【JavaScript数据结构系列】05-链表LinkedList
码路工人 CoderMonkey
转载请注明作者与出处
1. 认识链表结构(单向链表)
链表也是线性结构,
- 节点相连构成链表
- 每个节点包含数据存储域和指针域
- 节点之间的关系靠指针域表示
链表结构示意图参考下文 append 方法中的贴图
相较于数组,链表:
- 不需要指定初始大小
- 无需扩容缩容
- 内存利用率高
- 便于插入删除元素
--
- 没法直接通过下标访问,需要挨个探查
2. 链表的常用方法
我们将实现下列常用方法:
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| append(data) | 向链表添加元素 |
| insert(position, data) | 向指定位置插入元素 |
| remove(data) | 删除元素 |
| removeAt(position) | 删除指定位置元素 |
| update(position, data) | 更新指定位置元素 |
| getItem(position) | 查找指定位置元素 |
| indexOf(data) | 获取元素位置 |
| size() | 获取链表大小 |
| isEmpty() | 判断链表是否为空 |
| clear() | 清空链表 |
| toString() | 字符串化 |
注:我们此时暂不考虑复杂引用类型的情况
3. 代码实现
注:
ES6 版的代码实现请查看 npm 包 data-struct-js 代码
Github/Gitee 上都能找到
npm install data-struct-js
封装链表类
/**
* 链表:单向链表
*/
function LinkedList() {
// 记录链表首个元素
this.__head = null
// 记录链表元素个数
this.__count = 0
// 用Node表示链表内部元素
function Node(data) {
this.data = data
this.next = null
Node.prototype.toString = function () {
return this.data.toString()
}
}
}3.1 append(data)
实现分析:
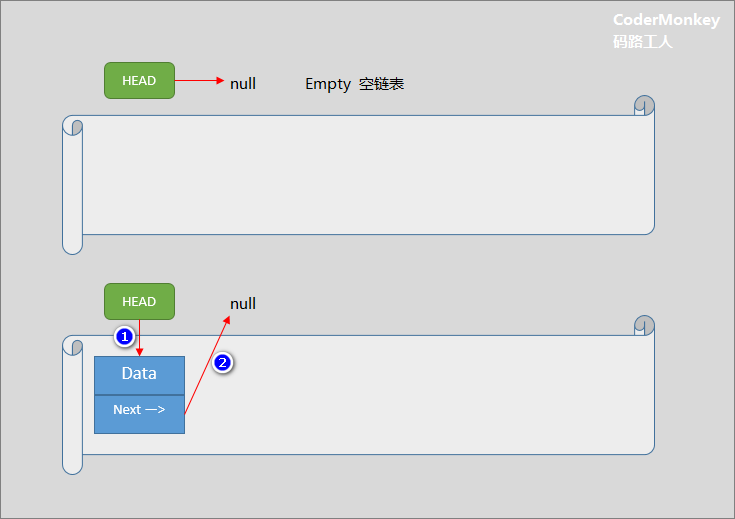
- 插入到空链表时:
1.1 HEAD指向新插入节点
1.2 新节点的Next指向Null
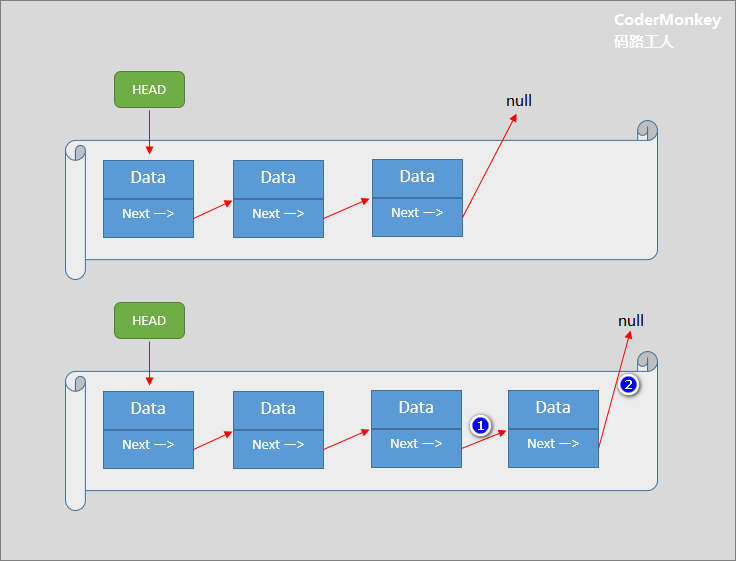
- 插入到非空链表时:
2.1 链表末尾元素的Next指向新元素
2.2 新元素的Next指向Null
LinkedList.prototype.append = function (data) {
// 1.创建新元素
var newNode = new Node(data)
// 2.1链表为空时,直接添加到末尾
if (this.__count === 0) {
this.__head = newNode
}
// 2.2链表非空时,探查到末尾元素并添加新元素
else {
var current = this.__head
while (current.next) {
current = current.next
}
current.next = newNode
}
// 3.内部计数加1
this.__count += 1
return true
}注:
添加元素方法,记得最后给元素个数记录加1
通过上图示例,体会:HEAD 概念和元素节点的 Next 指向修改
3.2 insert(position, data)
实现分析:
- 插入方法接收两个参数:位置,数据
- 可插入位置的范围:0~length
- 插入目标位置:0 的情况
- 新元素的 next 指向原首位元素
- 将HEAD指向新元素
- 循环到指定位置
- 期间记录上一个元素及当前元素
- 在上一个元素与当前元素中间加入要插入的元素
- (修改相关指向,具体参考下面代码)
- 插入元素方法,记得最后给元素个数记录加1
LinkedList.prototype.insert = function (position, data) {
// 1.边界检查(插入位置)
if (position < 0 || position > this.__count) return false
// 2.创建新元素
var newNode = new Node(data)
// 3.1插入到链表头部
if (position === 0) {
newNode.next = this.__head
this.__head = newNode
}
// 3.2以外(包括插入到末尾)
else {
var previous = null
var current = this.__head
var index = 0
while (index < position) {
previous = current
current = current.next
index++
}
previous.next = newNode
newNode.next = current
}
// 4.内部计数加1
this.__count += 1
return true
}注:只有在 insert 时的 position 检查规则与其它不同
3.3 remove(data)
实现分析:
- 删除元素方法接收一个参数:数据
- 根据指针循环查找
- 将从参数收到的数据与当前元素的数据进行比较
#复杂引用类型的时候通过传入自定义比较的回调函数来解决- 找到指定元素后,修改上一元素的 next 指向
注意当删除第一个元素时的特殊情况(修改HEAD指向)
