Vert.x Web API Contract模块在Vert.x Web的基础上进行扩展,支持OpenAPI 3.0规范。
使用上有两种方式
- 编程方式
预定义HTTPRequestValidationHandler,并在route中传入,就像手册给的那样 - 配置文件方式
预先定义好接口描述文件,通过OpenAPI3RouterFactory加载并挂载到Router上
val openAPI3RouterFactoryList = mutableListOf<OpenAPI3RouterFactory>()
listOf(
"/webroot/swagger/openapi-admin.yaml"
).forEach { configPath ->
awaitResult<OpenAPI3RouterFactory> {
OpenAPI3RouterFactory.create(vertx, configPath, it)
}.apply {
openAPI3RouterFactoryList.add(this)
}
}
val mainRouter = Router.router(vertx)
openAPI3RouterFactoryList.forEach { routerFactory ->
mainRouter.mountSubRouter("/", routerFactory.mountServicesFromExtensions()..router)
}
通过这种方式加载,Vert.x能够自动解析描述文件,提供自动挂载验证handler和securityHandler的能力,在请求不符合配置文件定义的约束时,能够自动以合适的状态码回绝用户请求。
问题
使用配置文件方式生成Route,不增加额外Handler的情况下,在遇到验证失败或空指针异常之类的情况时,Vert.x处理验证错误和内部错误的方式是直接报400 Bad Request和500 Internal Error,没有任何附加信息,日志上也不会有任何输出,这为问题排查和API使用者都是很不友好的方式。
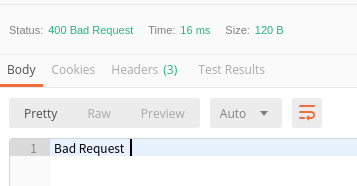
解决方案
通过查看手册和源码跟踪,找到如下处理方式,在Router上挂载一个全局的400和500错误处理器,对错误信息进行详细解析
val OpenAPIErrorTypeMap = mapOf(
Pair(ValidationException.ErrorType.NO_MATCH, "格式错误"),
Pair(ValidationException.ErrorType.NOT_FOUND, "缺失"),
Pair(ValidationException.ErrorType.UNEXPECTED_ARRAY, "不应为数组"),
Pair(ValidationException.ErrorType.UNEXPECTED_SINGLE_STRING, "必须为数组"),
Pair(ValidationException.ErrorType.FILE_NOT_FOUND, "文件未找到"),
Pair(ValidationException.ErrorType.WRONG_CONTENT_TYPE, "请求头Content-Type错误"),
Pair(ValidationException.ErrorType.EMPTY_VALUE, "值不应为空"),
Pair(ValidationException.ErrorType.UNEXPECTED_ARRAY_SIZE, "数组容量不匹配"),
Pair(ValidationException.ErrorType.DESERIALIZATION_ERROR, "反序列化失败"),
Pair(ValidationException.ErrorType.OBJECT_FIELD_NOT_FOUND, "缺失"),
Pair(ValidationException.ErrorType.JSON_NOT_PARSABLE, "JSON无法解析"),
Pair(ValidationException.ErrorType.JSON_INVALID, "格式错误"),
Pair(ValidationException.ErrorType.XML_INVALID, "格式错误")
)
// 针对OpenAPI的参数校验错误
mainRouter.errorHandler(400) {
if (it.failure() is ValidationException) {
val failure = it.failure() as ValidationException
val msg = JsonObject()
.put("errCode", "BadRequest")
.put("errMsg", it.failure().message)
.put("userMsg", "请求参数 ${failure.parameterName()} ${OpenAPIErrorTypeMap[failure.type()]}")
it.response()
.setStatusCode(it.statusCode())
.putHeader("Content-type", "application/json")
.putHeader("Content-length", "${msg.toString().toByteArray().size}")
.write(msg.toBuffer()).end()
}
}
如此,若再发生请求参数验证错误,将给出明确的问题所在,而不是靠猜测。
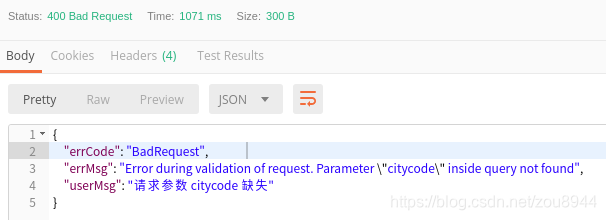
方案出处
遇到这个问题时,我个人倾向于Vert.x应该会提供一个打印详细报错信息的开关之类的东西,但在手册中并没有找到,于是通过源码定位到如下报错地点。
io.vertx.ext.web.api.validation.impl.BaseValidationHandler#handle()
@Override
public void handle(RoutingContext routingContext) {
try {
RequestParametersImpl parsedParameters = new RequestParametersImpl();
parsedParameters.setPathParameters(validatePathParams(routingContext));
parsedParameters.setQueryParameters(validateQueryParams(routingContext));
parsedParameters.setHeaderParameters(validateHeaderParams(routingContext));
parsedParameters.setCookieParameters(validateCookieParams(routingContext));
// . . . . . .
routingContext.next();
} catch (ValidationException e) {
routingContext.fail(400, e);
}
}
可以看到,在验证失败时,它直接将routingContext设置为了400错误,并将异常一并传入,查看routingContext.fail()方法定义,明确说明,如果没有任何错误处理器对该状态码进行处理,将直接向客户端响应状态码对应的默认响应,对于400的默认响应,就是statucode=400和statusmessage=Bad Request
/**
* Fail the context with the specified throwable and the specified the status code.
* <p>
* This will cause the router to route the context to any matching failure handlers for the request. If no failure handlers
* match It will trigger the error handler matching the status code. You can define such error handler with
* {@link Router#errorHandler(int, Handler)}. If no error handler is not defined, It will send a default failure response with provided status code.
*
* @param statusCode the HTTP status code
* @param throwable a throwable representing the failure
*/
void fail(int statusCode, Throwable throwable);
因此,就此处来讲,定义针对400的处理器是非常有必要的,同时也是官方推荐的处理方式,官方文档中特意提到了错误处理的管理方式,有如下两种,很明显,对于很多path的情况,使用第二种更好。
- 单独为一个路径增加错误处理器
router.get("/awesome/:pathParam")
// Mount validation handler
.handler(validationHandler)
//Mount your handler
.handler((routingContext) -> {
// Your logic
})
//Mount your failure handler to manage the validation failure at path level
.failureHandler((routingContext) -> {
Throwable failure = routingContext.failure();
if (failure instanceof ValidationException) {
// Something went wrong during validation!
String validationErrorMessage = failure.getMessage();
}
});
- 为一个状态码增加错误处理器
// Manage the validation failure for all routes in the router
router.errorHandler(400, routingContext -> {
if (routingContext.failure() instanceof ValidationException) {
// Something went wrong during validation!
String validationErrorMessage = routingContext.failure().getMessage();
} else {
// Unknown 400 failure happened
routingContext.response().setStatusCode(400).end();
}
});
延伸
关于在Router上为某个特定的状态码增加错误处理器的处理,不仅在于此处,个人认为是可以通用的,对高频发生的状态码,可以这样增加一个全局处理器,使得不至于丢失错误信息。
此外,这也衍生出另一个问题,Vert.x的全局错误处理,对于运行中错误的漏网之鱼,要定义合适有效的全局处理器,使得不放过任何错误,这一点要注意。