In the big cities, the subway systems always look so complex to the visitors. To give you some sense, the following figure shows the map of Beijing subway. Now you are supposed to help people with your computer skills! Given the starting position of your user, your task is to find the quickest way to his/her destination.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤ 100), the number of subway lines. Then N lines follow, with the i-th (i=1,⋯,N) line describes the i-th subway line in the format:
M S[1] S[2] … S[M]
where M (≤ 100) is the number of stops, and S[i]'s (i=1,⋯,M) are the indices of the stations (the indices are 4-digit numbers from 0000 to 9999) along the line. It is guaranteed that the stations are given in the correct order – that is, the train travels between S[i] and S[i+1] (i=1,⋯,M−1) without any stop.
Note: It is possible to have loops, but not self-loop (no train starts from S and stops at S without passing through another station). Each station interval belongs to a unique subway line. Although the lines may cross each other at some stations (so called “transfer stations”), no station can be the conjunction of more than 5 lines.
After the description of the subway, another positive integer K (≤ 10) is given. Then K lines follow, each gives a query from your user: the two indices as the starting station and the destination, respectively.
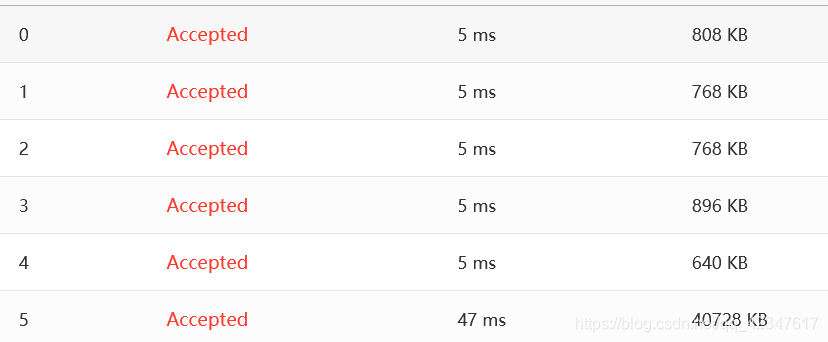
The following figure shows the sample map.
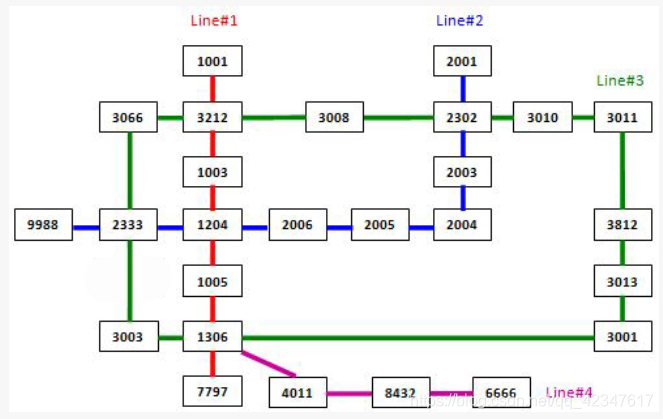
Note: It is guaranteed that all the stations are reachable, and all the queries consist of legal station numbers.
Output Specification:
For each query, first print in a line the minimum number of stops. Then you are supposed to show the optimal path in a friendly format as the following:
Take Line#X1 from S1 to S2.
Take Line#X2 from S2 to S3.
......
where Xi’s are the line numbers and Si’s are the station indices. Note: Besides the starting and ending stations, only the transfer stations shall be printed.
If the quickest path is not unique, output the one with the minimum number of transfers, which is guaranteed to be unique.
Sample Input:
4
7 1001 3212 1003 1204 1005 1306 7797
9 9988 2333 1204 2006 2005 2004 2003 2302 2001
13 3011 3812 3013 3001 1306 3003 2333 3066 3212 3008 2302 3010 3011
4 6666 8432 4011 1306
3
3011 3013
6666 2001
2004 3001
Sample Output:
2
Take Line#3 from 3011 to 3013.
10
Take Line#4 from 6666 to 1306.
Take Line#3 from 1306 to 2302.
Take Line#2 from 2302 to 2001.
6
Take Line#2 from 2004 to 1204.
Take Line#1 from 1204 to 1306.
Take Line#3 from 1306 to 3001.