删除元素完成后,记得最后给元素个数记录减1
LinkedList.prototype.remove = function (data) {
var current = this.__head
var previous = null
while (current) {
// 找到指定数据的元素,让当前元素不再被引用
if (current.data == data) {
if (previous == null) {
// 没有前元素,要删除的是首元素,修改 Head 指针
this.__head = current.next
} else {
// 修改前元素内部指针
previous.next = current.next
}
// 内部计数减1
this.__count -= 1
// 处理完成,返回 true
return true
}
previous = current
current = current.next
}
// 查找到最后没有找到指定数据的元素,返回 false
return false
// 注:
// 也可以通过调用 indexOf 获取下标后再调用 removeAt 来实现
// 只是返回值会不同,看实际需要
}3.4 removeAt(position)
实现分析:
- 删除指定位置元素,接收一个参数:位置下标值
- 基于元素指向循环查找
- 到达指定下标元素时,将其前后元素关联,即达到删除效果
删除元素完成后,记得最后给元素个数记录减1
LinkedList.prototype.removeAt = function (position) {
// 1.边界检查
if (position < 0 || position >= this.__count) return false
var index = 0
var previous = null
var current = this.__head
// 2.找到指定位置元素
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current
current = current.next
}
// 3.使当前元素不再被引用
if (previous == null) {
// position=0 删除首元素的时候
this.__head = current.next
} else {
previous.next = current.next
}
// 4.内部计数减1
this.__count -= 1
return current.data
}3.5 update(position, data)
实现分析:参看注释
LinkedList.prototype.update = function (position, data) {
// 1.边界检查
if (position < 0 || position >= this.__count) return false
var current = this.__head
var index = 0
// 2.找到指定位置元素
while (index++ < position) {
current = current.next
}
// 3.修改当前元素数据
current.data = data
// 4.修改完成,返回 true
return true
}3.6 getItem(position)
获取指定位置元素的值
LinkedList.prototype.getItem = function (position) {
// 边界检查
if (position < 0 || position >= this.__count) return
var index = 0
var current = this.__head
while (index < position) {
current = current.next
index += 1
}
return current.data
}3.7 indexOf(data)
实现分析:
- 获取元素所在位置下标值方法,接收一个参数:元素的数据
- 根据元素 next 指向循环查找
- 找到时返回当前下标
- 找不到时返回 -1
LinkedList.prototype.indexOf = function (data) {
var current = this.__head
var index = 0
while (current) {
if (current.data == data) {
return index
}
current = current.next
index += 1
}
return -1
}3.8 size()
查看元素个数方法
LinkedList.prototype.size = function () {
return this.__count
}3.9 isEmpty()
判空方法
LinkedList.prototype.isEmpty = function () {
return this.__count === 0
}3.10 clear()
实现分析:
Head指向置空
计数清零
LinkedList.prototype.clear = function () {
this.__head = null
this.__count = 0
}3.11 toString()
为了方便查看实现的字符串化方法
LinkedList.prototype.toString = function () {
var str = '[HEAD] -> '
var current = this.__head
while (current) {
str += current.data + ' -> '
current = current.next
}
