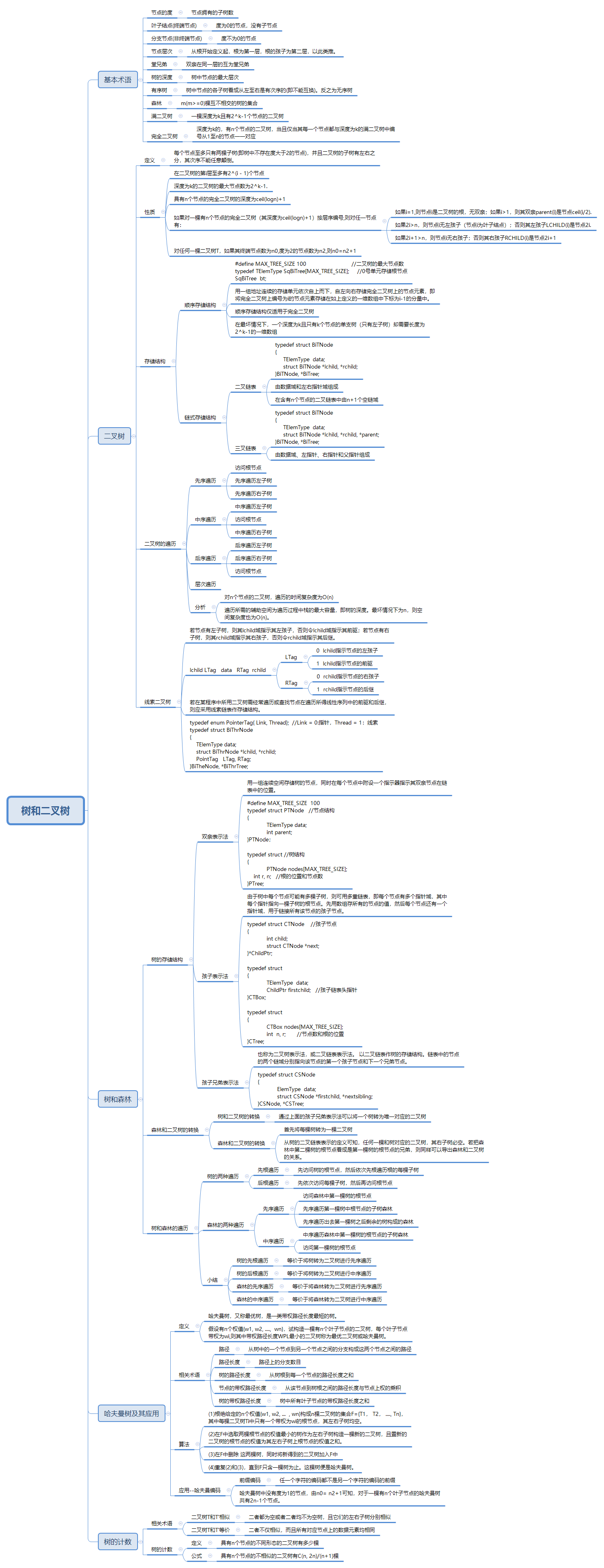
树形结构是一类重要的非线性数据结构,而且应用十分广泛。本篇博客首先以思维导图的形式来介绍树和二叉树的基本概念你,涉及到树的定义、基本术语、遍历方式以及扩展(线索化),然后再以源码的形式实现出来。
一、代码实现(C++语言)
1.二叉树
这里对二叉树各种操作代码实现提供了递归和非递归两种版本,如前序、中序、后序和层次遍历二叉树,获取度为0/1/2的节点数目,以及根据前序和中序恢复一棵二叉树,或者根据中序和后序恢复一棵二叉树等操作。
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef char ElemType;
typedef struct BiTNode //二叉树的结构体定义
{
ElemType data;
struct BiTNode *lchild, *rchild;
}BiTNode, *BTree;
//分配一个节点,注意思考为什么把这个函数定义成static?
