文章目录
2.3 会话、张量、变量OP
学习目标
- 目标
- 应用sess.run或者eval运行图程序并获取张量值
- 应用feed_dict机制实现运行时填充数据
- 应用placeholder实现创建占位符
- 知道常见的TensorFlow创建张量
- 知道常见的张量数学运算操作
- 说明numpy的数组和张量相同性
- 说明张量的两种形状改变特点
- 应用set_shape和tf.reshape实现张量形状的修改
- 应用tf.matmul实现张量的矩阵运算修改
- 应用tf.cast实现张量的类型
- 说明变量op的特殊作用
- 说明变量op的trainable参数的作用
- 应用global_variables_initializer实现变量op的初始化
- 应用
- 无
- 内容预览
2.3.1 会话
一个运行TensorFlow operation的类。会话包含以下两种开启方式
- tf.Session:用于完整的程序当中
- tf.InteractiveSession:用于交互式上下文中的TensorFlow ,例如shell
1 TensorFlow 使用 tf.Session 类来表示客户端程序(通常为 Python 程序,但也提供了使用其他语言的类似接口)与 C++ 运行时之间的连接
2 tf.Session 对象使用分布式 TensorFlow 运行时提供对本地计算机中的设备和远程设备的访问权限。
2.3.1.1 init(target=’’, graph=None, config=None)参数
with tf.Session() as session:里面有的一些参数