if (str === '[HEAD] -> ') {
str = '[HEAD] -> Null'
}
return str
}总结两点:
- 跟位置下标值相关的操作,
都是通过循环来找到下标值的,
链表结构不同于数组,自己本身没有下标。
- 所有接收下标值的方法,
都要进行边界检查,其中 insert 时可以等于 length
3.12 完整代码
/**
* 链表:单向链表
*/
function LinkedList() {
// 记录链表首个元素
this.__head = null
// 记录链表元素个数
this.__count = 0
// 用Node表示链表内部元素
function Node(data) {
this.data = data
this.next = null
Node.prototype.toString = function () {
return this.data.toString()
}
}
/**
* 添加节点
*/
LinkedList.prototype.append = function (data) {
// 1.创建新元素
var newNode = new Node(data)
// 2.1链表为空时,直接添加到末尾
if (this.__count === 0) {
this.__head = newNode
}
// 2.2链表非空时,探查到末尾元素并添加新元素
else {
var current = this.__head
while (current.next) {
current = current.next
}
current.next = newNode
}
// 3.内部计数加1
this.__count += 1
return true
}
/**
* 插入节点
*/
LinkedList.prototype.insert = function (position, data) {
// 1.边界检查(插入位置)
if (position < 0 || position > this.__count) return false
// 2.创建新元素
var newNode = new Node(data)
// 3.1插入到链表头部
if (position === 0) {
newNode.next = this.__head
this.__head = newNode
}
// 3.2以外(包括插入到末尾)
else {
var previous = null
var current = this.__head
var index = 0
while (index < position) {
previous = current
current = current.next
index++
}
previous.next = newNode
newNode.next = current
}
// 4.内部计数加1
this.__count += 1
return true
}
/**
* 删除节点
*/
LinkedList.prototype.remove = function (data) {
var current = this.__head
var previous = null
while (current) {
// 找到指定数据的元素,让当前元素不再被引用
if (current.data == data) {
if (previous == null) {
// 没有前元素,要删除的是首元素,修改 Head 指针
this.__head = current.next
} else {
// 修改前元素内部指针
previous.next = current.next
}
// 内部计数减1
this.__count -= 1
// 处理完成,返回 true
return true
}
previous = current
current = current.next
}
// 查找到最后没有找到指定数据的元素,返回 false
return false
// 注:
// 也可以通过调用 indexOf 获取下标后再调用 removeAt 来实现
// 只是返回值会不同,看实际需要
}
/**
* 删除指定位置节点
*/
LinkedList.prototype.removeAt = function (position) {
// 1.边界检查
if (position < 0 || position >= this.__count) return false
var index = 0
var previous = null
var current = this.__head
// 2.找到指定位置元素
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current
current = current.next
}
// 3.使当前元素不再被引用
previous.next = current.next
// 4.内部计数减1
this.__count -= 1
return current.data
}
/**
* 更新节点
*/
LinkedList.prototype.update = function (position, data) {
// 1.边界检查
if (position < 0 || position >= this.__count) return false
var current = this.__head
var index = 0
// 2.找到指定位置元素
while (index++ < position) {
current = current.next
}
// 3.修改当前元素数据
current.data = data