static BiTNode* BuyTNode(const ElemType data)
{
//分配内存空间,nothrow表示不抛出异常
BiTNode *pTmp = new (nothrow) BiTNode; //不抛出bad_alloc异常,分配失败返回NULL
if (NULL == pTmp)
{
return NULL;
}
pTmp->rchild = NULL;
pTmp->lchild = NULL;
pTmp->data = data;
return pTmp;
}
//先序创建一棵二叉树
void CreateBTree(BTree &root)
{
char ch = getchar();
if (ch == '#')
{
root = NULL;
}
else
{
root = BuyTNode(ch);
CreateBTree(root->lchild);
CreateBTree(root->rchild);
}
}
//递归先序遍历二叉树--根左右
void PreOrderTraverse(const BTree &root)
{
if (NULL != root)
{
cout << root->data << " ";
PreOrderTraverse(root->lchild);
PreOrderTraverse(root->rchild);
}
}
//递归中序遍历一棵二叉树--左根右
void InOrderTraverse(const BTree &root)
{
if (NULL != root)
{
InOrderTraverse(root->lchild);
cout << root->data << " ";
InOrderTraverse(root->rchild);
}
}
//递归后序遍历一棵二叉树--左右根
void PostOrderTraverse(const BTree &root)
{
if (NULL != root)
{
PostOrderTraverse(root->lchild);
PostOrderTraverse(root->rchild);
cout << root->data << " ";
}
}
//递归实现打印第k层的所有节点
void PrintKLevel(const BTree &root, int k)
{
if (NULL == root || k < 1)
{
return;
}
if (1 == k)
{
cout << root->data << " ";
}
PrintKLevel(root->lchild, k - 1);
PrintKLevel(root->rchild, k - 1);
}
int Max(int a, int b)
{
return (a > b ? a : b);
}
//递归求二叉树的深度
int GetTreeDepth(const BTree &root)
{
if (NULL == root)
{
return 0;
}
return 1 + Max(GetTreeDepth(root->lchild), GetTreeDepth(root->rchild));
}
//递归层次遍历二叉树
void LevelTraverse(const BTree &root)
{
if (NULL == root)
{
return;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= GetTreeDepth(root); ++i)
{
PrintKLevel(root, i);
cout << endl;
}
}
//递归求树中节点总数
int GetNodeNum(const BTree &root)
{
if (NULL == root)
{
return 0;
}
return 1 + GetNodeNum(root->lchild) + GetNodeNum(root->rchild);
}
//递归获取叶子节点的数目
int GetLeafNode(const BTree &root)
{
if (NULL == root)
{
return 0;
}
if ((NULL == root->lchild) && (NULL == root->rchild))
{
return 1;
}
return GetLeafNode(root->lchild) + GetLeafNode(root->rchild);
}
//递归获取度为1的节点数目
int GetDegree1Num(const BTree &root)
{
if (NULL == root)
{
return 0;
}
if ((NULL == root->lchild && NULL != root->rchild))
{
return 1 + GetDegree1Num(root->rchild);
}
if ((NULL == root->rchild && NULL != root->lchild))
{
return 1 + GetDegree1Num(root->lchild);
}
return GetDegree1Num(root->lchild) + GetDegree1Num(root->rchild);
}
//递归获取度为2的节点数目
int GetDegree2Num(const BTree &root)
{
if (NULL == root)
{
return 0;
}
if (NULL != root->lchild && NULL != root->rchild)
{
return 1 + GetDegree2Num(root->lchild) + GetDegree2Num(root->rchild);
}
return GetDegree2Num(root->lchild) + GetDegree2Num(root->rchild);
}
//递归判断两个二叉树是否相等
bool Equal(const BTree &lhs, const BTree &rhs)
{
return ((NULL == lhs && NULL == rhs) ||
(NULL != lhs && NULL != rhs && Equal(lhs->lchild, rhs->lchild) && Equal(lhs->rchild, rhs->rchild)
&& (lhs->data == rhs->data)));
}
/*
* 非递归前序遍历二叉树
* 思路:前序遍历二叉树的顺序是根左右,先访问根节点,再访问左子树,最后访问右子树。
* (1)如果根节点不为NULL,则先将根节点入栈
* (2)如果栈不空,则从栈中弹出栈顶元素并访问(访问根节点)
* (3)如果该节点有右孩子,则将右孩子入栈;如果该节点有左孩子,则将左孩子入栈;之所以
* 先将右孩子入栈,原因在于我们要先访问左孩子,而栈的访问特点是先进后出,所以应该
* 先将右孩子入栈。
* (4)重复(2)、(3)直到栈空
*/
void NCPreOrderTraverse(const BTree &root)
{
if (NULL == root)
{
return;
}
stack<BiTNode*> pStack;
pStack.push(root);
