1. Why is there a shortage of people in network security?
The reason for the lack of people is that there are new needs

In the past, all enterprises centered on products. It didn't matter what loopholes you had, whether your user information was leaked or not, as long as the products I made were popular.
All this came to an abrupt end with the promulgation of a series of laws and regulations related to network security, such as the "Network Security Law", "Data Security Law", and "Network Security Review Measures". The country and the individual have begun to pay attention to network security. You see You can feel the strong concern that the recent national network security review of Didi has aroused.
According to the requirements of the new network security laws and regulations, if your company has a network security problem, not only the company must be punished, but also the person in charge of the company should be punished jointly, or even sentenced to prison. Do you think which boss knows the seriousness of this problem and can sit still?
So there is a gap in cybersecurity personnel.
2. What kind of people are missing?

**A.** Most companies need someone who understands general security protection. The specific requirement is to at least ensure that there are no loopholes in the enterprise's portal website, that the internal information of the enterprise will not be leaked, and that it will not be held accountable by relevant departments. The enterprises mentioned here refer to enterprises with a certain scale and informatization needs, excluding small workshops, small processing factories and the like.
**B.** Enterprises providing Internet products need people who understand R&D security. Due to the previous environment, most R&D personnel did not have knowledge about network security. As a result, those who understand R&D do not understand security, and those who understand security do not understand R&D. Understand. Although this situation is gradually improving, it is still a great dilemma for such enterprises.
**C.** Enterprises providing Internet services need people who understand business security. I personally think that business security is actually the most difficult part, because it is not the same as R&D security. After all, R&D personnel have certain network and information knowledge, and they have a lot in common with network security, many places - click and connect. Business security needs to be very familiar with the business process. However, most people who are very familiar with the business are the backbone of the business, and generally do not have much energy to study network security in depth, which also leads to the occurrence of many business logic loopholes.
**D.** Large-scale enterprises (such as large state-owned enterprises and multinational enterprises) need people who understand network security traceability Q and emergency response. Such enterprises often have a large number of information assets and complex network structures, requiring specialized departments to conduct control inspections within the enterprise, and at the same time trace and deal with problems found.
**E.**What network security products and service providers need is what we call network security personnel who understand offense and defense. If you want Party A’s father to give you projects and funds, network security product and service providers need to prove their strengths. The best way to prove their strengths is to accept the "Voting Certificate Q", which is your service ability to dig out loopholes and the protection capabilities of your product.
What I listed above is just a general classification, and cannot cover all situations, and the needs of each type of enterprise listed are not separate, but only focus on direction. For example, a multinational Internet company needs people who understand conventional security protection, R&D security, business security, traceability and disposal, and so on. .

