I recently received a private message from a fan, worrying about my current work status:
I have been in this company for more than half a year, and now I mainly do shopping malls similar to Taobao. I used to do application systems and other things, but I feel that the company's software testing positions are all irrelevant, because all I do are functional tests. For a long time, I have never been exposed to technical things. I have done the development and then verified the functions. I have never touched any code, performance, and stress tests, and I haven’t even written much test cases!
When I have nothing to do, I play with my mobile phone. For example, now, because I don’t have internet at work, and I’m reading books and doing other things, I always feel that I’m wasting my time now. Since I just graduated, I can’t just stop doing it, but if I continue like this, It really doesn't make any sense, what should I do?
What are the ways for test engineers to improve themselves?
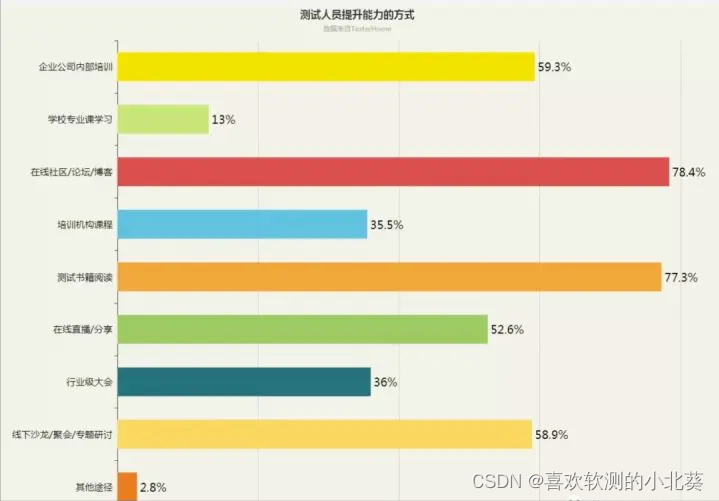
Judging from the survey data, the way most test engineers improve is still focused on forum communities, reading books, and internal training in salons.
Of course, these methods and approaches are easy to obtain, but how can I improve myself in my daily work?
give an example
For example, the subject thinks that testing is a waste of time. Maybe most of the time is spent doing one thing: test case -> submit bug -> return bug. When I first entered the industry, I was not familiar with the process, and I may still feel that I have gained something. If you are familiar with the road behind, you will feel that it is a waste of time.
At this time, you need to improve your technology. Let's explain it from one point: teach you to thoroughly master interface testing!
1. What is interface testing?
The so-called interface refers to the data transmission interface between modules in the same system, front-end and back-end interaction, and cross-system, cross-platform, and cross-database connection. The interface test is to compare the output through the input in different situations of the interface to see whether it meets the functional, security and performance requirements stipulated in the interface specification.
2. Why do interface tests?
1. Compared with system testing, intervene in testing earlier to improve efficiency
2. You can find problems that cannot be tested by the front end and improve the quality of the version
3. The interface is standardized, it is easier to realize automation and continuous integration, and reduce the cost of testing
Therefore, in the requirements of software testing recruitment positions, whether it is functional testing, automated testing, performance testing or test development positions, interface testing must be mastered!
3. How to carry out interface testing?
The development of interface testing generally includes 5 parts: interface document analysis, interface use case design, interface use case execution, locating bugs, submitting and tracking, and outputting interface test reports.
Interface document analysis
Interface documents are generally provided by back-end development, which can be online swagger or word.
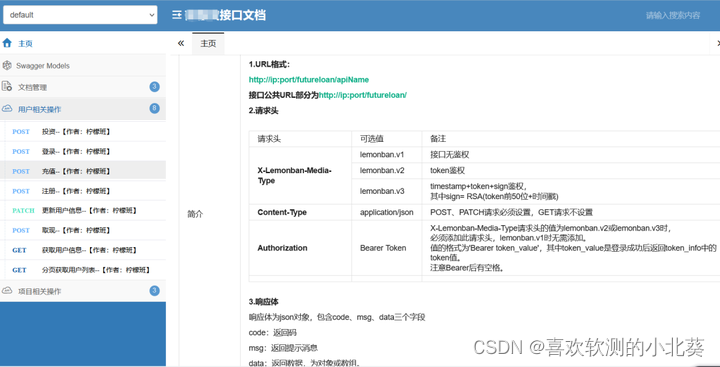
If the development does not provide interface documents, you can use the packet capture tool fiddler or charles to capture interface information for analysis and interface testing.
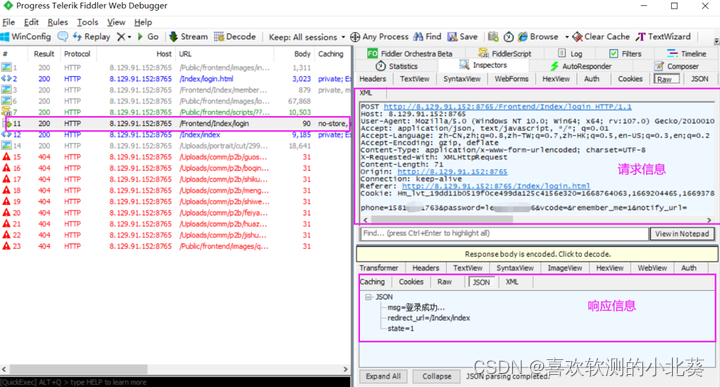
After obtaining the interface document, we need to sort out the request and response information contained in each interface, which can be summarized into five elements of interface information:
1) Interface address url:
Example registration interface address: http://api.lemonban.com:8765/futureloan/member/register
http-request protocol, api.lemonban.com-domain name or ip, 8765-port number, /futureloan/member/register-resource path
2) Request method:
See what the request method defined by the development is, and what method is applied to the test. Common request methods in restful style are post, get, put, patch, delete, etc.