-
思路 1:Dijkstra + DFS
最后一个点会超时!直接堆优化后可通过,剪枝的方案还没考虑… -
code:
最后一个点 TLE 的 Dijkstra:
void Dijkstra(int start, int destination){
fill(d, d + maxn, INF);
memset(vis, false, sizeof(vis));
d[start] = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < stops.size(); ++i){
int now = -1, Min = INF;
for(int j = 0; j < stops.size(); ++j){
int tmps = stops[j];
if(vis[tmps] == false && d[tmps] < Min){
Min = d[tmps];
now = tmps;
}
}
if(now == -1 || now == destination) return;
vis[now] = true;
for(int j = 0; j < G[now].size(); ++j){
int nex = G[now][j];
if(vis[nex] == false){
if(d[now] + 1 < d[nex]){
d[nex] = d[now] + 1;
pre[nex].clear();
pre[nex].push_back(now);
}else if(d[now] + 1 == d[nex]){
pre[nex].push_back(now);
}
}
}
}
}
- 关于堆优化:减少的是每轮中找Min(当前d[]最小的点)的时间开销
使用结构体记录点的id 和 d(到源点的最短距离),并重载<使按d排序,构造优先队列priority_queue<node> pq;
step 1:最开始将node{id = 源点,d = 0} push 进 pq
step 2:进入循环后(while(!pq.empty())), 每次将当前最优点出队,并以该点为跳点更新所有没访问过的点 p2,并将更新的点入队,【注意】pq中存放的是副本,外部的修改对pq内元素没有影响。所以,还是需要一个数组d[]来记录最优结果。同时,对同一个点可能被多次优化push进了pq,也就是pq中存在重复id的node。但是,由于队首始终是最优的那个(最优的总是先出队),所以第二次访问到相同id的节点 vis[id] == true; 要跳过continue; p1
- 坑点:
-
Wrong 1:样例 1 3 不能直接用has来找中转站,环的头尾重合has[start]=2;
开始我用每个stop出现的次数来识别是否是中转站,if has[i]>1:true;,这样不行,环型线路首尾重合,如has[3011] == 2 -
Wrong 2:%04d :样例4
老坑了,n位编号,要对齐输出
堆优化后的Dijkstra:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 10010, INF = 0x3fffffff;
vector<int> G[maxn], stops;
int d[maxn], has[maxn], line[maxn][maxn];
bool vis[maxn];
struct node{
int id, d;
node(int _id, int _d) : id(_id), d(_d) {}
bool operator < (const node & a) const { //成员函数前的const是为了防止对this的修改
return d > a.d;
}
};
vector<int> pre[maxn];
void Dijkstra(int start, int destination){
fill(d, d + maxn, INF);
memset(vis, false, sizeof(vis));
d[start] = 0;
priority_queue<node> q;
q.push(node(start, 0));
while(!q.empty()){
node now = q.top();
q.pop();
if(now.id == destination) return;
if(vis[now.id]) continue; //p1 过滤掉编号重复的点!
vis[now.id] = true;
for(int i = 0; i < G[now.id].size(); ++i){
int nex = G[now.id][i];
if(vis[nex] == false){ // p2
if(now.d + 1 < d[nex]){
d[nex] = now.d + 1;
pre[nex].clear();
pre[nex].push_back(now.id);
q.push(node(nex, d[nex]));
}else if(now.d + 1 == d[nex]){
pre[nex].push_back(now.id);
q.push(node(nex, d[nex]));
}
}
}
}
}
int min_tranfer;
vector<int> tmp, ans;
void DFS(int id, int start){
if(id == start){
tmp.push_back(id);
int cnt_transfer = 0;
for(int i = tmp.size() - 2; i > 0; --i){
int pre_stop = tmp[i+1], now_stop = tmp[i], nex_stop = tmp[i-1];
if(line[pre_stop][now_stop] != line[now_stop][nex_stop]){ //now_stops是中转站
cnt_transfer++; //Wrong 1:样例 1 3 不能直接用has来找中转站,环的头尾重合has[start]=2;
}
}
if(cnt_transfer < min_tranfer){
min_tranfer = cnt_transfer;
ans = tmp;
}
tmp.pop_back();
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < pre[id].size(); ++i){
int nex = pre[id][i];
tmp.push_back(id);
DFS(nex, start);
tmp.pop_back();
}
}
void Print(){
int i = ans.size() - 1, j = i - 1, len = ans.size() - 1, pre_line;
