What are WLAN, LAN, and WAP?
Earlier in Computer Networks we explained the main technology of LAN, Ethernet. At the same time, the Ethernet's multiple access control protocol CSMA/CD is mentioned. Local area network can be divided into wired local area network - Ethernet and wireless local area network - WLAN (Wireless LAN). So our article mainly talks about three parts:
- What is the difference between WLAN and LAN?
- What is the multi-access control protocol of WLAN?
- WLAN security.
1. The difference between WLAN and LAN
Unlike LAN, WLAN data is transmitted through electromagnetic waves , which is often referred to as air transmission. WLAN uses electromagnetic waves to send and receive data through the air without the need for a cable medium.
WLAN communicates using the ISM (Industrial, Scientific, Medical) radio band.
IEEE 802.11 subdivides WLAN standards such as:
802.11a – 54 Mbps transmission rate, on the 5 GHz frequency band, the maximum supported speed is 54 Mbps.
802.11b – 11 Mbps transmission rate, on the 2.4 GHz frequency band, supports maximum speeds of 11 Mbps and 54 Mbps respectively.
802.11i – Improved security
2.WLAN's multi-access control protocol
802.11 wireless local area network, like CSMA/CD, cannot send and detect collisions at the same time. The reasons are:
(1) The ability to detect collisions requires the station to have simultaneous transmission ( station's own signal) and the ability to receive (detect whether other stations are also transmitting). Because on an 802.11 adapter, the strength of the received signal is usually much smaller than the strength of the transmitted signal, it is expensive to manufacture hardware capable of detecting collisions.
(2) All possible conflicts cannot be detected: hidden stations, signal fading
So what is a hidden station?
- Nodes A and C can both reach node B, but A and C cannot communicate with each other - "hidden" each other
- Node B encounters the problem that the signals from nodes A and C collide with each other.
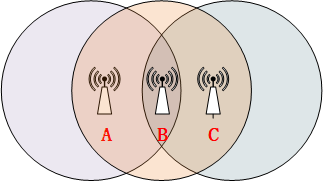
Therefore, WLAN uses the Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Avoidance mechanism Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Avoidance (CSMA/CA).
3. WLAN security.
To secure WLANs, the original encryption protocol used was Wired Equivalent Protocol (WEP) – used in IEEE802.11b. The WEP protocol is based on a symmetric private key that is shared between the access point and the computers on the network. WEP is based on the insecure RC4 encryption algorithm, which can be easily cracked. Therefore, today's WLAN is more inclined to use WPA or better WPA (AES) as the encryption protocol. However, if Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) is used, an attacker can use brute force decoding to obtain the WPS password and thus make WPA/WPA2 insecure as well.