会话可能拥有的资源,如 tf.Variable,tf.QueueBase和tf.ReaderBase。当这些资源不再需要时,释放这些资源非常重要。因此,需要调用tf.Session.close会话中的方法,或将会话用作上下文管理器。以下两个例子作用是一样的:
- 用with as的话会默认调用close语句
def session_demo():
"""
会话演示
:return:
"""
a_t = tf.constant(10)
b_t = tf.constant(20)
# 不提倡直接运用这种符号运算符进行计算
# 更常用tensorflow提供的函数进行计算
# c_t = a_t + b_t
c_t = tf.add(a_t, b_t)
print("tensorflow实现加法运算:\n", c_t)
# 开启会话
# 传统的会话定义
# sess = tf.Session()
# sum_t = sess.run(c_t)
# print("sum_t:\n", sum_t)
# sess.close()
# 开启会话
with tf.Session() as sess:
# sum_t = sess.run(c_t)
# 想同时执行多个tensor
print(sess.run([a_t, b_t, c_t]))
# 方便获取张量值的方法
# print("在sess当中的sum_t:\n", c_t.eval())
# 会话的图属性
print("会话的图属性:\n", sess.graph)
return None
- target:如果将此参数留空(默认设置),会话将仅使用本地计算机中的设备。可以指定 grpc:// 网址,以便指定 TensorFlow 服务器的地址,这使得会话可以访问该服务器控制的计算机上的所有设备。
- graph:默认情况下,新的 tf.Session 将绑定到当前的默认图。
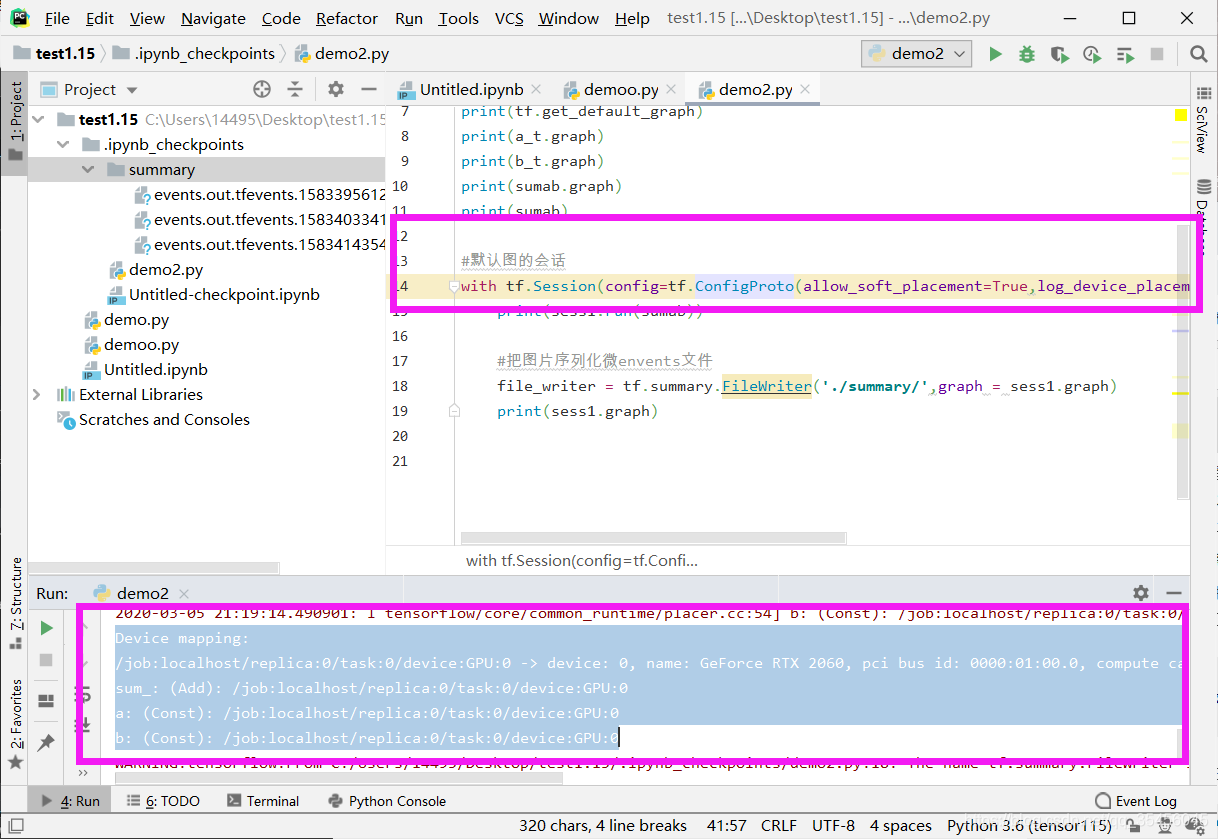
- config:此参数允许您指定一个 tf.ConfigProto 以便控制会话的行为。例如,ConfigProto协议用于打印设备使用信息
# 运行会话并打印设备信息
sess = tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(allow_soft_placement=True,
log_device_placement=True))
会话可以分配不同的资源在不同的设备上运行。
/job:worker/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:0
device_type:类型设备(例如CPU,GPU,TPU)
下面是所有的三个节点操作用的设备
可以指定节点预算的设备不一样
2.3.1.2 会话的run()及其参数
- run(fetches,feed_dict=None, options=None, run_metadata=None)
- 通过使用sess.run()来运行operation
- fetches:单一的operation,或者列表、元组(其它不属于tensorflow的类型不行)