while (!pStack.empty())
{
BiTNode *pTop = pStack.top();
cout << pTop->data << " ";
pStack.pop();
if (NULL != pTop->rchild) //注意,如果有右孩子,则应该先将右孩子入栈
{
pStack.push(pTop->rchild);
}
if (NULL != pTop->lchild)
{
pStack.push(pTop->lchild);
}
}
}
/*
* 非递归中序遍历二叉树
* 思路:前序遍历二叉树的顺序是根左右,先访问左子树,再访问根节点,最后访问右子树。
* (1)先判断根节点是否为空,如果不空,则将根节点入栈,然后指向其左孩子
* (2)如果当前根节点为空,说明我们已经访问到了左子树的叶子结点,则从栈中弹出栈顶元素(子树的根节点)
* 进行访问,此时已经访问完了左子树和根,然后判断其是否有右孩子,如果有则将右孩子入栈。
* (3)重复(1)、(2)直到栈空
*/
void NCInOrderTraverse(const BTree &root)
{
if (NULL == root)
{
return;
}
stack<BiTNode*> pStack;
BiTNode *p = root;
while (p || !pStack.empty())
{
if (NULL != p)
{
pStack.push(p);
p = p->lchild;
}
else
{
p = pStack.top();
cout << p->data << " ";
pStack.pop();
p = p->rchild;
}
}
}
/*
* 非递归输出二叉树第K层的节点
* 思路:本质就是一个层次遍历二叉树的过程,利用队列来实现
*/
void NCPrintKLevel(const BTree &root, int k)
{
if (NULL == root)
{
return;
}
BiTNode* pTmp = root;
queue<BiTNode*> pQueue;
pQueue.push(pTmp);
while (!pQueue.empty())
{
int iSize = pQueue.size();
--k;
for (int i = 0; i < iSize; ++i) //每次循环都是一层,注意这里不能将iSize替换成pQueue.size()
{
pTmp = pQueue.front();
pQueue.pop();
if (0 == k) //到达目标层次,访问节点信息
{
cout << pTmp->data << " ";
}
if (NULL != pTmp->lchild)
{
pQueue.push(pTmp->lchild);
}
if (NULL != pTmp->rchild)
{
pQueue.push(pTmp->rchild);
}
}
}
cout << endl;
}
/*
* 非递归层次遍历二叉树
* 思路:利用队列来实现,大家可以将这个函数和NCPrintKLevel()实现进行对比,两者本质是一样的,
* 只是在NCPrintKLevel()中加了一个层次控制
*/
void NCLevelTraverse(const BTree &root)
{
if (NULL == root)
{
return;
}
queue<BiTNode*> pQueue;
BiTNode *p = root;
pQueue.push(p);
while (!pQueue.empty())
{
int iCount = pQueue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < iCount; ++i)
{
p = pQueue.front();
pQueue.pop();
if (NULL != p->lchild)
{
pQueue.push(p->lchild);
}
if (NULL != p->rchild)
{
pQueue.push(p->rchild);
}
cout << p->data << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
/*
* 非递归获取二叉树的深度
* 思路:凡是需要求二叉树层次信息的,利用队列这个万金油来实现
*/
int NCGetTreeDepth(const BTree &root)
{
int iDepth = 0;
if (NULL != root)
{
queue<BiTNode*> pQueue;
BiTNode *pTmp = root;
pQueue.push(pTmp);
while (!pQueue.empty())
{
++iDepth; //层次计数
int iCount = pQueue.size(); //pQueue.size();记录每一层的节点数
for (int i = 0; i < iCount; ++i)
{
pTmp = pQueue.front();
pQueue.pop();
if (NULL != pTmp->lchild)
{
pQueue.push(pTmp->lchild);
}
if (NULL != pTmp->rchild)
{
pQueue.push(pTmp->rchild);
}
}
}
}
return iDepth;
}
/*
* 非递归获取二叉树的节点数
* 思路:本质就是前序遍历来获取二叉树的节点数
*/
int NCGetNodeNum(const BTree &root)//前序遍历获取节点个个数
{
int iNodeNum = 0;
if (NULL != root)
{
stack<BiTNode*> pStack;
pStack.push(root);
while (!pStack.empty())
{
BiTNode *p = pStack.top();
pStack.pop();
if (NULL != p->rchild)
{
pStack.push(p->rchild);
}
if (NULL != p->lchild)
{
pStack.push(p->lchild);
}
++iNodeNum;
}
}
return iNodeNum;
}
//////////////////////////////
//可以根据一棵树的前序序列和中序序列恢复一棵二叉树
//获取元素在中序序列中的位置
int IsIndex(char *is, char x, int n)
{
for (int iIndex = 0; iIndex < n; ++iIndex)
{
if (is[iIndex] == x)
{
return iIndex;
}
}
return -1;
}
BiTNode* CreatePI(char *ps, char *is, int n)
{
BiTNode *s = NULL;
if (n > 0)
{
s = BuyTNode(ps[0]);
int pos = IsIndex(is, ps[0], n);
if (-1 == pos)
{
exit(1);
}
s->lchild = CreatePI(ps + 1, is, pos);