3) Request header:
Send a request to the server, including header information. Common content-types.
4) Request body:
Send a request to the server, specifying the data to be passed. For example, to complete the call of the registration interface, the request body includes mobile phone number mobile_phone, password pwd, username reg_name, and verification code verification_code.
5) Response content:
Comparing the response content described in the interface document with the actual result of the interface test, it can be judged whether the current interface is passed. The response content includes: response code-http status code, response header, and response body.
Interface use case design
The design of interface use cases is similar to the thinking of functional testing, which requires:
1) Clear project business
2) Use 8 major methods of use case design: equivalence class, boundary value, scenario method, cause and effect diagram, decision table, orthogonal test method, state transition method, and error guessing method.
The following is the interface use case template reference:
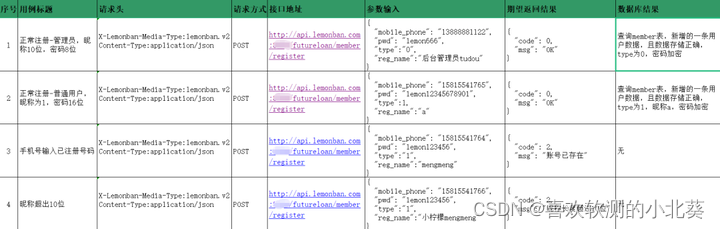
Execute interface use cases and conduct interface tests
Interface test principle:
Simulate a process in which the client sends a request to the server, the server receives the request and processes it, returns a response to the client, and the client receives the response.
According to the principle of interface testing, it is known that tools or codes are needed for interface testing. Mainstream interface testing tools Jmeter, postman.
Using tools to write scripts needs to be designed in conjunction with the specific application scenarios of the interface project, using technologies such as association, parameterization, and assertion.
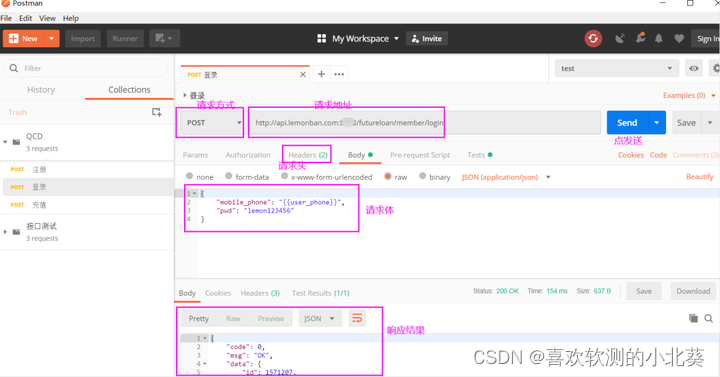
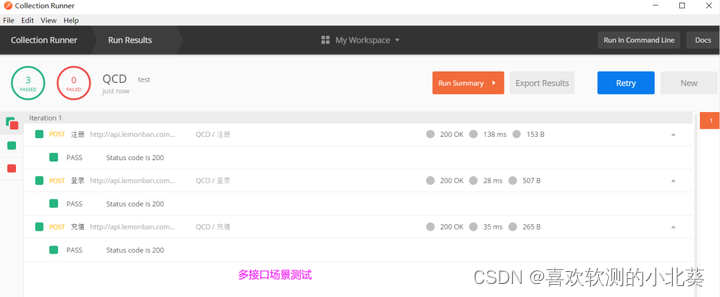
Find bugs, locate, submit and track
How to judge whether it is a bug?
1) The response result in the interface test is wrong, and the wrong code and msg information are returned:
Judging the request: whether the request address, method, request header, and request body are correct, if not, modify the corresponding request information and send it again; if correct, it means that it is a server-side problem
Further check server logs, database information, and organize information to submit bugs
2) In the interface test, the response result, code and msg are correct, but the returned data is incorrect:
Check the correctness and integrity of the database data, and combine the server logs to sort out the information and submit bugs
3) The response result in the interface test is correct, but if the business operation is added, deleted or modified:
It is necessary to further confirm the correctness of data addition, deletion and modification at the database level
4) Consider security: the general interface will impose some restrictions on requests, such as the number of requests and the frequency of requests; whether sensitive information is encrypted
Interface Test Report
The organization of the interface test report depends on the company's requirements. Some companies compile a unified test report after the entire project test is completed. Some companies will require the output of periodic test reports.
There is a long way to go, and you can learn as you go, every like from you is the motivation for the author to create, hey [cute]!