- feed_dict:参数允许调用者覆盖图中张量的值,运行时赋值
- 与tf.placeholder搭配使用,则会检查值的形状是否与占位符兼容。
打印多个值用列表
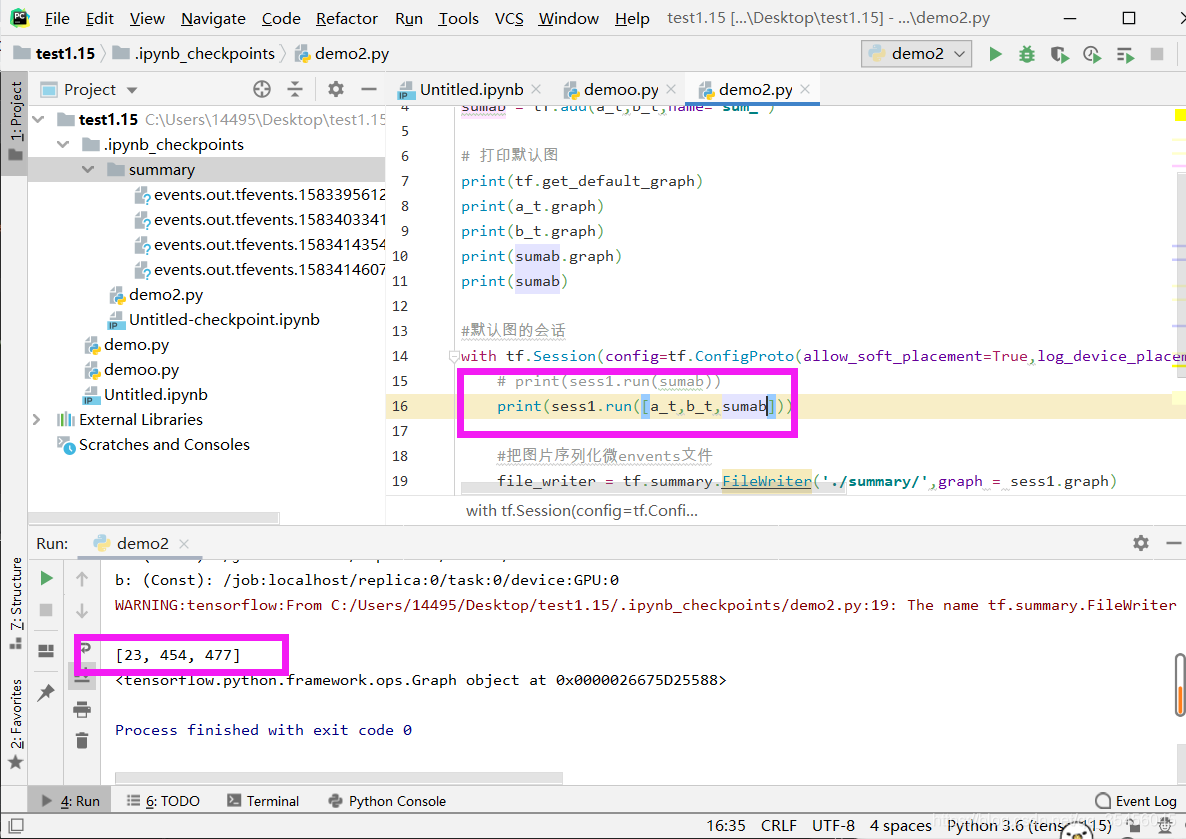
- 与tf.placeholder搭配使用,则会检查值的形状是否与占位符兼容。
使用tf.operation.eval()也可运行operation,但需要在会话中运行
# 创建图
a = tf.constant(5.0)
b = tf.constant(6.0)
c = a * b
# 创建会话
sess = tf.Session()
# 计算C的值
print(sess.run(c))
print(c.eval(session=sess))
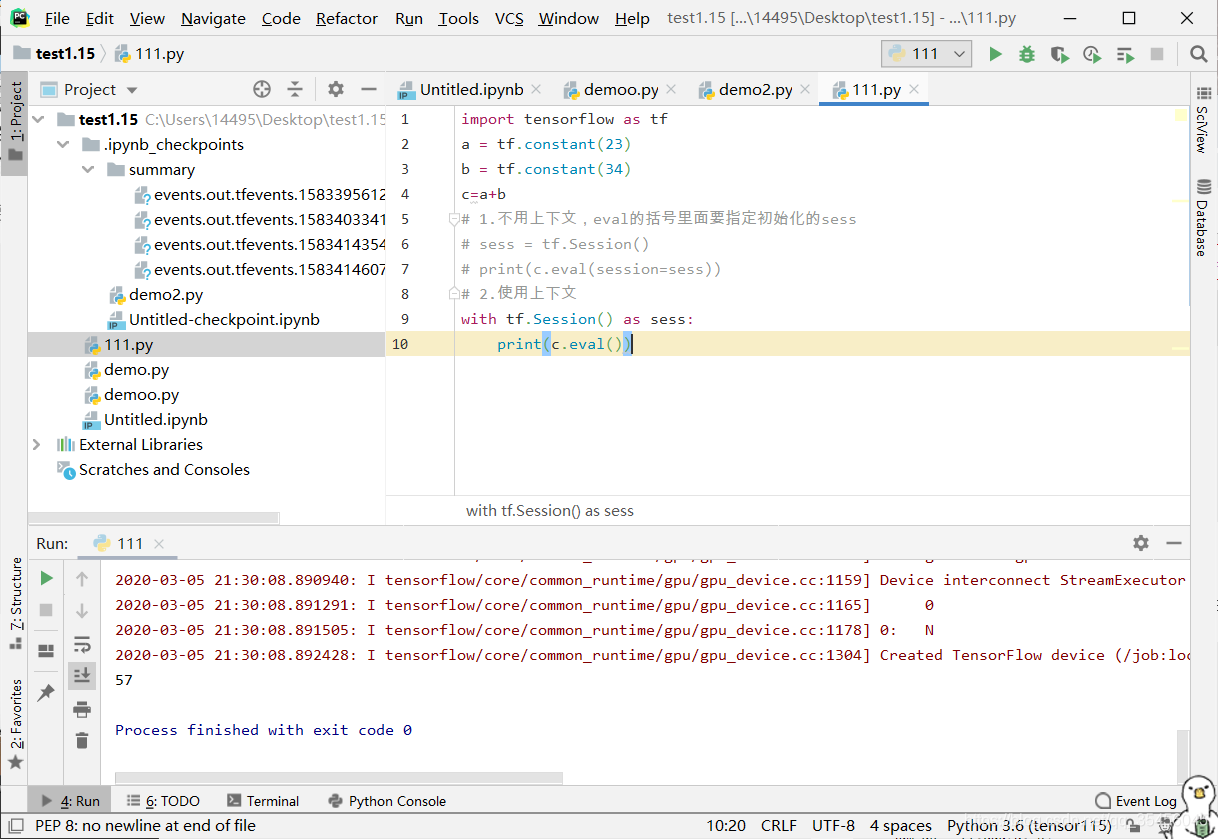
import tensorflow as tf
a = tf.constant(23)
b = tf.constant(34)
c=a+b
# 1.不用上下文,eval的括号里面要指定初始化的sess
# sess = tf.Session()
# print(c.eval(session=sess))
# 2.使用上下文
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(c.eval())
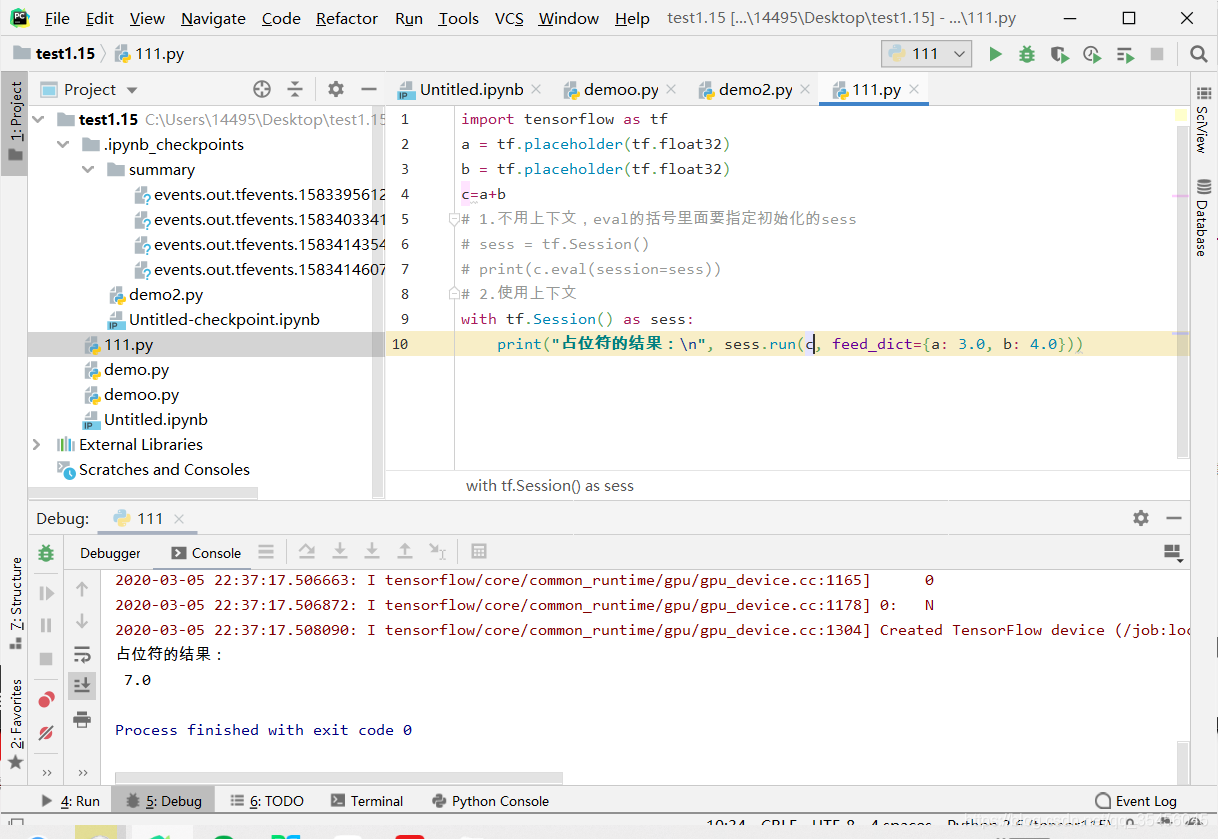
2.3.1.3 feed操作
- placeholder提供占位符,run时候通过feed_dict指定参数