s->rchild = CreatePI(ps + pos + 1, is + pos + 1, n - pos - 1);
}
return s;
}
BiTNode* CreateTreePI(char *ps, char *is, int n)
{
if (NULL == ps || NULL == is || n < 1)
{
return NULL;
}
return CreatePI(ps, is, n);
}
//可以根据一棵树的后序序列和中序序列恢复一棵二叉树
BiTNode* CreateIL(char *is, char *ls, int n)
{
BiTNode *s = NULL;
if (n > 0)
{
s = BuyTNode(is[n - 1]);
int pos = IsIndex(is, ls[n - 1], n);
if (-1 == pos)
{
exit(1);
}
s->lchild = CreateIL(is, ls, pos);
s->rchild = CreateIL(is + pos + 1, ls + pos, n - pos - 1);
}
return s;
}
BiTNode* CreateTreeIL(char *ps, char *ls, int n)
{
if (NULL == ps || NULL == ls || n < 1)
{
return NULL;
}
return CreateIL(ps, ls, n);
}
int main(void)
{
char ps[] = "ABCDEFGH"; //前序遍历序列
char is[] = "CBEDFAGH"; //中序遍历序列
char ls[] = "CEFDBHGA"; //后序遍历序列
int n = sizeof(ps) / sizeof(*ps) - 1;
BTree root = CreateTreePI(ps, is, n);
PreOrderTraverse(root);
cout << endl;
InOrderTraverse(root);
cout << endl;
PostOrderTraverse(root);
cout << endl;
cout << NCGetNodeNum(root) << endl;
LevelTraverse(root);
NCPrintKLevel(root, 1);
NCPrintKLevel(root, 2);
NCPrintKLevel(root, 3);
NCPrintKLevel(root, 4);
return 0;
}
2.线索二叉树
在线索树上遍历,只要先找到序列中的第一个节点,然后依次找节点后继直至其后继为空时为止。这里提供中序线索二叉树的实现,原因在于中序线索二叉树比前序或后序线索二叉树更实用。
若在某程序中所用二叉树需经常遍历或查找节点在遍历所得线性序列中的前驱和后继,则应采用线索链表作存储结构。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
typedef char TElemType;
typedef enum PointerTag
{
Link, //Link == 0, 指针
Thread //Thread == 1, 线索
};
typedef struct BiThrNode
{
TElemType data;
struct BiThrNode *lchild, *rchild;
PointerTag LTag, RTag;
}BiThrNode, *BiThrTree;
void InOrderTraverse_Thr(BiThrTree root);
void InThreading(BiThrTree p);
void InOrderThreading(BiThrTree &thrt, BiThrTree &t);
BiThrNode* BuyNode(char ch)
{
BiThrNode* p = (BiThrNode*)malloc(sizeof(BiThrNode));
assert(NULL != p);
p->data = ch;
p->lchild = NULL;
p->rchild = NULL;
p->LTag = Link;
p->RTag = Link;
return p;
}
void CreateThrBiTree(BiThrTree &root)
{
char ch = getchar();
if (ch != '#')
{
root = BuyNode(ch);
CreateThrBiTree(root->lchild);
CreateThrBiTree(root->rchild);
}
else
{
root = NULL;
}
}
//中序遍历线索二叉树
void InOrderTraverse_Thr(BiThrTree root)
{
if (NULL == root)
{
return;
}
BiThrNode* p = root->lchild;
while (p != root)
{
while (p->LTag == Link) //左孩子为指针
{
p = p->lchild;
}
printf("%c ", p->data);
while (p->RTag == Thread && p->rchild != root)
{
p = p->rchild; //让p指向其后继节点
printf("%c ", p->data);
}
p = p->rchild;
}
}
BiThrNode* pre;
void InThreading(BiThrTree p)
{
if (p)
{
InThreading(p->lchild); //左子树线索化
if (!p->lchild) //前驱线索
{
p->LTag = Thread;
p->lchild = pre;
}
if (!pre->rchild) //后继线索
{
pre->RTag = Thread;
pre->rchild = p;
}
pre = p; //保持pre指向p的前驱
InThreading(p->rchild); //右子树线索化
}
}
void InOrderThreading(BiThrTree &thrt, BiThrTree &t)
{//thrt为头结点,t为二叉树根节点
if (!(thrt = (BiThrTree)malloc(sizeof(BiThrNode))))
{
return;
}
thrt->LTag = Link;
thrt->RTag = Thread;
thrt->rchild = thrt;
if (!t)
{
thrt->lchild = thrt;
}
else
{
thrt->lchild = t;
pre = thrt;
InThreading(t);
pre->rchild = thrt;
pre->RTag = Thread;
thrt->rchild = pre;
}
}
int main(void)
{
//创建二叉树时的序列示例:AB#E##C#H##
BiThrTree bt;
CreateThrBiTree(bt);
BiThrTree head;
InOrderThreading(head, bt);
InOrderTraverse_Thr(head);
return 0;
}