3. Ways to solve the security personnel gap
According to the above content we analyze one by one.
**A.** People who understand conventional security protection: Generally, the information department of an enterprise will solve the problem by itself. At this time, the enterprise information department will consider whether it is necessary to recruit a separate security officer based on cost and demand. After all, many routine security protections can be solved by ordinary information operation and maintenance personnel by themselves, such as patching, closing high-risk port Q, and modifying weak passwords.
**B.** People who understand R&D security: There are very few people who understand both R&D and security. At present, the commonly used method is to test the code through related network security products, and there are also capable companies to conduct research on R&D personnel. Network security training, in this regard, the industry also has many cases that can be used for reference.
**C.** People who understand business security: It is almost impossible to recruit such people directly. If necessary, they can only be cultivated from within the business department.
**D.** People who understand safety traceability and emergency response: This type of people is almost only needed by large companies, and only one team is needed. The team size does not need to be particularly large, and it is generally trained internally Combined with external recruitment, the recruitment is also for people with high technical strength.
**E.** Network security personnel who understand offense and defense: This part is what we often call network security personnel.
4. How to learn safety
So what skills do you need to master to become a network security engineer with a zero-based entry into network security? Regardless of self-study or looking for training courses, is it difficult to get started in network security as a zero-basic novice? Generally speaking, getting started with network security generally requires the following knowledge, you can refer to the roadmap:
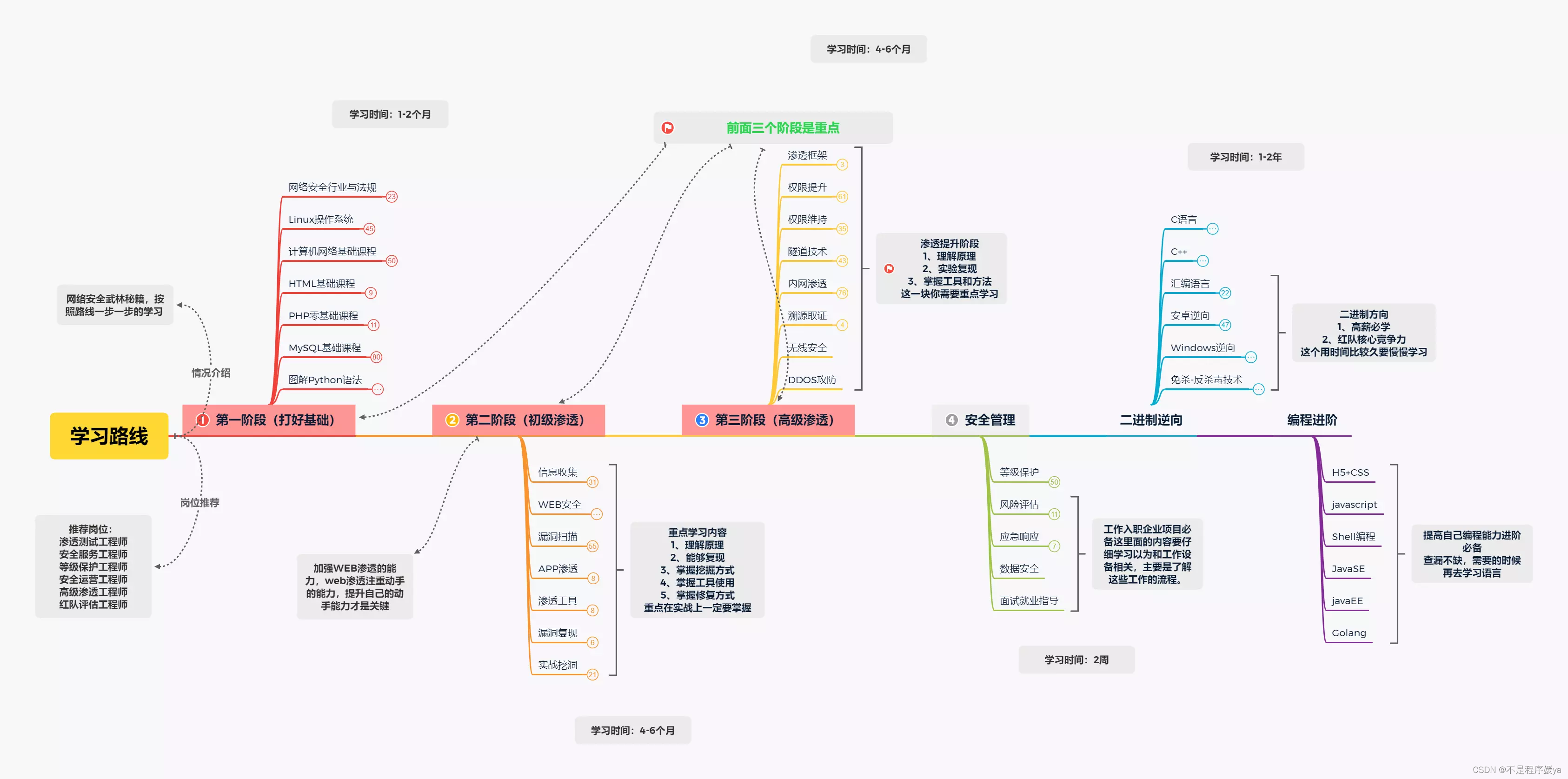
(Each module can be expanded, so I won’t expand it one by one here, the length 1 is a bit long, and the content is more)
If you are learning other technologies and have strong self-discipline, then learning by yourself is enough, otherwise it is not recommended to learn by yourself. Since network security itself is a major with strong offensive and defensive combat capabilities, the field of network security must be practical, and true knowledge comes from practice! The situation that requires practice is not something that can be touched by self-study, and other assistance is needed.
How to get started?
Let's get down to the specific technical points, the network security learning route, the overall learning time is about half a year, depending on each person's situation.
If you refine the content you need to learn every week to this level, you still worry that you won’t be able to learn it, and you won’t be able to get started. In fact, you have learned it for two months, but you have to learn from east to west, what? The content is just a taste, and I haven't gone deep into it, so I have the feeling that I can't get started after studying for 2 months.
Step 1: Computer Basics
This first step, in fact, has little to do with network security, but a basic ability that anyone entering the IT field must master. The following five major courses were taught to us by university teachers back then. No matter what technical direction you are in, it is best to learn the technology well. Now it seems that it is still not out of date:
- computer network
- Principles of computer composition
- operating system
- Algorithms and Data Structures
- data
In fact, each of these courses has its own universe, and basically it cannot be mastered in one study, but along with everyone's career, different technical stages will have different understandings and feelings. For specific learning, it is recommended to refer to agile development and continue to iterate: have a rough understanding** -> have a further understanding -> thoroughly grasp -> review the past to learn the new. **Don't worry about learning all of one course before moving on to the next one.
Step 2: Programming ability
After having some of the above basic skills, it is time to start writing some codes and hone your programming skills. The following three are the languages that practitioners in the security industry are best able to master:
- Shell script : master commonly used Linux commands, be able to write simple shell scripts, and handle some simple affairs.
- C language (C++ optional) : C language has no complicated features. It is the ancestor of modern programming languages. It is suitable for writing low-level software, and it can also help you understand computer knowledge such as memory, algorithms, and operating systems. It is recommended to learn it.
- Python : C language helps you understand the bottom layer, and Python helps you write functional software such as network, crawler, data processing, and image processing. It is a programming language that programmers, especially hackers, love very much and have to learn.
Step 3: Safety First Experience
With the foundation of the previous two steps, it's time to get in touch with some network security technologies. At this stage, don't circle yourself and only learn technologies in a certain direction. At this stage, my suggestion is: but when dabbling, see the past. Network protocol attack, Web service attack, browser security, vulnerability attack, reverse cracking, tool development, etc., to know what it is, to discover your own interests in the process, and let yourself be familiar with various fields of network security. The technology has a preliminary understanding.
Step 4: Divide the direction
In the third step, slowly discover your interest points, whether you like to develop various tools, or like to break into websites, or obsessed with host computer attacks... At this time, you can think about your future direction, and then focus on Start to focus on this direction, and continue to cultivate deeply through the technologies in the respective directions in the above mind map, and become a master in a certain field.
I also sorted out some learning materials and notes for you, most of which are quite good, I hope it will be helpful to you!

There is no threshold for obtaining the above resources. As long as you really want to learn about network security, go ahead and do it boldly!
5. Summary
The field of network security is like a towering tree full of fruit. There are countless onlookers standing under it. They all claim that they like network security and want to pick the fruit from the tree, but they are hesitant when faced with the vine branches that hang down from time to time. indecision.
In fact, you can climb this tree by just grabbing any vine branch. What most people lack is such a beginning.