def session_run_demo():
"""
会话的run方法
:return:
"""
# 定义占位符
a = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
b = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
sum_ab = tf.add(a, b)
print("sum_ab:\n", sum_ab)
# 开启会话
with tf.Session() as sess:
print("占位符的结果:\n", sess.run(sum_ab, feed_dict={a: 3.0, b: 4.0}))
return None
占位符的使用
请注意运行时候报的错误error:
RuntimeError:如果这Session是无效状态(例如已关闭)。 TypeError:如果fetches或者feed_dict键的类型不合适。 ValueError:如果fetches或feed_dict键无效或引用 Tensor不存在的键。
在编写 TensorFlow 程序时,程序传递和运算的主要目标是tf.Tensor
2.3.2 张量(Tensor)
TensorFlow 的张量就是一个 n 维数组, 类型为tf.Tensor。Tensor具有以下两个重要的属性
- type:数据类型
- shape:形状(阶)
2.3.2.1 张量的类型
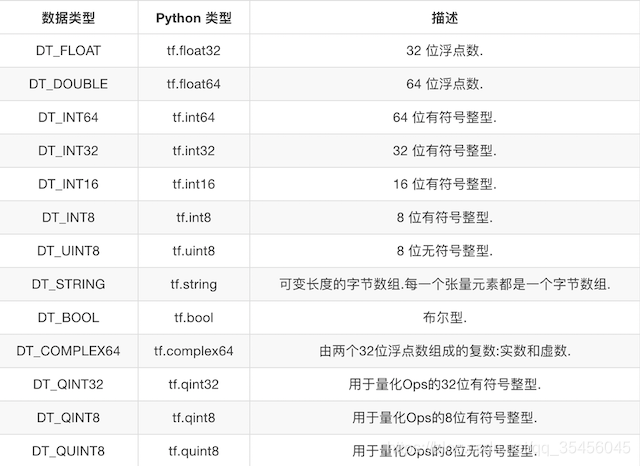
2.3.2.2 张量的阶

形状有0阶、1阶、2阶….
