducting business. Fill in the name of the tariff package, select the billing rule method, and click the "Confirm" button to create a tariff package, as shown in the figure below.
The charging rule is the rule that charging follows. The OKCC system currently designs the following three billing methods (which will be expanded in the future), mainly including billing by duration, billing by time, and billing by cycle. Let’s explain one by one: For system issues, please look at the blogger’s name. Welcome to have technical exchanges with the blogger.
Billing by duration: Billing is based on the duration of the call, that is, from the time the customer connects on the landing line side to the time the customer hangs up (actively or passively). The call charges for less than 1 minute will be calculated as 1 minute.
Pay-per-view: The call fee is calculated according to the number of call records actually connected.
Billing by cycle: That is, the rent service is collected periodically. The system can collect rent according to a fixed value, or calculate the rent according to one or more attributes of the number of user lines, the number of queens, and the number of seats; the billing cycle includes , week, month, year, usually months.
Minimum billing: Set the minimum consumption of the enterprise, and the system can charge rent according to a fixed value; the billing cycle includes daily, weekly, monthly, and annual, usually monthly.
2. Line configuration module
Here I mainly introduce the commonly used SIP trunk functions.
Fill in the SIP trunk name, user ID, authentication password, IP/domain name, port, etc., and click the "OK" button to add it successfully, as shown in the figure below.
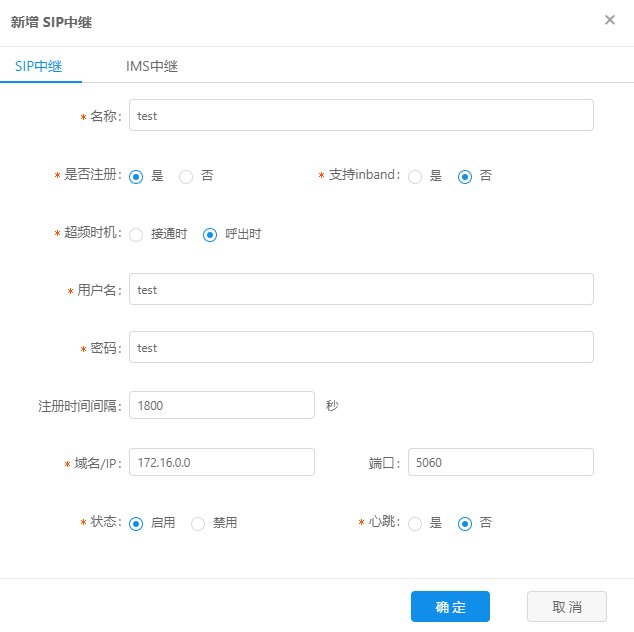
The configuration parameters are explained one by one below:
Name: The name of the SIP trunk, the name should be short and concise;
Whether to register: Select 'Yes' to use it by registering to the peer relay, and 'No' to use it for normal docking;
Whether to support inband: The inband method is to put the buffer generated by the button into the voice rtp stream and transmit it together. The data buffer of each button can be generated by an algorithm, or the corresponding sound can be directly recorded to a file. Then package it into various RTP formats and transmit them to the listening terminal on the voice channel;
Overclocking timing: It is divided into when making an outgoing call and when the call is connected. The overclocking is recorded when the customer picks up the phone when the call is put through. The overclocking is recorded when the call is made when the call is initiated. When enabling called overclocking, you need to choose carefully;
Registration interval: register once with the proxy server, vos, etc. according to the set number of seconds;
Username: The number registered to the peer relay in registration mode;
Password: the authentication password when registering with the peer in registration mode;
Domain name/IP: Indicates the domain name or IP address of the peer relay;
Port: the port occupied by the peer relay sip service;
Status: 'Normal' means it is being enabled, 'Disabled' means the relay has expired;
Heartbeat: 'Yes' means sending heartbeat messages to the peer relay regularly, otherwise it will not be sent regularly;
3. Business report module
Mainly introduces the business volume report function, business volume statistics, which is to collect statistics on the business volume data of enterprise customers of the system, including manual call minutes, preview outbound call minutes, voice group call minutes, incoming call minutes, and total business Amount (minutes).
As shown in the figure below, business volume statistics can support querying data by month and corporate customers.

Set the query conditions and click "OK" to view the customer business volume of the corresponding month, as shown in the figure below.

4. Blacklist module
Blacklist, that is, the global blacklist of the system, the OKCC system supports outgoing and incoming blacklists. Outgoing blacklist, that is, when calling out, it will check whether the number belongs to the blacklist. Some numbers will produce bad usage records in actual services. For called numbers with bad records, the system must impose special call restrictions on them to improve system efficiency. The incoming call blacklist means adding a blacklist to the incoming call service, targeting individual numbers to make malicious incoming calls to the call center, interfering with the normal work of customer service. These numbers can be added to the blacklist to prevent incoming calls.
Fill in the blacklist number, select incoming or outgoing calls, and click the "Confirm" button to add an incoming/outgoing blacklist number, as shown in the figure below.

It is currently possible to import blacklisted numbers from a file to the OKCC system. You can download templates in txt and xls(x) formats, click the "File Import" button, and the data configuration box will pop up to download the template.
Fill in the data, click "File Import", and the configuration box as shown below will pop up. Click to import the file or drag the blacklist number file into the dotted box area at the top of the window. After importing, the system will display the number of successful entries and the number of failed entries.
5. Overclocking module of calling and called
Caller overfrequency, that is, the upper limit of the number of times the calling number can be called. This function is mainly to prevent enterprises from frequently using the same calling number, causing a large number of customer complaints, resulting in the number being shut down.
Fill in the name, frequency limit, select number type, number, monitoring cycle, cycle length, and click "Confirm".
Let's explain the configuration parameters one by one:
Name: The name of the caller overclocking, just use a famous quote that is concise and comprehensive;
Number type: user calling number and DID large number;
Monitoring cycle: The unit of monitoring cycle, including minutes, hours, days, weeks, months, and years.
Period length: Indicates the time interval of monitoring;
Frequency upper limit: The number of transparent transmissions that cannot be exceeded within the monitoring period. The configuration as shown in the figure means that the number of times of use is checked every 30 minutes. If the frequency limit exceeds 2000, then the number will be refused to be selected again during the period;