printf("%d\n", ans.size() - 1);
while(j >= 0){
pre_line = line[ans[i]][ans[j]];
while(j > 0 && line[ans[j]][ans[j - 1]] == pre_line) j--;
printf("Take Line#%d from %04d to %04d.\n", pre_line, ans[i], ans[j]); //Wrong 2:%04d :样例4
i = j--;
}
}
int main(){
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
int ns, tmps, pres;
scanf("%d", &ns);
for(int j = 0; j < ns; ++j){
scanf("%d", &tmps);
has[tmps]++;
if(has[tmps] == 1) stops.push_back(tmps);
if(j != 0){
line[pres][tmps] = line[tmps][pres] = i;
G[pres].push_back(tmps);
G[tmps].push_back(pres);
}
pres = tmps;
}
}
int nq;
scanf("%d", &nq);
for(int i = 0; i < nq; ++i){
int ts, td;
scanf("%d %d", &ts, &td);
Dijkstra(ts, td);
min_tranfer = INF;
DFS(td, ts);
Print();
ans.clear();
}
return 0;
}
-
思路 2:直接DFS,找到路径后不断优化取最优
-
坑点:
-
DFS过程中要记录访问过的节点(
vis[id] = true;),防止回头。但是,从这一节点出发所有路线都跑完回溯以后,要将这一节点“开锁(vis[id] = false;)”,因为从其他路线可能也要经过这个点(cross) -
Wrong 1:两个标尺问题,更新第一个标尺的同时,千万不要忘了顺带更新第二个标尺,否则第一个标尺相同时,无法在第一个标尺基础上更新第二个标尺
- code:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 10000, INF = 0x3fffffff;
vector<int> G[maxn];
int line[maxn][maxn];
bool vis[maxn];
vector<int> tmp, ans;
void DFS(int id, int destination, int pre, int cnt_transfer, int & min_stop, int & min_tran){
if(tmp.size() > min_stop) return;
if(id == destination){
tmp.push_back(id);
// int cnt_transfer = 0; //最找到路径计算一次,重复计算量大
// for(int i = tmp.size() - 2; i > 0; --i){
// int pre = tmp[i+1], now = tmp[i], nex = tmp[i-1];
// if(line[pre][now] != line[now][nex]){
// cnt_transfer++;
// }
// }
if(tmp.size() < min_stop){
min_stop = tmp.size();
//Wrong 1:样例 0 3 :这里也要更新第二标尺:中转站数量;
min_tran = cnt_transfer;
ans = tmp;
}else if(tmp.size() == min_stop && cnt_transfer < min_tran){
min_tran = cnt_transfer;
ans = tmp;
}
tmp.pop_back();
return;
}
vis[id] = true;
for(int i = 0; i < G[id].size(); ++i){
int nex = G[id][i];
if(vis[nex] == false){
// int pre = tmp.size() > 0 ? tmp.back() : 0;
tmp.push_back(id);
if(tmp.size() > 0 && line[pre][id] != line[id][nex]){
DFS(nex, destination, id, cnt_transfer + 1, min_stop, min_tran);
}else{
DFS(nex, destination, id, cnt_transfer, min_stop, min_tran);
}
tmp.pop_back();
}
}
vis[id] = false;
}
void Print(){
int i = 0, j = i + 1, pre_line;
printf("%d\n", ans.size() - 1);
while(j < ans.size()){
pre_line = line[ans[i]][ans[j]];
while(j < ans.size() - 1 && line[ans[j]][ans[j + 1]] == pre_line) j++;
printf("Take Line#%d from %04d to %04d.\n", pre_line, ans[i], ans[j]); //04d :样例4
i = j++;
}
}
int main(){
int n, nq;
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
int ns, tmps, pres;
scanf("%d", &ns);
for(int j = 0; j < ns; ++j){
scanf("%d", &tmps);
if(j != 0){
line[pres][tmps] = line[tmps][pres] = i;
G[pres].push_back(tmps);
G[tmps].push_back(pres);
}
pres = tmps;
}
}
scanf("%d", &nq);
for(int i = 0; i < nq; ++i){
int ts, td, min_stop = INF, min_tran = INF;
scanf("%d %d", &ts, &td);
DFS(ts, td, ts, 0, min_stop, min_tran);
Print();
ans.clear();
}
return 0;
}