tensor1 = tf.constant(4.0)
tensor2 = tf.constant([1, 2, 3, 4])
linear_squares = tf.constant([[4], [9], [16], [25]], dtype=tf.int32)
print(tensor1.shape)
# 0维:() 1维:(10, ) 2维:(3, 4) 3维:(3, 4, 5)
2.3.3 创建张量的指令
- 固定值张量

- 随机值张量

- 其它特殊的创建张量的op
- tf.Variable
- tf.placeholder
2.3.4 张量的变换
2.3.4.1 类型改变

2.3.4.2 形状改变
TensorFlow的张量具有两种形状变换,动态形状和静态形状
- tf.reshape
- tf.set_shape
关于动态形状和静态形状必须符合以下规则
- 静态形状
- 转换静态形状的时候,1-D到1-D,2-D到2-D,不能跨阶数改变形状
- 对于已经固定的张量的静态形状的张量,不能再次设置静态形状
- 动态形状
- tf.reshape()动态创建新张量时,张量的元素个数必须匹配
def tensor_demo():
"""
张量的介绍
:return:
"""
a = tf.constant(value=30.0, dtype=tf.float32, name="a")
b = tf.constant([[1, 2], [3, 4]], dtype=tf.int32, name="b")
a2 = tf.constant(value=30.0, dtype=tf.float32, name="a2")
c = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[2, 3, 4], name="c")
sum = tf.add(a, a2, name="my_add")
print(a, a2, b, c)
print(sum)
# 获取张量属性
print("a的图属性:\n", a.graph)
print("b的名字:\n", b.name)
print("a2的形状:\n", a2.shape)
print("c的数据类型:\n", c.dtype)
print("sum的op:\n", sum.op)
# 获取静态形状
print("b的静态形状:\n", b.get_shape())
# 定义占位符
a_p = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[None, None])
b_p = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[None, 10])
c_p = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[3, 2])
# 获取静态形状
print("a_p的静态形状为:\n", a_p.get_shape())
print("b_p的静态形状为:\n", b_p.get_shape())
print("c_p的静态形状为:\n", c_p.get_shape())
# 形状更新
# a_p.set_shape([2, 3])
# 静态形状已经固定部分就不能修改了
# b_p.set_shape([10, 3])
# c_p.set_shape([2, 3])
# 静态形状已经固定的部分包括它的阶数,如果阶数固定了,就不能跨阶更新形状
# 如果想要跨阶改变形状,就要用动态形状
# a_p.set_shape([1, 2, 3])
# 获取静态形状
print("a_p的静态形状为:\n", a_p.get_shape())
print("b_p的静态形状为:\n", b_p.get_shape())
print("c_p的静态形状为:\n", c_p.get_shape())
# 动态形状
# c_p_r = tf.reshape(c_p, [1, 2, 3])
c_p_r = tf.reshape(c_p, [2, 3])
# 动态形状,改变的时候,不能改变元素的总个数
# c_p_r2 = tf.reshape(c_p, [3, 1])
print("动态形状的结果:\n", c_p_r)
# print("动态形状的结果2:\n", c_p_r2)
return None
2.3.5 张量的数学运算
- 算术运算符
- 基本数学函数
- 矩阵运算
- reduce操作
- 序列索引操作
详细请参考: https://www.tensorflow.org/versions/r1.8/api_guides/python/math_ops
这些API使用,我们在使用的时候介绍,具体参考文档
2.3.6 变量
TensorFlow变量是表示程序处理的共享持久状态的最佳方法。变量通过 tf.Variable OP类进行操作。变量的特点:
- 存储持久化
- 可修改值
- 可指定被训练
2.3.6.1 创建变量
-
tf.Variable(
initial_value=None,trainable=True,collections=None
,name=None)
- initial_value:初始化的值
- trainable:是否被训练
- collections:新变量将添加到列出的图的集合中collections,默认为[GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES],如果trainable是True变量也被添加到图形集合 GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES
-
变量需要显式初始化,才能运行值
def variable_demo():
"""
变量的演示
:return:
"""
# 定义变量
a = tf.Variable(initial_value=30)
b = tf.Variable(initial_value=40)
sum = tf.add(a, b)
# 初始化变量
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# 开启会话
with tf.Session() as sess:
# 变量初始化
sess.run(init)
print("sum:\n", sess.run(sum))
return None
2.3.6.2 使用tf.variable_scope()修改变量的命名空间
会在OP的名字前面增加命名空间的指定名字
with tf.variable_scope("name"):
var = tf.Variable(name='var', initial_value=[4], dtype=tf.float32)
var_double = tf.Variable(name='var', initial_value=[4], dtype=tf.float32)
<tf.Variable 'name/var:0' shape=() dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'name/var_1:0' shape=() dtype=float32_ref>