// 4.修改完成,返回 true
return true
}
/**
* 获取指定位置节点
*/
LinkedList.prototype.getItem = function (position) {
// 边界检查
if (position < 0 || position >= this.__count) return
var index = 0
var current = this.__head
while (index < position) {
current = current.next
index += 1
}
return current.data
}
/**
* 获取节点位置下标
*/
LinkedList.prototype.indexOf = function (data) {
var current = this.__head
var index = 0
while (current) {
if (current.data == data) {
return index
}
current = current.next
index += 1
}
return -1
}
/**
* 获取链表长度
*/
LinkedList.prototype.size = function () {
return this.__count
}
/**
* 是否为空链表
*/
LinkedList.prototype.isEmpty = function () {
return this.__count === 0
}
/**
* 清空链表
*/
LinkedList.prototype.clear = function () {
this.__head = null
this.__count = 0
}
LinkedList.prototype.toString = function () {
var str = '[HEAD] -> '
var current = this.__head
while (current) {
str += current.toString() + ' -> '
current = current.next
}
if (str === '[HEAD] -> ') {
str = '[HEAD] -> Null'
}
return str
}
}4. 测试一下
// ---------------------------------------------
// Test: LinkedList
// ---------------------------------------------
console.log('----Test: LinkedList----')
var lst = new LinkedList()
lst.append('a')
lst.append('b')
lst.append('c')
console.log(lst.toString())
lst.insert(1, 'insert-1')
console.log(lst.toString())
lst.insert(4, 'insert-4')
console.log(lst.toString())
lst.insert(0, 'insert-0')
console.log(lst.toString())
lst.remove('c')
console.log(lst.toString(), 'remove-c')
console.log('indexOf-b : ', lst.indexOf('b'))
lst.update(3, 'b-updated')
console.log('update-b : ', lst.toString())
lst.removeAt(3)
console.log('after removeAt(3) : ', lst.toString())
lst.clear()
console.log('after clear : ', lst.toString())查看输出结果:
----Test: LinkedList----
[HEAD] -> a -> b -> c ->
[HEAD] -> a -> insert-1 -> b -> c ->
[HEAD] -> a -> insert-1 -> b -> c -> insert-4 ->
[HEAD] -> insert-0 -> a -> insert-1 -> b -> c -> insert-4 ->
[HEAD] -> insert-0 -> a -> insert-1 -> b -> insert-4 -> remove-c
indexOf-b : 3
update-b : [HEAD] -> insert-0 -> a -> insert-1 -> b-updated -> insert-4 ->
after removeAt(3) : [HEAD] -> insert-0 -> a -> insert-1 -> insert-4 ->
after clear : [HEAD] -> Null结果正确。
收工。
做了一份 npm 工具包 data-struct-js ,
基于 ES6 实现的 JavaScript 数据结构,
虽然这个小轮子很少会被使用,
也许对于初学者学习 JavaScript 会有点帮助。
只要简单 install 一下即可,感兴趣的话还可以去
GitHub / Gitee 看源码。(Star 表支持~)
npm install data-struct-js --save-devhttps://github.com/CoderMonkie/data-struct-js
https://gitee.com/coder-monkey/data-struct-js
最后,感谢您的阅读和支持~